土壤重金属处理对烟草中As、Cd、Hg和Pb的累积与分布的影响
2016-11-16魏益华何俊海冯小虎王利兵周瑶敏李琰琰袁丽娟罗林广
魏益华,何俊海,冯小虎,王利兵,周瑶敏,李琰琰,袁丽娟,罗林广
1 江西省农业科学院农产品质量安全与标准研究所,江西省南昌市南莲路602号 330200;2 江西省烟草公司抚州市公司,江西省抚州市大公路115号 344000
土壤重金属处理对烟草中As、Cd、Hg和Pb的累积与分布的影响
魏益华1,何俊海1,冯小虎2,王利兵2,周瑶敏1,李琰琰2,袁丽娟1,罗林广1
1 江西省农业科学院农产品质量安全与标准研究所,江西省南昌市南莲路602号 330200;2 江西省烟草公司抚州市公司,江西省抚州市大公路115号 344000
为了解不同重金属处理烟草中重金属的累积及分布特征,进行了高、中、低浓度的砷(As)、镉(Cd)、汞(Hg)、铅(Pb)及其复合处理盆栽试验。结果表明:烟叶中As、Cd和Pb元素含量随时间变化规律为:初期>收获期、中期,Hg为中期>收获期>初期。重金属污染胁迫下,烟草中重金属累积分布特征为:As和Pb为根>茎>叶,Cd为茎>根>叶,Hg为根>叶>茎(对照:叶>根>茎)。烟草中重金属(除Hg)含量总体随外源添加浓度的增大而显著增大(p<0.05)。复合处理烟叶中重金属含量低于单元素处理。烟叶中重金属增幅顺序为As>Cd>Pb>Hg,As和Cd处理间烟草(根、茎和叶)中As和Cd含量均差异显著。可见,烟草对土壤As和Cd污染最为敏感,烟草种植时应尽量选择土壤As和Cd含量较低的区域以避免其过度累积。
烟叶;重金属;累积;分布
随着人们对“吸烟与健康”的日益关注,烟叶安全性问题越来越受重视,其中烟草与重金属的关系已成为国内外烟草研究热点之一。以往研究表明,烟草中重金属含量与土壤重金属含量及其土壤理化性质有着密切的联系[1-4],并受到烟草品种[5,6]、耕作栽培措施[7-9]和气候[10]等多因素作用。重金属在烟草中过量累积势必对其生长发育[11,12]、酶活性[13,14]、光合作用[15,16]及其品质[17,18]造成影响。
目前,土壤重金属污染胁迫下有关重金属在烟草中的累积与分布规律研究不多,且研究主要集中在Cd和Pb两种元素,研究结论亦存在一定差异。关于Cd和Pb在烟株中主要积累的部位,张玉涛等[19]、米艳华等[20]、王学锋等[21]等研究结果是不一致的;有关烟草中重金属含量是否随外源添加浓度增加而显著增大的研究结果同样存在差异,如孟建玉等[1]、王绍坤等[22]的研究。故有必要继续开展重金属在烟草中的累积、迁移等行为研究,进一步探索烟草对重金属的吸收累积规律。此外,有关重金属复合污染下烟草积累重金属的研究报道亦较少,
至今为止,关于As、Cd、Hg和Pb 4种重金属污染及其复合污染在烟草根、茎和叶中吸收累积与分布特征研究尚未见报道。本文通过盆栽试验,以As、Cd、Hg和Pb为污染因子,研究了这4种元素单一污染及复合污染下烟叶中重金属含量随时间变化规律以及重金属在烟草体内累积与分布特征,旨在为有效控制烟草中重金属含量、烟草安全生产及合理规划烟草种植等提供科学依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料与品种
土样取自江西省抚州市烟草局农场(抚州市临川区东馆镇)红壤土。成土母质为第四纪红色粘土,其亚类为红壤。土样风干后磨碎过2 mm 尼龙筛,备用。土壤的基本性质见表 1。烟草选用江西主栽烤烟品种K326。
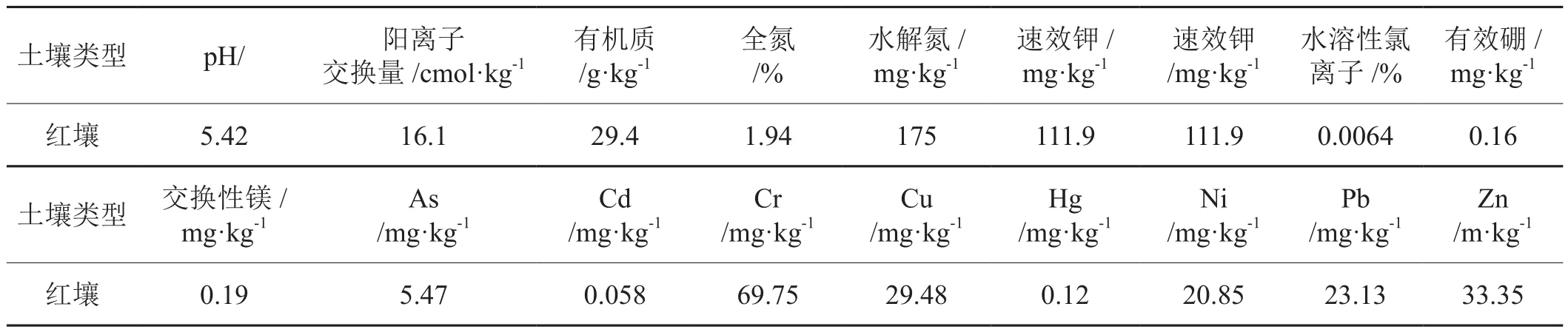
表1 供试土壤基本理化性质Tab. 1 Physicochemical properties of the tested soil
1.2 试验设计
盆栽试验于2013年江西省抚州市烟草局农场内进行。试验用的化合物为Na3AsO4·12H2O,CdCl2·2.5H20、HgSO4、PbCl2,重金属处理浓度以纯As、Cd、Hg和Pb计。各化合物按各处理浓度所需之量溶于水后用喷雾器喷撒于土中使之与土壤均匀混合,然后装盆,第盆土壤重10 kg。试验采用完全随机设计,设置15 个重金属添加处理,第个处理 5个重复,平衡老化1 个月后进行烟苗移栽种植。种植前第盆施加纯 N 2.0 g,并按照m(N)∶m(P2O5)∶m(K2O)=1∶1∶2的比例施加磷和钾肥。试验过程保持土壤含水量为田间最大持水量的 60% ~70%。
烟草移栽时间为3月 20日,收获时间为7月13日,盆栽生育期共计115d。烟草移栽第20(移栽初期)、30、50、60(移栽中期)、80、115(收获期)d时,采集烟叶(中部叶)样品,第次采叶数不少于10片。烟草重金属含量以干重计。
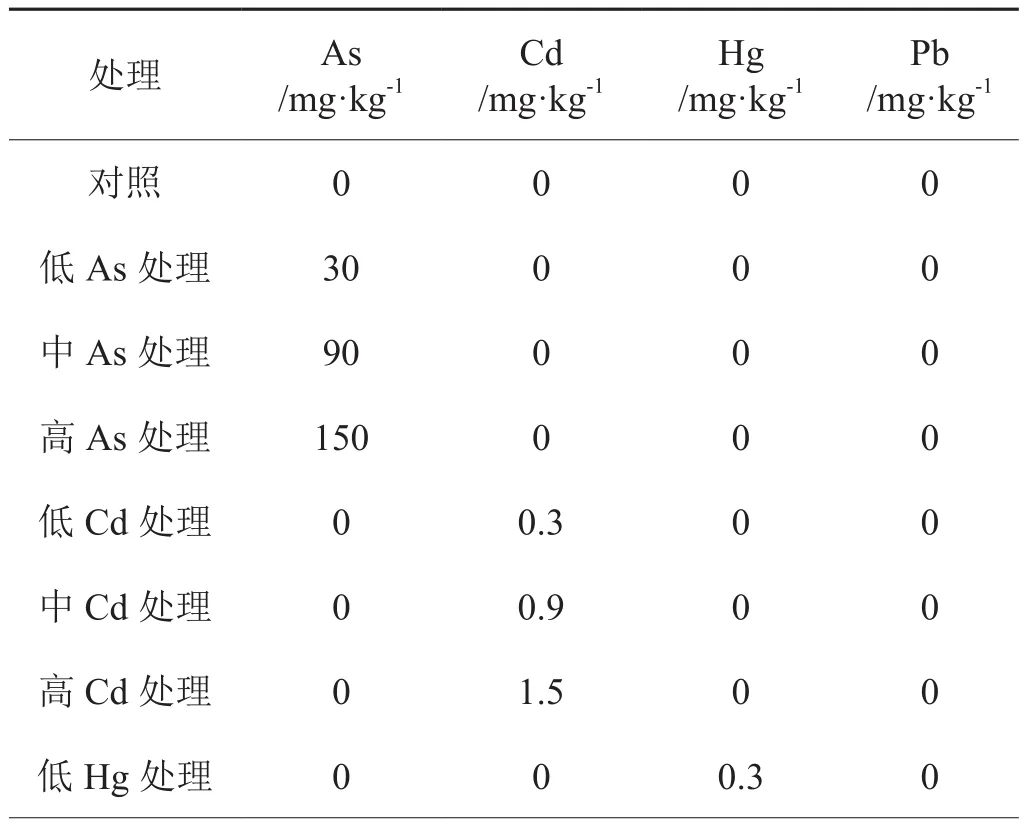
表2 土壤盆栽试验重金属添加浓度Tab. 2 Addition concentrations of heavy metals in pot experiment
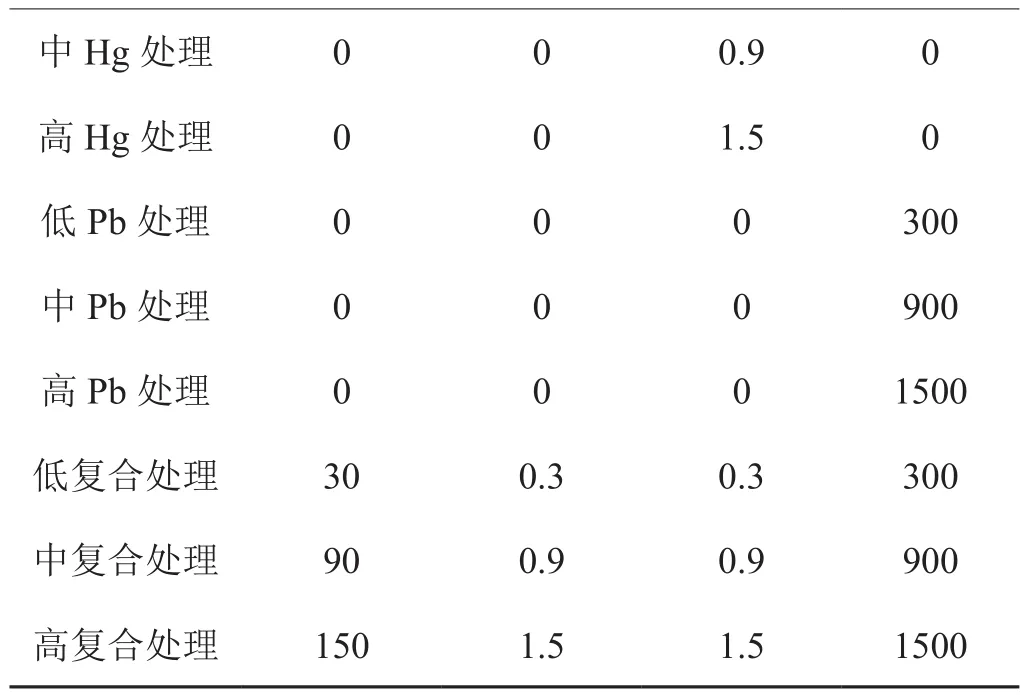
续表2
1.3 样品处理
