长春地区孕妇牙周炎症状况相关性调查
2016-07-07张安玲林泓兵王丽萍
张安玲 林泓兵 王丽萍 贾 林
长春地区孕妇牙周炎症状况相关性调查
张安玲 林泓兵 王丽萍 贾 林
【摘要】目的 探讨影响长春地区孕妇牙周状况的相关因素,从而提出针对性的口腔卫生预防指导。方法 随机选取2014年11月~2015年5月在吉林大学第四医院一汽总医院妇产科围产检查的650名孕妇,年龄20~37岁,孕周12~36周,通过牙周检查对孕妇进行牙周炎症状况相关性的横向研究。本研究通过医院伦理委员会审核,所有孕妇在明确了解此项调查目的的情况下自愿参加。应用SPSS 17.0统计软件,对牙周检查表中的数据进行t检验。结果 受教育程度和工作状况对孕妇是否患有牙周炎症有统计学意义,P值均为0.000,有统计学意义。年龄对于孕妇是否患有牙周炎症无统计学意义,P=0.960。而对于患有牙周炎的孕妇,年龄、受教育程度和工作状况对于炎症的轻重程度有影响,P值分别是0.000,0.003和0.000,有统计学意义。结论 通过本调查可得出,有必要对孕妇进行有针对性的个性化指导。
【关键词】孕妇;牙周炎症;长春地区
Objective To explore the periodontal influential factors of pregnant women in Changchun,and then puts forward the oral healthy guidance. Methods Randomly selected 650 pregnant women,20~37 years old,12~36 pregnancy weeks,conducted correlation cross-sectional study through the questionnaire survey on the oral hygiene and periodontal status. SPSS 17.0 statistical was used to do variance analysis. The study was audited by ethics committee. Results According to periodontitis,level of education and job status were the deciding factors,with statistical significance (P=0.05),but age without statistical significance (P>0.05,P=0.960). According to the pregnant women with periodontitis,level of education,job status and age were the deciding factors,with statistical significance (P=0.000,0.003 and 0.000). Conclusion This study concluded that pregnant women in Changchun area lack of oral healthy knowledge,so it is necessary to do individualized instruction to the pregnant women.
【Key words】 Pregnant women,Periodontitis state ,Changchun
