海洋鱼类和甲壳类抗菌肽的研究进展与应用前景
2016-08-24王克坚
彭 会,王克坚*
(1.海洋生物制备技术国家地方联合工程实验室,海洋与地球学院,厦门大学,福建 厦门 361102;
海洋鱼类和甲壳类抗菌肽的研究进展与应用前景
彭会1,2,王克坚1,2*
(1.海洋生物制备技术国家地方联合工程实验室,海洋与地球学院,厦门大学,福建 厦门 361102;
2.福建省海洋生物资源开发利用协同创新中心,福建 厦门 361102)
抗菌肽的发现与研究已有几十年的历史,抗菌肽是一类生物体中普遍存在并具有广谱抗微生物活性的小分子多肽,被科学家誉为“天然抗生素”。海洋动物抗菌肽是鱼、虾、蟹、贝等海洋动物的非特异性免疫防御系统的重要组成部分,在海洋环境中对于防御外源病原菌的入侵起到重要作用。海洋抗菌肽的研发与应用,不仅具有重要的医学开发价值,也是减少抗生素污染、实现海水健康养殖的重要保障。本文主要以鱼类抗菌肽和甲壳类抗菌肽为例,从抗菌肽的来源与分类、结构特点以及生物学活性等方面,简要概述近年来海洋鱼类和甲壳类抗菌肽的一些研究进展及其开发利用前景。
海洋动物;抗菌肽;鱼类;甲壳动物;应用前景
抗生素的长期过量使用,已经导致许多病原生物对几乎所有的抗生素药物都具有不同程度的耐药性,是目前影响我国畜牧、水产养殖业可持续发展乃至人类健康的重大科技问题。抗菌肽是一类生物体中普遍存在并具有广谱抗微生物活性的小分子多肽,已证实是天然免疫系统的重要组成部分,在防御病原微生物中起着重要作用,被科学家誉为“天然抗生素”。由于最初人们仅发现这类活性多肽对细菌的作用,所以命名为抗菌肽,后来随着对抗菌肽的深入研究发现绝大多数抗菌肽具有多重生物学功能,除了广谱抗细菌外,还具有抗病毒、真菌和寄生虫等活性,以及具有抗肿瘤、中和毒素、趋化和免疫调节、促进血管生成和创伤修复等生物学功能[1-3],因而又被称为“抗微生物肽”。抗菌肽的抗菌机理普遍认为是通过膜裂解机制或非膜裂解机制抑杀细菌,不易产生微生物耐药性,无有害残留等问题,所以被视为抗生素的有效替代品,在医药、畜牧水产业等多个领域都具有重要的潜在应用价值[4-5]。
抗菌肽的发现与研究已有几十年的历史,最早在1972年,瑞典科学家Boman首先在果蝇中发现一种可能的抗菌肽并阐明其免疫功能[6]。直至1981年,Steiner等在使用大肠杆菌感染惜古比天蚕蛾(Hyalophoracecropia)时分离获得了第一个抗菌肽天蚕素,并测定获得其氨基酸序列,才有了世界上第一个真正意义上分离鉴定的抗菌肽[7]。此后,越来越多的抗菌肽从细菌、真菌、动物和植物等多种物种中被鉴定出来。为了更好地对这些抗菌肽进行研究,各国学者建立了各种数据库来搜集抗菌肽的信息,如APD数据库、ANTIMIC数据库、SAPD数据库和AMSDb数据库等,极大地方便了不同生物源抗菌肽的比较研究和新抗菌药物的筛选。
1 研究进展与应用实例
海洋拥有地球上约80%的生物资源,近年来国内外学者高度认识到海洋生物中蕴藏着丰富的抗菌活性物质,从海洋生物中研究开发具有抗耐药性细菌的抗生素有效替代品将是未来医学、农业、药学等发展的必然方向。海洋生物抗菌肽的研发与应用,不仅具有重要的医学开发前景,而且还将是减少抗生素污染、实现海水健康养殖的重要保障。目前已从海洋动物中分离到多种多样的抗菌肽,其中鱼、虾和蟹等种类的抗菌肽报道较多。
