地铁车辆基地库房设计高度及其经济效益分析
2016-12-19肖锋
肖 锋
(广州地铁设计研究院有限公司,510010,广州∥高级工程师)
地铁车辆基地库房设计高度及其经济效益分析
肖 锋
(广州地铁设计研究院有限公司,510010,广州∥高级工程师)
通过对现行地铁车辆基地库房设计高度的调查和研究,结合地铁车辆检修不同于铁路的特点,分析车辆工艺、接触网、建筑、结构、通风空调等专业所需高度要求,提出科学、经济、合理的库房和上盖设计高度标准,并进行工程造价的对比分析。
地铁; 车辆基地; 检修库; 运用库; 工程造价
Author′s address Guangzhou Metro Design & Research Instinte Co.,Ltd.,510010,Gungzhou,China
车辆基地作为城市轨道交通线路的综合检修基地,其建设对轨道交通具有重要意义和影响。由于车辆基地占地面积大,少则十几hm2,多则五、六十hm2,导致近年来车辆基地的选址越来越困难。为发挥最大效益,继新加坡、香港等城市对车辆基地进行上盖物业开发后,国内城市也有开始大规模进行车辆基地上盖物业开发的趋势,有的车辆基地为进行上盖物业开发或者考虑周边环境的需要,甚至需设计为地下式。车辆基地的检修、运用库房面积大,特别是进行上盖物业开发的车辆基地和地下式车辆基地,库房的设计高度合理与否,对工程造价的影响相当大。因此,在满足检修工艺要求的前提下,研究能否降低车辆基地库房设计高度,不仅具有显著的经济效益,也具有十分重要的现实意义。
1 库房设计高度现状分析
根据功能的不同,地铁车辆基地主要有停车列检库、双周/三月检库等运用设施建筑和大架修库、定临修库、转向架检修间等检修设施建筑。各库房的设计高度主要取决于地铁车辆高度、车辆检修工艺、库内管线安装、上盖开发业态、结构部件尺寸等。
GB 50157—2013《地铁设计规范》对车辆基地的库房设计高度没有明确要求,只是提出“定修库、临修库、架修库和大修库均应设电动桥式或梁式起重机,起重机走行轨的高度应根据车辆高度、架车方式、架车高度、车顶作业要求和起重机的结构尺寸计算确定。”