将采集到的根、茎和叶用蒸馏水冲洗表面,低温(60℃)烘干后过0.20 mm尼龙筛。称取约0.5 g烟草样品于微波消解管中,加入 4mL HNO3(德国MERCK公司,高纯级)和 2 mL H2O2(德国MERCK公司,高纯级)进行微波消解(美国CEM公司,Xpress)。消解完毕冷却后,用超纯水定容至50 mL塑料容量瓶中,并加入1 mL 0.5 mg·L-1内标Rh溶液,摇匀,待测。用电感耦合等离子质谱仪(美国PerkinElmer公司,DRC-e)测定消解液中As、Cd、Hg和Pb浓度。
1.4 数据分析
试验数据采用SPSS 14.0进行处理,运用LSD法进行差异显著性检验。借助 Excel 对相关数据进行绘图。
2 结果与分析
2.1 烟叶中重金属元素含量随时间变化规律
2.1.1 As处理和复合处理烟叶中As含量随时间变化规律
收获期,烟叶中As含量高低顺序为:高As处理>高复合处理>中As处理>中复合处理>低As处理>低复合处理>对照。As处理和复合处理烟叶中As含量均以移栽初期最高,至第30天时快速降至最低,此后又缓慢上升。烟叶中As含量随时间变化规律为:初期>收获期>中期。
2.1.2 Cd处理和复合处理烟叶中Cd含量随时间变化规律
收获期,烟叶中Cd含量顺序为:高Cd处理>中Cd处理>高复合处理>中复合处理>低Cd处理>低复合处理>对照。烟叶中Cd含量随时间变化规律为:初期>收获期≈中期。
2.1.3 Hg处理和复合处理烟叶中Hg含量随时间变化规律
收获期,烟叶中Hg含量顺序为:中Hg处理>高Hg处理>高复合处理>低Hg处理>低复合处理>中复合处理>对照。烟叶中Hg含量随时间变化规律为:中期>收获期>初期。
2.1.4 Pb处理和复合处理烟叶中Pb含量随时间变化规律
收获期,烟叶中Pb含量顺序为:高Pb处理>低Pb处理>中Pb处理>高复合处理>中复合处理>低复合处理>对照。烟叶中Pb含量随着时间呈先快速下降后缓慢上升的趋势。烟叶中Pb含量随时间变化规律为:初期>收获期≈中期。
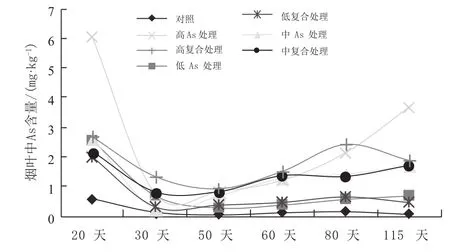
图1 As处理和复合处理烟叶中As含量随时间变化规律Fig. 1 Change rules of As content in tobacco leaf under As treatment and compound treatments with time
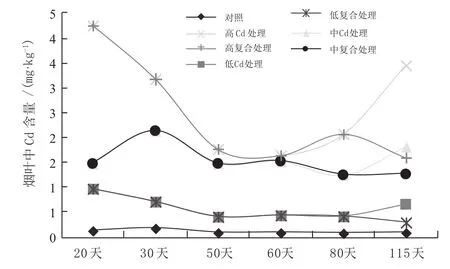
图2 Cd处理和复合处理烟叶中Cd含量随时间变化规律Fig. 2 Change rules of Cd content in tobacco leaf under Cd treatment and compound treatments with time
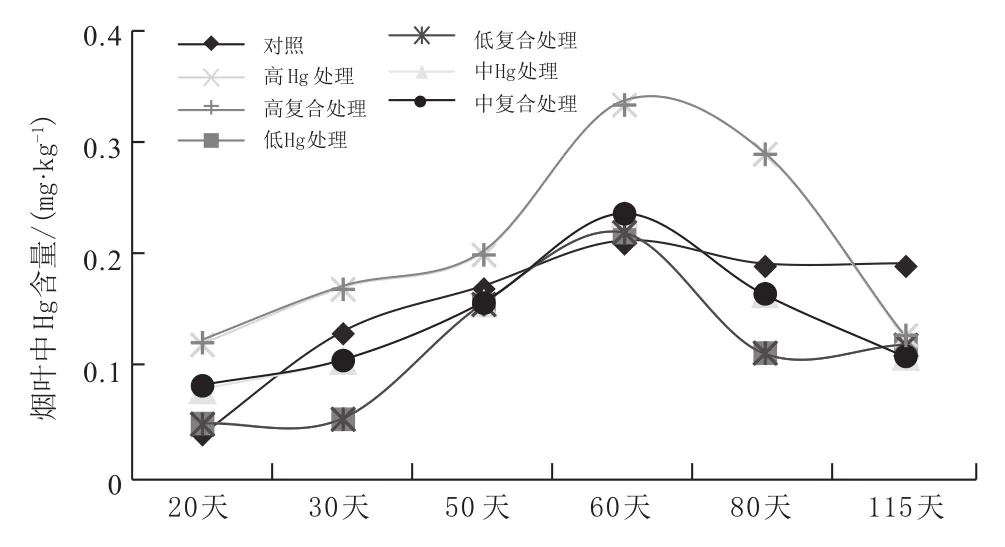
图3 Hg处理和复合处理烟叶中Hg含量随时间变化规律Fig. 3 Change rules of Hg content in tobacco leaf under Hg treatment and compound treatments with time
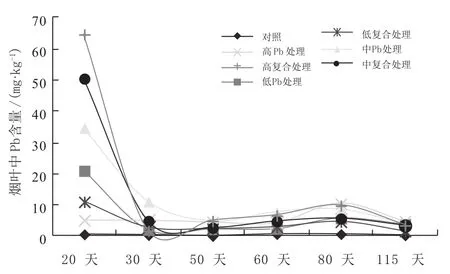
图4 Pb处理和复合处理烟叶中Pb含量随时间变化规律Fig. 4 Change rules of Pb content in tobacco leaf under Pb treatment and compound treatments with time
2.2 烟草不同部位中重金属的累积分布特征
2.2.1 As处理对烟草不同部位累积重金属含量的影响
对照烟草中4种重金属累积分布特征为:As和Pb均为根>茎>叶,Cd为茎>根>叶,Hg为叶>根>茎。可见,在未受重金属污染胁迫下烟草中As和Pb主要累积于根部,Cd主要累积于茎中,Hg主要累积于叶中。
As处理下,烟草中As累积分布特征与对照烟草一致。As处理烟草根、茎和叶中As含量均与对照差异显著,且As处理间烟草根、茎和叶中As含量亦差异显著。与对照相比,As处理烟草根茎中Pb含量显著下降,降幅分别为63%~81%和42%~46%;烟叶中其它3种重金属(Cd、Hg和Pb)含量与对照无显著差异。烟草根、茎和叶中As含量均随着外源As添加浓度增加而显著增大。
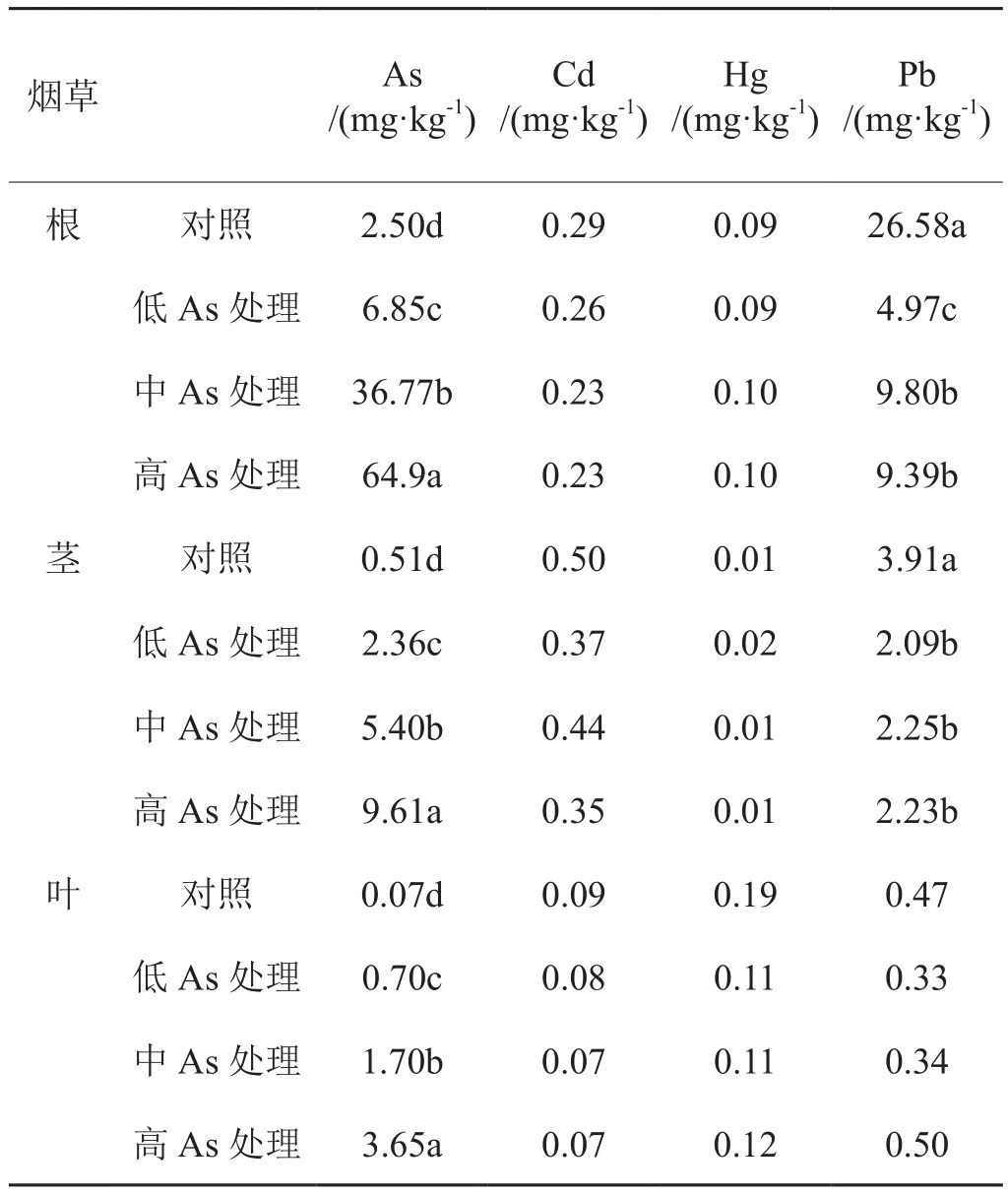
表3 As处理烟草根、茎和叶中重金属含量Tab. 3 Concentration of heavy metals in tobacco root, stem and leaf under As treatments
2.2.2 Cd处理对烟草不同部位累积重金属含量的影响
Cd处理下,烟草中Cd累积分布特征亦与对照烟草相同。Cd处理烟叶中Cd含量与对照差异显著,且Cd处理间亦存在显著差异。与As处理类似,Cd处理同样较为明显的抑制了烟草根茎对Pb的累积,其Pb含量在根茎中的降幅为56%~81%和11%~39%,但对叶部其它3种重金属(As、Hg和Pb)作用亦不明显。烟草根、茎和叶中Cd含量亦随着外源Cd添加量增加而显著增大。