1.1鱼类抗菌肽研究进展
鱼类生活在富含各种微生物的水环境中,抗菌肽是在其受到损伤或者病原入侵时迅速防御和杀伤入侵物质的重要的非特异性免疫因子,是鱼类自身先天免疫系统的重要组成部分,结构复杂,种类多样。鱼类抗菌肽按照生化和结构特点,可将其分为4类:①不含半胱氨酸可以折叠成疏水或双亲性α螺旋结构,此种类型的抗菌肽由于富含一些碱性氨基酸和α螺旋结构,有利于在细菌细胞膜形成穿孔,而产生直接的抗菌活性,包括Piscidins[8-10],Pleurocidins[11-12]、Moronecidin[13-14]等;②含多个半胱氨酸,可以形成β折叠结构,主要包括Hepcidin[15-19],Cathelicidins[20-21]等;③源于组蛋白的抗菌肽,这类抗菌肽的氨基酸序列与组蛋白H2A和H2B等相似,如Parasin I[22-23];④经酰胺化或糖基化修饰的抗菌肽,这类抗菌肽经高尔基体加工时,会在相关酶的作用下脱掉C端一个或多个氨基酸,或再与一些糖基结合,从而变成具有活性的成熟肽,如从鳗鲡皮肤分离出的一种糖基化的抗菌肽[24]。常见鱼类抗菌肽的研究进展如表1所示。
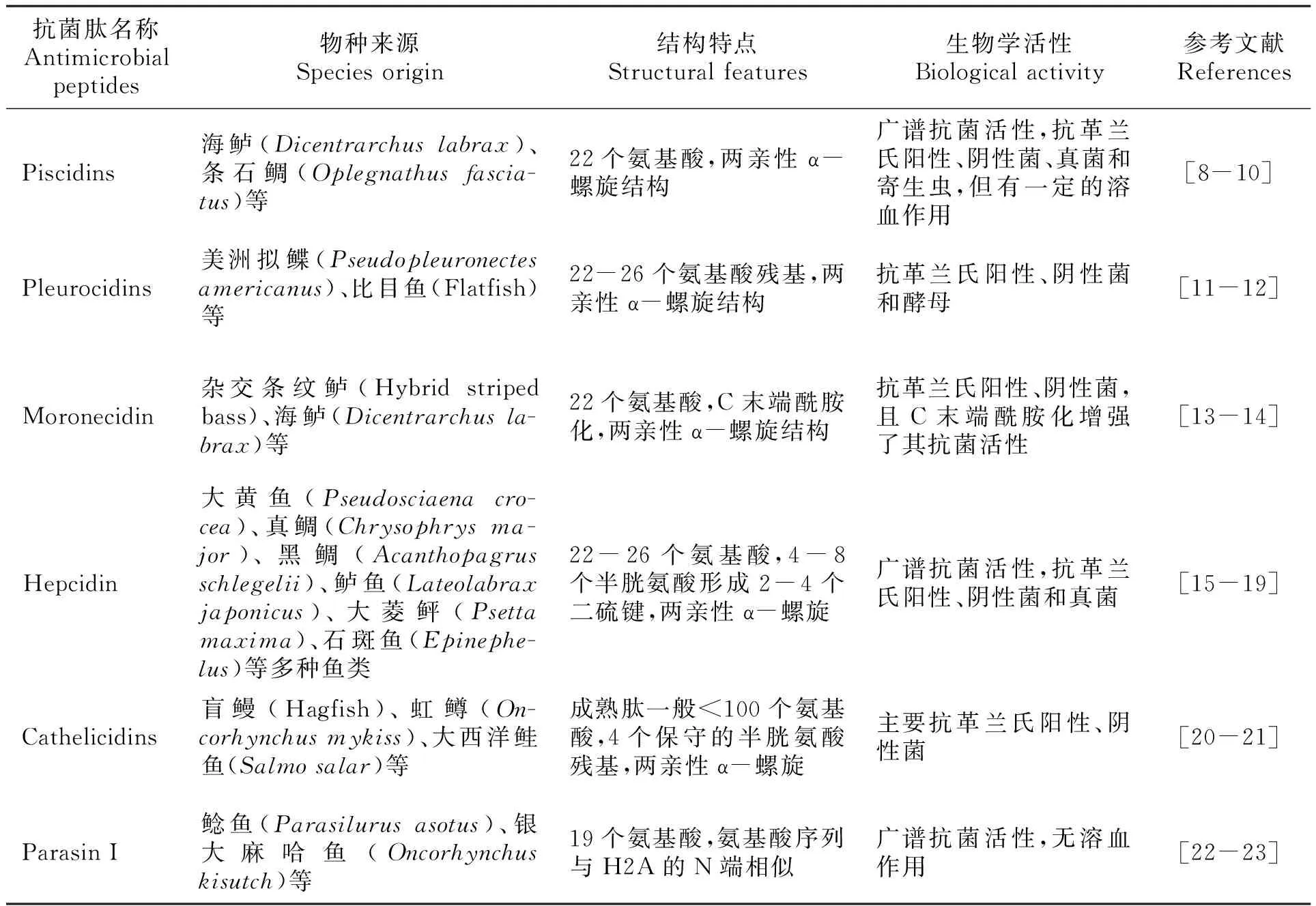
表1 常见鱼类抗菌肽列表
鱼类抗菌肽hepcidin的研究:Hepcidin是一类富含半胱氨酸、具有二硫键结构的抗菌肽。2000年,Krause等首先从人血液中分离纯化出的一个由25个氨基酸组成的具有抗菌活性的新型抗菌肽,因其在肝脏中高表达,命名为LEAP-1(Liver expressed antimicrobial peptide)[25]。鱼类抗菌肽hepcidin是Shike等于2002年首次从杂交斑纹鲈鱼(Moronesaxatilis×Moronechrysops)的鳃中分离获得了hepcidin的成熟肽片段[15]。此后发现hepcidin广泛存在于多种鱼类中。Hepcidin的基因序列和结构高度保守,从多个物种中分离得到的hepcidin基因的分子结构相似,基因均含有3个外显子和2个内含子。Hepcidin蛋白结构富含精氨酸、赖氨酸,由信号肽(Signal peptide)、前导肽(Prodomain)和成熟肽(Mature peptide)组成。Hepcidin的合成过程为首先形成一个包括信号肽和前导肽以及成熟肽的前多肽原(Pre-pro-peptide),经酶切去除信号肽后,由前导肽和成熟肽组成的前体肽(Pro-peptide)进入血液循环,最后通过前体肽转化酶切割形成具有生物活性的成熟肽。多数hepcidin成熟肽含有8个半胱氨酸残基,其位置在不同的生物中具有高度的保守性,可以形成4个二硫键,二硫键的连接方式为Cys1-Cys8、Cys3-Cys6、Cys2-Cys4和Cys5-Cys7。近年来在鱼类中也发现了部分成熟肽含有4、5、6或7个半胱氨酸残基的hepcidin。利用圆二色光谱和核磁共振谱等技术方法已经证实人类、鲈鱼(Lateolabraxjaponicus)和大黄鱼(Pseudosciaenacrocea)的hepcidin成熟肽在磷酸盐缓冲液中通过4个二硫键形成了2个稳定的β-折叠和1个Loop结构,呈发卡形式[26-27]。
