银杏叶提取物对肠炎小鼠肠黏膜通透性的影响
2016-11-30赵红伟岳月红康薇
赵红伟++++++岳月红++++++康薇

[摘要] 目的 探索银杏叶提取物(EGB 761)对肠炎模型小鼠肠黏膜通透性的影响。 方法 30只C57BL/6小鼠随机分为正常组(10只)、模型组(10只)、EGB 761组(10只),建立急性结肠炎小鼠模型。观察小鼠一般情况及结肠病理变化;应用偶氮基质显色法测定血清中脂多糖(LPS)的含量;采用异硫氰酸荧光素(FITC-D)标记的右旋葡聚糖法以及细菌移位来检测肠黏膜通透性;免疫荧光染色及组织化学测定结肠组织中occludin、Claudin-1蛋白的变化。 结果 经EGB 761治疗后模型小鼠的一般情况及结肠组织病理学表现均有明显改善,EGB 761组小鼠血清中LPS的含量(0.14±0.04)与模型组(0.20±0.06)比较明显降低(P < 0.01);EGB 761组FITC-D的渗透率与模型组(4200.80±326.60)比较明显降低(P < 0.01);EGB 761组细菌移位率(40%)与模型组(80%)比较也明显降低(P < 0.01)。免疫荧光染色及组织化学染色结果显示,EGB 761组可增加Claudin-1、occludin蛋白阳性细胞染色。 结论 EGB 76可降低肠炎模型小鼠肠黏膜的通透性。
[关键词] EGB 761;急性肠炎;动物模型;肠黏膜通透性
[中图分类号] R574 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-4721(2016)09(a)-0008-04
[Abstract] objective To investigate the effects of Gingko Biloba extract on the intestinal mucosal permeability in the colitis. Methods Thirty of C57BL/6 mice were randomly grouped as follows: control group (10 mice), model group (10 mice), EGB 761 group (10 mice). Models of acute colitis were established, general condition and colon pathological changes were observed, the serum of LPS was detected by Azo matrix chromogenic method; intestinal mucosal permeability were detected by FITC-D and bacterial translocation, the expressions of occludin and Claudin-1 proteins were detected by immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry. Results General condition