颅骨修补术后血管反应性与认知功能改善的相关性研究
2016-11-25焦明义盛建春赵明光郭学军宋振全梁国标
焦明义 盛建春 赵明光 郭学军 宋振全 梁国标
(1辽宁医学院沈阳军区总医院研究生培养基地; 2沈阳军区总医院神经外科,辽宁 沈阳 110840)
·功能神经外科疾病研究·
颅骨修补术后血管反应性与认知功能改善的相关性研究
焦明义1盛建春2赵明光2*郭学军2宋振全2梁国标2
(1辽宁医学院沈阳军区总医院研究生培养基地;2沈阳军区总医院神经外科,辽宁 沈阳 110840)
目的探讨创伤性颅骨缺损修补对认知功能及脑血管反应性(CVR)的影响, 并对其相关性进行分析。方法选择2014年4月至2015年2月在我院神经外科住院的54例颅脑损伤术后颅骨缺损且欲行颅骨修补的患者为研究对象,于术前1天及术后2周应用联合型瑞文智力测验(CRT) 评价其认知功能,屏气试验评价CVR,采用配对t检验和Pearson相关分析进行统计分析。结果颅骨修补术后,患者在CRT6个单元的评定分显著高于术前(Plt;0.05);比较修补术前、后患者患侧屏气指数(BHI)及总BHI,其差异均有统计学意义(Plt;0.05);相关分析显示,BHI与CRT6个单元评分均呈正相关(Plt;0.05)。结论颅骨修补术可明确改善患者的认知功能、CVR,并且患者的认知水平随CVR的提高而得到明显改善。
颅骨缺损; 认知功能; 屏气指数; 血管反应性
近年来研究表明,颅骨缺损患者的认知功能障碍并非完全由原发脑损伤造成,其颅骨缺损本身对认知功能也存在一定的影响[1]。Chibbaro等[2]对43例患者进行分析,结果显示其中91%患者的认知功能得到明显改善,简易精神状态量表(MMSE)评分均值由颅骨缺损时的18分(16~20分)上升至颅骨修补术后的25分(19~30分);颅骨修补后全部患者的脑灌注血流量均得到改善。此外,还有研究明确指出,颅骨修补术可明显改善患者缺损区域局部脑组织的血流及循环速度[3,4]。因此可推断颅骨修补术后患者认知功能的改善与脑血流量的增加有一定的相关性,然而血流量的增加是否与脑血管自我调节能力的变化所引起,认知功能的改善与血管调节能力的提高是否存在直接关系目前仍不清楚;因此本研究于2014年4月至2015年2月对我院神经外科住院的54例颅骨缺损患者进行调查研究,对颅骨缺损患者行修补术前后的血管反应性、认知功能及其相关性进行分析。
对象与方法
一、研究对象
选择2014年4月至2015年2月在我院神经外科住院的54例颅脑损伤术后颅骨缺损患者为研究对象,其中男性40例,女性14例;年龄12~60岁,平均(41.30±12.55)岁;术前GOS评分3~5分,平均(4.35±0.77)分;颅骨缺损部位分别为:双侧额部、左侧颞顶部2例(3.7%),双侧额颞顶部1例(1.9%),双额颞部1例(1.9%),右侧额颞部2例(3.7%),右侧额颞顶部23例(42.6%),右额颞部、左额部1例(1.9%),左侧顶枕部2例(3.7%),左侧额颞顶部22例(40.7%)。颅脑损伤去骨瓣减压术后行修补术的时间窗最短为2个月12 d,最长为2年3个月,平均时间(113.2±28.7)d。所有患者均于入院后行三维钛网修补术。并于手术前1天完善相关检查并于术后2周复查。所有患者既往无脑血管病、精神病及认知缺陷病史,无检查不配合的患者。
