A53T α-synuclein抑制SH-SY5Y细胞2型囊泡单胺转运体的表达
2016-09-13满建梅郭军堂张代娟陈安琪
满建梅,郭军堂,张代娟,陈安琪
(潍坊医学院临床医学院,潍坊 261053)
A53T α-synuclein抑制SH-SY5Y细胞2型囊泡单胺转运体的表达
满建梅,郭军堂,张代娟,陈安琪
(潍坊医学院临床医学院,潍坊261053)
目的研究稳定表达A53T α-synuclein对神经母细胞瘤SH-SY5Y细胞中2型囊泡单胺转运体(VMAT2)蛋白表达的影响。方法构建A53Tα-synuclein真核表达载体,用脂质体lipofectamineTM2000转染SH-SY5Y细胞,经G418筛选获得稳定转染单克隆细胞株;分别采用 Western blotting及DCFH-DA染色检测细胞系A53T α-synuclein过表达对VMAT2蛋白的表达及细胞内活性氧类物质(ROS)水平的影响。结果Western blotting结果显示VMAT2的表达在稳定表达A53T α-synuclein的细胞系中明显降低。DCFH-DA染色结果显示稳定表达A53T α-synuclein细胞系内DCF signal (507.3±7.1)较对照组 (410.7±10.5)明显增多 (P<0.05)。结论A53T α-synuclein能够通过抑制VMAT2的表达,增加细胞内的ROS水平,在帕金森病的发病过程中发挥重要作用。
帕金森氏病;A53T α-synuclein;VMAT2
帕金森氏病(Parkinson′s disease, PD)的主要病理特征是黑质多巴胺能神经元的选择性变性及Lewy body(LB)的形成,α-synuclein是LB的重要成分[1]。A53T α-synuclein是人们在常染色体显性家族PD患者中发现的突变体[2],与PD的发病密切相关,但具体机制还不清楚。研究发现A53T α-synuclein可与VMAT2在体外发生特异性分子间相互作用[3],提示A53T α-synuclein参与了多巴胺(DA)的代谢调节过程,在PD的多巴胺神经元选择性变性过程中发挥作用。本研究目的是建立稳定表达A53T α-synuclein的细胞系,并研究其对VMAT2蛋白表达的影响, 为研究PD的发病机制提供新思路。
1 材料和方法
1.1材料
神经母细胞瘤SH-SY5Y细胞购自中国医学科学院基础所细胞中心;携带A53T α-synuclein的T载体及β-半乳糖苷酶的pcDNA3.0-Lacz真核细胞表达载体为本室保存;LipofectamineTM2000购自Gibco BRL;山羊抗人VMAT2多克隆抗体、小鼠抗人α-synuclein多克隆抗体、小鼠抗人β-actin单克隆抗体购自Santa Cruz;辣根酶(HRP)标记IgG购自中杉金桥; XhoI、HindIII、T4DNA连接酶、高保真Pyrobest DNA聚合酶购自大连宝生物;2’-7’-二氯荧光素双醋酸盐 ( DCFH-DA)、X-gal购自Sigma;G418购自Amersco;PCR引物由上海博亚公司合成。
1.2方法
1.2.1真核表达载体构建:合成正义引物 cttcataagcttcgacagtgtggt(含HindIII内切酶位点)和反义引物taagatctcgaggaaactgggagcaaag(含XhoI内切酶位点),以携带A53T α-synuclein的T载体为模板进行PCR反应。条件:94℃ 变性1 min,60℃退火30 s,72℃延伸 30 s,25个循环。回收的PCR产物与pcDNA3.0分别用HindIII和XhoI酶切。酶切产物纯化后加入T4连接酶4℃连接过夜后转化DH 5α感受态大肠杆菌,挑取单菌落小量扩增,提取质粒,用HindIII和XhoI酶切鉴定并进行测序,测序正确的克隆命名为pcDNA3.0-A53T。
1.2.2细胞培养及转染:将SH-SY5Y接种于高糖DMEM培养基(含10%胎牛血清,100 IU/mL青霉素,100μg/mL链霉素)中,37℃,5% CO2培养;取对数生长期细胞接种到24孔板内,当细胞密度达到50%~80%时,按照脂质体LipofectamineTM2000(Gibco BRL)说明书进行转染。24 h后加入抗生素含G418的完全培养基进行持续筛选,两周后挑选单克隆进行扩大培养并继续保持筛选压力到2个月以上。稳定表达A53T α-synuclein的细胞系为实验组,稳定表达β-半乳糖苷酶的细胞系为对照组。