目前,对于国内地铁车辆基地各种库房的设计高度,设计人员基本沿袭了铁路机务段、车辆基地的设计标准,即:运用库(含停车列检库、双周/三月检库)设计高度为7.2 m(地面至屋架下弦),大架修库、定临修库、转向架检修间起重机走行轨顶面至库内地面的设计高度为8.4 m,缺乏认真细致的检算。
铁路机车车辆与地铁车辆的车体高度及限界不同,车辆部件组成不同,同时检修工艺也有别。目前,地铁车辆基地的库房设计高度沿用铁路的设计标准,主要存在以下问题:
(1) 库房高度增加,导致土建、通风空调、电气照明、安全防护等投资增加,提高了工程造价,造成投资的较大浪费。特别是对于进行上盖开发的车辆基地和地下式车辆基地,造成的投资浪费更大。
(2) 库房高度过高,造成车辆基地投入使用后库房内通风空调、电气照明、消防等设备的运营维护非常困难,同时也增加了运营成本。
2 库房设计高度优化分析
2.1 大架修库(含临修库)
大架修库的设计高度主要由检修工艺确定,要考虑的因素包括地铁车辆高度、架车方式、检修时吊出的部件尺寸、库房跨度、起重机规格等。大架修库高度示意图如图1所示。
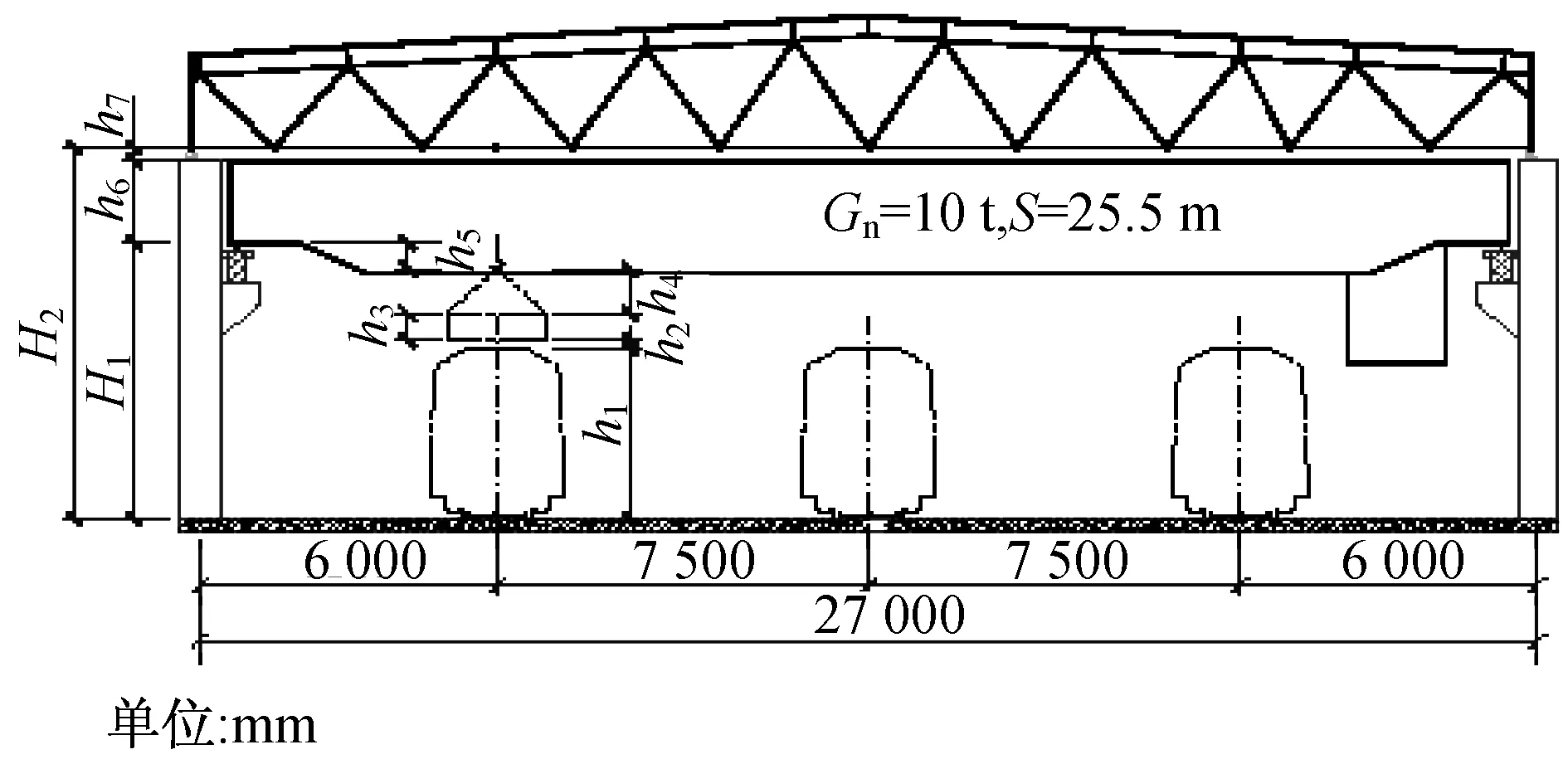
图1 大架修库高度示意图
根据设计规范,库内设3条检修线的大架修库其跨度为27 m,库内设2条检修线的大架修库其跨度为20 m,本文按照最大跨度27 m考虑。另外,大架修库内设10 t电动双梁桥式起重机,采用固定式作业时完全可以满足工艺和检修作业的要求。
大架修库起重机走行轨顶面至库内地面的计算高度H1为:
H1=h1+h2+h3+h4+h5
式中:
h1——车辆高度,地铁A型车、B型车最大高度为3 810 mm;
h2——吊出工件(空调机组)和车辆顶部的间距,取200 mm;
h3——空调机组高度,目前国内地铁车辆空调机组高度为455~575 mm,取最大高度575 mm;
h4——起重机吊钩的工作高度,与空调机组的尺寸和吊索长度有关,根据计算及现场实际测量,地铁车辆空调机组的吊出工作高度1 000 mm;
h5——起重机走行轨顶面至吊钩的距离,10 t电动双梁起重机的为335 mm。
根据上述计算公式,当大架修库采用10 t电动双梁起重机时,H1为5 920 mm;
