不同处理对绿豆芽中亚硝酸盐含量影响的研究
2016-11-25王晓晶宋春梅
王晓晶+宋春梅


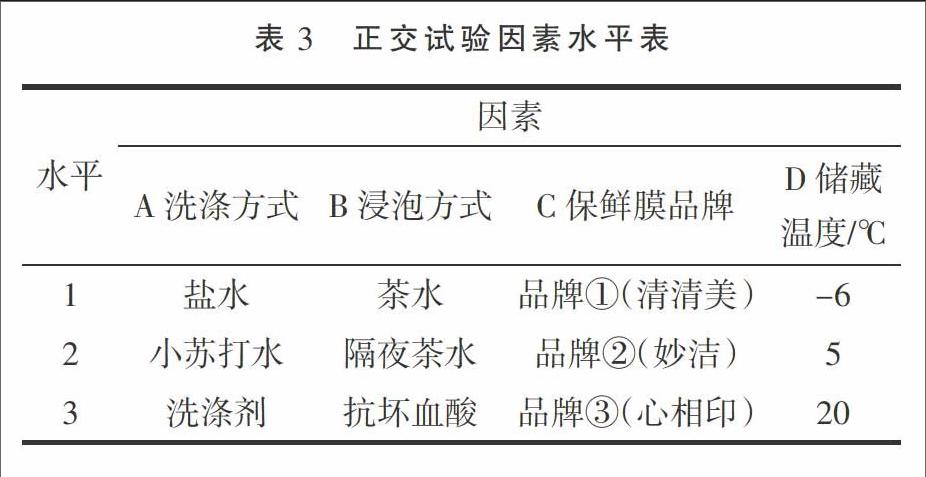
摘 要:以绿豆芽为试验材料,研究在不同储藏温度(-6,5,20,25,30 ℃)、不同保鲜膜覆盖(品牌①清清美、品牌②妙洁、品牌③心相印、品牌④茶花、品牌⑤南亚)、不同浸泡方式(淡盐水、茶水、隔夜茶水、抗坏血酸溶液)、不同洗涤方式(自来水、盐水、淘米水、小苏打水、洗涤剂)这四种处理方式下绿豆芽中亚硝酸盐含量的变化,并对绿豆芽做这四种处理的正交实验,选出一个亚硝酸盐含量最少的、最佳的处理方案。试验结果表明:绿豆芽中的亚硝酸盐含量随着温度的升高而增加;自来水、盐水、淘米水、小苏打水和洗涤剂均对绿豆芽中的亚硝酸盐有去除作用,并且洗涤剂的去除作用优于其它四种洗涤方式;不同的浸泡方式去除作用不同,其中抗坏血酸溶液的去除作用为最佳;这五种保鲜膜中品牌②的效果最好;做正交实验时,绿豆芽在用小苏打水洗涤、茶水浸泡、品牌②的保鲜膜覆盖保存在5 ℃的温度下亚硝酸盐的含量最低,即绿豆芽的最佳处理方式。
关键词:储藏方式;浸泡方式;洗涤方式;绿豆芽;亚硝酸盐
中图分类号:S522 文献标识码:A DOI 编码:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6500.2016.10.006
Abstract: In this experiment, the mung bean sprout was used as the experimental material, the changes of nitrite content in mung bean sprouts under different treatments were studied. The first condition was temperature(-6, 5, 20, 25, 30 ℃). The second condition was plastic wraps(Clear beauty, Miaojie, Heart phase printing, Camellia, South Asia).The third condition was immersion method(light salt water, tea, last night's tea, ascorbic acid solution), The last condition was washing method (running water, salt water,rice water, soda water, detergent).And the orthogonal experiment of mung bean sprouts was done to select an optimal solution for the least nitrite content. The results showed that the nitrite content in mung bean sprouts increased with the increase of the temperature; Running water, salt water, rice water, baking soda water and detergent solution had the effect of removing nitrite in mung bean sprouts, and the effect of detergent was the best; Under different immersion methods, the effects were different, the removal effect of ascorbic acid was the best. The effect of second plastic wraps named Miaojie was the best. In the orthogonal experiment, the content of nitrite was the lowest when the mung bean sprout was washed with baking soda, soak with tea, covered with plastic wraps named Miaojie and kept at 5 ℃.
Key words: storage method; immersion method; washing method; mung bean sprout; nitrite
蔬菜是人们日常生活必不可少的食物,而绿豆芽作为一种常见的营养价值较高的蔬菜,具有很好的研究价值。 绿豆在发芽的过程中,会产生很多有益于人体的营养物质,绿豆发芽后,会释放出更多的锌、铁等矿物质,维生素类物质的含量也大幅增加,其中VB2的含量会增加大约4倍,胡萝卜素含量会增加大约3倍,Vc的含量会增加达6%,叶酸和维生素B6的含量也有所增加。绿豆芽中还含有许多有益于人体的营养物质,具有很好的食用价值[1-3]。
蔬菜中的亚硝酸盐已引起食品卫生界的广泛重视。医学研究证明,过多的摄入亚硝酸盐会导致人体中毒,同时,亚硝酸盐还有致癌性和致畸性,因此我国食品卫生标准规定,无公害蔬菜亚硝酸盐含量不得超过4 mg·kg-1[4]。
近年来,国内外的诸多学者对不同条件下蔬菜中硝酸盐与亚硝酸盐含量的变化,及其测定方法等方面都做出很多研究。一些学者在豆芽的硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐污染状况及安全食用的研究中得出,在常温和冰箱中储藏的豆芽其亚硝酸盐含量均呈现先升后降的趋势,但常温储藏时变幅更大,而豆芽中硝酸盐含量则随贮藏时间的延长而逐渐减少[5-6]。一些学者在不同储藏条件和洗涤方式对蔬菜中亚硝酸盐含量影响的研究中得出,低温条件下更利于蔬菜的贮藏;洗涤剂对蔬菜的清洗作用优于盐水[7-9]。