1.2.3β-半乳糖苷酶活性检测:培养细胞72 h后,用冰冷的PBS洗涤细胞两次,10%甲醛固定液室温固定 5 min。 PBS 洗涤两次后加入X-gal染色液(1g/L),37 ℃ 孵 育12 h。显微镜下观察,蓝染细胞为表达β-半乳糖苷酶阳性细胞。
1.2.4Western blotting检测蛋白表达:胰酶消化细胞后,1 000 g离心10 min, PBS 洗3次后,弃上清液,加入1/5 体积的6×SDS蛋白质上样缓冲液,混匀后100 ℃煮沸10 min进行12% SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳,蛋白转移到PVDF膜后,用TBST稀释的5%脱脂奶粉室温摇动封闭1 h,一抗(VMAT2抗体1∶500,α-synuclein抗体1∶500,β-actin抗体1∶500)室温孵育4 h,1∶5 000二抗室温孵育1 h, ECL 化学发光与曝光。
1.2.5流式细胞仪检测细胞内ROS水平:培养细胞24 h后,用胰酶进行消化;将细胞重新悬浮于预冷的无血清培养基中,加入DCFH-DA(10 μmol/L),孵育20 min后, 离心收集细胞,PBS重新洗涤细胞3次,最后重新悬浮于500 μL PBS, 流式细胞仪(E6155, BD FACS Calibur)中检测荧光强度,每次10 000个,重复3次,记录平均DCF signal。
2 结果
2.1pcDNA3.0-A53T真核表达载体的鉴定
Hind III和XhoI双酶切pcDNA3.0和pcDNA3.0-A53T,酶切产物电泳可见1泳道有500 bp左右大小的条带,与预期结果一致(见图1)。DNA测序结果与Genbank报道的序列一致。

M:DNA marker;1:pcDNA3.0-A53T;2:pcDNA3.0图1 pcDNA3.0-A53T真核表达载体的酶切鉴定M: DNA marker; Lane 1: pcDNA3.0-A53T; Lane 2: pcDNA3.0.Fig.1 Identification of eukaryotic expression vector pcDNA3.0-A53T
2.2稳定表达β-半乳糖苷酶细胞系的鉴定
真核表达载体pCMVSYN-A53T没有β-半乳糖苷酶基因,在细胞中无法产生β-半乳糖苷酶,无法作用于X-gal中的吲哚环而显蓝色。想反,稳定转染β-半乳糖苷酶基因的细胞系能够产生β-半乳糖苷酶,细胞则有明显的蓝染,提示β-半乳糖苷酶在细胞系中稳定表达。如图2所示。
2.3Western blotting结果
Western blotting结果显示,在SH-SY5Y细胞中有野生型α-synuclein蛋白的表达,但α-synuclein蛋白的表达量在稳定转染A53T α-synuclein的细胞系中(实验组)较稳定表达β-半乳糖苷酶细胞系(对照组)明显增多,提示细胞系中有A53T α-synuclein的过表达,而VMAT2在实验组中的表达量较实验组明显降低。如图3所示。
2.4细胞内ROS水平的变化
如图4所示, 稳定表达A53T α-synuclein细胞系的DCF signal (507.3±7.1)较稳定表达β-半乳糖苷酶细胞系(410.7±10.5)明显增高 (P<0.05),提示A53Tα-synuclein过表达能够明显增加细胞ROS的产生。
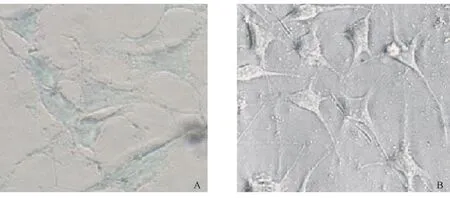
注:A:稳定表达β-半乳糖苷酶细胞系; B:稳定表达A53Tα-synuclein细胞系图2 X-gal染色检测β-半乳糖苷酶的表达Note. A: Cells stably expressing β-galactosidase; B: Cells stably expressing A53T α-synuclein.Fig.2 The detection of β-galactosidase by X-gal staining
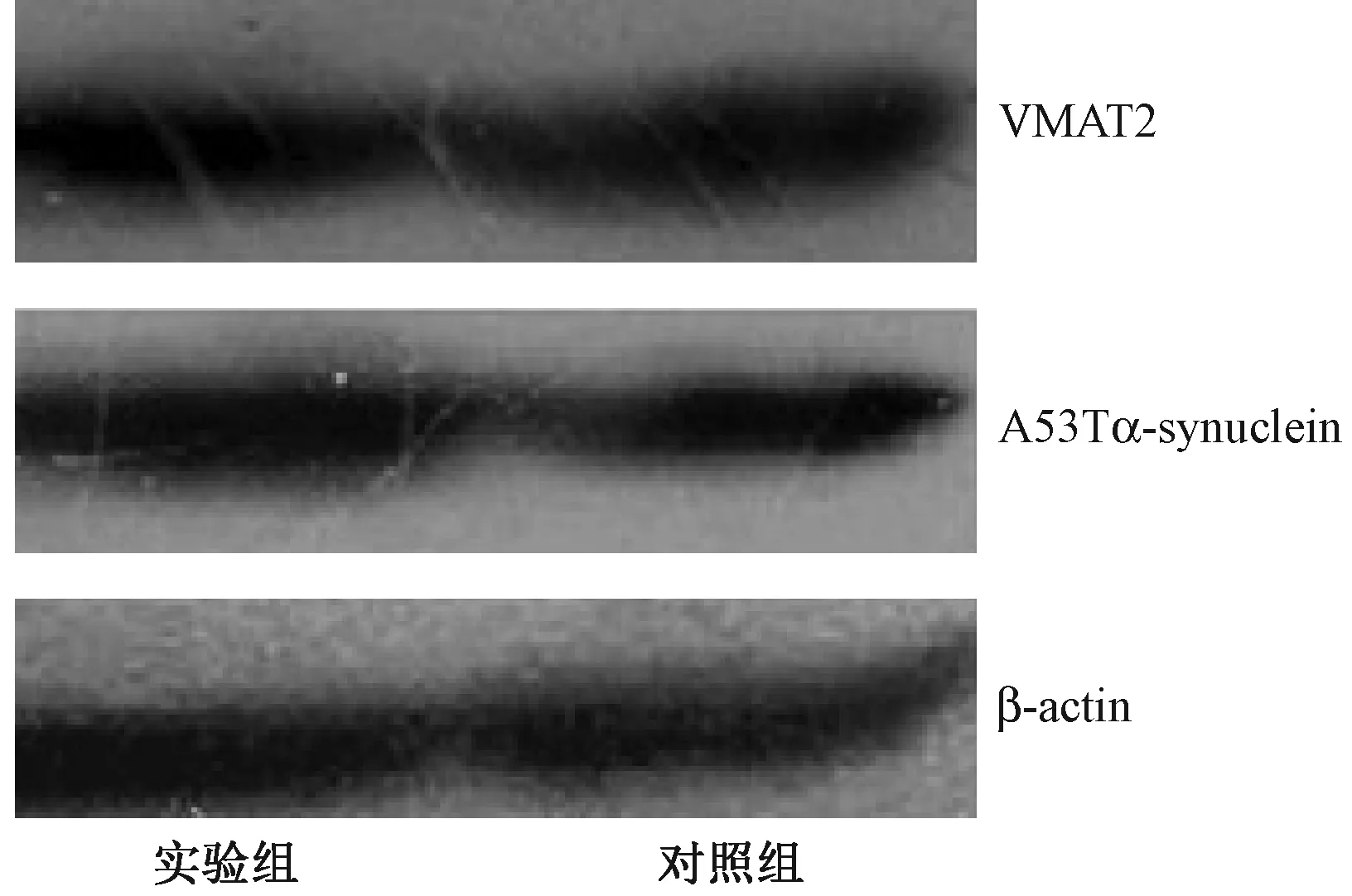
注:实验组:稳定表达A53Tα-synuclein细胞系;对照组:稳定表达β-半乳糖苷酶细胞系图3 Western blotting检测A53T α-synuclein及VMAT2的表达Note. Experimental group: Cells stably expressing A53T α-synuclein. Control group: Cells stably expressing β-galactosidase.Fig.3 Expression of A53T α-synuclein and VMAT2 detected by Western blotting

