姜黄素抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路诱导乳腺癌细胞凋亡的机制研究
2016-11-07赵轶峰魏玉磊王敏敏王金科
赵轶峰,魏玉磊,王 萍,王敏敏,王金科
(1. 河北北方学院附属第一医院,河北 张家口 075061;2. 河北省张家口市优抚医院,河北 张家口 075000)
姜黄素抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路诱导乳腺癌细胞凋亡的机制研究
赵轶峰1,魏玉磊1,王萍2,王敏敏2,王金科1
(1. 河北北方学院附属第一医院,河北 张家口 075061;2. 河北省张家口市优抚医院,河北 张家口 075000)

目的研究姜黄素对人乳腺癌细胞株BT549细胞凋亡的诱导作用及其机制。方法取对数生长期BT549细胞,制成单细胞悬液,计数并接种于96孔培养板,每孔约5 000个细胞,24 h后加浓度分别为 0,10,20,40,80 μmol/L的姜黄素,培养12,24,48 h后采用MTT实验检测BT549细胞增殖抑制率;分别用0,10,20,40,80 μmol/L姜黄素处理细胞,48h后采用TUNEL染色法检测细胞凋亡指数;分别用0,10,20,40,80 μmol/L姜黄素处理细胞,48 h后采用Western blot实验检测细胞增殖、凋亡相关蛋白的表达量。结果MTT结果显示,随培养时间延长,姜黄素0,20,40,60,80 μmol/L组BT549细胞增殖抑制率逐渐增高(P均<0.05),且同时间点内姜黄素0,20,40,60,80 μmol/L组细胞增殖抑制率随剂量增加逐渐增高(P均<0.05)。TUNEL染色结果显示,姜黄素0,20,40,60,80 μmol/L组BT549细胞凋亡指数随剂量增加逐渐增加(P均<0.05)。Western blot实验结果显示,随着姜黄素浓度的增加,总蛋白中β-catenin的表达不受影响(P>0.05), 而细胞核中β-catenin的表达逐渐减少(P<0.05)。结论姜黄素通过Wnt/β-catenin信号传导通路抑制乳腺癌细胞株BT549细胞的增殖和诱导其凋亡,并呈现时间、剂量依赖性。
姜黄素;Wnt/β-catenin;乳腺癌细胞;凋亡
乳腺癌是女性常见的肿瘤,严重威胁着妇女的健康。Wnt基因是从小鼠乳腺癌中克隆出的原癌基因,可调节乳腺细胞的生长和分化,Wnt信号通路参与乳腺癌的发生发展,而Wnt/β-catenin是目前研究最多的与乳腺癌有关的Wnt通路[1]。研究显示,抑癌基因失活和癌基因的激活可异常激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,β-catenin降解障碍,可导致CyclinD1、C-myc等靶基因激活,细胞周期调控异常,从而引起乳腺癌的发生发展[2]。Jang等[3]研究显示抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可阻滞乳腺癌肿瘤干细胞和肿瘤细胞的生长,抑制乳腺癌生长;Zhao等[4]研究显示,抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可阻滞细胞周期于G2/M期,促进癌细胞凋亡。姜黄素为姜科植物提取的有效成分,具有明显的抗肿瘤效果,对肺癌[5]、肝癌[6]等多种肿瘤的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路有调节作用,但姜黄素对乳腺癌Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的调节作用尚少见报道。因此,笔者研究了姜黄素抑制人乳腺癌细胞株BT549细胞Wnt/β-catenin信号通路诱导乳腺癌细胞凋亡的作用机制,以期能为乳腺癌的临床治疗开辟新的途径。现报道如下。
1 实验资料
1.1材料人乳腺癌细胞株BT549细胞购自上海细胞生物研究所。1640培养基和无支原体胎牛血清购自Gibco,胰酶购自美国Invitrogen公司,青链霉素购自Biowest公司,姜黄素购自Sigma公司。MTT试剂盒购自Sigma公司,TUNEL试剂盒购自Roche公司,兔抗β-catenin、Histone H3购自Santa Cruz公司,鼠抗β-actin抗体购自中山金桥。
1.2细胞培养人乳腺癌细胞株BT549细胞培养于含10%胎牛血清、1%青链霉素的1640培养基中,置于37 ℃、5% CO2的培养箱中培养。
1.3MTT实验检测BT549细胞增殖抑制率取对数生长期BT549细胞,制成单细胞悬液,计数并接种于96孔培养板,每孔约5 000个细胞,24 h后换新鲜1640培养基并分别加入浓度为 0,10,20,40,60,80 μmol/L姜黄素。培养12,24,48 h后,PBS冲洗2遍,加入含10 μL MTT的1640培养基100 μL,4 h后每孔加200 μL DMSO,振荡10 min用酶标仪检测吸光度(OD) 值。增殖抑制率=(1-加药组平均OD值/对照组平均OD 值)×100%。