二、联合型瑞文智力测验(combined raven's test,CRT)
主要用于评估患者的认知功能,共由72题组成,分为AB、A、B、C、D、E六个单元,每单元12题。题目难度逐组增加,每组内部题目也是由易到难排列。具体情况如下:AB主要测试图形比较与想象能力;A组题测验知觉辨别力;B组测验类同、比较、图形组合等;C组测验比较、推理、图形组合;D组测验系列关系、图形套合;E组测验套合、互换等抽象推理能力。前3个单元图形为彩色型,后3个图形为黑白型。计分时对照标准答案,每答对1题记1分,先将每个单元分别计分,各单元满分为12分。测验时间为20~40 min。
三、屏气试验
主要用于评价患者的脑血管反应性(cerebrovascular reactivity,CVR)。在安静舒适的环境下,患者取仰卧位,通过经颅多普勒仪器,检测大脑中动脉平静呼吸状态下的血流情况,然后平静吸气末屏气25 s再次测量,恢复平静呼吸10 min后检测对侧,分别记录双侧静息状态及屏气后的血流速度,取3次测量值的平均值,计算屏气指数(breath holding indexes,BHI)=(屏气后平均血流速度-静息状态平均血流速度)/静息状态平均血流速度×100/屏气时间。及计算总BHI=双侧BHI的平均值。
四、统计学分析
采用SPSS 13.0软件包对资料进行分析,采用配对t检验对修补术前后患侧与健侧BHI和VMCA的差异进行分析,并对修补术后BHI与认知功能进行Pearson相关分析,Plt;0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结 果
一、颅骨修补术前后CRT情况
颅骨修补前患者在AB、A、B、C、D、E6个单元的平均得分是(9.26±2.73)分、(9.87±2.58)分、(7.80±2.79)分、(5.74±2.85)分、(4.91±3.25)分、(2.57±2.16)分;修补术后患者在该6个单元的评分存在统计学提高,其分值分别为(10.65±0.85)分、(10.65±0.71)、(10.11±1.63)分、(8.04±2.50)分、(7.44±3.47)分、(4.17±3.62)分。其CRT各单元测试结果变化(图1)。
二、修补前后BHI变化
颅骨缺损术前患侧BHI明显低于健侧(t=3.095,P=0.004);修补术前后患者患侧BHI及总BHI差异均有统计学意义,而健侧BHI改变差异无统计学意义(表1)。
三、修补术后BHI与认知功能的关系
BHI与CRT6个单元评分均呈正相关(Plt;0.05),即BHI改善,认知功能也随之发生好转。
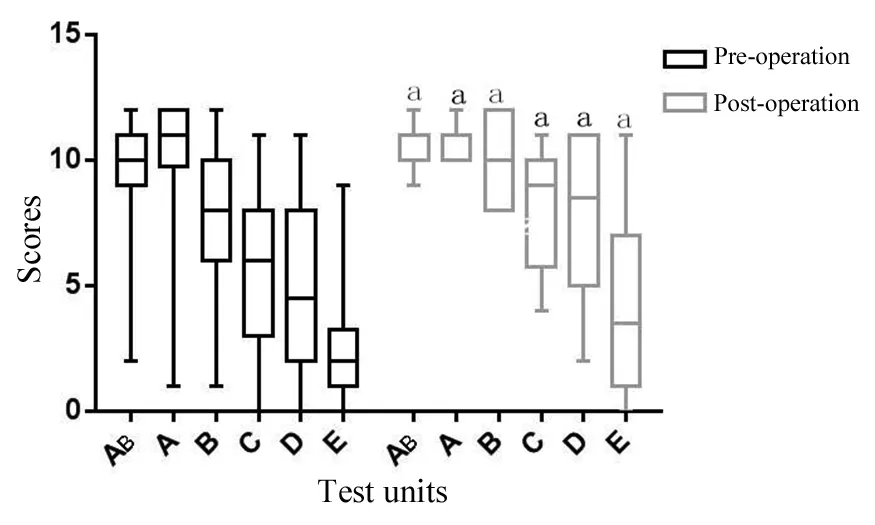
图1 颅骨缺损修补术前后CRT各单元得分分布情况
Fig 1 Distributions of the pre- and post-cranioplasty scores of each unit of the CRT
aPlt;0.05,vspre-operation.