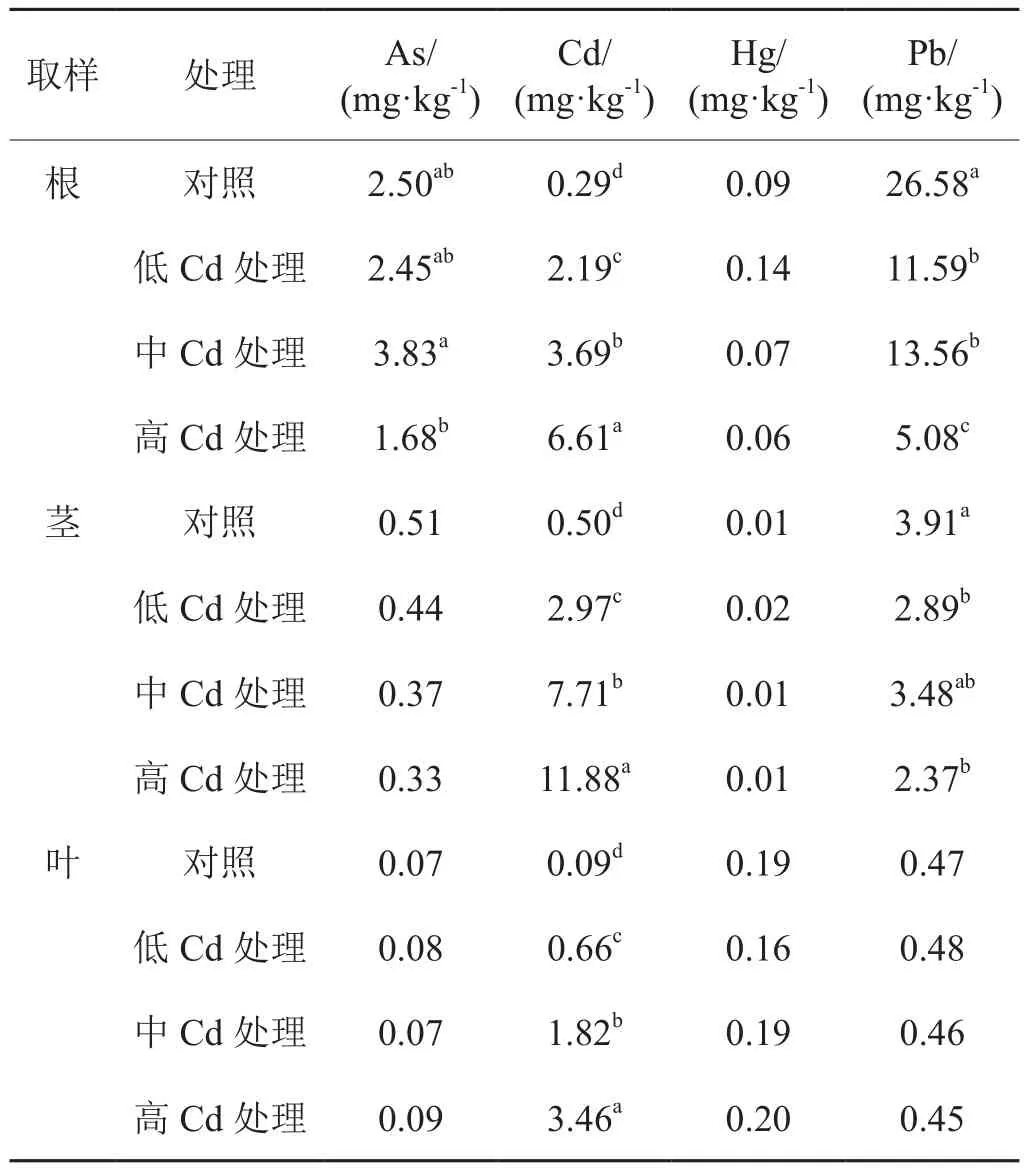
表4 Cd处理烟草根、茎和叶中重金属含量Tab. 4 Concentration of heavy metals in tobacco root, stem and leaf under Cd treatment
2.2.3 Hg处理对烟草不同部位累积重金属含量的影响
Hg处理烟草中Hg累积分布特征为根>叶>茎,与对照烟草中Hg累积分布特征不同,对照烟草中Hg为叶>根>茎。Hg处理下,仅烟草根中Hg含量显著高于对照。Hg处理在一定程度上促进了烟草根部对Pb的累积,其增幅为19%~60%。Hg处理烟叶中As、Cd和Pb均与对照无显著差异,其茎叶中Hg含量仅随外源Hg浓度增大而稍有增大,但无统计学上意义。
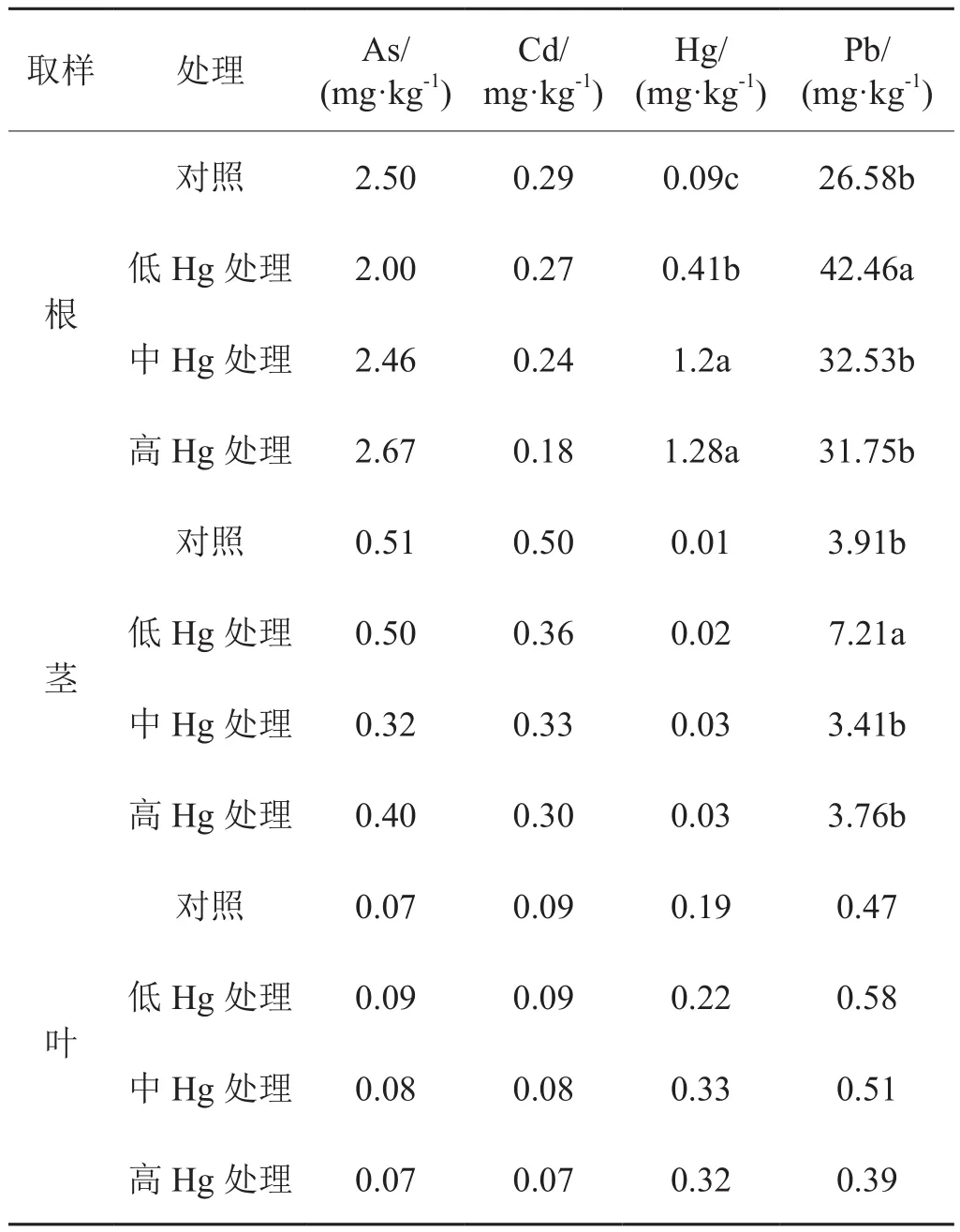
表5 Hg处理烟草根、茎和叶中重金属含量Tab. 5 Concentration of heavy metals in tobacco root, stem and leaf under Hg treatment
2.2.4 Pb处理对烟株不同部位累积重金属含量的影响
Pb处理烟株中Pb累积分布特征与对照一致。Pb处理烟株根、茎和叶中Pb含量均与对照差异显著;但3个Pb处理间仅烟株根中Pb含量差异显著,茎叶中Pb含量总体上差异不显著。低Pb处理和中Pb处理烟叶中Pb含量、中Pb处理和高Pb处理茎中Pb含量均无显著差异。Pb处理明显促进了烟株根部对As的累积,其增幅为21%~100%;烟叶中其它3种重金属(As、Cd和Hg)含量与对照无显著差异。烟株中Pb含量总体上随着外源加入量的增大而增大。
单元素处理下,烟株中重金属分布特征为:As和Pb为根>茎>叶,Cd为茎>根>叶,Hg为根>叶>茎,仅Hg分布特征与对照烟株有所不同。4种重金属元素在根茎中的增幅从高至低顺序为Pb>As、Cd>Hg,而在烟叶中增幅顺序为As>Cd>Pb>Hg。
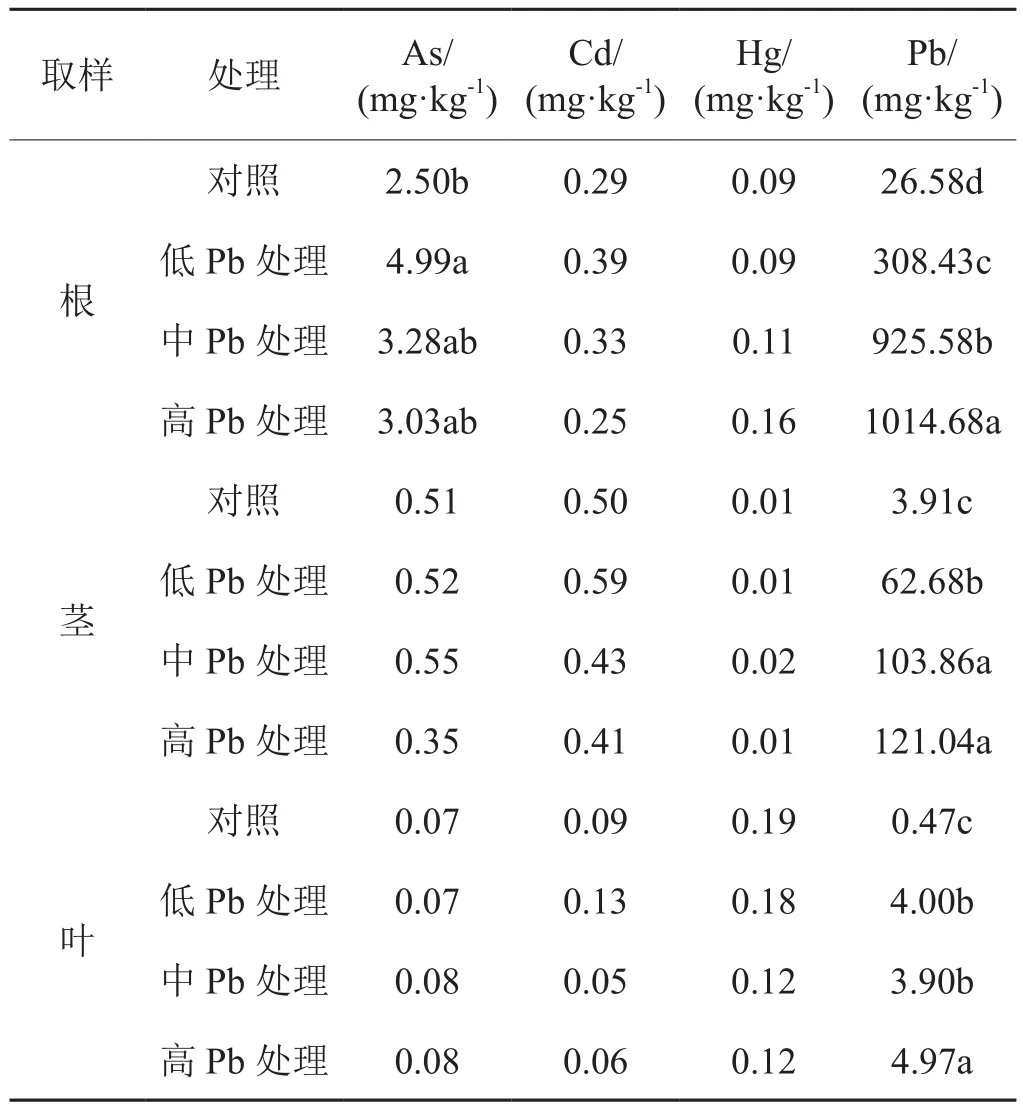
表6 Pb处理烟株根、茎和叶中重金属含量Tab. 6 Concentrations of heavy metals in tobacco root, stem and leaf under Pb treatment
2.2.5 重金属复合处理处对烟株不同部位累积重金属含量的影响
复合处理烟叶中重金属(除Hg)含量显著高于对照。重金属复合处理间(低、中和高浓度)烟叶中Cd含量差异显著,但As和Pb含量总体上差异不显著。复合处理下,烟株中重金属累积分布特征单元素处理类似,亦表现为根部>茎部、叶部。
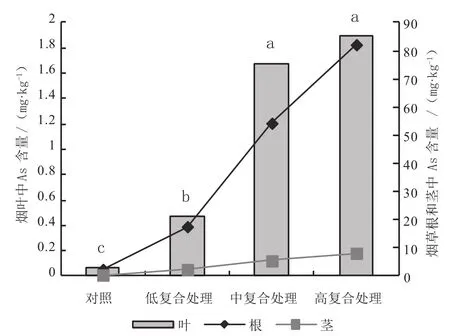
图5 复合处理烟株中As分布特征Fig.5 Distribution characteristics of As in tobacco under compound treatments
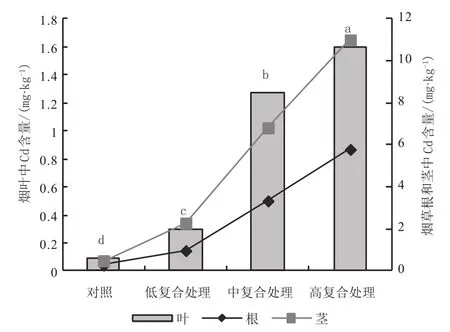
图6 复合处理烟株中Cd分布特征Fig.6 Distribution characteristics of Cd in tobacco under compound treatments
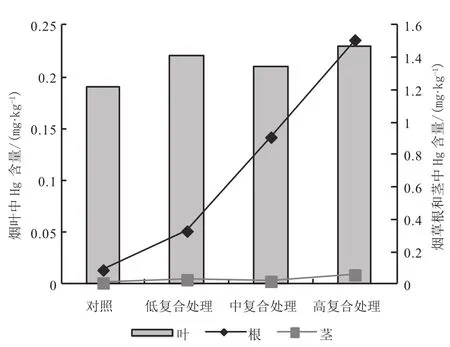
图7 复合处理烟株中Hg分布特征Fig.7 Distribution characteristics of Hg in tobacco under compound treatments
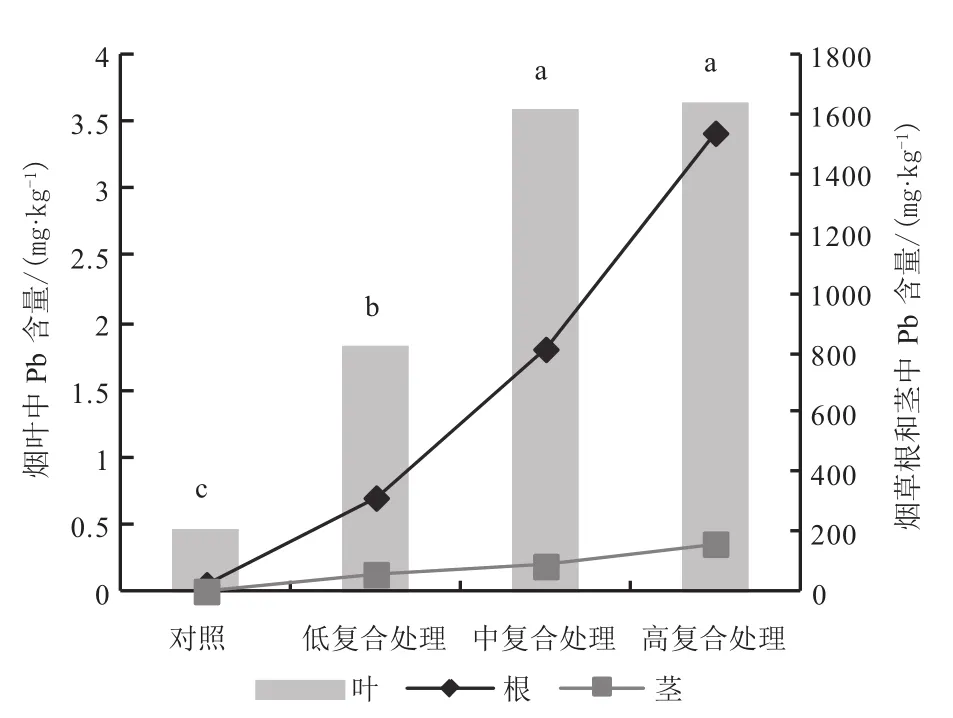
图8 复合处理烟株中Pb分布特征Fig.8 Distribution characteristics of Pb in tobacco under compound treatments
复合处理烟株根中As、Pb含量>单元素As、Pb处理,Cd含量<单元素Cd处理,Hg含量与单元素Hg处理相近;茎中4种重金属含量与单元素处理总体差异不大;叶中4种重金属含量<单元素处理。复合处理下,重金属元素在根茎中增幅顺序为Pb>Cd、As>Hg,而叶中的增幅顺序为As>Cd>Pb>Hg。
3 讨论
烟叶中As、Cd和Pb含量均以移栽初期最高,中期和收获期较低,其随时间变化规律总体为先快速下降后缓慢上升,呈波浪式状;而烟叶中Hg含量却以中期最高,呈倒V字状。随着外源重金属(除Hg)添加量的增大,烟株中重金属残留量总体上呈明显增加趋势,其中又以根部表现最为显著。As和Cd处理显著促进烟根、茎和叶中As和Cd的积累,并随外源添加量的增大而显著增大,表现出明显的剂量效应。Cd处理间烟叶中Cd含量差异显著,此结论与王绍坤[22]研究不一致。我们推测,可能是由于本试验Cd处理浓度远大于王绍坤试验(其Cd添加浓度仅为0.15、0.30和0.60 mg/kg)所致。Hg处理仅显著促进了烟株根部对Hg的吸收,对茎叶部作用不明显。出现这种现象的原因可能是烟株对Hg具有一定的滞阻效应,从而较为明显的抑制了Hg从根部向茎叶的传输。对照烟株中叶部Hg含量高于根茎,与其它重金属分布特征不同,这可能与烟叶中Hg含量受大气环境条件影响较大所致[23]。复合处理烟株中重金属累积分布特征与单元素处理大致类似,但又存在一定差异,造成这种差异可能是由于土壤-烟株系统中多种重金属元素之间产生了复杂的交互作用。