设计时H1可按建筑模数取整,即大架修库起重机走行轨顶面至库内地面的高度按6 000 mm设计可以满足检修要求。
大架修库屋架下弦至库内地面的计算高度H2为:
H2=H1+h6+h7
式中:
h6——起重机走行轨顶面至起重机梁顶高度,10 t电动双梁起重机的为1 830 mm;
h7——起重机梁顶至屋架下弦的安全距离,10 t电动双梁起重机的为300 mm。
根据上述计算公式,当采用10 t电动双梁起重机时,H2为8 130 mm;
根据上述计算和分析,大架修库屋架下弦至库内地面的高度按8 200 mm设计即可满足大架修的工艺要求。
如果车辆基地进行上盖物业开发或者是采用地下式,则库内需进行机械通风和防排烟,需另外考虑风管等各种管线的安装。根据通风空调专业的计算和分析,风管的最大高度为800 mm,另外考虑安装支架50 mm,风管计算高度按900 mm完全可以满足要求。此时大架修库屋架下弦(即梁底)至库内地面的高度H3为9 030 mm。
即车辆基地进行上盖物业开发或者是采用地下式车辆基地时,大架修库梁底至库内地面的高度按9 100 mm设计即可满足检修工艺要求。
考虑结构梁高度1 600 mm,此时建筑层高为10 700 mm,按照建筑模数取整,即大架修库层高按照10.8 m设计即可。
2.2 运用库(含停车列检库和双周/三月检库)
运用库的高度(见图2)需考虑接触网的安装要求和检修工艺需求。检修工艺主要考虑检修人员在车顶上进行检查和临修作业时的高度要求。
根据《地铁设计规范》,地上线路接触线距离轨面的高度宜为4 600 mm,车辆基地的地上线路接触线距轨面高度宜为5 000 mm。因此,运用库接触线的架设高度按5 000 mm考虑。
另外,接触线距屋架下弦的高度需按1 500 mm考虑,因此,运用库内轨面距屋架下弦高度按6 500 mm设计可满足接触网的安装要求。此高度也满足检修人员在车顶上进行检修作业的要求。
如果车辆基地进行上盖物业开发或者是采用地下式,此时机械通风和防排烟的风管安装可以避开接触网安装支架,因此不需要考虑其附加的安装高度。
考虑到结构梁的高度为1 600 mm,因此建筑层高按8 100 mm设计,即运用库层高按照8.1 m设计即可。