ItemnBeforecranioplastyAftercranioplasty Affectedside4966.54±20.8877.84±11.45a Un⁃affectedside4974.46±16.5978.68±16.43a TotalBHI5470.53±17.1578.26±13.17a
aPlt;0.05,vspre-operation
讨 论
自1905年首次行去骨瓣减压术救治颅脑损伤患者以来,该手术方式已成为颅脑外伤后恶性颅高压,特别是脑疝患者的首选治疗手段,但因颅骨缺损导致的眩晕、头痛、易疲劳、记忆力下降、抑郁等一系列症状也越来越受到人们关注。颅骨修补术不但可以进行美容修复,而且可以改善这些症状并保护脑组织,尤其患者的认知功能及脑血流动力学方面也可得到很大的改善[5~9]。
CRT是全图、非文字性的一种测验方法,它克服了文化背景影响和语言交往困难,具有操作简单、省时省力、可集体施测等优点,使用范围较广,故本研究应用CRT检测患者修补术前、后的认知功能。结果显示,修补术后图形比较与想象能力,知觉辨别能力,类同、比较、图形组合能力,比较、推理、图形组合能力,系列关系、图形套合能力,套合、互换等抽象推理能力均有改善。究其原因是修补术后使患者的颅内压趋于稳定、脑脊液循环改善,脑血流速度加快,促进脑细胞代谢,改善脑神经生理功能,从而使患者的认知功能得到较大程度的提高[10~12]。本研究结果还显示套合、互换等抽象推理能力得分仍然较低,仅为(4.17±3.62)分,这说明患者的高级推理能力还需进一步加强,究其原因可能是患者术后大脑血流的不对称性还未得到完全纠正,脑功能仍处于修复状态,但也可能是因为套合、互换等抽象推理单元的图形比较繁琐、难度较大且属于最后一个单元,患者因生理原因或心理厌倦并不能集中精力去做题,导致分数较低。
既往研究认为颅骨缺损造成血管受压,增加血流阻力,修补术降低舒张期血管的收缩,使脑微小血管舒张能力增加,小血管阻力降低,使脑血流量增加[13,14]。相对血流速度而言,CVR可更好地体现血管自身的收缩及舒张性,BHI作为CVR的评价指标可以更好的反映脑血管的扩张性及储备能力,而且操作简单、属无创性检查,患者也能够配合。高永哲等通过对55例阿尔茨海默病( Alzheimer's disease,AD)患者的对比研究发现AD 脑存在广泛的皮质及皮质下区域的局部脑血流量下降,同时,特征性地在前脑特别是额叶皮质表现为CVR的下降,从而证实了缺血会造成认知功能的损害[15]。本研究结果显示,修补术后患者患侧BHI及总BHI值高于术前,这说明颅骨缺损后大气压使缺损部位的皮瓣下陷,导致血管外周阻力显著增加,脑血流减少,血管的收缩能力受限,而术后有效地降低了血管外周阻力和血管壁张力,使脑血流量的代偿能力恢复,维持了的脑组织正常灌注,促进脑血流循环代谢恢复,进而改善认知功能[16];有学者认为,行颅骨修补后,受损的脑微小血管舒张能力得以恢复,可更好地发挥脑血管储备能力的功能,使脑血流量增加,减少了对局部微血管的压迫,减轻微循环障碍,从而使脑血流循环灌注改善,促进能量代谢、葡萄糖利用、蛋白合成等功能提高,使皮层对信息认识、整合等过程得以恢复、认知反应和处理能力提升,最终使认知功能得到最大程度的改善[17]。这与本研究的BHI与CRT6个单元评分正相关基本相符。
综上所述,颅骨修补术可改善创伤性颅骨缺损患者缺损区域的VMCA及整体CVR,并能提高其认知功能,对于颅骨缺损患者可采取适当治疗措施,增加患者脑部血流,及早改善患者的认知功能。
1Di Stefano C,Sturiale C,Trentini P,et al. Unexpected neuropsychological improvement after cranioplasty:a case series study [J]. Br J Neurosurg,2012,26(6):827-831.
2Chibbaro S,Vallee F,Beccaria K,et al. The impact of early cranioplasty on cerebral blood flow and its correlation with neurological and cognitive outcome. Prospective multi-centre study on 24 patients [J]. Rev Neurol (Paris),2013,169(3):240-248.