重金属污染胁迫下烟株中As、Cd、Hg和Pb累积分布规律均为根>茎>叶。张玉涛等[19]研究亦认为在Cd和Pb在烟株中含量为根>茎>叶,而米艳华等[20]认为Cd主要积累于烟叶,Pb主要积累于根部;王学锋等[21]却认为Cd和Pb主要积累于烟株的茎叶。土壤中的多种重金属可通过联合作用,对植物生长产生相加、协同和拮抗等效应[24]。本试验发现,As和Cd处理抑制了烟株对Pb的吸收,Hg处理促进了烟株对Pb的吸收,Pb处理促进了烟株对As的吸收,这些作用均以在烟株根部作用最为明显。米艳华等[20]认为As、Pb对 Cd 在烟株中的积累为协同作用,Cd 对 Pb 为拮抗作用。王学锋等[21]认为Cd抑制了烟株对 Pb 元素的吸收,而Pb却促进了烟株对 Cd 元素的吸收;复合处理(CdPbCuZnMn)烟叶中Cd浓度>单元素,而其Pb浓度<单元素。章钢娅等[25]认为Cd 浓度的增加促进了烟株对Pb吸收。这些研究结论之间以及与本研究之间既有相同之处又有不同之处。导致这些差异的原因可能是由于外源重金属添加种类及浓度不同和试验所采用的土壤类型及理化性质不同所致。
4 结论
烟株对重金属的吸收累积、分布特征与重金属元素添加种类、浓度及烟株部位均密切相关。从4种重金属在烟叶中的增幅高低顺序可知,烟叶对土壤中As和Cd污染最为敏感,其次为Pb,对Hg最不敏感。故种植烤烟时要尽量避开As和Cd含量较高的区域,防止As和Cd在烟叶中的过度累积。复合处理烟叶重金属含量总体低于单元素处理,可能是由于4种重金属元素之间拮抗作用起主导作用所致;但其根中As、Cd浓度大于单元素As、Pb处理,而Cd浓度小于单元素Cd处理,造成这种现象的机理机制可能比较复杂,有待下一步深入考察。
[1] 孟建玉, 商胜华, 陆宁, 等. 土壤重金属含量对烟叶和烟气中重金属的影响[J]. 中国烟株科学, 2012, 33(3): 1-6.Meng Jianyu, Shang Shenghua, Lu Ning, et al. The e ff ect of soil heavy metal contents on heavy metals in tobacco leaves and in the course of smoking[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science,2012, 33(3): 1-6. (in Chinese)
[2] 高志强, 胡鑫, 谢会雅, 等. 植烟区烟草重金属含量及其与土壤环境因子相关性研究[J]. 作物研究, 2014, 28(8):912-914.Gao Zhiqiang, Hu Xin, Xie Huiya, et al. Study on relationship between the heavy metal contents in tobacco in tobacco area and soil environmental factors[J]. Crop Research, 2014, 28(8):912-914. (in Chinese)
[3] 王卫, 梁振飞, 李菊梅, 等. 土壤性质对烟草中镉富集的影响及预测模型研究[J]. 土壤, 2014, 46(1): 178-183.Wang Wei, Liang Zhenfei, Li Jumei, et al. Studies on e ff ects of soil properties on Cd accumulation in tobacco and prediction model[J]. Soils, 2014, 46(1): 178-183. (in Chinese)
[4] Goliaa E E, Dimirkoua A, Mitsios I K. Heavy - metal concentration in tobacco leaves in relation to their available soil fractions[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2009, 40: 106–120.
[5] 赵秀兰,刘晓.不同品种烟草生长和镉及营养元素吸收对镉胁迫响应的差异[J].水土保持学报, 2009, 23(1):117-121.Zhao Xiulan, Liu Xiao. Differences in plant growth, Cd and nutrient uptake, Cd translocation between two tobacco cultivars under Cd stress[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2009, 23(1): 117-121. (in Chinese)