图4 细胞系内ROS水平的变化Fig.4 Changes of intracellular ROS level
3 讨论
α-Synuclein是一种具有非β-淀粉样结构(NAC)的可溶性蛋白质,主要分布于中枢神经系统突触前末梢和核周,在突触囊泡转运、神经递质的释放及多巴胺的代谢过程中具有重要的调节作用[4,5]。α-Synuclein蛋白正常、错误折叠及其寡聚化之间存在动态平衡,失衡后如出现大量错误折叠,会导致寡聚体及纤维体的形成。Peelaerts W等[6]认为纤维态是主要的毒性物质,它可引起进行性运动功能损害和细胞死亡,具体的机制尚不清楚。目前研究认为导致PD发病的重要因素可能与DA异常代谢产生的ROS有关,它能够引起神经元细胞的氧化损害[7]。细胞内的DA,尤其是DA的代谢产物能够与α-synuclein相互作用,促进α-synuclein的异常聚集及纤维化,形成LB小体[8]。生理条件下,多巴胺一旦在神经元中合成,立即可以通过VMAT2转运到突触囊泡中进行储存,否则中枢神经系统内的DA能够通过自身氧化和酶降解产生ROS[9]。
本研究通过Western blotting检测显示A53T α-synuclein在SH-SY5Y细胞系中稳定高效表达,为进一步研究PD发病机制提供了良好的细胞模型。在稳定表达A53T α-synuclein细胞系中的VMAT2表达水平明显低于对照组,提示其有抑制VMAT2蛋白表达的作用。为了进一步探讨A53T α-synuclein抑制VMAT2表达可能对细胞系产生的影响,我们通过DCFH-DA染色检测细胞内ROS水平的变化,结果显示A53T α-synuclein过表达能够明显的增加细胞内的ROS水平,这可能与其抑制VMAT2的表达有密切的关系。据此,我们认为过表达的A53T α-synuclein作用于VMAT2,下调其蛋白表达水平,打破了细胞内DA的平衡,致使细胞内ROS累积,造成对细胞的损害。A53Tα-synuclein如何影响VMAT2基因的表达及具体功能有待于进一步研究。
[1]Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, et al. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies [J]. Nature, 1997, 388(6645): 839-840.
[2]Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson′s disease [J]. Science, 1997, 276(5321): 2045-2047.
[3]陈安琪,王建英,牟青杰, 等. A53Tα-synuclein与II型单胺囊泡转移体相互作用的鉴定[J]. 中国临床实用医学, 2008(7): 43-45.
[4]Lashuel HA1, Overk CR, Oueslati A, et al. The many faces of α-synuclein: from structure and toxicity to therapeutic target [J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2013, 14(1): 38-48.
[5]Venda LL1, Cragg SJ, Buchman VL, et al. α-Synuclein and dopamine at the crossroads of Parkinson′s disease [J].Trends Neurosci, 2010, 33(12): 559-568
[6]Peelaerts W, Bousset L, Van der Perren A, et al. α-Synuclein strains cause distinct synucleinopathies after local and systemic administration [J]. Nature, 2015, 522(7556): 340-344.
[7]Jenner P, Olanow CW. Understanding cell death in Parkinson′s disease [J]. Ann Neurol, 1998, 44(3 Suppl 1): S72-84.
