氢吗啡酮应用于妇科腹腔镜手术超前镇痛的效果
2016-10-19陈乃葆朱苗苗田雪丹
陈乃葆 张 岩,2▲ 朱苗苗 田雪丹
1.潍坊医学院麻醉学系,山东潍坊261000;2.潍坊医学院附属医院麻醉科,山东潍坊261000
氢吗啡酮应用于妇科腹腔镜手术超前镇痛的效果
陈乃葆1张岩1,2▲朱苗苗1田雪丹1
1.潍坊医学院麻醉学系,山东潍坊261000;2.潍坊医学院附属医院麻醉科,山东潍坊261000
目的探讨静脉注射氢吗啡酮用于妇科腹腔镜手术超前镇痛中的效果及其不良反应发生情况。方法选择我院择期行妇科腹腔镜手术的60例患者(ASAⅠ~Ⅱ级),随机分为H组和C组,各30例。C组在缝皮前不予任何镇痛药,H组缝皮前15 min静脉注射氢吗啡酮0.01 mg/kg。两组患者分别于术后1 h(T1)、4 h(T2)、8 h(T3)采集VAS、BCS评分,当患者的VAS评分为10分,BCS评分为0级时,以哌替啶50 mg肌注镇痛,并记录术后初次使用哌替啶的时间及使用次数、例数,随访记录不良反应的发生率。结果H组术后T2、T3时点的VAS评分明显低于C组,而BCS评分明显高于C组(P<0.05);H组术后使用哌替啶例数及次数低于C组,哌替啶的初次使用时间长于C组(P<0.05);H组和C组咽喉疼痛发生率分别为6.7%和53.3%(P<0.05);两组的不良反应中头昏嗜睡和恶心呕吐的比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论氢吗啡酮用于妇科腹腔镜手术的超前镇痛,对术后切口疼有显著镇痛效果,且可减少术后静脉镇痛药用量,减少不良反应的发生,患者术后苏醒安全迅速。
氢吗啡酮;超前镇痛;妇科;腹腔镜
[Abstract]Objective To investigate the effect and safety of preemptive analgesia with hydromorphone in gynaecological laparoscopic surgery through intravenous injection.Methods 60 female adult patients(ASAⅠorⅡ)who underwent the gynaecological laparoscopic surgery were randomly divided into two groups(30 cases of each group):hydromorphone group(group H)and placebo group(group C).Patients in group C were not given any analgesics before suture.Patients in group H were given 0.01 mg/kg hydromorphone through intravenous injection before suture,the interval was 15 minutes. After operation,the pain of incision was assessed by VAS and BCS scores at 1 h(T1),4 h(T2)and 8 h(T3)respectively. When the VAS scores reached 10 and the BCS score was 0,patients were given intramuscular administration of 50 mg meperidine to relieve the pain.The time used and intervals of meperidine,the cases of using meperidine,and the incidence of sore throat in patients were recorded.Results The VAS scores of patients at T2and T3after operation in group H were significantly lower than that of group C,while the BCS scores were higher than that of group C(P<0.05);The times of using meperidine,and the cases of using meperidine in group H were lower than those in group C,the initial use time of meperidine of group H was longer than that of group C(P<0.05).The incidence of sore throat was lower in group H than that of group C(6.7%vs 53.3%)(P<0.05),while there were no differences between the two groups in the incidence of vomiting and nausea(P>0.05).Conclusion Preemptive analgesia with hydromorphone can lighten the postoperative pain effectively,it can also reduce the usage of analgesics and adverse reactions,and has the advantages of safety and promote a faster recovery.