[6] 王浩浩,刘海伟,石屹, 等. 烤烟品种对镉吸收累积敏感性差异研究[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2013, 34(6): 64-69.Wang Haohao, Liu Haiwei, Shi Yi, et al. Sensibility variation of cadmium uptake and accumulation among flue-cured tobacco varieties[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2013, 34(6):64-69. (in Chinese)
[7] 陈庆园, 商胜华, 陆宁. 不同打顶方式对烤烟吸收重金属的影响[J]. 中国烟草学报, 2011, 17(2): 49-53, 62.Cheng Qingyuan, Shang Shenghua, Lu Ning. E ff ect of topping on heavy metal absorption in flue-cured tobacco[J]. Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 2011, 17(2): 49-53, 62. (in Chinese)
[8] 李晓婷, 常寿荣, 孔宁川, 等. 不同有机肥与无机肥配施对烤烟生长及铅、镉含量的影响[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2013,34(5): 37-41.Li Xiaoting, Chang Shourong, Kong Ningchuan, et al. E ff ects of combining application of various organic and chemical fertilizers on the growth and lead and cadmium contents of flue-cured tobacco[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2013, 34(5):37-41. (in Chinese)
[9] Tsadilas C D, Karaivazoglou N A, Tsotsolis N C, et al.Cadmium uptake by tobacco as affected by liming, N form,and year of cultivation[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2005,134(2): 239-246. (in Chinese)
[10] 黄爱缨, 木志坚, 王强, 等. 土壤-气候和烤烟品种及其互作对昭通烟叶重金属含量的影响[J].中国烟草科学,2013, 34(5): 1-6.Huang Aiying, Mu Zhijian, Wang Qiang, et al. E ff ect of soilclimate conditions, tobacco varieties and their interactions on heavy metal contents of tobacco leaves in Zhaotong, Yunnan Province[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2013, 34(5): 1-6. (in Chinese)
[11] 黄浩, 周冀衡, 陈初, 等. 重金属铅、镉叶面喷施对烤烟上部叶生长的影响[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2012, 23: 59-60, 63.Huang Hao, Zhou Jiheng, Chen Chu, et al. Effect of foliar spraying lead and cadmium on growth of tobacco upper leaf[J].Huan Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 23: 59-60, 63. (in Chinese)
[12] 贺远, 王树声, 刘海伟, 等. 镉浓度对烤烟幼苗镉含量及生长和生理指标的影响[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2014, 35(2):37-42.He Yuan, Wang Shusheng, Liu Haiwei, et al. Effect of Cd concentration on Cd content and growth and Physiological indices of tobacco seedlings. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2014,35(2): 37-42. (in Chinese)