1.4TUNEL染色法检测细胞凋亡情况分别用0,10,20,40,60,80 μmol /L姜黄素处理细胞,48 h后用4%多聚甲醛固定,按照试剂盒要求操作,DAB显色后封片,在微镜下随机选取5个视野计数凋亡细胞个数,算出凋亡指数。
1.5Western blot实验检测细胞增殖、凋亡相关蛋白表达量分别用0,10,20,40,60,80 μmol/L姜黄素处理细胞,48 h后裂解细胞提取蛋白,配胶,处理蛋白后煮沸样品,以80 μg /30 μL每孔上样,电泳后转膜,脱脂牛奶封闭4 h。一抗4 ℃冰箱平放过夜;次日用辣根过氧化物酶标记的二抗于室温下孵育2 h。用Odyssey扫描条带,并用Image J灰度分析软件分析各样品目的蛋白与β-actin的比值,求出相对灰度值。

2 结 果
2.1姜黄素对BT549细胞增殖的影响MTT结果显示,随培养时间延长,姜黄素0,20,40,60,80 μmol/L组BT549细胞增殖抑制率逐渐增高(P<0.05),且同时间点内姜黄素0,20,40,60,80 μmol/L组细胞增殖抑制率逐渐增高(P<0.05)。见表1。

表1 不同浓度姜黄素作用BT549细胞不同时间 对细胞增殖的抑制情况±s,%)
2.2姜黄素对BT549细胞凋亡的影响TUNEL染色结果显示,姜黄素0,20,40,60,80μmol/L组BT549细胞凋亡指数分别为(8.1±3.3)%,(19.4±2.7)%,(32.5±4.3)%,(57.2±4.1)%,(76.3±1.8)%。随着姜黄素浓度的增加,BT549细胞凋亡指数明显增高(F=31.667,P<0.05)。
2.3姜黄素对细胞增殖、凋亡相关蛋白表达的影响Western blot实验结果显示,随着姜黄素浓度的增加,总蛋白中β-catenin的表达不受影响(P>0.05), 而细胞核中β-catenin的表达逐渐减少(P<0.05)。见图1及表2。
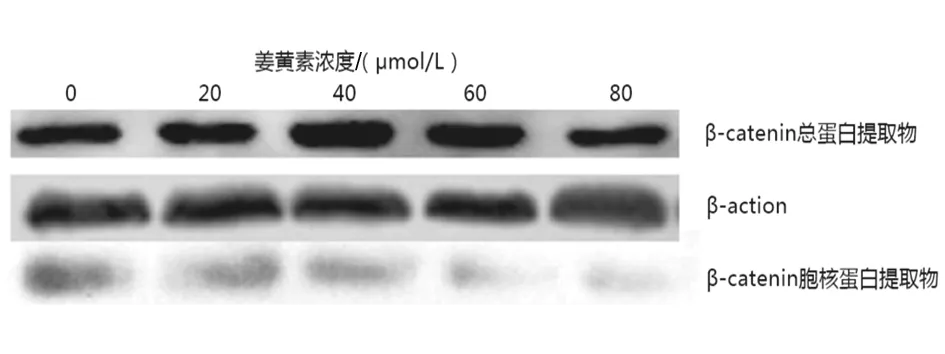
图1 不同浓度姜黄素处理BT549细胞后总蛋白、 核蛋白中β-catenin蛋白表达情况表2 不同浓度姜黄素处理BT549细胞对β-catenin 蛋白表达的影响
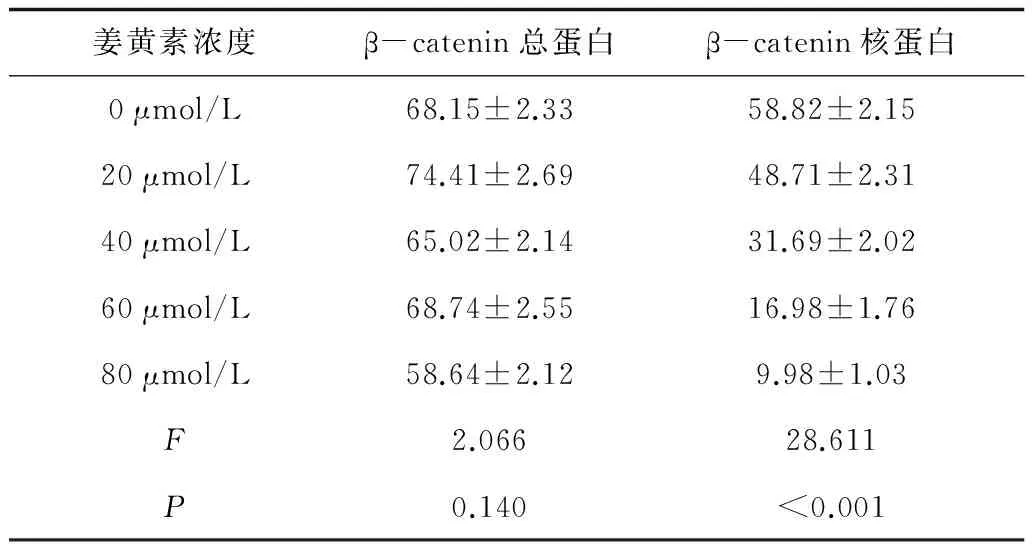
姜黄素浓度β-catenin总蛋白β-catenin核蛋白0μmol/L68.15±2.3358.82±2.1520μmol/L74.41±2.6948.71±2.3140μmol/L65.02±2.1431.69±2.0260μmol/L68.74±2.5516.98±1.7680μmol/L58.64±2.129.98±1.03F2.06628.611P0.140<0.001
3 讨 论
乳腺癌是女性常见的恶性肿瘤,目前临床上常用的治疗手段能明显提高患者的生存时间和生活质量,但是肿瘤耐药和复发依然严重威胁着患者的健康。因此研究新药物并探究其机制在乳腺癌的治疗中具有重要的临床意义。姜黄素是中药姜黄的主要成分,是天然存在的多酚类化合物,毒性很低,曾被用作食品添加剂,并且在抗炎、降血脂、保护神经等方面有重要作用[7-8]。近年来大量实验表明姜黄素可以抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖、凋亡、迁移和侵袭等,能减慢荷瘤小鼠肿瘤的生长速度[9-12]。韦达等[13]研究显示,姜黄素可上调乳腺癌MCF-7细胞bax基因表达,下调bcl-2基因表达,阻滞细胞于G1/S,诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡。但姜黄素诱导乳腺癌细胞凋亡的详细机制尚有待进一步研究。
细胞凋亡是由基因调控的细胞主动死亡过程,与细胞增殖失控两者一起在肿瘤发生发展中发挥关键作用。Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路参与多种肿瘤的发生发展过程,β-catenin是Wnt信号通路中最关键的通道传递分子,β-catenin转移到核内是该通路被激活的标志[14]。正常情况下Wnt通路处于关闭状态,β-catenin与Ecadherin、APC、Axin、GS-3β等结合,介导黏附和磷酸化降解功能,细胞质β-catenin水平维持在较低水平[15]。在肿瘤细胞中,Wnt通路异常激活,β-catenin的降解受到抑制,游离的β-catenin可与Tcf/lef结合进入细胞核,启动CyclinD1、C-myc等下游靶基因的转录,CyclinD1和C-myc是细胞周期和生成调控基因,过度表达可导致细胞周期调控出现异常,引起肿瘤的发生,DKK家族是Wnt信号抑制通路,上调DKK表达可抑制乳腺癌的形成[16]。曾令瑞等[17]应用免疫组化EnVision两步法对乳腺癌中β-catenin和CyclinD1的表达进行检测,结果显示乳腺癌原发癌灶中β-catenin异位表达率和CyclinD1的阳性表达率分别为54.3%和63.0%,淋巴结转移癌灶中β-catenin异位表达率和Cyclin D1阳性表达率分别为76.1%和82.6%。结果提示Wnt/β-catenin通路异常激活可能是乳腺癌发生发展的重要机制,抑制Wnt信号通路的激活可作为乳腺癌临床治疗的新靶点。