[Key words]Hydromorphone;Preemptive analgesia;Gynecology;Laparoscopy
氢吗啡酮作为一种强效阿片类镇痛药,在临床上已经开始广泛应用[1]。作为一种半合成阿片类药物,氢吗啡酮主要激动中枢神经系统μ-阿片受体发挥镇痛作用。氢吗啡酮因其在化学结构上的变化使其在镇痛作用、理化性质等方面均优于吗啡[2]。本研究拟采用氢吗啡酮静脉注射用于妇科腹腔镜手术的超前镇痛,并观察其术后镇痛效果及不良反应发生情况,为其在临床应用提供参考。现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料
选择2015年11月~2016年3月在我院择期行妇科腔镜手术的60例患者(ASAⅠ~Ⅱ级),排除患有严重心、肝、肾疾病及其他系统疾病者。将患者随机分为氢吗啡酮组(H组)和对照组(C组),各30例。术前告知视觉模拟评分法(visual analogue scale,VAS)和舒适度评分(bruggrmann comfort scale,BCS)的评分方法[3]。本研究经院伦理委员会同意,患者知情并签署知情同意书。两组一般资料的比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表1。
表1 两组一般资料比较[(±s)]

表1 两组一般资料比较[(±s)]
组别n年龄(岁)身高(cm)体重(kg)BMI(kg/m2)C组30 H组30 t值P 40.67±5.77 39.97±6.72 0.431>0.05 162.43±6.91 163.23±5.62 0.582>0.05 59.63±5.36 58.97±4.92 0.237>0.05 22.61±1.64 22.13±1.48 0.145>0.05
1.2方法
患者入室开放静脉通道,常规监测生命体征,行气管插管全身麻醉。手术结束前15 min,H组患者静注0.01 mg/kg氢吗啡酮(宜昌人福药业生产,产品批号:1150401),C组不给予任何镇痛药物,当患者VAS评分为10分,BCS为0级时,予哌替啶50 mg肌注镇痛。
1.3观察指标
术中监测患者血氧饱和度、心率、血压、心电图。术后1 h(T1)、4 h(T2)、8 h(T3)进行随访,进行疼痛评分及舒适度评分,分别依据VAS评分法[4]和BCS评分标准。记录术后初次使用哌替啶的时间及使用例数、次数。记录不良反应的发生率。
1.4统计学方法
采用SPSS18.0软件进行数据的统计分析,计数资料以[n(%)]表示,行χ2检验;计量资料以(x±s)表示,比较行t检验及方差分析。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1两组患者术后各时点VAS评分、BCS评分比较
H组患者术后T2、T3时点的VAS评分明显低于C组(P<0.05),BCS评分明显高于C组(P<0.05),见表2、3。
表2 两组患者术后各时点VAS评分(±s,分)

表2 两组患者术后各时点VAS评分(±s,分)
组别n T1T2T3C组H组t值P 30 30 1.00±0.79 0.17±0.38 1.264>0.05 5.57±0.73 1.47±0.51 6.438<0.05 7.03±0.81 3.93±1.11 6.015<0.05
表3 两组患者术后各时点BCS评分(±s,分)

表3 两组患者术后各时点BCS评分(±s,分)
组别n T1T2T3C组H组t值P 30 30 3.47±0.51 3.70±0.47 0.965>0.05 1.47±0.51 2.70±0.47 4.667<0.05 0.47±0.51 1.40±0.77 4.153<0.05