与人类及其他哺乳动物显著不同,鱼类hepcidin抗菌肽存在明显的多基因变体现象,真鲷(Chrysophrysmajor)、鲈鱼、黑鲷(Chrysophrysmajor)、尼罗罗非鱼(OreochromisNiloticus)等hepcidin都存在2个以上的基因变体。如黑鲷有7个不同基因变体AS-hepc1-7,在正常状态下的组织分布、细菌感染下的诱导表达模式及生物活性,在不同鱼类和不同变体(如黑鲷的AS-hepc2和AS-hepc6)都存在较显著的差异[16],这种变体现象反映出鱼类在复杂的海洋环境下可能需要多基因变体参与自身的免疫防御功能,预示抗菌肽hepcidin是海水养殖鱼类普遍存在的重要免疫防御因子,为hepcidin抗菌肽的广泛应用提供了理论依据。同时发现这与已经报道的人、鼠hepcidin基因的表达模式显著不同,肝脏不是普遍认为的唯一的hepcidin基因高效表达的器官,而肾脏是另一个主要高表达的器官[17,28]。这些新的研究结果提示,不同鱼类的hepcidin因其不同的生存环境可能采取不同的免疫机制。
鱼类抗菌肽hepcidin的抗菌活性已被广泛研究,无论是从体内提取的hepcidin成熟肽、体外人工合成的hepcidin成熟肽,还是体外重组表达的hepcidin成熟肽或前体肽都具有广谱抗菌活性。化学合成的罗非鱼hepcidin TH1-5对李斯特菌、肠球菌和金黄色葡萄球菌具有一定的抑制作用,TH2-3对海水弧菌和创伤弧菌均有一定的抗菌活性[29]。体外重组表达的牙鲆(Paralichthysolivaceus)hepcidin对被测的大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌等具有较好的抗菌活性[30]。人工合成的海水青鳉(Oryziasmelastigma)hepcidin成熟肽(OM-hep1)和原核表达前体肽(Pro-OMhep1)对革兰氏阳性菌如谷氨酸棒杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌,对革兰氏阴性菌如大肠杆菌、嗜水气单胞菌和施氏假单胞菌都具有较好的抗菌活性,对被测的弧菌无抗菌活性[31]。此外,鱼类hepcidin除了具有抗菌活性外,还具有抗病毒和肿瘤的活性。人工合成的海水青鳉hepcidin成熟肽OM-hep1和重组表达的前体肽Pro-OMhep1都可以抑制虾白斑综合征病毒的复制,还可以抑制人类肝癌细胞的生长[31];人工合成的罗非鱼hepcidin TH1-5对HepG2、HeLa、HT1080等多种肿瘤细胞的生长具有抑制作用[32]。鱼类hepcidin抗菌、抗病毒、抗肿瘤功能及其免疫调节机制等的研究将为抗菌肽hepcidin的应用奠定基础。
1.2甲壳动物抗菌肽的研究进展