and colon pathological were changed in the EGB 761 group compared with that of the model group; serum levels of the LPS in the EGB 761 group (0.14±0.04) was obviously decreased compared with those of the model group (0.20±0.06)(P < 0.01); the level of the FITC-D in EGB 761 group was decreased obviously (1266.40±222.90) compared with that of the model group (4200.80±326.60) (P < 0.01); Bacterial translocation was significantly decreased in the EGB 761 group (40%) compared with the model group (80%) (P < 0.01); the results of immunofluorescence and immunohistochemical staining showed that the expressions of the Claudin-1 and occludin proteins in colonic tissues increased in EGB 761 group. Conclusion The administration of EGB 761 may be adjusted the intestinal mucosal permeability in the acute experimental colitis.
[Key words] EGB 761; Acute colitis; Animal model; Intestinal mucosal permeability
溃疡性结肠炎(Ulcerative colitis,UC)是一种慢性反复发作的肠道炎症性病变,目前多数人认为该病是在一定环境下使肠道黏膜屏障的作用削弱,肠黏膜的通透性增高,致使肠道的致病菌群容易穿过其屏障,从而导致炎症反复发生[1-5],可见肠道黏膜通透性的增高与UC的发生有着紧密的联系[6-12]。有研究表明,银杏叶提取物761(Ginkgo Biloba extract 761,GBE 761)对该病有治疗作用,但是否对肠黏膜屏障的通透性有调节作用仍需进一步研究。
1 对象与方法
1.1 试剂与造模方法
右旋葡聚糖硫酸钠(DSS)(Sigma公司,美国);银杏叶提取物(EGB 761,金纳多注射液,德国威玛舒培药厂,批号:7320400);异硫氰酸荧光素(FITC)-Dextrans Sigma显色基质鲎试剂盒(上海榕柏生物技术有限公司);鼠抗闭合蛋白(occludin)、Claudin-1抗体(美国Santa Cruz公司)。急性期造模及EGB 761干预:30只雄性C57BL/6小鼠购于北京维通利华实验动物技术有限公司[合格证号:SCXK(京)2006-0009],体重19~24 g;9~13周。按随机数字表随机分为正常组(10只)、模型组(10只)、EGB 761组(10只)。模型组动物自由饮用2% DSS,持续1周,正常组及EGB 761组动物饮用蒸馏水,持续1周。EGB 761组小鼠从实验开始至结束,每天予EGB 761(200 mg/kg)1 mL灌肠;正常组和模型组予PBS灌肠作对照,时间均为1周,第8天处死所有动物。
