硫醇衍生化的纳米金与癌胚抗原相互作用的光学分析
2016-06-15曾红娟赵然琳王德舜李彩霞刘贻尧
曾红娟,赵然琳,王德舜,李彩霞,刘贻尧
电子科技大学生命科学与技术学院,四川 成都 611731
硫醇衍生化的纳米金与癌胚抗原相互作用的光学分析
曾红娟,赵然琳,王德舜,李彩霞,刘贻尧
电子科技大学生命科学与技术学院,四川 成都 611731
纳米金已在在药物靶向传输体系、疾病检测、分子识别、生物标签等领域有着广泛的应用,但是,由于纳米金的表面效应,大量的表面原子具有巨大剩余成键能力,使得纳米金粒子较容易团聚、沉聚,影响了其稳定性。为了实现对肿瘤靶标之一-癌胚抗原的痕量检测,需要制备出对癌胚抗原检测具有良好的增色效应与荧光增敏效应的纳米材料。该工作采用纳米金的硫醇衍生法制备了一种新型的硫醇衍生化的纳米金材料,并对此新型硫醇衍生化的纳米金材料的特性用透射电子显微镜,紫外-可见吸收光谱,荧光发射光谱和红外光谱等方法进行了研究。紫外-可见吸收光谱,荧光发射光谱的实验结果表明,在新的配体乙二硫醇存在下,有更多的电子从配体的轨道跃迁到与中心离子相关的轨道上,导致荧光增强。这种新型硫醇衍生化的纳米金与癌胚抗原作用时表现出增色效应与荧光增敏效应,而纳米金与癌胚抗原作用时看不到这种增色效应与荧光增敏效应。红外方法的研究结果表明,这种材料的蛋白增色机理为当硫醇衍生化纳米金与癌胚抗原蛋白作用时,体系中蛋白的—OH表现出更多的面外弯曲振动,有利于电子从硫醇衍生化纳米金配合物向蛋白转移而导致其增色和荧光增敏效应。因而这种新的硫醇衍生化纳米金材料比纳米金将具有更好的生物检测应用价值。