早在二十世纪六七十年代就发现甲壳动物血液和其他组织中含有抗菌活性物质,但直至1996年,Schnapp等才从岸蟹(Carcinusmaenas)血淋巴细胞中分离获得甲壳动物的第一个抗菌肽[33],该抗菌肽富含脯氨酸,分子量6.5 kDa,对革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌都具有抗菌活性。迄今为止已有300多条甲壳动物抗菌肽序列被报道,甲壳动物抗菌肽主要包括:①Penaeidins是一类N端富含脯氨酸/精氨酸功能域,C端富含六个半胱氨酸形成三个二硫键功能域的阳离子抗菌肽,Penaeidins除了具有抗菌功能,还可以结合几丁质[34-36];②Crustin是一类富含半胱氨酸和C端具有WAP结构域的阳离子抗菌肽,分子量大小7.0~14.0 kDa,具有抗菌抗病毒、抑制蛋白酶活性以及参与体液免疫调节等多种功能[37-39];③ALF是一类包含两个保守的半胱氨酸以及高度疏水的N末端的阳离子抗菌肽,分子量大小约11.0 kDa,具有广谱抗菌抗病毒活性[40-43];④除上述3类抗菌肽外,甲壳动物中还发现了许多有抗菌功能的小肽,如雄性性腺高表达的抗菌肽Scygonadin[44-46]和SCY2[47]、对虾血蓝蛋白的裂解片段[48]、对虾组蛋白的裂解片段[49]、青蟹组蛋白片段Sphistin[50]、蟹类抗菌肽Arasin[51]和Hyastatin[52]等。甲壳动物抗菌肽大部分属于小分子多肽,主要来源于甲壳纲的虾、蟹等。常见的虾蟹类抗菌肽研究进展如表2所示。
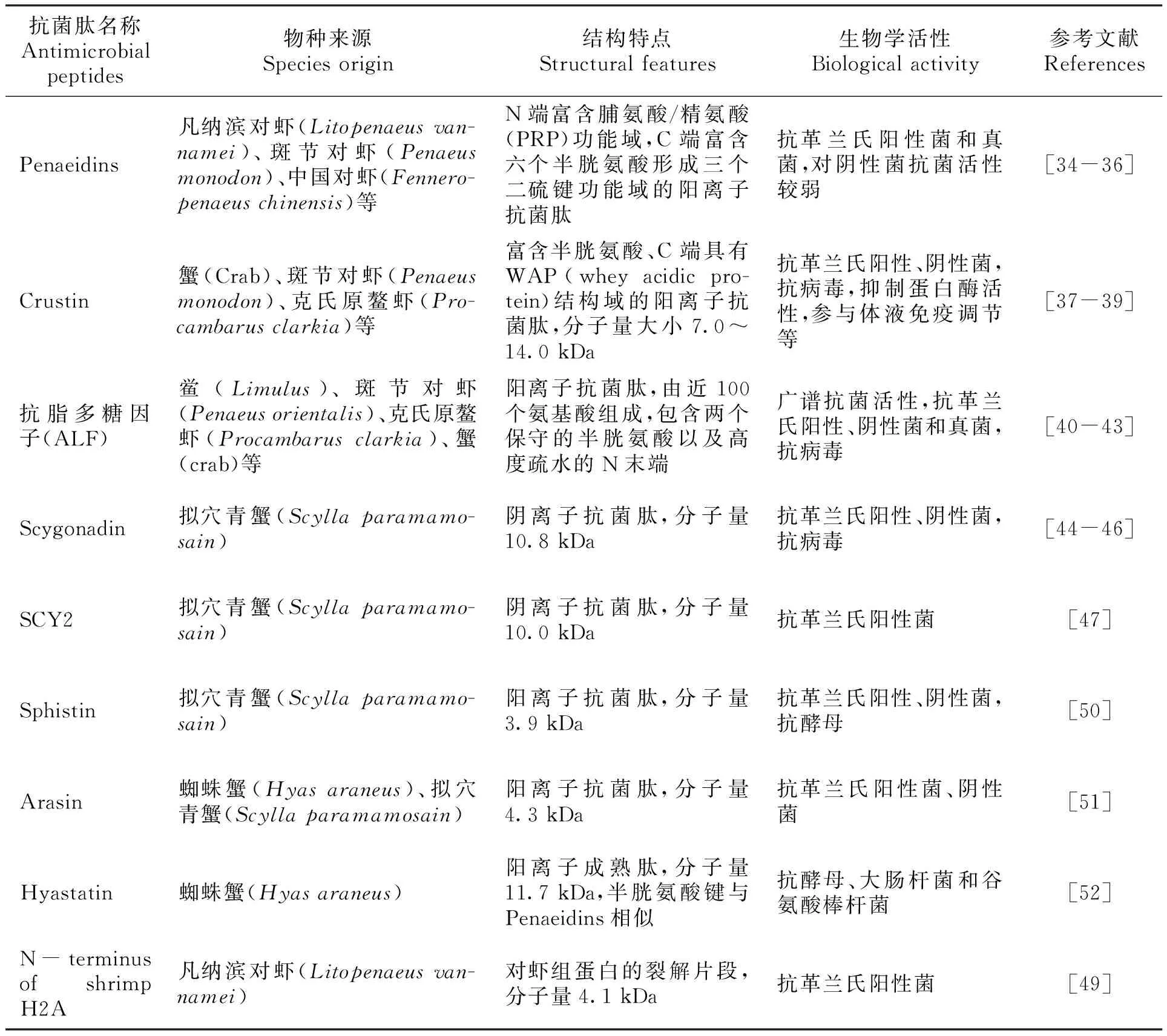
表2 常见虾蟹类抗菌肽列表
雄性性腺高表达的抗菌肽Scygonadin和SCY2的研究:青蟹是我国南方最重要的海水养殖蟹类品种,近些年来,随着青蟹养殖规模不断扩大,多种病害频繁发生引起养殖青蟹大量死亡,严重影响了我国青蟹养殖业的发展。青蟹以先天性免疫为主,抗菌肽是先天性免疫系统中重要免疫因子,对抵抗病原微生物感染具有重要作用。迄今,大多数抗菌肽来源于血液、皮肤和黏液,而从动物生殖系统中分离、鉴定甚少。厦门大学2006年首次报道了在锯缘青蟹[后经鉴定我国的锯缘青蟹(Scyllaserrata)应为拟穴青蟹(Scyllaparamamosain)]的精浆中分离获得了一个新型抗菌肽,命名为Scygonadin。Scygonadin基因主要在成熟的雄性锯缘青蟹的射精管中高效表达,是迄今为止在甲壳动物中发现的一种与生殖免疫相关的阴离子抗菌肽,具有抗菌、抗病毒活性,Scygonadin的发现丰富了甲壳动物抗菌肽理论[44-46]。SCY2是课题组近些年来在青蟹中发现的又一种新型阴离子抗菌肽,与Scygonadin基因的序列相似性为65%,分子质量约为10.0 kDa,等电点为4.84,是一种阴离子抗菌肽。SCY2基因主要在雄性青蟹射精管中高表达,其它组织以及雌性青蟹体内的多器官和组织只有微弱表达;并发现该抗菌肽基因在胚胎发育Ⅱ期表达量相对较高,在其它几个时期较低。