1.2 小鼠一般情况及结肠病理组织染色
观察动物的体重、毛发光泽度、精神状态、大便性状、活动情况、食欲等。造模后处死小鼠,取部分结肠组织置于多聚甲醛内固定、包埋、切片,HE染色,行组织病理学观察。
1.3 脂多糖(LPS)含量的测定
实验结束后,应用注射器行心脏穿刺取血,取血后以3000 r/min离心15 min,取出血清,按试剂盒说明书应用偶氮基质显色法测定LPS含量。
1.4 结肠黏膜的通透性的检测
实验结束前4 h动物禁食水,应用FITC-D灌胃,(60 mg FITC-D/100 g),然后采取血清,应用荧光分光光度计检测每个样本的荧光密度,计算出每只小鼠血清中FITC-D的浓度。
1.5 肠系膜淋巴结细菌移位率的检测
实验结束后,用无菌剪刀剪取小鼠的全部肠系膜淋巴结(Mesenteric lymph nodes,MLN),称重后并匀浆,将匀浆组织各0.1 mL分别涂在普通琼脂培养基上37℃孵箱中培养24 h。计算细菌移位率,细菌移位率=(阳性的只数/培养的总只数)×100%。
1.6 结肠黏膜免疫组织化学及荧光染色
实验结束后,截取结肠组织行冰冻切片,严格按照实验步骤,一抗Claudin-1、occludin蛋白在37℃孵育2 h,洗涤,二抗37℃孵育30 min,结束后在光镜下观察Claudin-1、occludin蛋白的表达。免疫荧光染色:其他步骤同上,二抗滴加标记红色荧光的抗小鼠Cy3,室温1 h,红色的亮光为阳性表达。在阴性对照组中应用PBS替代一抗,其他的方法同上。
1.7 统计学方法
采用SPSS 13.0统计学软件进行数据分析,计量资料数据用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,两组间比较采用t检验;多组间比较采用单因素方差分析;计数资料用率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验,以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 小鼠的一般情况
正常组的小鼠大便、饮食、精神状态正常、体重增加、毛发光泽;模型组小鼠第1天一般状况较正常;第3天开始出现食欲、体重下降,精神萎靡,懒于活动,毛发无光泽,拉稀便或黏液血便;第5天上述各种症状明显加重,粪便潜血试验呈强阳性;第7天小鼠体重减轻明显,肛周可见肉眼血便。EGB 761组第5~7天后,稀便,未见脓血便,状态接近正常,但体重仍明显减轻。
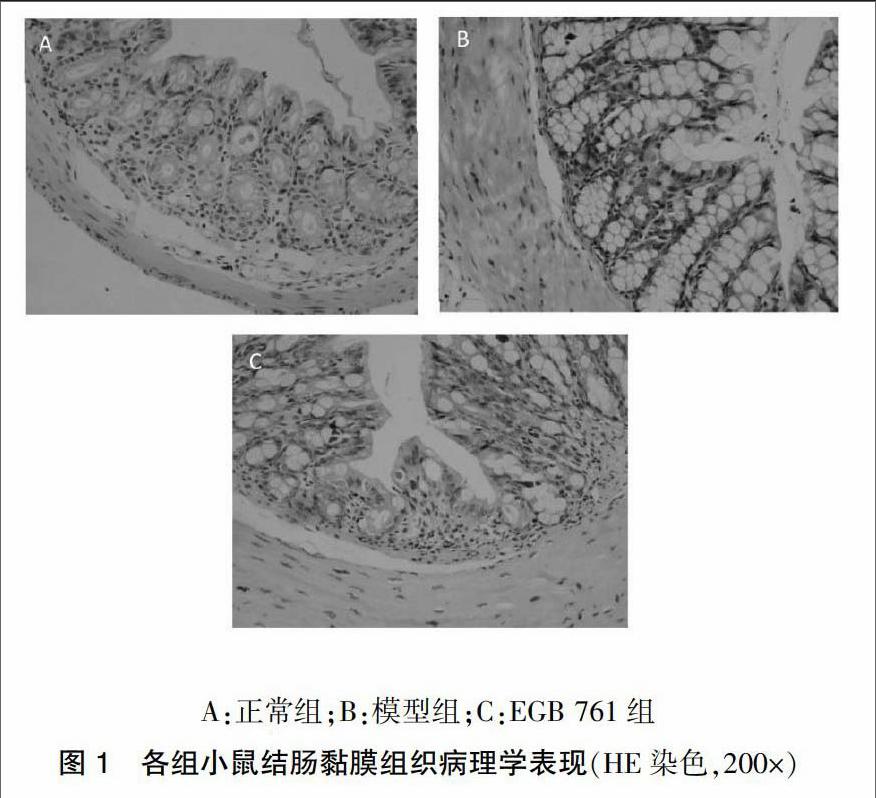
2.2 EGB 761对小鼠结肠组织病理学表现的影响