2.2两组患者术后应用哌替啶的情况比较
术后H组初次使用哌替啶的时间长于C组,且使用哌替啶的例数及次数均少于C组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表4。
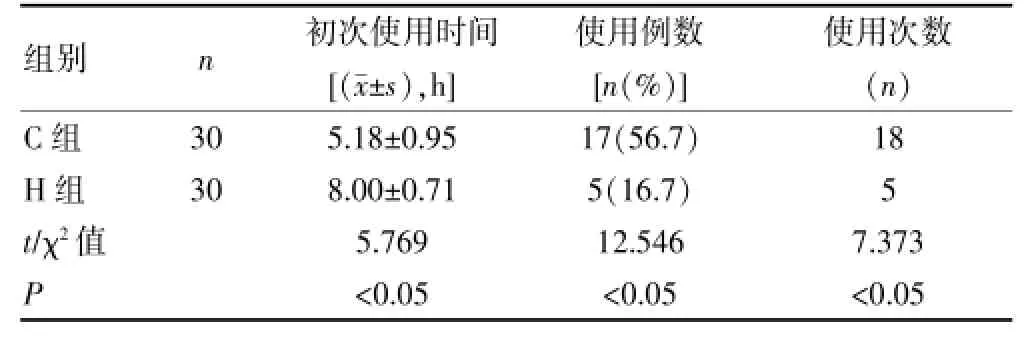
表4 两组患者术后应用哌替啶的情况比较
2.3两组患者不良反应发生情况比较
与H组2例(6.7%)相比,C组16例(53.3%)发生咽喉疼痛,组间差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);H组头昏嗜睡与恶心呕吐的发生率高于C组,但组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);试验过程两组患者均未发现呼吸抑制,见表5。

表5 两组患者不良反应发生情况比较n(%)
3 讨论
近年来学界在疼痛治疗中提出了“超前镇痛”这一概念,“超前镇痛”主要通过抑制外周和中枢神经系统的敏感化来阻断疼痛的产生,从而起到术后镇痛的作用[5]。目前,妇科腹腔镜手术因其创伤小而被广泛应用于临床,但患者术后仍存在疼痛刺激,对患者的住院时间及恢复有很大的影响。
氢吗啡酮主要作用于阿片受体,其与传统吗啡的化学结构不同,其镇痛作用是吗啡的5~10倍。氢吗啡酮与μ和δ受体的亲和力高于吗啡,氢吗啡酮的镇痛效果更显著[6]。在术后镇痛中氢吗啡酮有着极其显著的优势,其不良反应与其他阿片药物相比要少很多[7]。氢吗啡酮的脂溶性是吗啡的10倍,易穿透血脑屏障快速作用于中枢神经系统,生物利用率高[8]。相关研究显示[9-12],与吗啡相比静脉注射氢吗啡酮的成瘾率低、不良反应少,且代谢产物无活性。
本研究采用手术结束前15 min静脉注射氢吗啡酮0.01 mg/kg,结果在术后T2、T3时点H组患者的疼痛VAS评分明显低于C组,BCS评分明显高于C组,表明氢吗啡酮对腹腔镜手术术后切口性疼痛镇痛效果明显。术后H组患者初次使用哌替啶的时间相对于C组延长,且使用哌替啶的例数及次数均低于C组患者,差异有统计学意义,并且H组T2、T3时点VAS评分明显低于C组(P<0.05)。但氢吗啡酮静脉注射的作用持续时间仅为2~3 h,由于给药时间点的差异,作用时间有了显著的差异,单从药理学机制无法解释这一现象,其可能与氢吗啡酮超前镇痛抑制了中枢和外周疼痛敏化,从而能使H组患者的痛阈维持在较高水平,不产生过激的疼痛反应,进而延长镇痛作用时间有关[13],氢吗啡酮的这一药理学特性可以起到良好的苏醒期镇痛作用,弥补术中所用的麻醉性镇痛药物在苏醒期的作用减弱或者消失后导致的不良后果[14]。
在不良反应发生率方面,相对于C组16例(53.3%),H组只有2例(6.7%)发生咽喉疼痛,两组之间的差异有统计学意义;两组患者头昏嗜睡与恶心呕吐发生率比较差异无统计学意义;两组患者均未出现呼吸抑制。结果表明氢吗啡酮不增加妇科腹腔镜手术后恶心呕吐的发生率,氢吗啡酮超前镇痛降低患者咽喉疼痛的发生率明显低于C组,说明预注氢吗啡酮超前镇痛能有效降低术后相关不良反应的发生率[15]。
综上所述,氢吗啡酮超前镇痛用于妇科腹腔镜手术,对术后疼痛有显著的镇痛作用,可以减少术后镇痛药的使用和不良反应发生,且符合快速康复这一理念,值得临床推广应用。
[1]Oh E,Ahn HJ,Sim WS,et al.Synergistic effect of intravenous ibuprofen and hydromorphone for postoperative pain:Prospective randomized controlled trial[J].Pain Physician,2016,19(6):341-348.