进一步研究发现LPS、细菌及真菌感染等不能诱导SCY2表达,但在交配诱导条件下青蟹抗菌肽SCY2有显著的诱导表达变化,结合SCY2随青蟹发育的季节性表达规律,发现SCY2的诱导表达模式与青蟹的性成熟规律一致,推测激素水平变化与SCY2的表达相关;进一步研究了激素诱导下青蟹抗菌肽SCY2的表达模式,阐明SCY2的表达模式是交配诱导表达,说明其表达特性与生殖免疫功能相关。体外抗菌活性试验表明其主要抗革兰氏阳性菌,而体内的抗菌活性试验发现,海洋动物致病菌副溶血弧菌与SCY2共孵后再注射拟穴青蟹,青蟹的存活率在16 h后仍有23.0%,而对照组青蟹的存活率仅6.7%,说明SCY2蛋白在青蟹抵御病原微生物过程中可发挥重要的免疫作用[47]。抗菌肽Scygonadin和SCY2的研究将为维护青蟹亲体和胚胎健康、解决我国青蟹人工育苗中的关键科学问题等提供科学依据。
2 应用前景
抗菌肽具有极大的潜在应用价值,已成为医药、食品、畜牧和水产养殖业等领域的研究热点,随着对抗菌肽的开发利用研究,抗菌肽最终将会实现产业化推广应用。在医药领域,欧美等经济和技术较发达的国家走在前列,已经有多家公司和机构致力于抗菌肽类新药物的研究和开发。抗菌肽可与传统的抗生素联合使用,也可作为单独的抗菌剂使用,其临床应用潜力很大。恩夫韦地(Enfuvirtide)已于2003年批准上市,用于成人和6岁以上儿童的抗艾滋病治疗药物。目前已有十余种通过美国食品与药品管理局审批上市的抗菌肽类药物[53],多数抗菌肽药物限于局部的抗感染治疗。国外主要是针对抗菌肽的医用医药价值开展研究,而针对畜牧及水产业等的应用报道较少,尤其是源于海洋生物的抗菌肽基因工程产品迄今未有临床试验与应用的报道。
抗菌肽不仅可以作为药物治疗细菌感染和癌症等疾病,同时也被作为饲料添加剂广泛应用于畜禽水产养殖中,为促进畜禽和水产养殖业的发展做出了贡献。目前国内关于天蚕素类的抗菌肽作为饲料添加剂应用于畜禽水产养殖业的报道较多[54-55],而利用来自海洋动物抗菌肽作为饲料添加剂及其在水产养殖业中的应用报道相对较少。厦门大学海洋动物抗菌肽研发团队,自2002年以来,针对我国海水养殖产业链中存在的抗生素污染等重大生产问题,以研发可替代某些抗生素或降低抗生素用量的环保型抗菌肽饲料、抗菌肽防腐剂等为目标,在我国率先开展了海洋鱼类和蟹类新型抗菌肽的研究。其所研制的海洋动物抗菌肽基因工程产品经国家权威资质部门的检测以及通过在海水养殖场几年的中试试验,证明安全有效。2015年已获得我国首个农业部批准的大黄鱼抗菌肽生产应用的安全证书,预示着源于海洋动物的抗菌肽基因工程产品可以在我国畜牧水产养殖业乃至医药业等进行开发应用。
海洋动物抗菌肽的研发与应用,不仅具有重要的医学开发前景,也可应用于水产养殖业,保障其健康发展和水产品安全。海洋动物抗菌肽基因工程产品的开发利用预期产业化前景广阔。
[1]Leuschner C,Hansel W.Membrane disrupting lytic peptides for cancer treatments[J].Current pharmaceutical design,2004,10(19):2299-2310.