牙周炎是口腔两大类主要疾病之一,其患病率在我国更居于龋病之上。妊娠期口腔卫生状况明显下降,牙龈炎及牙周炎发病率明显上升。研究显示,孕妇严重牙周炎可导致早产、低体重儿等不良妊娠结局,其具体机制仍不清楚[1]。本研究在之前研究的基础上,对牙周炎症程度及相关性因素进行比较,从而有针对性地对孕妇进行口腔健康指导和治疗。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料
随机选取2014年11月~2015年5月在吉林大学第四医院一汽总医院妇产科就诊的650名孕妇,年龄20~37岁,孕周12~36周。本研究通过医院伦理委员会审核,所有孕妇在明确了解此项调查目的的情况下自愿参加。
1.2填写调查问卷
由专人指导孕妇进行问卷调查(详见图1),包括年龄、孕产次、文化程度、是否工作、刷牙习惯等进行选项。
1.3检查方法
牙周检查,包括探诊深度、附着丧失水平、牙齿松动度等内容。
1.4统计学分析
采用SPSS 17.0统计软件进行分析,对检查结果的计数资料进行χ2检验。

图1 孕期口腔保健调查表
2 结果
2.1孕妇牙周状况分析
受教育程度高、有工作的孕妇较受教育程度低、无工作的孕妇牙周状况好,P值均为0.000,有统计学意义。而年龄对于孕妇是否患有牙周炎症无影响,P=0.960,无统计学意义,见表1。
2.2患有牙周炎孕妇的炎症程度相关性分析
对于患有牙周炎的孕妇,年龄、受教育程度和工作状况对于炎症的轻重程度有影响,P值分别是0.000,0.003和0.000,有统计学意义,见表2。
3 讨论
牙周炎在人群中广泛存在,是一种以炎症破坏为特征、长期存在的慢性感染性疾病,可能引发局部和全身的炎性免疫反应,且与多种疾病关系密切[2-4]。有研究表明,妊娠中期合并重度牙周炎的孕妇发生早产、低体重儿的风险分别是无口腔疾病孕妇的2.45倍和3.47倍[5-6]。母体牙周感染对胎儿的生长和发育有害,部分细菌不仅可以播散至母体的子宫,而且可以播散至胎儿血液,特别是在母体和胎儿交换营养素的重要位置,导致胎儿生长受限,炎症导致子宫收缩引起早产等[7-9]。本研究得出,受教育程度和工作状况会影响孕妇的牙周状况(正常、牙龈炎、牙周炎),有统计学意义,而年龄无统计学意义。但是对于已患有牙周炎的孕妇,年龄、受教育程度和工作状况对于牙周炎的炎症程度(轻度、中度、重度)均有统计学意义。Piscoya等[10]研究认为,年龄在多因素分析时失去了它在统计学上的显著意义,可能是因为年龄相对其他危险因素而言是一个长期累积性的危险因素。但在本研究中年龄对患有牙周炎孕妇的炎症程度有影响,且不同炎症程度的患者中20~30岁的患者多于31~45岁,这有可能与激素水平有关,在今后的研究中我们将进一步验证。
参考文献
[1]Rakoto-Alson S,Tenenbaum H,Davideau JL. Periodontal diseases preterm births,and low birth weight:findings from a homogeneous cohort of women in Madagascar[J]. J Periodontol,2010,81(2):205-213.
[2]Prasanna SJ. Causal relationship between periodontitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. J Indian Soc Periodontol,2011,15(4):359-365.
[3]Ahdi M,Gerdes VE,Hoekstra JB,et al. Diabetes mellitus[J]. Ned Tijdschr Tandheelked,2012,119(2):65-71.