[2]Gulur P,Koury K,Arnstein P,et al.Morphine versus hydromorphone:Does choice of opioid influence outcomes[J]. Pain Research and Treatment,2015,2015(48):2081.
[3]Ren C,Zhang X,Liu Z,et al.Effect of intraoperative and postoperative infusion of dexmedetomidine on the quality of postoperative analgesia in highly nicotine-dependent patients after thoracic surgery:A consort-prospective,ran domized,controlled trial[J].Medicine,2015,94(32):e1329.
[4]Ferreira-Valente MA,Pais-Ribeiro JL,Jensen MP,et al. Validity of four pain intensity rating scales[J].Pain,2011,152(10):2399-2404.
[5]卢静,兰志勋.超前镇痛机制及其临床应用进展[J].实用医院临床杂志,2013,20(6):210-212.
[6]Kumar P,Sunkaraneni S,Sirohi S,et al.Hydromorphone efficacy and treatment protocol impact on tolerance and mu-opioid receptor regulation[J].European Journal of Pharmacology,2008,597(1-3):39-45.
[7]Chandler SW,Trissel LA,Weinstein SM.Combined administration of opioids with selected drugs to manage pain and other cancer symptoms:Initial safety screening for compatibility[J].Journal of Pain and Symptom Management,1996,12(3):168-171.
[8]Junker U,Figge V.Controlled-release hydromorphone in elderly patients with severe pain of different etiologies. Results of an observational study[J].MMW Fortschritte der Medizin,2005,147(3):91-96.
[9]Pergolizzi J,Boger RH,Budd K,et al.Opioids and the management of chronic severe pain in the elderly:Consensus statement of an international expert panel with focus on the six clinically most often used World Health Organization StepⅢopioids(buprenorphine,fentanyl,hydro morphone,methadone,morphine,oxycodone)[J].Pain Practice:The Official Journal of World Institute of Pain,2008,8(4):287-313.
[10]Hauber AB,Fleischmann J,Lothgren M,et al.Economic evaluation of OROS hydromorphone for chronic pain:A Pan-European perspective[J].Journal of Opioid Management,2011,7(4):287-296.
[11]Popping DM,Elia N,Marret E,et al.Opioids added to local anesthetics for single-shot intrathecal anesthesia in patients undergoing minor surgery:A meta-analysis of randomized trials[J].Pain,2012,153(4):784-793.
[12]Chang AK,Bijur PE,Davitt M,et al.Randomized clinical trial of an intravenous hydromorphone titration protocol versus usual care for management of acute pain in older emergency department patients[J].Drugs&Aging,2013,30(9):747-754.
[13]Katz J,Clarke H,Seltzer Z.Review article:Preventive analgesia:quovadimus?[J].AnesthesiaandAnalgesia,2011,113(5):1242-1253.
[14]Georges P,Lavand'homme P.Intrathecal hydromorphone instead of the old intrathecal morphine:The best is the enemyofthegood?[J].EuropeanJournalofAnaesthesiology,2012,29(1):3-4.
[15]王利祥,杨明乾,刘会长.氢吗啡酮预防全麻腹腔镜手术苏醒期躁动的效果[J].实用临床医药杂志,2014,(21):144-145.
Preemptive analgesia with hydromorphone in gynaecological laparoscopic surgery
CHEN Naibao1ZHANG Yan1,2ZHU Miaomiao1TIAN Xuedan1
1.Department of Anesthesiology,Weifang Medical University,Weifang261000,China;2.Department of Anesthesiology,Affiliated Hospital of Weifang Medical University,Weifang261000,China
R614
B
1673-9701(2016)24-0135-03
2016-05-08)