[13] 邓家军, 胡继伟, 李继新, 等. 重金属离子对烤烟叶片中铜锌超氧化物歧化酶活性的影响[J]. 中国烟草学报, 2010,16(3): 1-6.Deng JiaJun, Hu Jiwei, Li Jixin, et al. E ff ects of heavy metal ions on copper-zinc superoxide dismutase activity in fl ue-cured tobacco leaves[J]. Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 2010, 16(3): 1-6. (in Chinese)
[14] 葛淑芳, 章艺, 吴玉环, 等. 铜污染对烟草生长及其生理特性的影响[J]. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2014,37(2): 219-224.Ge Shufang, Zhang Yi, Wu Yuhuan, et al. Effect of copper pollution on the growth and physiological characters of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.)[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Normal University (Nat. Sci.), 2014, 37(2): 219-224. (in Chinese)
[15] 刘义新,陶 涌,孟丽华, 等. 烤烟品种 K326 和云烟 87对镉胁迫的生理响应及抗性差异[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2008,29(4): 1-5.Liu Yixin, Tao Yong, Meng Lihua, et al. Physiological Response and Resistance of K326 and Yunyan87 to Cadmium[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2008, 29(4): 1-5. (in Chinese)
[16] 吴坤, 吴中红, 邰付菊, 等. 镉胁迫对烟草叶激素水平、光合特性、荧光特性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(16):4517–4524.Wu Kun, Wu Zhonghong, Tai Fuju, et al. E ff ects of cadmium on the contents of phytohormones, photosynthetic performance and fluorescent characteristics in tobacco leaves[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(16): 4517-4524.(in Chinese)
[17] 马新明, 李春明, 袁祖丽, 等. 镉和铅污染对烤烟根区土壤微生物及烟叶品质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2005,16(11): 2182-2186.Ma Xinming, Li Chunming, Yuan Zuli, et al. Impacts of Cd and Pb pollution on soil microbes in tobacco root zone and on tobacco leaf quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology[J].2005, 16(11): 2182-2186. (in Chinese)
[18] 马新明, 李春明, 刘海涛, 等. Cd, Pb污染对烤烟ATP酶活性及烟叶品质的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2007,26(2): 708-712.Ma Xinming, Li Chunming, Liu Haitao, et al. Effect of Cd,Pb Pollution on ATPase Activity and Quality of Tobacco Leaves[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2007, 26(2):708-712. (in Chinese)