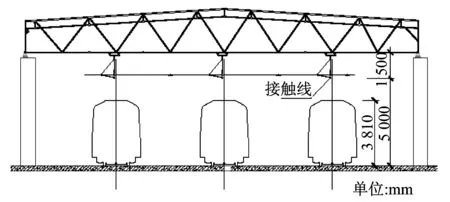
图2 运用库高度示意图
2.3 上盖物业盖板高度
在进行车辆基地上盖物业开发设计时,一般在运用库上面另外设置一层,作为上盖物业的汽车停车库,同时兼作结构和设备转换层。
一般住宅小区汽车库按停放小型车考虑,按照《汽车库建筑设计规范》,其最小净空高度为2 200 mm;由于需进行结构转换,结构转换梁高度按2 000 mm考虑;通风空调风管计算高度最大按500 mm考虑;另外,考虑喷淋安装高度150 mm、电缆桥架安装高度150 mm,以及预留100 mm的富余量,汽车库层高为5 100 mm。即车辆基地上盖物业二层汽车库的层高按照5.1 m设计可以满足规范和使用要求。
图3为车辆基地上盖开发剖面示意图。上盖物业开发盖板的总高度为13 200 mm,大于大架修库所需层高10 800 mm。即上盖物业二层盖板高度按照13.2 m设计,既可以满足大架修库检修工艺要求,也可以满足物业开发所需的汽车库层高要求。
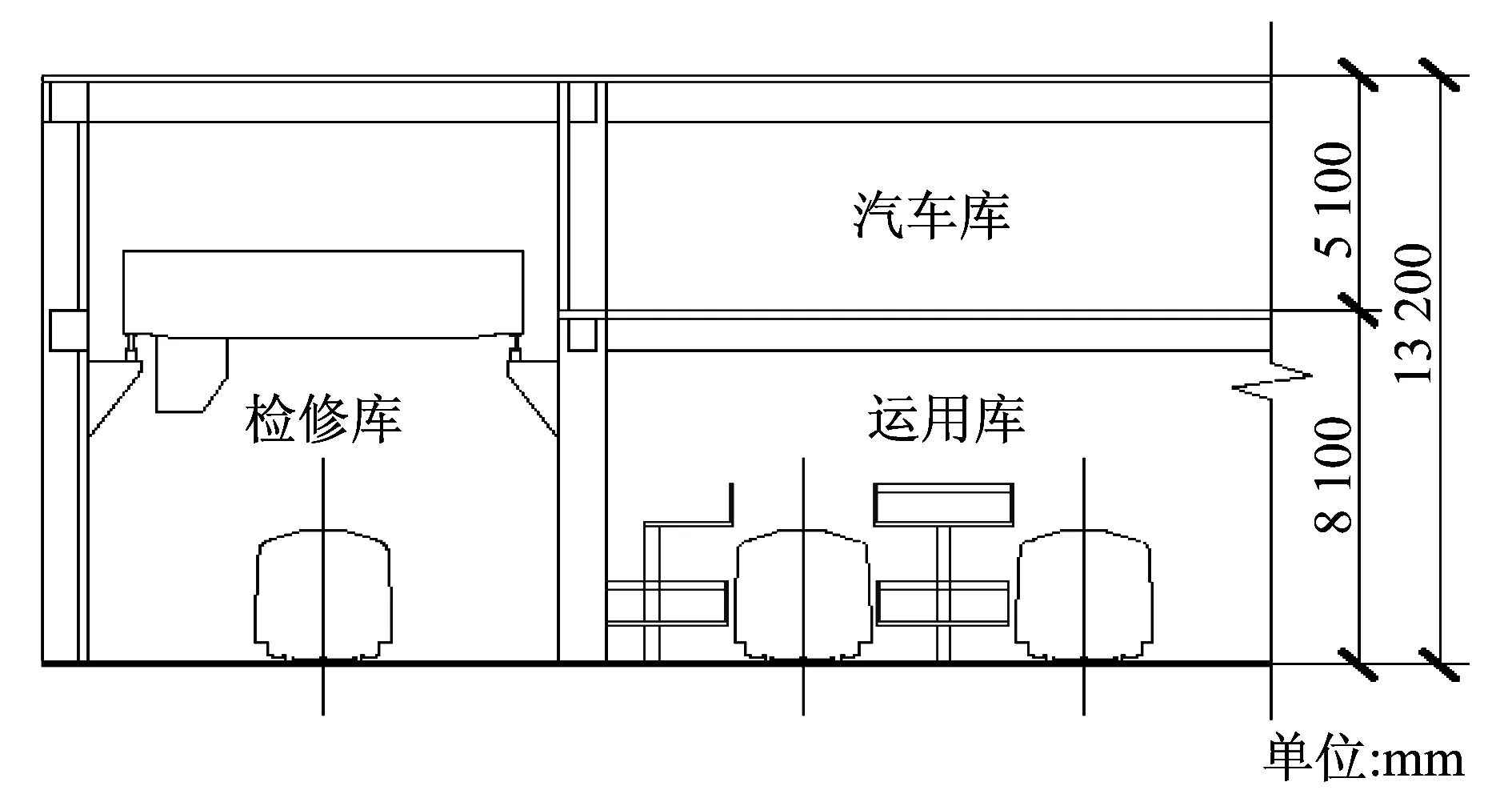
图3 车辆基地上盖开发剖面示意图
3 经济效益分析
经测算,地面普通车辆基地(网架结构)、地面进行上盖物业开发的车辆基地和地下式车辆基地,其库房高度每降低1 m可节省的土建工程量和造价如表1所示。
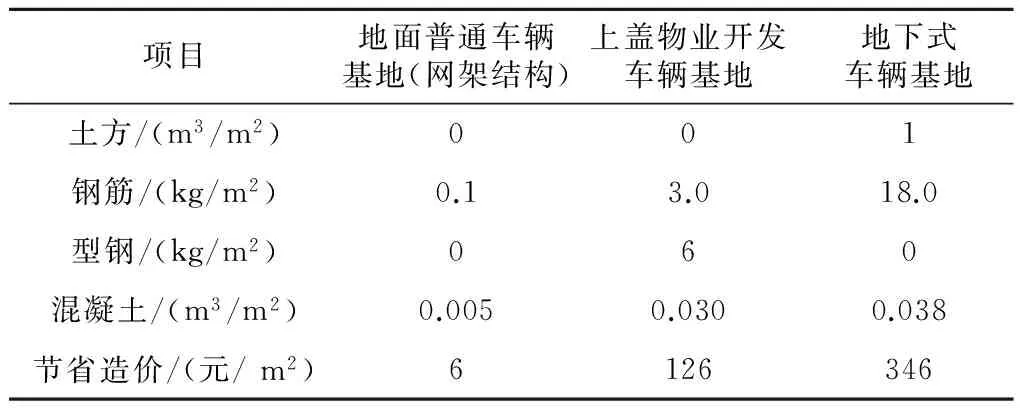
表1 车辆基地库房高度每降低1 m可节省的工程量和工程造价表
3.1 地面普通车辆基地(网架结构)
某大架修车辆基地,检修库面积为36 963 m2,屋架下弦设计高度为11.5 m;运用库面积为37 316 m2,屋架下弦设计高度为7.2 m。优化设计后,检修库高度可以降低3.3 m,运用库高度可以降低0.7 m,根据上述分析,可节省的投资为89万元。
3.2 上盖物业开发车辆基地
某车辆基地,进行上盖物业开发,目前,首层设计高度是9 m,二层设计高度是6 m,盖板设计高度为15 m,盖板总面积为282 688 m2。优化设计后,首层可以降低高度0.9 m,二层也可以降低高度0.9 m,合计可降低高度1.8 m,按照上述分析,可节省投资6 411万元