[2]Yang D,Biragyn A,Kwak L W,et al.Mammalian defensins in immunity:more than just microbicidal[J].Trends Immunol.,2002,23(6):291-296.
[3]Otte J M,Zdebik A E,Brand S,et al.Effects of the cathelicidin LL-37 on intestinal epithelial barrier integrity[J].Regul Pept.,2009,156(1):104-117.
[4]Brogden K A.Antimicrobial peptides:pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria?[J]Nat Rev Microbiol.,2005,3:238-250.
[5]Nguyen L T,Haney E F,Vogel H J.The expanding scope of antimicrobial peptide structures and their modes of action[J].Trends Biotechnol.,2011,29(9):464-472.
[6]Boman H G,Nilsson I,Rasmuson B.Inducible antibacterial defence system in Drosophila[J].Nature,1972,237(5352):232-235.
[7]Steiner H,Hultmark D,Engstrm A,et al.Sequence and specificity of two antibacterial proteins involved in insect immunity[J].Nature,1981,292(5820):246-248.
[8]Campagna S,Saint N,Molle G,et al.Structure and mechanism of action of the antimicrobial peptide piscidin[J].Biochemistry,2007,46(7):1771-1778.
[9]Umasuthan N,Mothishri M S,Thulasitha W S,et al.Molecular,genomic,and expressional delineation of a piscidin from rock bream(Oplegnathusfasciatus)with evidence for the potent antimicrobial activities of Of-Pis1 peptide[J].Fish Shellfish Immunol.,2016,48:154-168.
[10]Dezfuli B S,Pironi F,Giari L,et al.Immunocytochemical localization of piscidin in mast cells of infected seabass gill[J].Fish Shellfish Immunol.,2010,28(3):476-482.
[11]Patrzykat A,Gallant J W,Seo J K,et al.Novel antimicrobial peptides derived from flatfish genes[J].Antimicrob Agents Chemother.,2003,47(8):2464-2470.
[12]Syvitski R T,Burton I,Mattatall N R,et al.Structural characterization of the antimicrobial peptide pleurocidin from winter flounder[J].Biochemistry,2005,44(19):7282-7293.
[13]Lauth X,Shike H,Burns J C,et al.Discovery and characterization of two isoforms of moronecidin,a novel antimicrobial peptide from hybrid striped bass[J].J Biol Chem.,2002,277(7):5030-5039.
[14]Salerno G,Parrinello N,Roch P,et al.cDNA sequence and tissue expression of an antimicrobial peptide,dicentracin;a new component of the moronecidin family isolated from head kidney leukocytes of sea bass,Dicentrarchuslabrax[J].Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol.,2007,146(4):521-529.
[15]Shike H,Lauth X,Westerman M E,et al.Bass hepcidin is a novel antimicrobial peptide induced by bacterial challenge[J].Eur J Biochem.,2002,269(8):2232-2237.
[16]Yang M,Wang K J,Chen J H,et al.Genomic organization and tissue-specific expression analysis of hepcidin-like genes from black porgy(AcanthopagrusschlegeliiB)[J].Fish Shellfish Immunol.,2007,23(5):1060-1071.
[17]Wang K J,Cai J J,Cai L,et al.Cloning and expression of a hepcidin gene from a marine fish(Pseudosciaenacrocea)and the antimicrobial activity of its synthetic peptide[J].Peptides,2009,30(4):638-646.
[18]Qu H,Chen B,Peng H,et al.Molecular cloning,recombinant expression,and antimicrobial activity of EC-hepcidin3,a new four-cysteine hepcidin isoform fromEpinepheluscoioides[J].Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.,2013,77(1):103-110.
[19]Chen SL,Xu MY,Ji XS,et al.Cloning,characterization,and expression analysis of hepcidin gene from red sea bream(Chrysophrysmajor)[J].Antimicrob Agents Chemother.,2005,49(4):1608-1612.
[21]Chang C I,Zhang Y A,Zou J,et al.Two cathelicidin genes are present in both rainbow trout(Oncorhynchusmykiss)and atlantic salmon(Salmosalar)[J].Antimicrob Agents Chemother.,2006,50(1):185-195.
