Evaluation of coordinated development of regional resources and economy around Shandong Peninsula urban agglomerations
2016-12-11LINaWANGKuifeng
LI Na, WANG Kui-feng
1Shandong Xiehe University, Jinan 250109, China.
2Shandong Institute of Geological Sciences, Shandong Key Laboratory of Geological Process and Resource Utilization in Metallic Minerals, Key Laboratory of Gold Mineralization Process and Resource Utilization Subordinate to the Ministry of Land and Resource, Jinan 250013, China.
Abstract: Promoting coordinated development of resources and environment is an important aspect of building a harmonious society and ecologically sustainable civilization. Here we provide scientific basis to promote the development of ecologically sensitive civilization, via a mathematical statistics method that calculates the degree of coordinated development. This model is of great practical and social significance, providing strength to research around coordinated development of resources and economy. Based on evaluation of characteristics of the present resource environment and economic development of Shandong Peninsula city group, a coordinated measure of resource environment and economic development was calculated. Overall, the highest coordination measurement was found for Weihai, followed by Yantai, Qingdao, Ji’nan, Weifang, Rizhao, Zibo and Dongying. According to evaluation results of coordination measures for each city, we put forward suggestions for sustainable development of Shandong Peninsula region.
Keywords: Shandong Peninsula; Urban Agglomerations; Resources; Economic development;Coordinated development model; Sustainable development
Introduction
An outcome of the United Nations World Conference on the Environment and Development held Rio De Janeiro in 1992 determined a strategy for global sustainable development (United Nations, 1992). Although the current interpretation of the concept of ‘sustainable development’ is not wholly agreed upon by scholars, yet the core of the theory is consistent, being the coordinated development of the social economy (Ec), resources(Re) and the environment (En). The coordinated development of Ec-Re-En comprises the core of sustainable development. Furthermore, the degree of coordination among Ec-Re-En makes up the quantitative indicators of coordinated development,which are used as the assessment standards of sustainable development. The Communist Party of China (CPC) 18thNational Congress’s report made it clear that faster action is required to set up a system that can protect the ecological environment,improve institutions and mechanisms for developing geographical space, conserve resources,and promote modernization that features harmonious development between the man and the nature(HU Jin-tao, 2012).
Many scholars have dedicated qualitative and quantitative research to the relationship between the resource environment and economic development.Mutisya E and Yarime M (2014) evaluated the degree of coordination among environmental,economic, and societal factors in the management of development in Kenya, proposing a coordination among all three is necessary to achieve sustainable development outcomes. Other authors have used a coupling dynamic method to evaluate coordination between economic and environmental systems(Tretyakova E A, 2014; Yoo I T and Kim I, 2015).
In China, a number of scholars have conducted evaluations of the coordinated development of the ecological environment and the economy. By analysing interactions and relationships between groundwater and environmental, social and economic development factors, WANG Hai-ning et al. (2012) established a quantitative evaluation model for the coordinated development of resources for five administrative districts in Guanzhong of Shaanxi Province, using a minimization of deviation coefficient. For Gansu Province, ZHANG Zi-long et al. (2010) used a Structure Decomposition and Analysis (SDA)model to analyse the changing trends in temporal relationship between economic growth and environmental pressures for the period of 1990-2005. Other researchers established a dynamic coupling model for coordinated development of the regional economy and the ecological system in the Jiangsu province (JIANG Hong-li and HE Jian-min,2010) and investigated coordinated development of agriculture and the economy in the Shanxi Province with whilst maintaining the integrity of ecological systems (REN Zhi-yuan et al. 2011).
This study is focussed around the eight main cities of Shandong Peninsula-Jinan, Qingdao, Zibo,Weifang, Dongying, Yantai, Weihai and Rizhao.Using a statistical measurement model to calculate the degree of coordinated development in focus areas, we put forward suggestions for viable sustainable development options. The urban agglomeration of Shandong Peninsula is located in the economically developed coastal areas of North China, thereby possessing a unique advantage in being receptive to the outside world and developing an export-oriented economy. At the same time, a good domestic and international environment has provided a broad space for a spectrum of development in the area. Alongside economic development and urbanization, the conflict between demand for resource use and maintaining a healthy environment becomes more apparent and the negative outcomes more drastic. Clearly, the key is to protect the ecological environment whilst achieving sustainable development of resources on the Shandong Peninsula. This drive is specifically important to the construction of ecologicallysensitive civilizations of the future.