正常组小鼠结肠黏膜光滑,无水肿、充血等表现;模型组结肠黏膜缺损,可见黏膜、黏膜下层大量炎症细胞浸润,隐窝增生;EGB 761组可见炎症细胞浸润少,炎症程度较模型组明显减轻。见图1。
2.3 EGB 761对血清LPS、细菌移位率及FITC-D渗透率的影响
与模型组比较,正常组及EGB 761组血清中LPS的含量、结肠黏膜FITC-D渗透率、细菌移位率明显降低(P < 0.01)。见表1。
2.4 免疫组织化学染色法检测Claudin-1、occludin蛋白定位分布
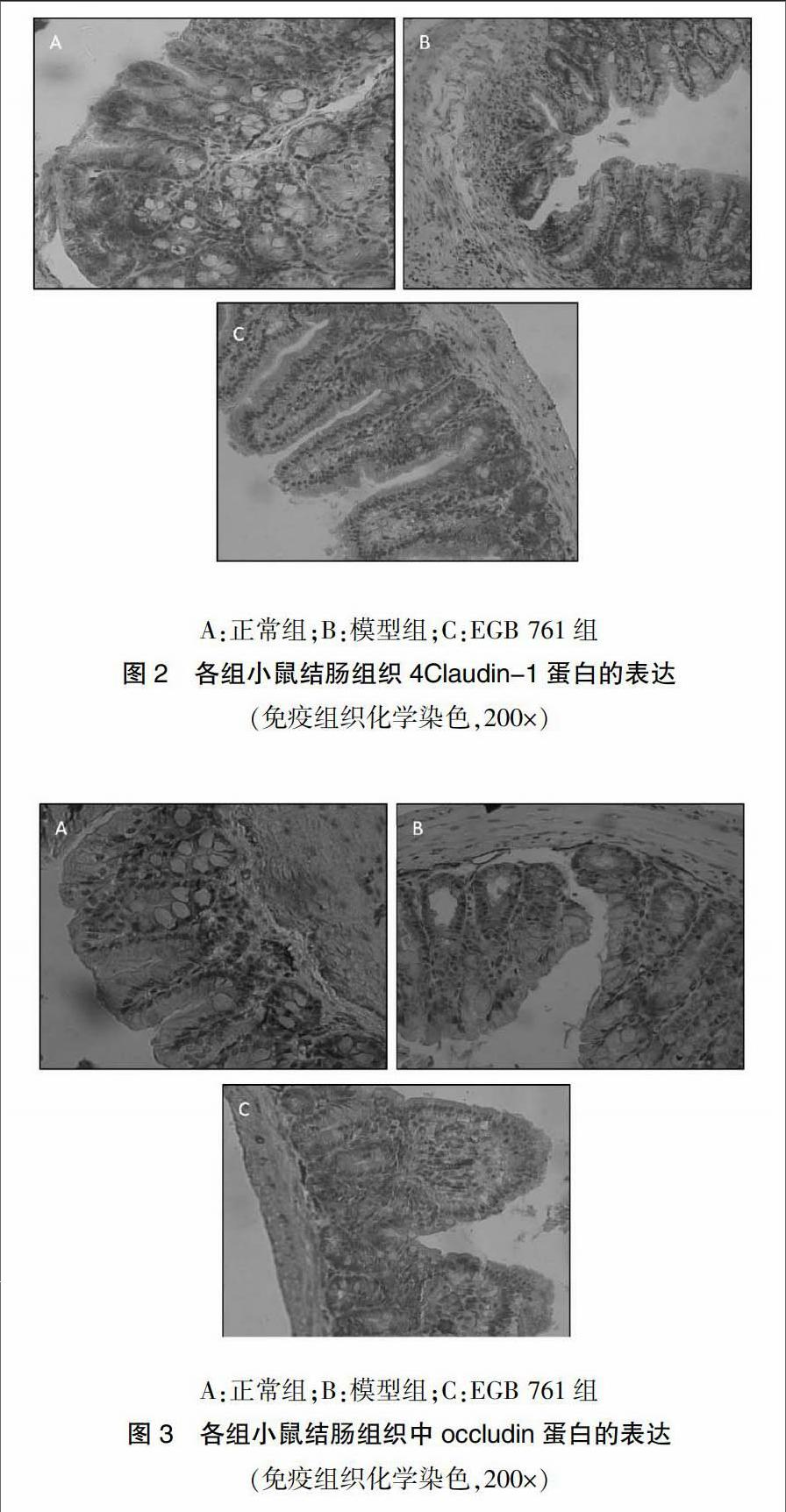
通过光镜观察正常组Claudin-1、occludin蛋白,阳性细胞主要呈棕黄色或褐色,分布于结肠组织上皮细胞的边缘以及细胞膜的顶端,均匀连续分布;模型组的蛋白分布不均染色变淡,线条模糊,边缘粗糙有刺状突起;EGB 761组Claudin-1、occludin蛋白在结肠黏膜上皮层中分布均匀,线条清晰。见图2~3。
2.5 免疫荧光染色检测结肠黏膜occludin和Claudin-1蛋白的定位分布
在激光共聚焦的显微镜下看到的Claudin-1和occludin蛋白均呈红色光亮,在正常组中Claudin-1、occludin蛋白染色可见红色的亮光沿细胞的胞膜分布,呈强光,细胞的胞膜边缘较光滑;在模型组中可见看到,红色的光亮沿细胞胞膜散在分布,荧光强度减弱;EGB 761组荧光仍沿胞膜分布,强度较强于模型组。见图4~5(封三)。
3 讨论
UC是一种病因不明的、高复发的肠道炎症性疾病,研究显示UC在各种微生物抗原刺激下,肠黏膜屏障通透性增高,使肠道致病菌群穿过黏膜屏障,激活体内免疫系统被激活,各种炎症细胞活化,肠黏膜组织产生炎性反应,而肠黏膜通透性,居于中心地位,可能是UC发病的始动因素,所以提高肠道黏膜屏障,降低其通透性可能为该病提供一个新思路。 在正常的情况下,肠道有完整的黏膜屏障,可以阻止有毒物质通过[13-16],UC发病时,肠黏膜屏障通透性增高[17-18]。
GBE 761广泛用于治疗呼吸系统、心脑血管系统等疾病,有调节循环系统、改善血液循环、保护组织等作用。GBE 761可通过抑制炎症细胞因子的表达,如肿瘤坏死因子-α、NF-κBp65、白介素-6,从而对大鼠实验性结肠炎具有保护作用,同时GBE 76灌肠也能抑制大鼠结肠炎的炎症细胞因子的分泌,减轻肠道炎性反应,减少肠黏膜的损伤[19-20]。
实验结果显示,GBE 761干预有促进动物食欲效果导致动物体重迅速增加;减少肠道出血和炎症细胞的浸润,正常组FITC-D含量、细菌移位率及LPS的含量降低。GBE 761干预使紧密连接蛋白分布于细胞边缘,沿细胞膜分布,加强了紧密连接,降低了黏膜的通透性;由此可见,GBE 761可降低肠黏膜通透性、降低肠道炎性反应,减轻肠黏膜病理反应,对UC的治疗有一定作用。
[参考文献]
[1] Dupont A,Kaconis Y,Yang I,et al. Intestinal mucus affinity and biological activity of an orally administered antibacterial and anti-inflammatory peptide [J]. Gut,2015,64(2):222-232.