[22]Patrzykat A,Zhang L,Mendoza V,et al.Synergy of histone-derived peptides of coho salmon with lysozyme and flounder pleurocidin[J].Antimicrob Agents Chemother.,2001,45(5):1337-1342.
[23]Park I Y,Park C B,Kim M S,et al.Parasin I,an antimicrobial peptide derived from histone H2A in the catfish,Parasilurusasotus[J].FEBS Lett.,1998,437(3):258-262.
[24]Lemaitrei C,Orange N,Sagli P,et al.Characterization and ion channel activities of novel antibacterial proteins from the skin mucosa of carp(Cyprinuscarpio)[J].Eur J Biochem.,1996,240:143-149.
[25]Krause A,Neitz S,Magert H J,et al.LEAP-1,a novel highly disulfide-bonded human peptide,exhibits antimicrobial activity[J].FEBS Lett.,2000,480(2-3):147-150.
[26]Jordan J B,Poppe L,Haniu M,et al.Hepcidin revisited,disulfide connectivity,dynamics,and structure[J].J Biol Chem.,2009,284(36):24155-24167.
[27]Lauth X,Babon J J,Stannard J A,et al.Bass hepcidin synthesis,solution structure,antimicrobial activities and synergism,and in vivo hepatic response to bacterial infections[J].J Biol Chem.,2005,280(10):9272-9282.
[28]Yang M,Chen B,Cai J J,et al.Molecular characterization of hepcidin AS-hepc2 and AS-hepc6 in black porgy(Acanthopagrusschlegelii):expression pattern responded to bacterial challenge and in vitro antimicrobial activity[J].Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol.,2011,158(2):155-163.
[29]Huang P H,Chen J Y,Kuo C M,et al.Three different Hepcidins from tilapia,Oreochromismossambicus:Analysis of their expressions and biological functions[J].Mol Immunol.,2007,44(8):1922-1934.
[30]Srinivasulu B,Syvitski R,Seo J K,et al.Expression,purification and structural characterization of recombinant hepcidin,an antimicrobial peptide identified in Japanese flounder,Paralichthysolivaceus[J].Protein Expr Purif.,2008,61:36-44.
[31]Cai L,Cai J J,Liu H P,et al.Recombinant medaka(Oryziasmelastigma)pro-hepcidin:Multifunctional characterization[J].Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol.,2012,161,140-147.
[32]Chang W T,Pan C Y,Rajanbabu V,et al.Tilapia(Oreochromismossambicus)antimicrobial peptide,hepcidin 1-5,shows antitumor activity in cancer cells[J].Peptides,2011,32(2):342-352.
[33]Schnapp D,Kemp G D,Smith V J.Purification and characterization of a proline-rich antibacterial peptide,with sequence similarity to bactenecin-7,from the haemocytes of the shore crab,Carcinusmaenas[J].Eur J Biochem.,1996,240:532-539.
[34]Yang Y,Poncet J,Garnier J,et al.Solution structure of the recombinant penaeidin-3,a shrimp antimicrobial peptide[J].J Biol Chem.,2003,278(38):36859-36867.
[35]Cuthbertson B J,Yang Y,Bachère E,et al.Solution structure of synthetic penaeidin-4 with structural and functional comparisons with penaeidin-3[J].J Biol Chem.,2005,280(16):16009-16018.
[36]Destoumieux D,Bulet P,Strub J M,et al.Recombinant expression and range of activity of penaeidins,antimicrobial peptides from penaeid shrimp[J].Eur J Biochem.,1999,266(2):335-346.
[37]Smith V J,Fernandes J M,Kemp G D,et al.Crustins:enigmatic WAP domain-containing antibacterial proteins from crustaceans[J].Dev Comp Immunol.,2008,32(7):758-772.
[38]JiaY P,Sun Y D,Wang Z H,et al.A single whey acidic protein domain(SWD)-containing peptide from fleshy prawn with antimicrobial and proteinase inhibitory activities[J].Aquaculture,2008,284:246-259.
[39]Antony S P,Singh I S,Sudheer N S,et al.Molecular characterization of a crustin-like antimicrobial peptide in the giant tiger shrimp,Penaeusmonodon,and its expression profile in response to various immunostimulants and challenge with WSSV[J].Immunobiology,2011,216(1-2):184-194.
[40]Tanaka S,Nakamura T,Morita T,et al.Anti-LPS factor:an anticoagulant which inhibits the endotoxin-mediated activation of coagulation system[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun.,1982,105:717-723.
[41]Yang Y,Boze H,Chemardin P,et al.NMR structure of rALF-Pm3,an anti-lipopolysaccharide factor from shrimp:model of the possible lipid A-binding site[J].Biopolymers.,2009,91(3):207-220.
[42]de la Vega E,O'Leary N A,et al.Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor in Litopenaeus vannamei(LvALF):a broad spectrum antimicrobial peptide essential for shrimp immunity against bacterial and fungal infection[J].Mol Immunol.,2008,45(7):1916-1925.