3.3 地下式车辆基地
某停车场,为全地下式停车场,地下室面积为65 800 m2,现设计高度为9 m,梁底设计净高为7.5 m。优化设计后,该地下式停车场可以降低高度1 m,按照上述分析,可节省投资2 277万元。
某停车场,为另一全地下式停车场,地下建筑面积为121 600 m2,现设计梁底净高为7.2 m。优化设计后,该地下停车场可以降低高度0.7 m,按照上述分析,可节省投资2 945万元
上述投资均只考虑了土建造价,尚不包括层高降低后节省的通风空调、电气照明、安全防护等机电设备的投资。
4 结语
综合上述分析,对车辆基地的库房设计,可以得出如下结论:
(1) 对于不进行上盖开发的地面普通车辆基地,其大架修库起重机走行轨顶面至库内地面的高度按6 000 mm设计,屋架下弦距库内地面高度按8 200 mm设计可以满足车辆检修工艺要求。
(2) 对于进行上盖物业开发的车辆基地或者地下式车辆基地,其大架修库起重机走行轨顶面至库内地面的高度按6 000 mm设计,梁底距库内地面高度按9 100 mm设计可以满足检修工艺要求。
(3) 对于车辆基地(不论是否进行上盖开发)或是地下式车辆基地的运用库(含双周检、三月检库),其屋架下弦(或梁底)距库内地面高度按6 500 mm、层高按8 100 mm设计可以满足检修和运营要求;上盖物业二层盖板高度按照13.2 m设计,既可以满足检修工艺要求,也可以满足物业开发层高要求。
(4) 库房设计高度经优化而降低后,对上盖开发车辆基地和地下式车辆基地,可以大大降低工程造价,具有非常显著的经济效益;同时也便于运营后各库房内设备设施的保养和维护。而这些效益的取得并不会牺牲相关库房检修和运营及维护作业的环境。
当然,地铁车辆基地库房设计高度涉及专业和因素较多,本文的优化分析重在方法和思路,提出的设计标准仅供参考,具体设计中应根据工程的实际情况因地制宜地进行全面分析。
[1] 中华人民共和国住房和域乡建设部.地铁设计规范:GBJ 017—2013[S].北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2013.
