血管活性肠肽(VIP)对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)大鼠脑组织IL-17A含量的影响
2016-11-29袁正洲吕志宇张淑江李晓红李作孝
杨 元,袁正洲,吕志宇,张淑江,李晓红,李作孝
(西南医科大学附属医院神经内科,四川 泸州 646000)
血管活性肠肽(VIP)对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)大鼠脑组织IL-17A含量的影响
杨 元,袁正洲,吕志宇,张淑江,李晓红,李作孝
(西南医科大学附属医院神经内科,四川 泸州 646000)
目的 探讨血管活性肠肽(vasoactive intestinal peptide, VIP)对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis,EAE)大鼠脑组织IL-17A含量的影响。方法 60只健康雌性Wistar大鼠随机分成正常对照组、EAE对照组、VIP低剂量防治组和VIP高剂量防治组。利用髓鞘碱性蛋白(MBP)+完全福氏佐剂(CFA)诱导建立EAE模型。自造模当日起,每隔一日分别对VIP低、高剂量防治组大鼠腹腔注射VIP 4 nmol/kg(0.2 mL)、16 nmoL/kg(0.8 mL),正常对照组及EAE对照组注射0.8 mL生理盐水,连续10 d。观察大鼠发病情况;ELISA法检测脑组织匀浆中IL-17A因子含量变化;免疫组化技术,利用抗胶质纤维酸性蛋白抗体(GFAP)检测脑组织内的星型胶质细胞活化情况。结果 VIP各剂量防治组大鼠发病潜伏期延长、进展期缩短、发病高峰期神经功能障碍评分(NDS)降低,脑组织匀浆中IL-17A含量降低,活化的星型胶质细胞即GFAP+细胞量减少,且各剂量组间存在一定剂量依赖关系。结论 VIP通过降低脑组织中IL-17A含量、抑制星型胶质细胞活化,发挥对EAE的防治作用。
血管活性肠肽;实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎;IL-17A;GFAP+星型胶质细胞
多发性硬化(multiple sclerosis, MS)作为一种中枢神经系统(central nervous system,CNS)的自身免疫性疾病,其病因尚不明确,各种病因通过破坏Th1/Th2细胞免疫平衡,最终导致CNS炎细胞浸润、白质脱髓鞘、轴突变性等病理改变[1,2]。随着对其动物模型实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)研究深入,越来越多的证据表明Th17细胞分泌的IL-17A因子在该疾病发病过程中也发挥重要的作用[3-5]。血管活性肠肽(vasoactive intestinal peptide, VIP)是一种非胆碱能非肾上腺能神经递质,由28个氨基酸残基组成,属于胰高血糖素-胰泌素家族[6,7]。研究表明VIP通过诱导免疫细胞增殖、分化、活化及迁移,抑制炎症因子(IL-17A、IFN-γ、NO等)的合成及分泌,发挥免疫调节的作用[8]。国内外有将VIP运用在类风湿关节炎(RA)的治疗报道[9,10],但尚未明确阐明VIP对MS发病中各种免疫细胞因子的具体作用,因此本实验通过探讨VIP对EAE大鼠脑组织IL-17A含量影响、星型胶质细胞活化影响,为临床应用VIP治疗MS提供理论依据。
1 材料和方法
1.1 主要实验动物、药物及试剂
健康雌性Wistar大鼠60只(200 g~250 g/只、6~8周龄)、健康豚鼠10只(250 g~300 g)/只,均购买于西南医科大学实验动物中心,均为一级合格动物【生产许可证号:SCXK(川)2013-17】(喂食清洁饲料和自来水,每日按时更换垫料,保持动物房的清洁、适宜的温度和湿度等,使用许可证号【SYXK(川)2013-181】);血管活性肠肽(北京博奥森生物技术有限公司);完全弗氏佐剂CFA(美国Sigma公司产品);IL-17A ELISA免疫试剂盒(广州雅怡生物科技有限公司 );兔抗GFAP多克隆抗体(1:160)(上海雅吉生物科技有限公司);SP免疫组化试剂盒(武汉博士德生物技术公司)。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 免疫抗原的制备:断颈处死10只豚鼠后,在无菌条件下迅速分离出脊髓,去脊膜,称重后移入玻璃匀浆器,与等量的0℃生理盐水混合后研磨成50%的全脊髓匀浆(WSCH)。将完全弗氏佐剂(CFA)与WSCH等体积混合,玻璃注射器抽打至油包水乳状,以滴在水面不散即为合格抗原。