纳米金; 硫醇衍生化的纳米金; 癌胚抗原; 增色效应; 荧光增敏效应
引 言
纳米金作为一种特性优良的纳米材料已在药物靶向传输体系、疾病检测、分子识别、生物标签等领域有着广泛的应用[1-3],在纳米金的各种特性中,粒子的粒度是影响其应用一个重要的因素,粒度较小的纳米金粒子已经成为研究的热点[4-5]。但是,由于纳米金的表面效应,随着纳米金粒子粒度减小,其表面原子数所占原子总数量的比例逐渐增加,大量的表面原子具有巨大剩余成键能力,使得纳米金粒子较容易团聚、沉聚,不很稳定,因而须对其进行修饰与保护,以实现纳米金更有效的利用[6]。目前不同的修饰配体一般分别通过三种方式与纳米金粒子发生作用,分别是静电作用、形成配位键以及空间位阻效应[7]。其中由于硫醇可以与纳米金粒子形成稳定的Au—S配位键(键能约170 kJ·mol-1)是一种较为稳定的结合方式,又因其在生物检测中具有更好的灵敏度而被广泛地研究,如Mirkin等利用巯基修饰的寡核苷酸组装于纳米金粒子表面,形成可与互补的靶分子杂交的纳米金探针,溶液中包含靶分子时,纳米金探针的等离子共振吸收峰由520 nm红移至600 nm,并形成网状聚集体而使纳米金溶液颜色由红变紫[8]; 又如Cossaro等将烷基硫醇自组装到纳米金表面形成的单分子膜,使得纳米金具有了更好的稳定性和有序性[9]。但是,对硫醇衍生化的纳米金与蛋白相互作用体系光学特性的研究还少有报道,而此项研究可以帮助人们更好地认识和推广硫醇衍生化的纳米金在生物检测中的应用。本研究采用紫外-可见吸收光谱,荧光发射光谱和红外光谱等方法对硫醇衍生化的纳米金进行光学特性表征。结果表明,硫醇衍生化的纳米金不仅具有明显的光学增敏现象,而且硫醇衍生化的纳米金与蛋白作用后,使得蛋白体系中的—OH表现出更多的面外弯曲振动而出现新的红外吸收峰。