[2] 中华人民共和国铁道部.铁路客车车辆设备设计规范:GB 10029—2009[S].北京:中国铁道出版社,2002.
(Continued from Special Commentary)
Enhancing the awareness of the threat to national security and being prepared for dangers in times of peace are the important principle that we must always adhere to in governing the country and administering the Party.The same is true for the constructions and operation safety of the rail transport. For the urban rail transport, especially for the rapid rail transit with independent right of way, its main characteristic is large transport volumes and very fast speeds. Once an accident happens, it will cause mass deaths and mass wounds, resulting in the very serious consequences. Therefore, the safety management should be the most important in the rail transport constructions and operation management.
Since the “9·11” terrorist attacks in 2001, the world has not become peaceful although all the countries around the world continued to step up the anti-terrorism strength. The rail transport still faces the serious threat of the non-traditional security represented by the terrorism. On February 18, 2003, less than a year and a half after the "9·11" accident, the subway arson case happened in the third largest city Daegu in South Korea (the criminal's bringing the petrol into the subway). The fire burned for 3 hours before being extinguished. 198 people were killed, 146 people were injured, and 289 people were missing. All 12 cars of the two trains were burned down. A few months later the normal traffic was restored. On March 22, 2016, a series of bombs exploded at the airport of Belgium's capital Brussels. Shortly afterwards, the explosions took place in the metro station located nearby at the EU headquarters in Brussels. The two terrorist attacks were associated with each other. At least 34 people were killed and 202 people were injured. Therefore, rail transit safety education for the general public must emphasize the necessity of strictly implementing that dangerous goods are not allowed to be carried into stations when passengers enter stations to ride and passengers should be asked to accept the security check, so as not to let the criminals get their chances.
At present, our country faces the complex and volatile environment of security and development. All kinds of foreseeable and unforeseeable risk factors have been increasing markedly. Transportation risks are everywhere, and the key lies in prevention and control. The risk sources of rail transport are mainly from natural disasters, man-made destructions, equipment failures, staffing irregularities, and vulnerability in the management system etc. Professor James Reason of Manchester University in the United Kingdom put forward a "Swiss Cheese Model” theory. Every layer of defense has a lot of loopholes, just like Swiss cheese slices, which have many holes. Holes will not necessarily cause serious results on a slice. But once these holes connect a strung, they will lead to serious accidents. The key to the safety assessment of rail transportation is to rank the sequence of priority control from all kinds of risk points coming from all kinds of risk sources according to their high or low level of risk rating, to develop corresponding preventive measures and emergency plans and to take some walkthroughs. Combining the third party's security evaluation with the self-inspection of rail transport enterprises could greatly improve the safety management level and control the risk at an acceptable level. The main bases for the safety assessment of third parties are related regulations, the national standards and industry standards, so as to ensure reliability, availability, maintainability and safety of large-scale transport systems, as well as rail transit system, and its subsystems.
The security management includes the two parts of the risk control and the emergency management. And the emergency management can also be divided into two parts: emergency preparedness and emergency treatment. The author believes that in the interior of rail transport enterprises, safety education should focus on the universal education of safety management, and helping employees understand the new concept of security management and its basic technology course, so as to enable them to improve the security conscious of "defending the territory with a high degree of responsibility”, and “being strictly on guard and defending to the last" in their respective positions.
(Translated by SUN Zheng)
Economic Benefit Analysis of Warehouse Height Desig in Metro Vehicle Base XIAO Feng
Through investigation and research of the warehouse height design in existing metro vehicle bases, and combined with the characteristics of metro vehicle maintenance that is different from normal railway maintenance, the vehicle technology, catenary, construction, structure, ventilation and air conditioning, as well as other professional warehouse height requirements are analyzed, scientific, economic and reasonable design standards forthe height of warehouse and the upper cover are put forward, the engineering costs are also compared and analyzed.
metro; vehicle base; maintenance warehouse; operating warehouse; engineering cost
TU 248; F 530.7
10.16037/j.1007-869x.2016.05.032
2014-11-19)