1 Hydrogeological conditions of the study area
The urban agglomeration of the Shandong Peninsula is the key area for development of Shandong Province, and one of the important urban sites in North China. Market development in Shandong’s medium-sized cities is relatively sound with high competitiveness. The foundation for economic development in province relies on good information communication, and with high-speed broadband network now in place for the whole region, the advantages of the regional economy and social development are clear. Shandong Peninsula landforms include mountains, hills, plains, tidal flats and depressions, which form a typical estuarine delta in the Yellow River. Because of the complex terrains, the climate is warm and humid, and biological diversity is high. The marine biological resources are rich, and tourism opportunities are bountiful. The cultural landscape, natural landscape and folk tourism resources are abundant, and some have become a nation-class and even world-class tourist hot-spots. Unfortunately more than ever, the growing economy of the region has increased conflict among development requirements,resources and the environment. A serious shortage of water resources, lack of land reservation resource and serious environmental pollution are all factors contributing to the problem (WANG Kui-feng et al.2014a, b).
After repeated research and data analysis, the coordinated development model is used in the study to analyse the degree of coordination between resources, the environment and economic development in Shandong Peninsula urban agglomeration. To measure the degree of coordination, a quantitative description that reflects the degree of healthy development and coordination is used,determined through one or more indicators that assess the system of environment resources and economic development.
2 Coordinated evaluation model of resource environment and economic development for Shandong Peninsula urban agglomeration
The coordinated development of the resource environment and social economy system for the Shandong Peninsula urban agglomeration area is determined through the use of the coordinated development model proposed by LIAO Chong-bin(1999) as a quantitative index. In this study, the evaluation index system of coordinated development between the resource environment and the economy is based on previous research results. The frequency analysis method is used with“coordination” as a keyword to search on the internet and in the China National Knowledge Infrastructure database, and also the selection principle of the index system is considered. In the end, the resource environment and economic development are treated as two separate evaluation sub-systems to construct the corresponding index system. Then Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is used to calculate the weight of each index, and the weighted fuzzy membership function method,geometric mean method and the linearity-weightedsum method are used to evaluate comprehensively the level of resources and economic development sub-systems. The data used are derived from the Statistical Yearbook of Shandong Province,Statistical Yearbooks of Eight Cities. Finally the resource environment index and the economic development index are calculated .
2.1 Degree of coordination model
Here we define the economic development index f(x) and the environmental situation index g(x).According to the definition of coordination,coordinated development refers to a state that is mutual promotion and common development between the environment and economy (JIANG Hong-li et al. 2010). In order to ensure the deviation of f(x) and g(y) smaller, a coefficient of variation is used to calculate the degree of coordination model for the environment and economy. The coefficient of variation (C) is simply expressed as:
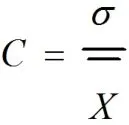
whereσis the standard deviation andis the average value. The calculation of σ (1) and(2) are performed using the following formula:
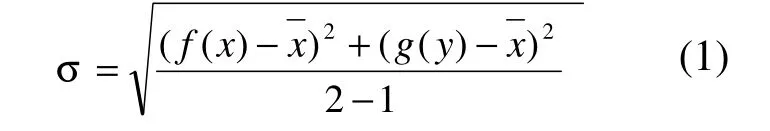
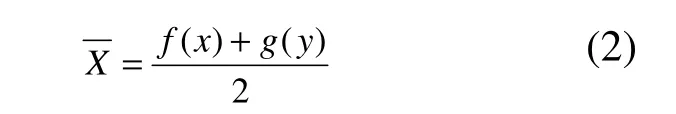
Expressed in full, the coefficient of variation(Cv) is as follows:
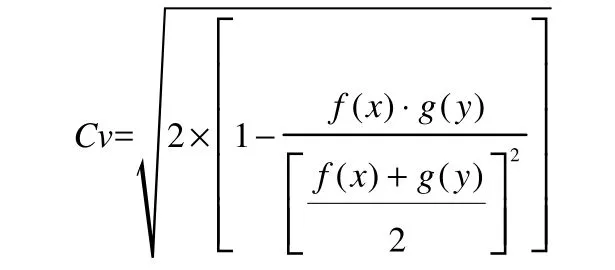
The smaller the coefficient of variation (Cv) is,the better the outcome for coordinated development. When Cvis as small as possible, the necessary and sufficient condition is that the equation (see below) is the bigger the better.