1 实验部分
1.1 仪器
样品的紫外-可见光吸收谱图由U-2910型(HITACHI ,High-Technologies Corporation)紫外-可见光分光光度仪测得,荧光发射谱图由F-4600型(HITACHI,High-Technologies Corporation)荧光分光光度仪测得,红外透射谱图由NEXUS 670型(Thermo Electron Corporation)傅里叶变换红外光谱仪测得。
纳米金的制备,取质量分数为0.01%的氯金酸水溶液100 mL,加热至沸腾搅动下准确加入质量分数为1%的柠檬酸三钠2 mL,继续煮沸15 min,溶液颜色由橙黄色变为酒红色,而后,冷却至室温并以蒸馏水恢复到原来的体积,置于4 ℃冰箱保存备用。
硫醇衍生化的纳米金制备,取10 mL纳米金溶液,向其中加入10 mL浓度为1 mmol·L-1的乙二硫醇的四氢呋喃溶液,搅拌溶液过夜。将纳米金-乙二硫醇样品进行离心,去除上清液,重复离心以彻底去除上清液中游离的配体分子,将离心管中可稳定分散的纳米金-乙二硫醇沉淀分散于20 mL的双蒸水中。
采用透射电子显微镜对纳米金以及硫醇衍生化的纳米金的超微结构进行分析; 采用U-2910型紫外-可见光分光光度仪,F-4600型荧光分光光度仪和NEXUS 