[8]Follmer C, Romão L, Einsiedler CM, et al. Dopamine affects the stability, hydration, and packing of protobrils andbrils of the wild type and variants of α-synuclein [J].Biochemistry, 2007, 46(4): 472-482.
[9]Parsons SM. Transport mechanisms in acetylcholine and monoamine storage [J]. FASEB J, 2000, 14(15): 2423-2434.
A53T α-synuclein decreases the expression of type 2 vesicular monoamine transporter in neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells
MAN Jian-mei, GUO Jun-tang, ZHANG Dai-juan, CHEN An-qi
(School of Clinical Medicine, Weifang Medical University, Weifang 261053, China)
ObjectiveTo investigate the effect of A53T α-synuclein on the expression of type 2 vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT2) in neuronblastoma SH-SY5Y cells stably expressing A53T α-synuclein. Methods A53T α-synuclein eukaryotic plasmid was constructed by transfection of the SH-SY5Y cells using LipofectamineTM2000, and a stable transfected monoclonal cell line was selected by G418. Western blotting and DCFH-DA staining were used to detect the effect of A53T α-synuclein overexpression on the expression of VMAT2 protein and level of reactive oxygen species (ROS). ResultsWestern blotting showed that compared with the control group, the expression of VMAT2 protein was significantly decreased, and DCFH-DA staining showed that DCF signal was significantly increased (507.3±7.1) than that in the cell line stably expressing A53T α-synuclein (410.7±10.5) (P<0.05). ConclusionsA53T α-synuclein can increase the intracellular ROS level by inhibiting the expression of VMAT2, thereby playing an important role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson′s disease.
Parkinson′s disease; A53T α-synuclein; VMAT2
山东省自然科学基金(ZR2011HM014);山东省自然科学基金(ZR2015HL126)。
满建梅(1989-),女,硕士研究生,专业:病理学与病理生理学。Email:1192746984@qq.com。
陈安琪(1981-),女。Email: chenanqi_1981@163.com。
研究报告
R-33
A
1671-7856(2016) 08-0066-04
10.3969.j.issn.1671-7856.2016.08.010
2016-03-09