Our study therefore defines the degree of coordination model of the resource environment and economic development about Shandong Peninsula urban agglomeration as the formula:
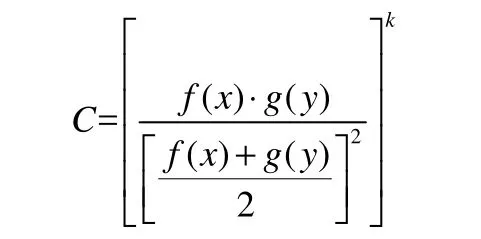
In the formula, C is the coordination degree and K is the adjustment coefficient. To ensure K is more than 2, this research gives K the value of 3.Using the standard deviation formula to calculate the degree of coordination, we can calculate the maximum benefit to both the resource environment and the economy; that is, when the sum of f(x) and g(y) are maximised. The degree of coordination C between the two values is expressed as a figure ranging between 0 and 1. Clearly, the degree of coordination is optimal when C is close to 1. On the contrary, a lack of coordination between the environment and economic development is indicated by a C value approaching 0.
2.2 Model for the degree of coordinated development
Coordinated development describes integration which emphasizes integrity, comprehensiveness and endogenous. Change in a single factor contributing to coordinated development can therefore have relatively little affect, emphasizing the comprehensive nature of the system based on harmony and mutual promotion of multiple elements. Interactive benign development is a common objective. Coordination is the beneficial constraints and regulations of the common behavior. While C is an index that can describe mutual coordination between the resource environment and the economy, it has difficulty reflecting the overall function or comprehensive environmental and economic benefits. The degree of coordination does not describe as absolute level,but only reveals the harmonious degree of the resource environment and economy. But the degree of coordinated development reflects the overall function of the resource environment and economic development. To reflect and evaluate the comprehensive and coordinated development level of the social economy and resource environment, a quantitative measurement model is used. This model is defined as the degree of coordinated development, and is expressed as D (3):
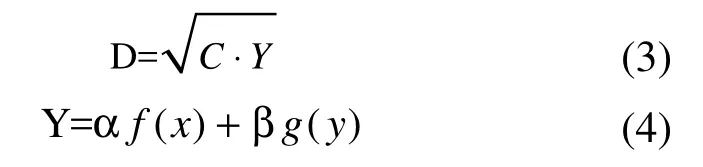
In the formula, D is the degree of coordinated development; C is the coordination degree. Y (4) is the evaluation index of the resource environment and economic development, wherebyα andβare weights. The contribution of each factor to the degree of coordinated development are counted as equally important, therefore given the same values of 0.5. Compared with the coordination degree model, the degree of coordinated development model demonstrates greater stability and a wider application range. It can be used for quantitative evaluation and comparison of the coordinated development between the resource environment and the economy for different cities or for different periods in the same city (Table 1). Furthermore,according to the relative size of resource environment evaluation index f(x) and economic development evaluation index g(y), as well as the size of coordination measure D, the type of development system can be subdivided into three different levels, containing three categories and five sub-categories (Table 2). When D is calculated to be 0.71-1.00, this indicates the city is one of coordinated development, which can be one of either two subgroups-excellent coordination and good coordinative development. When D is between 0.31-0.70, this demonstrates the city is one of excessive development, either intermediate coordinated development or primary coordinated development. D being less than 0.30 implies a city of imbalanced development.

Table 1 A classification of coordination measure based on the degree of coordinated development model D, where 0-0.30 indicates a city of imbalanced coordination between resources, the environment and the economy, and 0.86-1.00 represents cities of excellent coordination between these factors
In order to further discuss comprehensive development of the resource environment and the economy, more detailed third levels of classification are required. In this way, the type of coordinated development in the urban (or regional) resource environment and economy can be completely discriminated. Finally, according to the analysis results, this paper puts forward some suggestions for controlling the coordinated development of regional resources environment and economy. When a city demonstrates a “good” degree of coordination, this indicates a focus on improving the quality of the environment. A city belonging to the primary coordination category, is one where the main task is to develop the economy based on high environmental standards, whilst improving the coordinated development of the resource environment and economy at a higher level.