670型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪对纳米金,硫醇衍生化的纳米金,以及它们与癌胚抗原蛋白相互作用等进行光谱特性检测和分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 纳米金和硫醇衍生化纳米金的Transmission electron microscope (TEM)表征
利用TEM技术分别对制备的纳米金和硫醇衍生化纳米金粒子进行表征,结果如图1所示。图1(a)为纳米金,图1(b)为硫醇衍生化纳米金。从图中可以明显看出,硫醇衍生化纳米金粒子的形态更加规则而且分散性也更好。
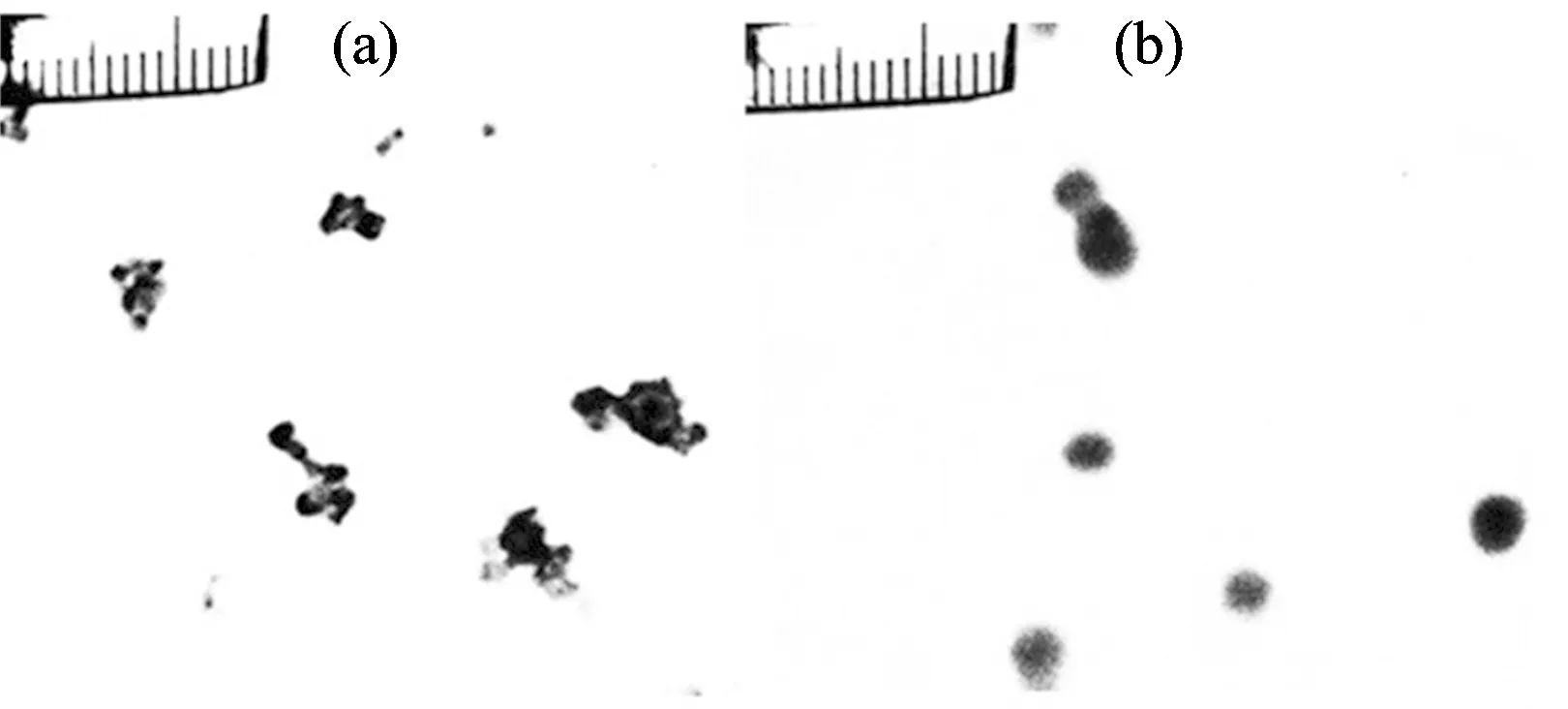
Fig.1 TEM images of nanogold particles (a) and mercaptan derivatives nanogold particles (b)
2.2 纳米金和硫醇衍生化纳米金的紫外-可见特性
金溶胶在硫醇衍生化过程中,颜色由酒红色变为蓝色并出现沉淀。紫外可见吸收光谱检测结果如图2所示,从图中可以明显看出纳米金的最大吸收峰位置在520 nm,硫醇衍生化纳米金的最大吸收峰位置在750 nm,说明硫醇衍生化纳米金具有比金溶胶粒径更大。将硫醇衍生化纳米金与纳米金溶胶以摩尔比为1∶1配制混合溶胶,其紫外吸收的强度明显比纳米金溶胶强。说明硫醇衍生化对纳米金有增色效应。
2.3 纳米金和硫醇衍生化纳米金的荧光特性