1.2.2 实验动物分组、制模及药物干预:将60只雌性Wistar大鼠随机分为四组(15只/组):正常对照组、EAE对照组、VIP低剂量防治组、VIP高剂量防治组。将免疫抗原注入EAE对照组、VIP低、高剂量防治组大鼠双侧后肢足掌皮下(0.2 mL/100 g)进行主动免疫,正常对照组给予等量生理盐水+CFA。自造模当日起,VIP低、高剂量防治组每隔一日分别腹腔注射VIP 4 nmoL/kg (0.2 mL)、16 nmoL/kg (0.8 mL),正常对照组及EAE对照组给予腹腔注射0.8 mL NS,连续10 d。
1.2.3 动态观察实验动物:自造模日起,每日早晨10 时 由同一观察者采用Kono’s评分标准对大鼠进行神经功能让障碍评分(NDS)。在发病高峰期(将连续3 d评分无加重、四肢瘫痪或死亡作为大鼠发病高峰期)处死大鼠,未发病大鼠饲养8周后处死。
1.2.4 检测脑组织匀浆中IL-17A含量变化:采用双抗体夹心(ABC-ELISA)法检测脑组织匀浆中IL-17A含量。
1.2.5 检测脑组织中星型胶质细胞的活化情况:利用免疫组织化学(SP)技术,采用抗胶质纤维酸性蛋白抗体(GFAP)检测各组大鼠脑组织内的星型胶质细胞活化情况。
将大鼠脑组织行石蜡切片后常规脱蜡、水化、清除内源性过氧化物酶活性、封闭组织蛋白后,逐次滴加一抗(以1∶160 稀释的兔抗GFAP多克隆抗体)、生物素标记的二抗 (山羊抗兔IgG抗体)、链霉卵白素(辣根酶标记),DAB显色液,复染,脱水,透明,封片。400倍光镜下观察大鼠脑组织GFAP+细胞表达情况,胞质呈棕黄色为阳性细胞。采用ImagePro Plus 软件分析GFAP+细胞的平均光密度值(IOD),对GFAP+表达行半定量测定。
2 统计学方法
3 结果
3.1 各组大鼠的发病情况
正常对照组大鼠未发病,EAE对照组、VIP各剂量组大鼠均出现不同程度的临床症状:发病大鼠先后表现为食量下降,精神萎靡,后肢无力,尾部拖地,在免疫后第14~17天病情症状最为典型:大鼠出现双侧后肢无力拖地、行走画圈、爬行困难、自伤后肢、精神极度衰弱、抽搐、甚至死亡。但与EAE对照组比较,VIP低、高剂量组大鼠症状明显缓解,表现为发病潜伏期时间延长、进展期时间缩短、发病高峰期NDS降低。见表1。
3. 2 各组大鼠脑组织中IL-17的含量变化
同正常对照组比较,EAE对照组、VIP各剂量组大鼠脑组织匀浆中IL-17A含量升高;与EAE对照组比较,VIP各剂量组大鼠脑组织匀浆中IL-17A含量明显降低;与VIP低剂量组比较,VIP高剂量组脑组织匀浆中IL-17A含量明显降低。说明在IL-17A在EAE发病过程中起促进作用;同时VIP可以降低EAE大鼠脑组织匀浆中IL-17A含量,且呈一定剂量依赖关系。见表2。
3.3 各组大鼠脑组织中星型胶质细胞活化情况
正常对照组大鼠脑组织未见GFAP+细胞表达;EAE对照组大鼠脑组织内活化的GFAP+细胞呈弥漫性分布;VIP各剂量组大鼠脑组织GFAP+细胞明显减少,主要延血管周围分布。见表3,图1。

Tab.1 Comparison of the incubation period, progression period and peak neurological dysfunction scores in the EAE control group and each dose VIP treatment group

组别Groups潜伏期(d)incubationperiod进展期(d)ProgressionperiodNDS(min)NDSscoresEAE对照组Contol10.34±2.137.85±1.654.16±0.77VIP低剂量组LowdoseVIP14.17±1.67★6.20±1.97☆3.75±0.98ΔVIP高剂量组HighdoseVIP20.73±1.98★●3.99±1.57★○2.59±0.58★●F37.4828.5418.95P<0.01<0.05<0.01
注: 与EAE对照组比较,★P<0.01、☆P<0.05、ΔP>0.05; 与VIP低剂量组比较,●P<0.01、○P<0.05.