[43]Liu H,Jiravanichpaisal P,Söderhäll I,et al.Antilipopolysaccharide factor interferes with white spot syndrome virus replication in vitro and in vivo in the crayfishPacifastacusleniusculus[J].J Virol.,2006,80(21):10365-10371.
[44]Wang K J,Huang W S,Yang M,et al.A male-specific expression gene,encodes a novel anionic antimicrobial peptide,scygonadin,inScyllaserrata[J].Mol.Immunol.,2007,44:1961-1968.
[45]Xu W F,Qiao K,Huang S P,et al.Quantitative gene expression and in situ localization of scygonadin potentially associated with reproductive immunity in tissues of male and female mud crabs,Scyllaparamamosain[J].Fish Shellfish Immunol.,2011,31:243-251.
[46]Peng H,Liu H P,Chen B,et al.Optimized production of scygonadin inPichiapastorisand analysis of its antimicrobial and antiviral activities[J].Protein Expres Purif.,2012,82:37-44.
[47]Qiao K,Xu W F,Chen H Y,et al.A new antimicrobial peptide SCY2 identified inScyllaParamamosainexerting a potential role of reproductive immunity[J].Fish Shellfish Immunol.,2006,51:251-262.
[48]Destoumieux-Garzón D,Saulnier D,Garnier J,et al.Crustaceanimmunity:Antifungal peptides are generated from the C terminus of shrimp hemocyanin in response to microbial challenge[J].J Biol Chem.,2001,276(50):47070-47077.
[49]Patat S A,Carnegie R B,Kingsbury C,et al.Antimicrobial activity of histones from hemocytes of the Pacific white shrimp[J].Eur J Biochem.,2004,271:4825-4833.
[50]Chen B,Fan D Q,Zhu K X,et al.Mechanism study on a new antimicrobial peptide Sphistin derived from the N-terminus of crab histone H2A identified in haemolymphs ofScyllaParamamosain[J].Fish Shellfish Immunol.,2015,47(2):833-846.
[51]Stensvag K,Haug T,Sperstad S V,et al.Arasin 1,a proline-arginine-rich antimicrobial peptide isolated from the spider crab,Hyasaraneus[J].Dev Comp Immunol.,2008,32(3):275-285.
[52]Sperstad S V,Haug T,Vasskog T,et al.Hyastatin,a glycine-rich multi-domain antimicrobial peptide isolated from the spider crab(Hyasaraneus)hemocytes[J].Mol Immunol.,2009,46(13):2604-2612.
[53]da Costa J P,Cova M,Ferreira R,et al.Antimicrobial peptides:an alternative for innovative medicines?[J].Appl Microbiol Biotechnol.,2015:1-18.
[54]黄自然,廖富蘋,黄国庆.转抗菌肽基因酵母安全评价及在饲料中应用[J].广东蚕业,2003,37(1):34-37.
[55]邓平建,房师松,杨冬燕,等.转抗菌肽CAD基因酵母饲料添加剂的安全性评价[J].卫生研究,2004,33(5):565-569.
Study and application of antimicrobial peptides from marinefish and crustacean
PENG Hui1,2,WANG Kejian1,2*
(1.State-Province Joint Engineering Laboratory of Marine Bioproducts and Technology,College of Ocean and Earth Sciences,Xiamen University,Xiamen 361102,China;2.Fujian Collaborative Innovation Center for Exploitation and Utilization of Marine Biological Resources,Xiamen 361102,China)
Antimicrobial peptides are a group of small peptides with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activities,which have been studied for several decades.Antimicrobial peptides are thought to be “natural antibiotics”.Marine antimicrobial peptides are considered to be one of the important components of innate immune defense system in fish,shrimp,crab,shellfish and other marine animals.Marine antimicrobial peptides play an important role in the defense of exogenous pathogens in the marine environment.The development and application of marine antimicrobial peptides not only has an important prospect of medical development,but also is an important safeguard to reduce antibiotic contamination and achieve the healthy breeding of marine animals.Here we make a brief introduction of the research and application prospects of antimicrobial peptides from marine fish and crustacean,and the source and classification of antimicrobial peptides,structural characteristics and biological activity will be clarified.
marine animals;antimicrobial peptides;fish;crustacean;application prospect
2016-04-21
福建省高校产学合作科技重大项目计划(2013N5010);福建省产业创新技术重大研发平台项目(2014N2004);厦门南方海洋研究中心项目(13GZP001NF06).
彭会(1980-),女,工程师,博士,研究方向:海洋生物技术.E-mail:penghui@xmu.edu.cn
王克坚(1964-),男,闽江学者特聘教授,博士,研究方向:海洋生物技术、海洋生物分子生物学与免疫毒理学.E-mail:wkjian@xmu.edu.cn
R931.77
A
1006-5601(2016)03-0254-09
彭会,王克坚.海洋鱼类和甲壳类抗菌肽的研究进展与应用前景[J].渔业研究,2016,38(3):254-262.