3 Results and discussions
According to the calculation formula of the measurement model, the classification system and the standard of coordinated development, measurement and classification of the degree harmony between resource use, the economy and the environment in the Shandong Peninsula urban agglomeration area can be calculated. The final evaluation results for the year 2014 are given in Table 3 and illustrated in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2.
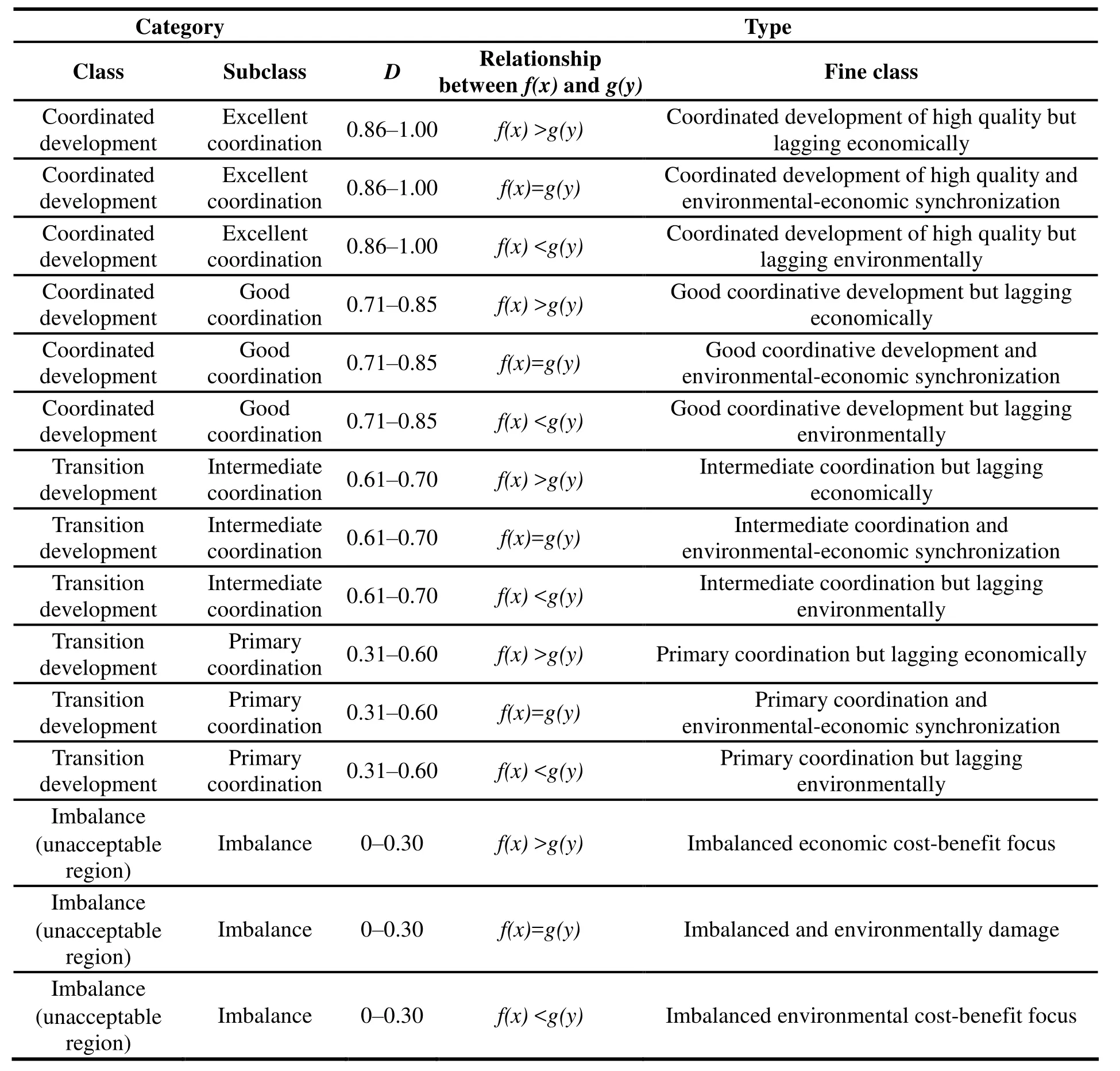
Table 2 The classification system and evaluation criteria of coordinated development based on the degree of coordinated development model D
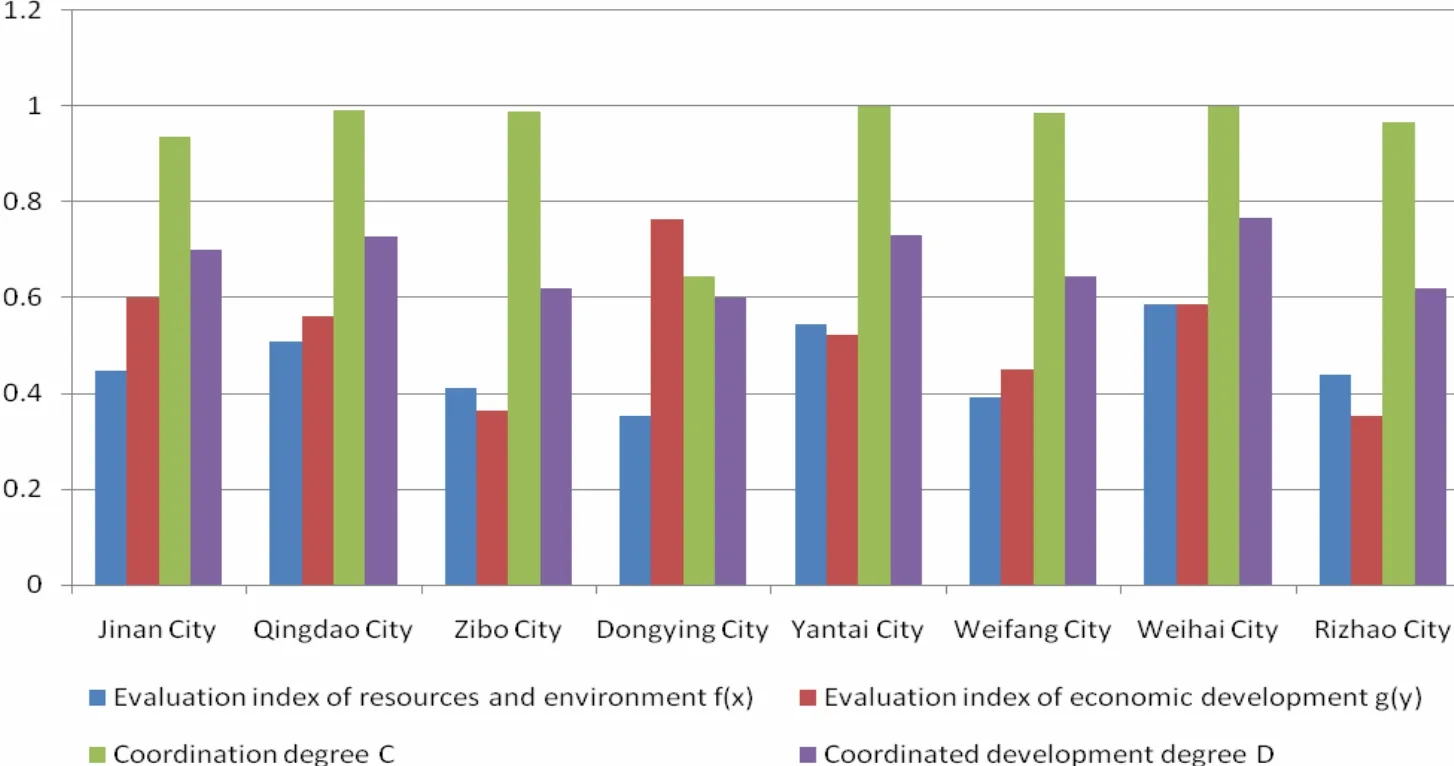
Fig. 1 Histogram of evaluation results of the Shandong Peninsula urban agglomeration area
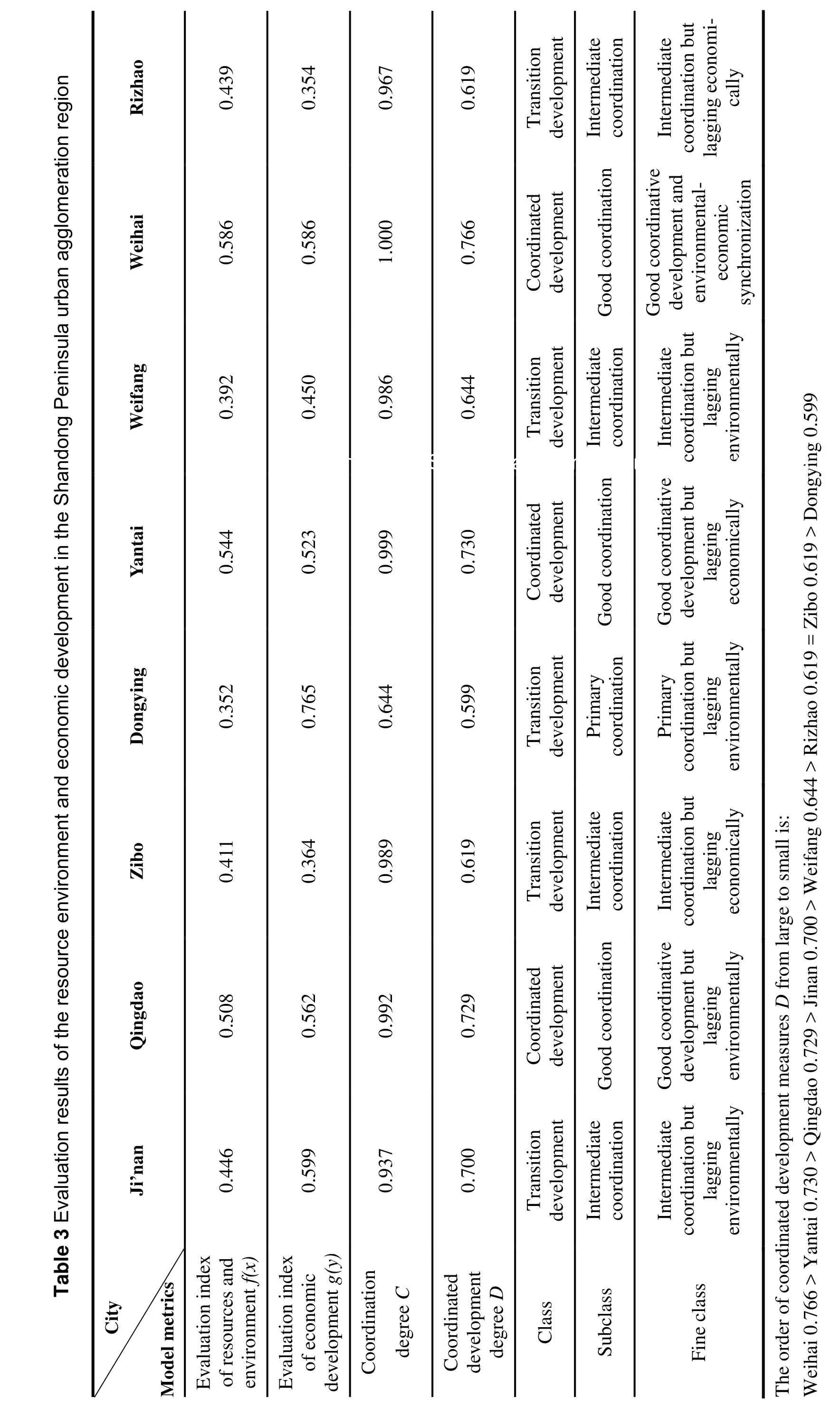
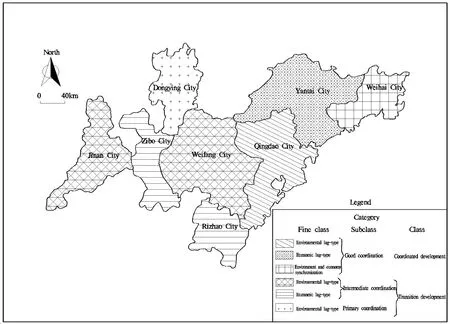
Fig. 2 Diagram of the evaluation model
During the construction and analysis of the coordination measure model, we found that the membership degree and measure value of each subsystem indicators has its urban characteristics.Overall for the Shandong Peninsula urban agglomeration, the highest measurement of coordination was for Weihai, followed by Yantai,Qingdao, Ji’nan, Weifang, Rizhao, Zibo and Dongying. We shall elaborate further the degrees of coordination for each city.