[19] 张玉涛, 杨兴平, 李琳, 等. 重金属 Pb、Cr、Cd 对烟草生长的影响及其分布规律[J]. 南方农业学报, 2012, 43(11):1697-1702.Zhang Yutao, Yang Xingping, Li Lin, et al. Physiological action, growth, and accumulation rules of Pb, Cr, and Cd in tobacco[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2012, 43(11):1697-1702. (in Chinese)
[20] 米艳华,陆琳,邹炳礼,等. 土壤-烤烟系统重金属复合污染的交互作用及其相关分析[J]. 江西农业学报, 2012,24(1): 154-157.Mi Yanhua, Lu Lin, Zou Bingli, et al. Interaction and correlation of heavy metal compound pollution in soil – fl ue- cured tobacco system[J]. Acta Agricultural Jiangxi, 2012,24(1): 154-157. (in Chinese)
[21] 王学锋,师东阳,刘淑萍,等. Cd- Pb复合污染在土壤-烟草系统中生态效应的研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2007, 38(4):737-740.Wang Xuefeng, Shi Dongyang, Liu Shuping, et al. Ecological effect of combined Cd - Pb pollution on soil - tobacco system[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2007, 38(4): 737-740. (in Chinese)
[22] 王绍坤, 程昌新, 罗华元, 等. 土壤重金属处理对烤烟烟叶中Pb,Cr,Cu,As,Cd和Hg的分布与累积的影响[J].烟草科技, 2013, 306(1): 39-41.Wang Shaokun, Cheng Changxin, Luo Huayuan, et al.Accumulation and distribution of Pb, Cr, Cu, As, Cd and Hg in flue-cured tobacco leaves grown in soil treated with six heavy metal solutions[J]. Tobacco Science &Technology, 2013,306(1): 39-41. (in Chinese)
[23] 李义强, 李成富, 许立峰, 等. 我国部分烟叶产区土壤和烟叶重金属现状及相关性研究[C] // 中国烟草学会 2006 年学术年会论文集. 北京: 中国烟草学会, 2006, 463-467.Li Yiqiang, Li Chengfu, Xu Lifeng, et al. The present situation of heavy metal levels in some tobacco growing soils and tobacco in China and their relativity[C] // China Tobacco Society Proceedings of 2006 Annual Academic Conference.Beijing, China Tobacco Society, 2006, 463-467. (in Chinese)
[24] 余国营, 吴燕玉. 土壤环境重金属元素间的相互作用及其对吸附特性的影响[J]. 环境化学, 1997, 1(2): 30-36.Yu Guoying, Wu Yanyu. E ff ects of heavy metals joint action on their characteristic of sorption and desorption in brown soil[J].Environmental Chemistry, 1997, 1(2): 30-36.(in Chinese)
[25] 章钢娅, 朱卫星, 招启柏, 等. 烟草对复合污染土壤中镉的吸收运转及改良的研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2008, 36(2):583-587.Zhang Gangya, Zhu Weixing, Zhao Qibai. Study on the absorption and translocation of cadmium in tobacco in compound pollution soil and the improvement effect on cadmium pollution by remediators[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2008, 36(2): 583- 587. (in Chinese)
Effects of heavy metal treated soil on accumulation and distribution of As, Cr, Hg and Pb in tobacco