姜黄素对多种肿瘤的Wnt通路均有抑制作用。贾佳等[18]研究发现姜黄素可抑制人结肠癌细胞HT-29增殖,且存在量效关系,HT-29细胞的β-catenin表达随着干预时间的延长逐渐降低,认为抑制Wnt通路的激活可能是姜黄素抑制结肠癌增殖的作用机制之一。赵琳琳等[6]研究则显示,姜黄素可下调肝癌细胞Bel7402、QGY7703细胞Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,降低β-catenin表达,诱导Bel7402和QGY7703凋亡。本研究结果显示,姜黄素能诱导乳腺癌BT549细胞的凋亡,抑制其增殖,并呈现出时间和剂量依赖性,而这种作用是通过β-catenin的细胞核内转运激活实现的,与赵琳琳等[6]研究结果一致。研究发现,姜黄素可与Dvl2特点区域结合,增加β-catenin复合体形成,降低游离β-catenin水平;姜黄素还可与Hsp90蛋白结合,去磷酸化AKT,激活GSK-3β,促进β-catenin复合体形成[19]。本研究结果显示,随着姜素浓度增加,β-catenin总蛋白量无显著变化,而β-catenin核蛋白量逐渐降低,进一步提示姜黄素可能通过促进β-catenin复合物形成、减少β-catenin在细胞核积聚发挥对Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的抑制作用。
综上所述,姜黄素通过Wnt/β-catenin信号传导通路抑制乳腺癌细胞株BT549细胞的增殖和诱导其凋亡,并呈现时间、剂量依赖性,为乳腺癌的临床治疗提供了一定的理论基础。但姜黄素激活Wnt /β-catenin信号传导通路的具体机制及下游原癌基因启动的调控还有待进一步研究。
[1]Roarty K,Baxley SE,Crowley MR,et al. Loss of TGF-beta or Wnt5a results in an increase Wnt/beta-catenin activity and redirects mammary tumour phenotype[J]. Breast Cancer Res,2009,11(2):R19
[2]Khalil S,Tan GA,Giri DD,et al. Activation status of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in normal and neoplastic breast tissues:relationship to HER2/neu expression in human and mouse[J]. PloS One,2012,7(3):e33421
[3]Jang GB,Hong IS,Kim RJ,et al. Wnt/beta-catenin small molecule inhibitor CWP232228 preferentially inhibits the growth of breast cancer stem-like cells[J]. Cancer Res,2015,75(8):1691-1702
[4]Zhao Z,Lu P,Zhang H,et al. Nestin positively regulates the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and the proliferation,survival and invasiveness of breast cancer stem cells[J]. Breast Cancer Res,2014,16(4):408
[5]岳秀,蒋幼凡,刘晓,等. 姜黄素通过Wnt信号转导通路抑制肺癌细胞A549增殖的研究[J]. 重庆医科大学学报,2008,33(12):1454-1457
[6]赵琳琳,陈剑群,徐学军. 姜黄素对肝癌细胞Bel7402、QGY7703增殖凋亡及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的影响[J/CD]. 中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2013,7(11):4902-4906
[7]王小玲,韦 红,张钰,等. 姜黄素通过抗炎机制减轻60%氧致新生鼠的肺损伤[J]. 免疫学杂志,2010,26(12):1059-1064