Note.★P<0.01,☆P<0.05 andΔP>0.05, Compared with the control group.●P<0.01,○P<0.05, Compared with the low-dose VIP group.

Tab.2 Content of IL-17A in the brain tissue of each group rats
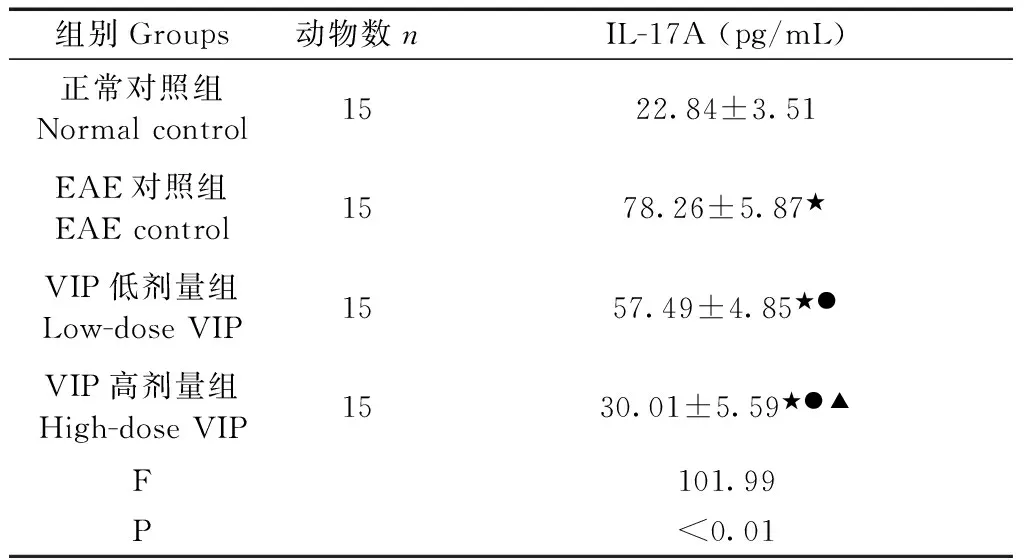
组别Groups动物数nIL-17A(pg/mL)正常对照组Normalcontrol1522.84±3.51EAE对照组EAEcontrol1578.26±5.87★VIP低剂量组Low-doseVIP1557.49±4.85★●VIP高剂量组High-doseVIP1530.01±5.59★●▲F101.99P<0.01
注:与正常对照组比较,★P<0.01;与EAE对照组比较,●P<0.01;与VIP低剂量组比较,▲P<0.01。
Note.★P<0.01, compared with the normal control group.●P<0.01, compared with the EAE control group.▲P<0.01, compared with the low-dose VIP group.

Tab.3 The average IOD of GFAP+cells in the brain tissue of EAE control group and each dose VIP group by immunohistochemistry(×10-2)
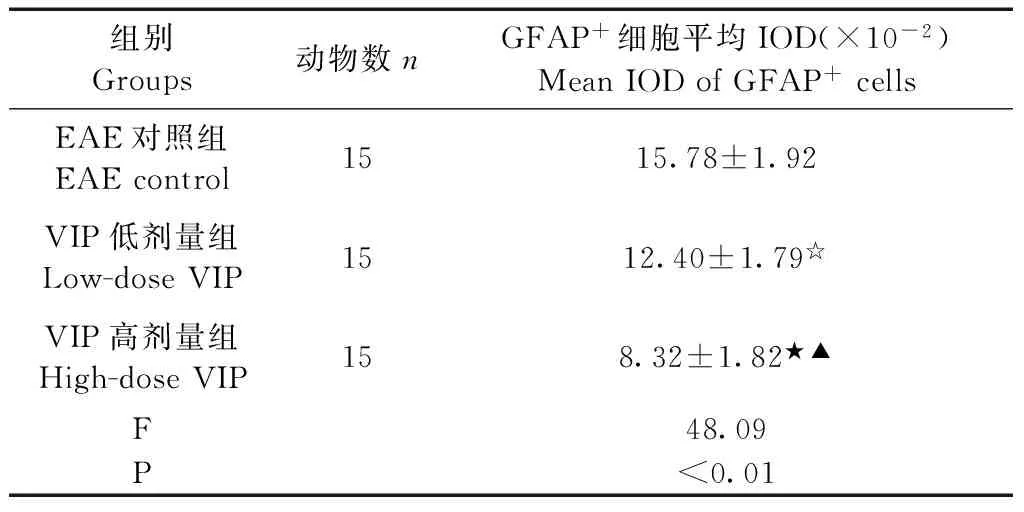
组别Groups动物数nGFAP+细胞平均IOD(×10-2)MeanIODofGFAP+cellsEAE对照组EAEcontrol1515.78±1.92VIP低剂量组Low-doseVIP1512.40±1.79☆VIP高剂量组High-doseVIP158.32±1.82★▲F48.09P<0.01
注: 与EAE对照组比较,★P<0.01、☆P<0.05;与VIP低剂量组比较,▲P<0.01。
Note.★P<0.01,☆P<0.05, compared with the EAE control group.▲P<0.01, compared with the low-dose VIP group.