纳米金和硫醇衍生化纳米金的荧光光谱如图3所示,从图中可以看出纳米金在520 nm波长的光激发下,在787 nm产生一个很强的荧光发射峰,与纳米金相比其强度增加5倍,这种荧光增强表明硫醇衍生化纳米金,其中心Au粒子在新的配体乙二硫醇存在下存在更多的电子由配体的轨道跃迁到与中心金粒子相关的轨道上,导致荧光增加。因此,硫醇衍生化纳米金会产生更强的荧光,更进一步说明硫醇衍生化对纳米金有荧光增敏作用。
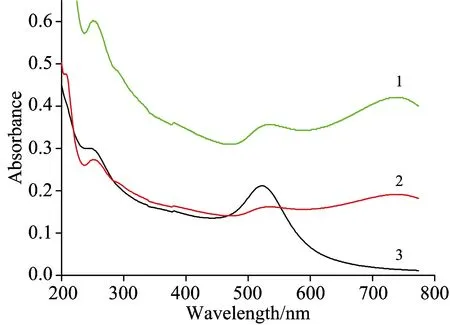
Fig.2 Ultraviolet absorption spectra of samples
1: nanogold particles; 2: mercaptan derivatives nanogold particles; 3: the mixed solution of nanogold particles and mercaptan derivatives nanogold particles, the concentration ratio is 1∶1
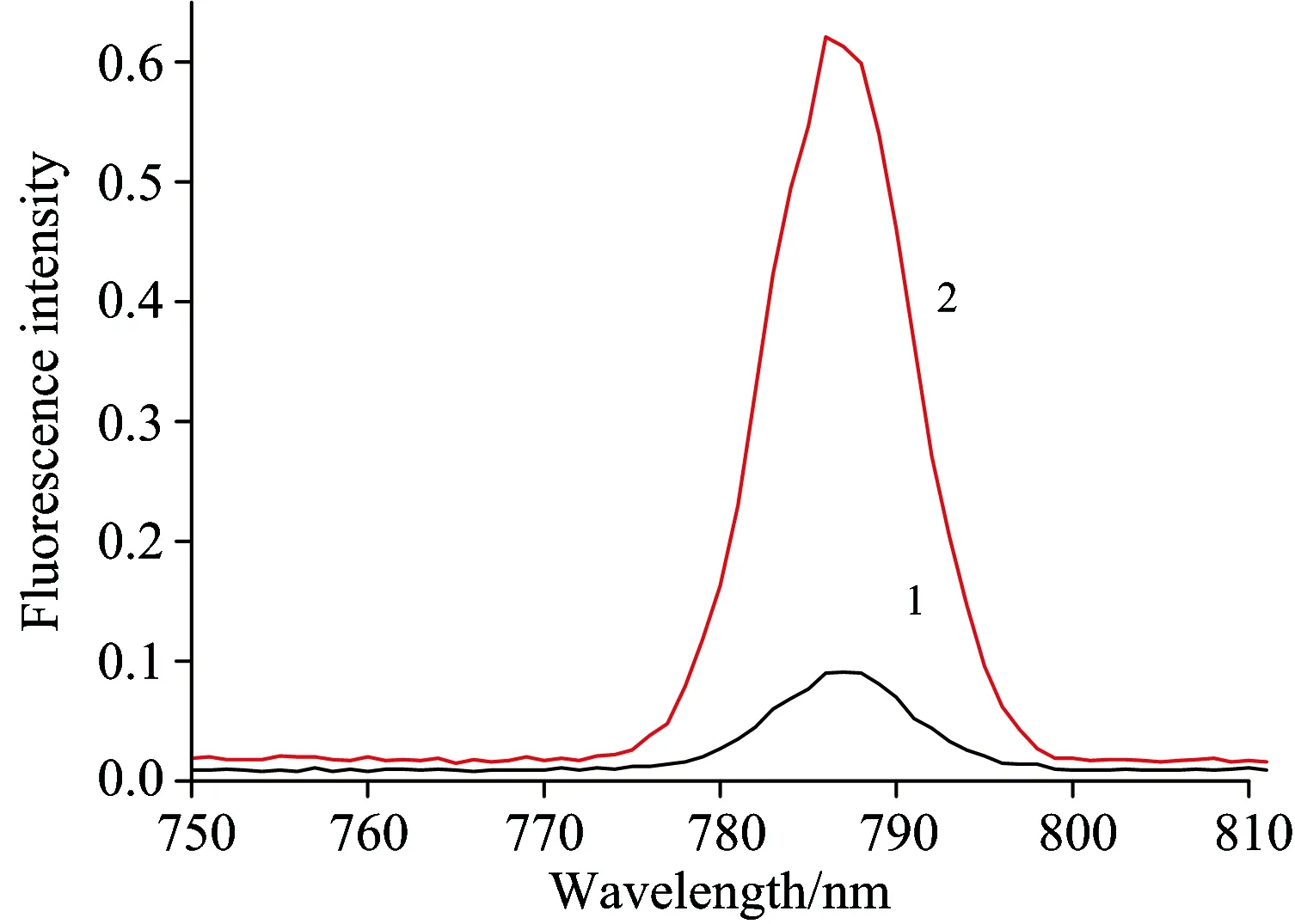
Fig.3 Fluorescence emission spectra of nanogold particles (1) and mercaptan derivatives nanogold particles (2)
2.4 硫醇衍生化纳米金与癌胚抗原蛋白作用的紫外-可见光分析