WEI Yihua1, HE Junhai1, FENG Xiaohu2, WANG Libing2, ZHOU Yaomin1, LI Yanyan2, YUAN Lijuan1, LUO Linguang1
1 Institute for Quality & Safety and Standards of Agricultural Products, Jiangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Nanchang 330200, China;2 Jiangxi Fuzhou Municipal Tobacco Company, Fuzhou 344000, China
Pot experiments with single treatments (As, Cd, Hg and Pb) and compound treatments were carried out to investigate the accumulation and distribution of heavy metals in tobacco. Results indicated that As, Cd and Pb contents in tobacco leaf changed with passing time in the following order: early stage>harvest stage, medium stage, while Hg content was highest at medium stage, followed by harvest stage and early stage. As and Pb contents distributed highest in root, followed by stem and leaf, Cd content highest in stem followed by root and leaf, and Hg highest in root followed by leaf and stem (control treatment: leaf>root>stem) under heavy metals pollution stresses. The accumulation of heavy metals (except Hg) in tobacco increased signi fi cantly (p<0.05) with the increase of additive concentration as a whole.The concentration of heavy metals in compound treatments was lower than that in single element treatments. The growth rates of heavy metals in tobacco leaf were: As>Cd>Pb>Hg. There were signi fi cant di ff erences between As content under As treatment and Cd content under Cd treatment in tobacco (root, stem and leaf). It was proved that tobacco was most sensitive to pollution of As and Cd in soil, and thus tobacco planting should select areas with low content of As and Cd to avoid excess accumulation.
tobacco; heavy metal; accumulation; distribution
魏益华,何俊海,冯小虎,等. 土壤重金属处理对烟草中As、Cd、Hg和Pb的累积与分布的影响[J]. 中国烟草学报,2016,22(1)
江西省烟草公司科技项目“抚州市无公害烟叶生产技术体系研究与示范”(201001017)
魏益华(1982—),硕士,助理研究员,农产品质量安全,Tel:0791-87090294,Email:weiyihua08@163.com
罗林广(1964—),博士,研究员,农产品质量安全,Tel:0791-87090293,Email:luolinguang@126.com
2015-02-05
:WEI Yihua, HE Junhai, FENG Xiaohu, et al. E ff ects of heavy metal treated soil on accumulation and distribution of As, Cr, Hg and Pb in tobacco[J]. Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 2016, 22(1)