[8]Zhao J,Yu S,Zheng W,et al. Curcumin improves outcomes and attenuates focal cerebral ischemic injury via antiapoptotic mechanisms in rats[J]. Neurochem Res, 2010,35(3):374-379
[9]Zanotto-Filho A,Braganhol E,Edelweiss MI,et al. The curry spice curcumin selectively inhibits cancer cells growth in vitro and in preclinical model of glioblastoma[J]. J Nutr Biochem,2012,23(6):591-601
[10] Banerjee M,Singh P,Panda D. Curcumin suppresses the dynamic instability of microtubules,activates the mitotic checkpoint and induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells[J]. FEBS J,2010,277(16):3437-3448
[11] Nautiyal J,Banerjee S,Kanwar SS,et al. Curcumin enhances dasatinib-induced inhibition of growth and transformation of colon cancer cells[J]. Int J Cancer,2011,128(4):951-961
[12]SundramV,ChauhanSC,EbelingM,etal.Curcuminattenuatesbeta-cateninsignalinginprostatecancercellsthroughactivationofproteinkinaseD1[J].PLoSOne,2012,7(4):e35368
[13] 韦达,唐金海,潘立群. 姜黄素诱导乳腺癌MCF-7细胞凋亡[J]. 江苏医药,2008,34(4):348-350
[14] Toledo EM,Colombres M,Inestrosa NC. Wnt signaling in neuroprotection and stem cell differentiation[J]. Prog Neurobiol,2008,86(3):281-296
[15] He Y,liu Z,Qiao C,et al. Expression and significance of Wnt signaling components and their target genes in breast carcinoma[J]. Mol Med Rep,2014,9(1):137-148
[16] Kim HY,Park JH,Won HY,et al. CBX7 inhibits breast tumorigenicity through DKK-1-mediated suppression of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway[J]. FASEB J,2015,29(1):300-313
[17] 曾令瑞,韩玉贞,朱玉红. 乳腺癌中Wnt信号蛋白β-catenin和cyclin D1的表达及其与侵袭转移的关系[J]. 中国普通外科杂志,2014,23(11):1517-1521
[18] 贾佳,赵逵,张银萍,等. 姜黄素对人结肠癌细胞HT-29中β-catenin、血管内皮生长因子的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2014,34(14):3940-3942
[19] Kurashina R,Ohyashiki JH,Kobayashi C,et al. Anti-proliferative activity of heat shock protein(HSP) 90 inhibitors via beta-catenin/TCF7L2 pathway in adult T cell leukemia cells[J]. Cancer Lett,2009,284(1):62-70
Study on the mechanism of curcumin inhibiting the apoptosis of breast cancer cells induced by Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