为了探讨硫醇衍生化纳米金是否会破坏肿瘤标志物蛋白结构,实验中以存在于大肠癌、乳腺癌和肺癌中的肿瘤标志物癌胚抗原(CEA)为模型,采用紫外-可见光分析法对硫醇衍生化纳米金与硫醇衍生化纳米金和癌胚抗原蛋白相互作用进行检测。结果如图4所示,硫醇衍生化纳米金并没有对蛋白的结构造成产生的影响,加入CEA溶液中时,在250~300 nm之间的吸收峰没有变化,说明硫醇衍生化纳米金不会破坏蛋白结构; 在200~250 nm之间出现很强的吸收峰,说明硫醇衍生化纳米金对CEA存在很好的增色效应,可以提高对CEA检测的灵敏度。
2.5 硫醇衍生化纳米金与CEA作用的荧光分析
为了进一步证明所制备的硫醇衍生化纳米金是否对CEA存在增色效应,采用荧光方法对它们之间的相互作用进行进一步的实验,结果如图5所示。发现在530 nm激发光作用下,加入CEA蛋白后的体系在783 nm的荧光发射峰明显增强,说明硫醇衍生化纳米金对靶标蛋白确实存在明显的荧光增敏作用。
2.6 CEA及硫醇衍生化纳米金与CEA作用的红外分析

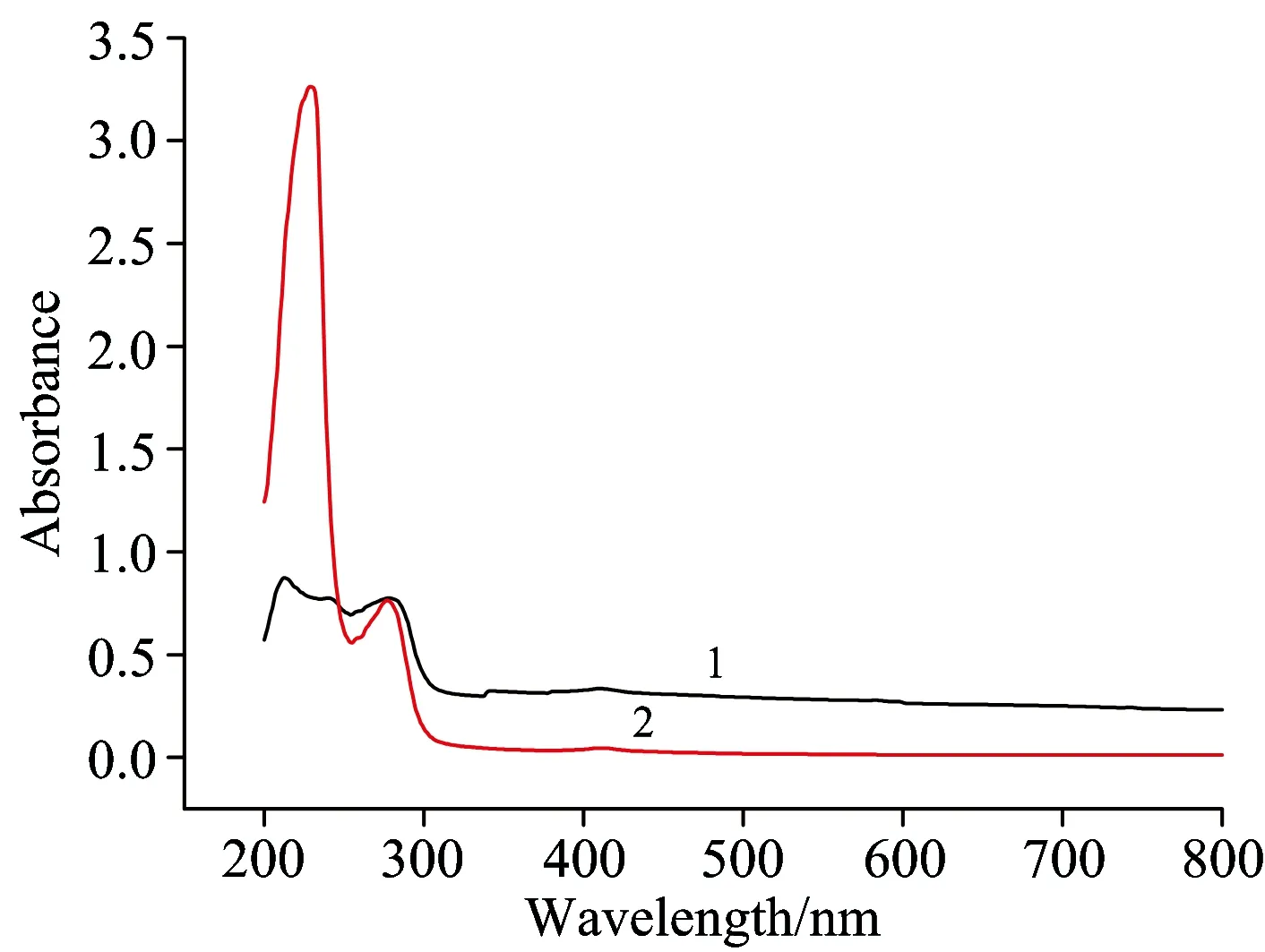
Fig.4 Ultraviolet absorption spectra of the CEA solution (1), the mixed solution of mercaptan derivatives nanogold particles and CEA (2)
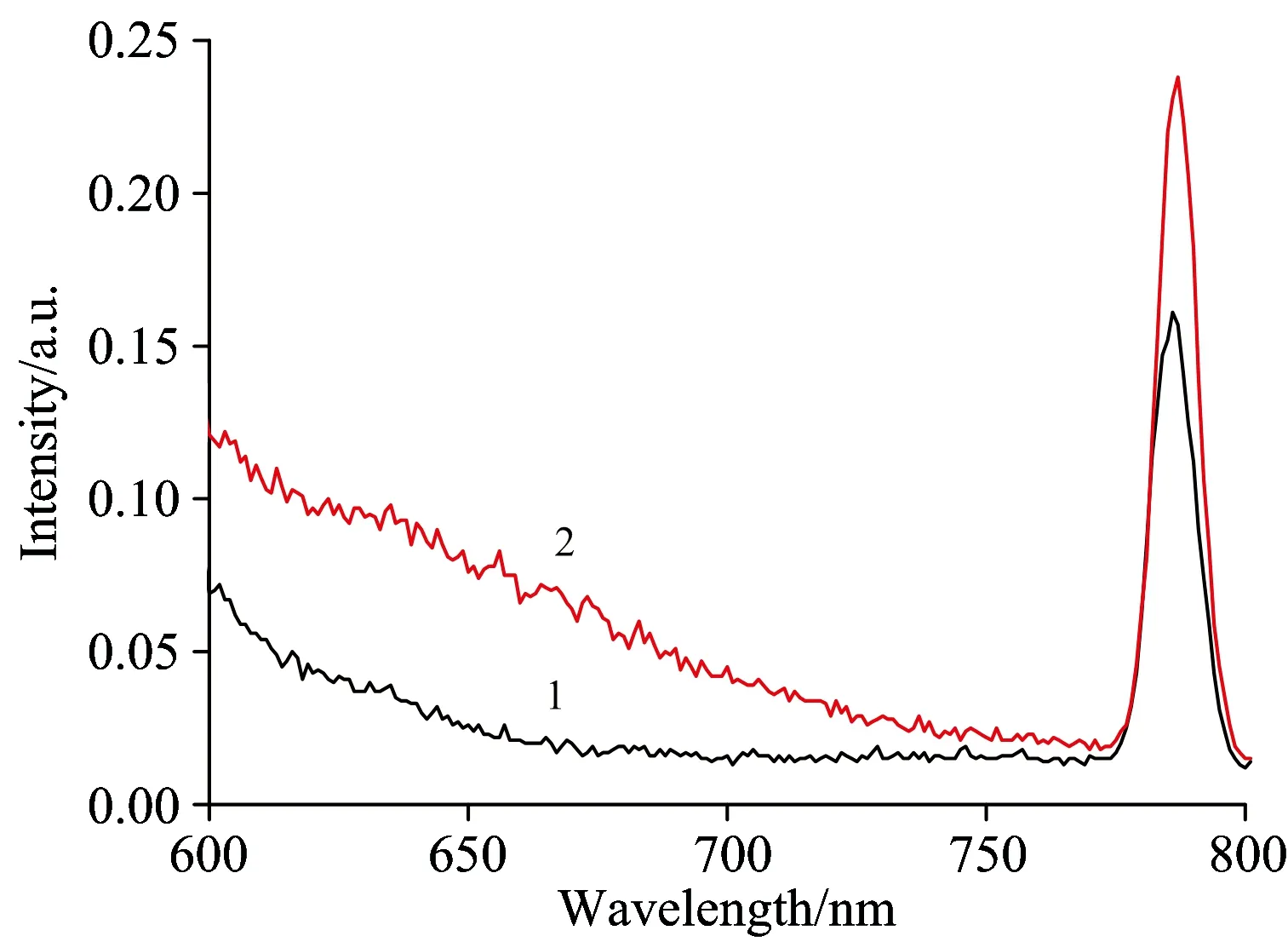
Fig.5 Fluorescence emission spectra of mercaptan derivatives nanogold particles (1), the mixed solution of mercaptan derivatives nanogold particles and CEA (2)