图1 各组大鼠侧脑室旁脑组织GFAP+细胞表达。免疫组化染色,(标尺=100 μm)。Fig.1 Expression of GFAP+ cells in the rat lateral ventricle of all group rats. Immunohistochemical staining.
3.4 相关性分析显示
利用Pearson 直线相关软件分析,结果显示发病大鼠脑组织匀浆中IL-17A因子含量与与发病高峰期NDS呈正相关 (r=0.798,P<0.05),与脑组织匀浆中GFAP+细胞平均IOD呈正相关(r=0.825,P<0.05)。
4 讨论
IL-17A作为一种具强促炎作用的细胞因子,其主要作用包括:①调节固有免疫[11,12]:IL-17A作为炎症介质,参与自身免疫性炎性疾病的发生和发展,通过作用于基因靶点产生急性反应蛋白、炎症趋化因子等物质,同时上调MHC-II抗原、集落共刺激因子、及T细胞刺激因子、促使T细胞活化,导致免疫失衡;②信号转导作用[13,14]:IL-17A作为细胞内及细胞间信使,参与信号的转导过程,可促进多种炎性蛋白的转录及合成,加速免疫紊乱。
星型胶质细胞作为中枢神经系统一种非特异性抗原提呈细胞(APC),参与复杂的免疫病理过程[15]。在EAE的炎症反应中,IL-17A通过Act1转录因子激活星型胶质细胞促进释放炎症因子,加速髓鞘脱失的发生发展[16,17],同时活化的星型胶质细胞通过上调GFAP+的表达,形成活化的胶质斑块[18]。因此抑制LI-17A产生、干预星型胶质细胞介导的炎症过程,是治疗EAE的一种有效方法。
本实验研究发现:与正常对照组相比,EAE对照组、VIP各剂量组大鼠脑组织匀浆中IL-17A含量升高(P均 <0.01)、脑组织中GFAP+细胞的平均光密度值(IOD)增加(P<0.01、P<0.05),表明IL-17A在EAE发生发展过程中起促进作用。与EAE对照组比较,VIP各剂量组大鼠脑组织匀浆中IL-17A含量均明显降低(P<0.01)、脑组织中GFAP+细胞的IOD明显降低(P<0.01),且两者呈正相关关系(r=0.825,P<0.05)。表明VIP通过降低发病大鼠脑组织匀浆中IL-17A含量,可明显缓解EAE大鼠脑组织星型胶质细胞活化的病理改变,从而减轻EAE的临床表现。
[1] Abad C, Waschek JA. Immunomodulatory roles of VIP and PACAP in models of multiple sclerosis [J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2011, 17(10): 1025-1035.
[2] Delgado M, Pozo D, Ganea D. The significance of vasoactive intestinal peptide in immunomodulation [J]. Pharmacol Rev, 2004, 56(2): 249-290.
[3] Domingues HS, Mues M, Lassmann H, et al. Functional and pathogenic differences of Th1 and Th17 cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis [J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(11): e15531.
[4] Kang ZZ, Altuntas CZ, Gulen MF, et al. Astrocyte-restricted ablation of interleukin-17-induced Act1-mediated signaling ameliorates autoimmune encephalomyelitis [J]. Immunity, 2010, 32(3): 414-425.
[5] Geremia A, Jewell DP. The IL-23 /IL-17 pathway in inflammatory bowel diseases [J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2012, 6( 2): 223-237.
[6] Vaudry D, Falluel-Morel A, Bourgault S, et al. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide and its receptors: 20 years after the discovery [J]. Pharmacol Rev, 2009, 61(3): 283-357.
[7] Delgodo M, Robledo D, Rueda B, et al. Genetic association of vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2008, 58(4): 1010-1019.