(1) The city with the highest degree of coordination-Weihai City
Since the city was founded in 1987, Weihai has continuously recognised resources and environmental protection as priority contributors to economic and social development. To ensure the coordinated development of the economy and the resource environment, policies around ecological protection of coastal area have been established.The goal of regional sustainable development in Weihai, relies primarily on focusing first on the development of the marine fishing industry,export-oriented aquaculture, processing and service enterprises to cater for these industries.Secondly, Weihai aims to strengthen protection around secondary natural forest. And thirdly,sustainable development will include strengthening the protection of the ocean territory and the construction of oceanic environment.
(2) The cities with a relatively high degree of coordination-Qingdao City and Yantai City
Qingdao city has a good economic foundation and awareness around ecological health and protection, following on from long-term ecological and environmental protection and restoration projects. Yantai City has a stronger economic development record than Qingdao, a higher GDP,higher potential value of mineral resources, better overall economic development, and a more reasonable industrial structure and layout. The main direction of future development is via strengthened environmental protection work around the key resources development zone, greater marine resource and environmental protection and thirdly in improved management of water and soil erosion.
(3) Cities with a moderate degree of coordination-Ji’nan City, Weifang City, Rizhao City and Zibo City
As an example of cities with a moderate degree of coordination, Ji’nan City is the economic and political centre of Shandong Province. It has one of the higher economic aggregates, heightened urbanization levels, greater land-use ratio, higher total export-import volume and higher per capita GDP within Shandong Province. The main direction of future development in this city is to construct a circular economic system such as the recycling of solid waste and a cultivated land resource ecological security system and thirdly the protection of the springs to restore Quancheng characteristics.
Economic development in Weifang City has made some progress. In recent years although the trending growth in pollution has been initially controlled, environmental pollution problems still exist. The carrying capacity of ecological environment is improved in Rizhao City. The strong economic foundation in Zibo City is matched by serious environmental pollution. In the future, the key direction of development in cities such as these is to first readjust industrial structure for efficiency, less pollution and environmental benefits and secondly to vigorously develop an environmental protection industry.
(4) The primary coordinated development city-Dongying City
The acknowledgement of the ecological environment system in Dongying city has a short history, resources are over-exploited and the ability for self recovery is weak. According to goals of ecologically-minded economic development,Dongying must invest heavily in the development of an oil replacement industry, and consider the constraints of natural resources, to ensure the stability of the stock of natural resources. The main direction for future development in Dongying will be to strengthen the management of inland pollution sources, to develop efficient agricultural practises and thirdly, to vigorously carry out water and soil erosion control.
4 Conclusions
(1) The relationship between the resource environment and economic development is an interactive one. When use of natural resources is in line with the carrying capacity, and development and type of use are appropriate, a positive outcome for economic development follows. Once a threshold is exceeded, however, it becomes the limiting factor for regional development.Economic development is not always passively subject to environmental factors. When economic activity is very high, there is commensurate level of investment in the protection of resources and the environment. In turn, this will assist in the protection and development of the resource environment. A low level of economic activity is usually paired with more eagerness to develop and use resources to further develop, but such an economy is also unable to protect environmental resources.
(2) Regional development focuses on coordination. In order to obtain the maximum economic benefits and social benefits, the relationship between environment and economy must be coordinated and a reasonable mode of development must be sought to maximize the efficiency of the resource environment.
(3) Due to the difficulty of data acquisition, the index of the measure of coordination model does not completely cover all factors. Furthermore, data employed in calculations are derived from the year 2014 alone. Ideally, in order to conduct dynamic and predictive research, a long-term data set is desirable. Thus, the evaluation results may be skewed and/or one-sided. Our study team aims to constantly improve in following research, to ensure that evaluation results are more scientifically robust and practical in application.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by Shandong Province Bureau of Statistics (No.KT15019). We are also greatly appreciated to the efforts of editors and reviewing experts for their contributions to the article.
杂志排行
地下水科学与工程(英文版)的其它文章
- Dynamic influence of Holocene characteristics on vadose water in typical region of central North China Plain
- Distribution characteristics and source of BTEX in groundwater in Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, P. R. China
- Exploration on compound water circulation system to solve water resources problems of North China Plain
- Evaluation of water resources carrying capacity of Gonghe basin based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method
- Comprehensive suitability evaluation of urban geological environment in Zhengzhou-Kaifeng area
- Optimization of geothermal water exploitation in Xinji, Hebei Province, P. R. China