ZHAO Yifeng1, WEI Yulei1, WANG Ping2, WANG Minmin1, WANG Jinke1
(1.The First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North College, Zhangjiakou 075061, Hebei, China; 2.Zhangjiakou Special Care Hospital, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei, China)
Objective It is to study the inducing effect of curcumin on apoptosis of human breast cancer cell line BT549 and its mechanism. Methods Logarithmic growth phase bt549 cells were counted and seeded on 96 hole culture plate with about 5 000 cells in each hole. After 24 h, 0,10,20,40,80 μmol/L curcumin were added to culture cells, and the proliferation inhibition rate of BT549 cells was detected by MTT assay after 12, 24 and 48 h culture. The cells were treated with 0,10,20,40,80 μmol/L curcumin respectively, and the apoptosis index was detected by TUNEL staining after 48 hours. The cells were treated with 0,10,20,40,80 μmol/L curcumin respectively, and the expression of cell proliferation and apoptosis related protein was detected by Western blot assay after 48 h. Results The MTT colorimetric assay results showed that at 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, the BT549 cells proliferation inhibition rate gradually increased in 0 μmol/L,20 μmol/L,40 μmol/L,60 μmol/L,80 μmol/L curcumin group(P<0.05).The results of TUNEL staining showed that the apoptotic index of BT549 cells increased gradually in the 0 μmol/L,20 μmol/L,40 μmol/L,60 μmol/L,80 μmol/L curcumin group(P<0.05).Blot Western showed that with the increase of the concentration of curcumin, the expression of β-catenin in the total protein was not affected (P>0.05), while the expression of β-catenin in the nucleus gradually decreased (P<0.05). Conclusion Curcumin can inhibit the proliferation and induce the apoptosis of breast cancer cell line BT549 cells by β-catenin beta Wnt/signaling pathway, and present time and dose dependence.
curcumin; Wnt/β-catenin; breast cancer cell; apoptosis
赵轶峰,男,主治医师,研究方向为胃肠肿瘤。
张家口市科技攻关计划项目(15211080)
10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2016.29.004
R-33
A
1008-8849(2016)29-3202-04
2016-02-28