3Honeybul S,Ho KM,Lind CR,et al. Observed versus predicted outcome for decompressive craniectomy:A population based study [J]. J Neurotrauma,2010,27(7):1225-1232.
4Mokri B. Orthostatic headaches in the syndrome of the trephined:resolution following cranioplasty [J]. Headache,2010,50(7):1206-1211.
5Honeybul S,Janzen C,Kruger K,et al. The impact of cranioplasty on neurological function [J]. Br J Neurosurg,2013,27(5):636-641.
6Ferro JM,Crassard I,Coutinho JM,et al. Decompressive surgery in cerebrovenous thrombosis:a multicenter registry and a systematic review of individual patient data [J]. Stroke,2011,42(10):2825-2831.
7李鑫,李晶,李京生. 外伤性颅骨缺损修复前后灌注 CT 评价脑血流变化的研究 [J]. 中华神经外科杂志,2015,31(7):702-706.
8伦鹏,刘鹏,王刚,等. CT灌注评价颅骨修补术后脑灌注与神经功能改善 [J]. 中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2014,13(3):272-273.
9Won YD,Yoo DS,Kim KT,et al. Cranioplasty effect on the cerebral hemodynamics and cardiac function [J]. Acta Neurochir Suppl,2008,102:15-20.
10Jelcic N,De Pellegrin S,Cecchin D,et al. Cognitive improvement after cranioplasty:a possible volume transmission-related effect [J]. Acta Neurochir,2013,155(8):1597-1599.
11Di Stefano C,Sturiale C,Trentini P,et al. Unexpected neuropsychological improvement after cranioplasty:a case series study [J]. Br J Neurosurg,2012,26(6):827-831.
12Ho CL,Wang CM,Lee KK,et al. Cerebral oxygenation,vascular reactivity,and neurochemistry following decompressive craniectomy for severe traumatic brain injury [J]. J Neurosurg,2008,108(5):943-949.
13Vicenzini E,Ricciardi MC,Altieri M,et al. Cerebrovascular reactivity in degenerative and vascular dementia:a transcranial Doppler study [J]. Eur Neurol,2007,58(2):84-89.
14Silvestrini M,Pasqualetti P,Baruffaldi R,et al. Cerebrovascular reactivity and cognitive decline in patients with Alzheimer disease [J]. Stroke,2006,37(4):1010-1015.
15高永哲,章军建,吴光耀,等. 阿尔茨海默病患者局部脑血流量及脑血管反应性研究 [J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志,2013,30(2):120-123.
16Weiner GM,Lacey MR,Mackenzie L,et al. Decompressive craniectomy for elevated intracranial pressure and its effect on the cumulative ischemic burden and therapeutic intensity levels after severe traumatic brain injury [J]. Neurosurgery,2010,66(6):1111-1118.
17Villeneuve S,Belleville S,Massoud F,et al. Impact of vascular risk factors and diseases on cognition in persons with mild cognitive impairment [J]. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord,2009,27(4):375-381.