[4]Pizzo G,Guiglia R,Lo Russo L,et al. Dentistry and internal medicine:from the focal infection theory to the periodontal medicine concept[J]. Eur J Intern Med,2010,21(6) :496-502.
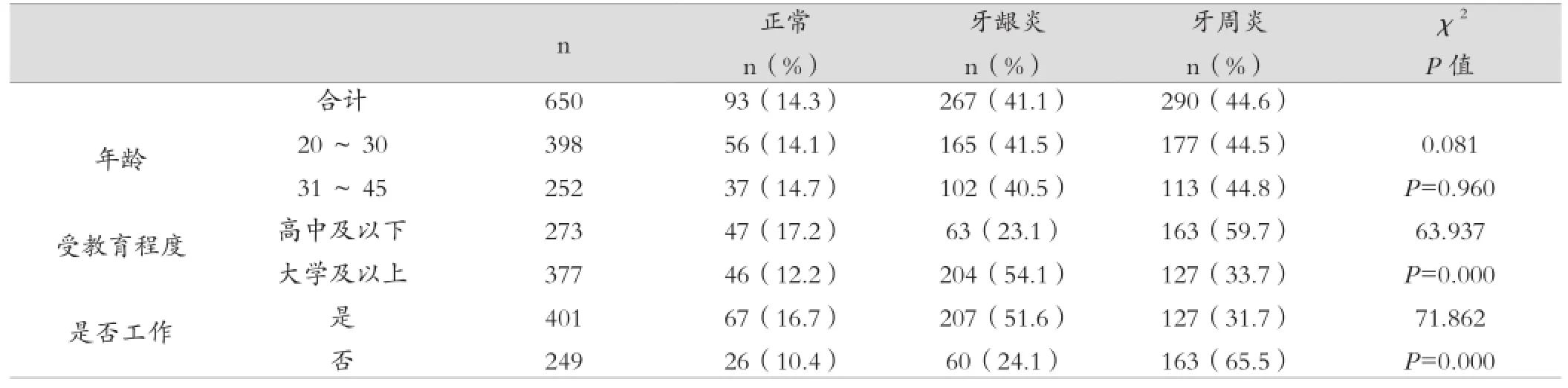
表1 牙周状况相关因素分析
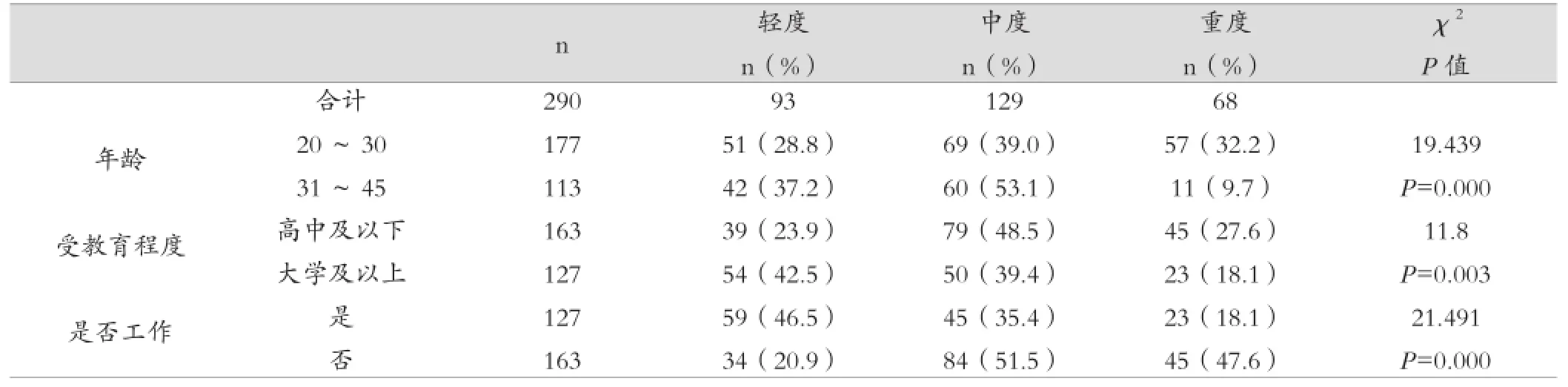
表2 牙周炎炎症程度相关因素分析
[5]Mannem S,Chava VK. The relationship between maternal periodontitis and preterm low birth weight:A case-control study[J]. Contemp Clin Dent,2011,2(2):88-93.
[6]赵云,肖梅,杨莉,等. 孕妇牙周炎与早产儿、小于胎龄儿相关性研究[J]. 中国实用口腔科杂志,2012,5(7):421-423.
[7]Chambrone L,Guglielmetti MR,Pannuti CM,et al. Evidence grade associating periodontitis to pretermbirth and/or low birth weight∶Ⅰ. A systematic review of prospective cohort studies[J]. J Clin Periodontol,2011,38(9):795-808.
[8]Chambrone L,Pannuti CM,Guglielmetti MR,et al. Evidence grade associating periodontitis with preterm birth and/or low birth weight∶Ⅱ:a systematic review of randomized trials evaluating the effects of periodontal treatment[J]. J Clin Periodontol,2011,38(10):902-914.
[9]王小红,王军青,王志军,等. HLA-G在子痫前期患者与正常妊娠胎盘中的差异表达[J].东南国防医药,2010,12(1):18-20.
[10]Piscoya MD,Ximenes RA,Silva GM,et al. Periodontitisassociated risk factors in pregnant women[J]. Clinics:Sao Paulo,2012,67(1):27-33.
Study on the Inflammatory State of Pregnant Women in Changchun
ZHANG Anling LIN Hongbing WANG Liping JIA Lin Department of stomatology,FAW General Hospital,Changchun Jilin 130011,China
【Abstract】
【中图分类号】R781
【文献标识码】A
【文章编号】1674-9316(2016)09-0011-03
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9316.2016.09.007
基金项目:中国第一汽车集团公司科技项目(KY2014-09)
作者单位:一汽总医院口腔科,吉林 长春 130011
通讯作者:张安玲,E-mail:762179814@qq.com