[8] Waschek JA. VIP and PACAP: neuropeptide modulators of CNS inflammation, injury, and repair [J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2013, 169(3): 512-523.
[9] Jimeno R, Gomariz RP, Garín M, et al.The pathogenic Th profile of human activated memory Th cells in early rheumatoid arthritis can be modulated by VIP [J]. J Mol Med (Berl), 2015, 93(4): 457-467.
[10] Jimeno R, Leceta J, Garín M, et al.Th17 polarization of memory Th cells in early arthritis: the vasoactive intestinal peptide effect [J]. Leukoc Biol, 2015, 98(2): 257-269.
[11] Patel DD, Kuchroo VK. Th17 cell pathway in human immunity: lessons from genetics and therapeutic interventions [J]. Immunity, 2015, 43(6): 1040-1051.
[12] Sharma J, Balakrishnan L, Datta KK, et al. A knowledge base resource for interleukin-17 family mediated signaling [J]. J Cell Commun Signal, 2015, 9(3): 291-296.
[13] Krstic J, Obradovic H, Kukolj T, et al. An overview of interleukin-17A and interleukin-17 receptor A structure, interaction and signaling [J]. Protein Pept Lett, 2015, 22(7): 570-578.
[14] Waisman A1, Hauptmann J, Regen T. The role of IL-17 in CNS diseases [J]. Acta Neuropathol, 2015, 129(5): 625-637.
[15] Yang JF, Tao HQ, Liu YM, et al. Characterization of the interaction between astrocytes and encephalitogenic lymphocytes during the development of experimental autoimmune encephalitomyelitis (EAE) in mice [J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2012, 170(3): 254-265.
[16] Kang ZZ, Altuntas CZ, Gulen MF, et al. Astrocyte-restricted ablation of interleukin-17-induced Act1-mediated signaling ameliorates autoimmune encephalomyelitis [J]. Immunity, 2010, 32(3): 414-425.
[17] Kang ZZ, Wang CH, Zepp J, et al. Act1 mediates IL-17-induced EAE pathogenesis selectively in NG2+ glial cells [J]. Nat Neurosci, 2013, 16(10): 1401-1408.
[18] Yan YP, Ding XL, Li K, et al. CNS-specific therapy for ongoing EAE by silencing IL-17 pathway in astrocytes [J]. Mol Ther,2012, 20(7): 1338-1348.
Effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) on the content of IL-17A in the brain tissue of rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE)
YANG Yuan, YUAN Zheng-zhou, LV Zhi-yu, ZHANG Shu-jiang, LI Xiao-hong, LI Zuo-xiao
(Department of Neurology. Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University,Luzhou Sichuan 646000, China)
Objective To explore the effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) on the content of IL-17A in the brain tissue of rat models of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Methods Sixty healthy female Wistar rats were randomly divided into normal control group, EAE control group, low-dose VIP group and high-dose VIP group. Ten healthy guinea pigs were used to prepare anti- IL-17A antibody. Myelin basic protein (MBP) + complete adjuvant (CFA) were used to establish the EAE model. Since the first day of modelling, the low-dose and high-dose VIP groups received intraperitoneal injection of VIP 4 nmol/kg (0.2 mL) and 16 nmol/kg (0.8 mL), respectively, every other day for 10 consecutive days. The normal control group and EAE group were injected with 0.8 mL saline instead of VIP. The incubation period, progression and the peak of neurological dysfunction scores (NDS) of the rats were recorded. The levels of IL-17A in the brain tissue was determined by ELISA assay, and the GFAP+astrocyte activation in brain at morbidity peak in the rats was examined using anti-GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein) antibodies. Results The incubation period were extended, the progression period was shortened and the peak neuological dysfunction score (NDS) was decreased in the VIP-treated groups, in a dose-response relationship. The cytokine levels of IL-17A and the astrocyte activation degree in brain tissue were reduced in each VIP dose group, in a dose-response relationship. Conclusions VIP exerts therapeutic effect on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through lowering the IL-17A content and inhibition of astrocyte activation in the brain tissue.
Vasoactive intestinal peptide; Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; IL-17A; GFAP+astrocytes; Rats; Guinea pigs
杨元,女,硕士,E-mail: lsh880801@163.com,电话:18715760908。
李作孝,男,教授,硕士生导师,E-mail: lzx3235@sina.cn,电话:13882794776。
R-33
A
1671-7856(2016)10-0032-04
10.3969.j.issn.1671-7856. 2016.10.007
2016-05-06