[2] Long TM,Nisa S,Donnenberg MS,Hassel BA. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli inhibits type I interferon- and RNase L-mediated host defense to disrupt intestinal epithelial cell barrier function [J]. Infect Immun,2014,82(7):2802-2814.
[3] Edogawa S,Takeuchi T,Kojima Y,et al. Current Topics of Strategy of NSAID-Induced Small Intestinal Lesions [J]. Digestion,2015,92(2):99-107.
[4] Ma TM,Xu N,Ma XD,et al. Moxibustion regulates inflammatory mediators and colonic mucosal barrier in ulcerative colitis rats [J]. World J Gastroenterol,2016,22(8):2566-2575.
[5] Nowarski R,Jackson R,Gagliani N,et al. Epithelial IL-18 Equilibrium Controls Barrier Function in Colitis [J]. Cell,2015,163(6):1444-1456.
[6] Hartog A,Belle FN,Bastiaans J,et al. A potential role for regulatory T-cells in the amelioration of DSS induced colitis by dietary non-digestible polysaccharides [J]. J Nutr Biochem,2015,26(3):227-233.
[7] Valentini L,Ramminger S,Haas V,et al. Small intestinal permeability in older adults [J]. Physiol Rep,2014,2(4):e00281.
[8] Kume H,Okazaki K,Takahashi T,et al. Protective effect of an immune-modulating diet comprising whey peptides and fermented milk products on indomethacin-induced small-bowel disorders in rats [J]. Clin Nutr,2014,33(6):1140-1146.
[9] Zhang X,Jiang X. Effects of enteral nutrition on the barrier function of the intestinal mucosa and dopamine receptor expression in rats with traumatic brain injury [J]. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr,2015,39(1):114-123.
[10] Rao YX,Chen J,Chen LL,et al. The impact of dietary methionine-restriction on tight junction expression and function in a rat colonitis mode [J]. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi,2013,52(6):503-509.
[11] Toumi R,Abdelouhab K,Rafa H,et al. Beneficial role of the probiotic mixture Ultrabiotique on maintaining the integrity of intestinal mucosal barrier in DSS-induced experimental colitis [J]. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol,2013,35(3):403-409.
[12] Molnár K,Vannay A,Sziksz E,et al. The role of intestinal alkaline phosphatase in pediatric inflammatory bowel and celiac diseases [J]. Orv Hetil,2012,153(35):1389-1395.
[13] Nowarski R,Jackson R,Gagliani N,et al. Epithelial IL-18 Equilibrium Controls Barrier Function in Colitis [J]. Cell,2015,163(6):1444-1456.
[14] Hartog A,Belle FN,Bastiaans J,et al. A potential role for regulatory T-cells in the amelioration of DSS induced colitis by dietary non-digestible polysaccharides [J]. J Nutr Biochem,2015,26(3):227-233.
[15] Rao YX,Chen J,Chen LL,et al. The impact of dietary methionine-restriction on tight junction expression and function in a rat colonitis mode [J]. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi,2013,52(6):503-509.
[16] Toumi R,Abdelouhab K,Rafa H,et al. Beneficial role of the probiotic mixture Ultrabiotique on maintaining the integrity of intestinal mucosal barrier in DSS-induced experimental colitis [J]. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol,2013,35(3):403-409.
[17] Sun T,Gao GZ,Li RF,et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation ameliorates oxidative stress and restores intestinal mucosal permeability in chemically induced colitis in mice [J]. Am J Transl Res,2015, 7(5):891-901.
[18] Liu X,Xu J,Mei Q,et al. Myosin light chain kinase inhibitor inhibits dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice [J]. Dig Dis Sci,2013,58(1):107-114.
[19] Wang L,Zhang T,Bai K. System evaluation on Ginkgo Biloba extract in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction [J]. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao:Yi Xue Ban,2015, 40(10):1096-1102.
[20] Stark M,Behl C. The Ginkgo Biloba Extract EGb 761 Modulates Proteasome Activity and Polyglutamine Protein Aggregation [J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med,2014, 2014(1):746.