AbstractOBJECTIVEThe authors' group recently published a novel technique for a navigation-guided frameless stereotactic approach for the placement of depth electrodes in epilepsy patients. To improve the accuracy of the trajectory and enhance the procedural workflow,the authors implemented the iSys1 miniature robotic device in the present study into this routine.METHODSAs a first step,a preclinical phantom study was performed using a human skull model,and the accuracy and timing between 5 electrodes implanted with the manual technique and 5 with the aid of the robot were compared. After this phantom study showed an increased accuracy with robot-assisted electrode placement and confirmed the robot's ability to maintain stability despite the rotational forces and the leverage effect from drilling and screwing,patients were enrolled and analyzed for robot-assisted depth electrode placement at the authors' institution from January 2014 to December 2015. All procedures were performed with the S7 Surgical Navigation System with Synergy Cranial software and the iSys1 miniature robotic device.RESULTSNinety-three electrodes were implanted in 16 patients (median age 33 years,range 3~55 years; 9 females,7 males). The authors saw a significant increase in accuracy compared with their manual technique,with a median deviation from the planned entry and target points of 1.3 mm (range 0.1~3.4 mm) and 1.5 mm (range 0.3~6.7 mm),respectively. For the last 5 patients (31 electrodes) of this series the authors modified their technique in placing a guide for implantation of depth electrodes (GIDE) on the bone and saw a significant further increase in the accuracy at the entry point to 1.18±0.5 mm (mean±SD) compared with 1.54±0.8 mm for the first 11 patients (P=0.021). The median length of the trajectories was 45.4 mm (range 19~102.6 mm). The mean duration of depth electrode placement from the start of trajectory alignment to fixation of the electrode was 15.7 minutes (range 8.5-26.6 minutes),which was significantly faster than with the manual technique. In 12 patients,depth electrode placement was combined with subdural electrode placement. The procedure was well tolerated in all patients. The authors did not encounter any case of hemorrhage or neurological deficit related to the electrode placement. In 1 patient with a psoriasis vulgaris,a superficial wound infection was encountered. Adequate physiological recordings were obtained from all electrodes. No additional electrodes had to be implanted because of misplacement.CONCLUSIONSThe iSys1 robotic device is a versatile and easy to use tool for frameless implantation of depth electrodes for the treatment ofepilepsy. It increased the accuracy of the authors' manual technique by 60% at the entry point and over 30% at the target. It further enhanced and expedited the authors' procedural workflow.
J Neurosurg. 2016 Aug 5:1-7. [Epub ahead of print]
Acorrelativestudyonimprovementsincerebrovascularreactivityandcognitivefunctionaftercranioplasty
JIAOMingyi1,SHENGJianchun2,ZHAOMingguang2,GUOXuejun2,SONGZhenquan2,LIANGGuobiao2
1LiaoningMedicalUniversity,GeneralHospitalofShenyangMilitaryCommand,Shenyang110840;2DepartmentofNeurosurgery,GeneralHospitalofShenyangMilitaryCommand,Shenyang110840,China
ObjectiveThe effects of cranioplasty for traumatic skull defects on cognitive function and cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR) are discussed and the correlations between them are analyzed.MethodsA total of 54 patients with skull defects after operation of traumatic brain injury who admitted to the General Hospital of Shenyang Military Command from April 2014 to February 2015 were enrolled in the study. All the subjects underwent three-dimensional (3D) titanium mesh cranioplasty following admission. The combined Raven's test (CRT) was conducted to evaluate the cognitive function of each patient at 1 d pre-operation and 2 w after operation. The breath-holding test was conducted to evaluate CVR. The statistical analysis was made by the pairedt-test and Pearson correlation analysis.ResultsThe evaluation scores of the six units of the CRT,the breath holding indexes (BHIs),and total BHIs of the patients after cranioplasty were significantly higher than those before cranioplasty (Plt;0.05). The correlation analysis showed that the BHI was positively correlated with the evaluation scores of the six units of the CRT (Plt;0.05).ConclusionCranioplasty can definitively improve the cognitive function and CVR of patients. The patients' cognitive function is dramatically improved with the increase of CVR.
Skull defects; Cognitive function; Breath holding indexes; Cerebrovascular reactivity
A novel miniature robotic device for frameless implantation of depth electrodes in refractory epilepsy
DorferC1,MinchevG1,CzechT1,StefanitsH1,FeuchtM2,PataraiaE3,BaumgartnerC4,KronreifG5,WolfsbergerS1
1DepartmentofNeurosurgery;2DepartmentsofPediatricsandAdolescenceMedicine;3DepartmentofNeurology,EpilepsyMonitoringUnit,MedicalUniversityVienna;4SecondNeurologicalDepartment,GeneralHospitalHietzing,Vienna;5AustrianCenterofMedicalInnovationandTechnology(ACMIT),WienerNeustadt,Austria
1671-2897(2016)15-305-04
R 749.1+2
A
焦明义,硕士研究生,E-mail:jiaomingyi123@163.com
*通讯作者:赵明光,副教授,副主任医师,E-mail:zhaomingguang1972@hotmail.com
2015-10-31;
2016-02-20)