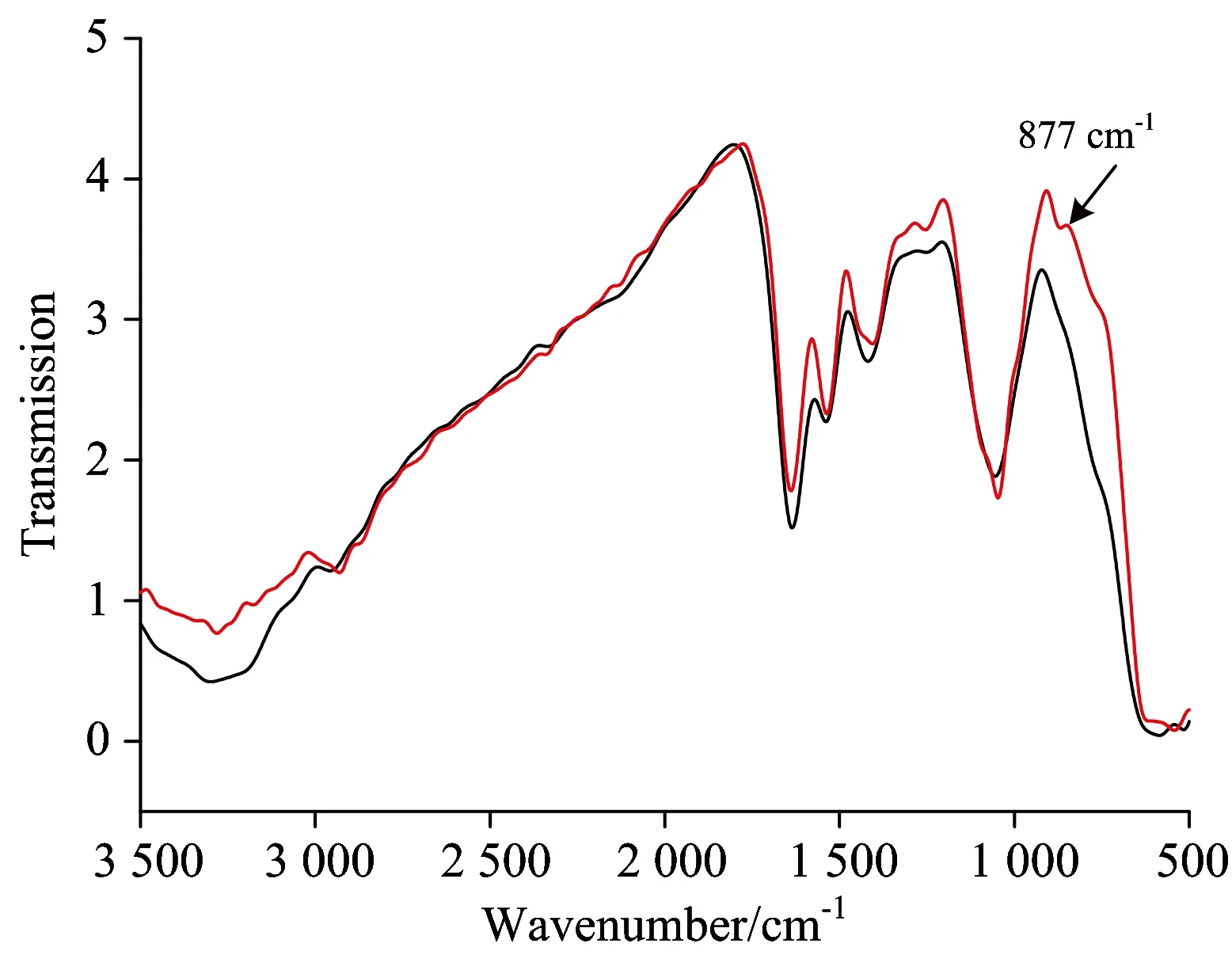
Fig.6 FTIR of the CEA solution (1), the mixed solution of mercaptan derivatives nanogold particles and CEA (2)
3 结 论
硫醇衍生化纳米金由于其配合物中存在新的硫醇配体,减少了Au离子的禁带宽度,使得更多的电子可以从价带进入导带而具有更强的吸收强度。而且发现这种硫醇衍生化纳米金由于其具有的荧光增敏而更适合于蛋白的检测,因而这种新的硫醇衍生化纳米金材料比纳米金将具有更好的生物检测应用价值。
[1] Dubertret B, Calame M, Libchaber A J. Nature Biotechnology, 2001, 19(2): 365.
[2] Elena P V, Ekaterina A L, Andrey M B, et al. Journal of Biotechnology, 2014, 182: 37.
[3] Bindhu M R, Umadevi M. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2014, 128: 37.
[4] Bagheri Z, Massudi R, Ghanavi J. Optics & Laser Technology, 2014, 58: 135.
[5] Naveen K, Raman S, Harish K. Analytical Biochemistry, 2014, 456: 43.
[6] Alessandro F, Cristina G, Pier R S, et al. Photoacoustics, 2014, 2(1): 47.
[7] YANG Qiang, WANG Li, XIANG Wei-dong, et al(杨 强,王 立,向卫东,等). Progress in Chemistry(化学进展), 2006, 18(2): 290.
[8] Mirkin C A, Letsinger R L, Mucic R C, et al. Nature, 1996, 382: 607.
[9] Cossaro A, Mazzarello R, Rousseau R, et al. Science, 2008, 321(5891): 943.
Optical Analysis of the Interaction of Mercaptan Derivatives of Nanogold Particles with Carcinoembryonic Antigen
ZENG Hong-juan, ZHAO Ran-lin, WANG De-shun, LI Cai-xia, LIU Yi-yao
School of Life Science and Technology, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 611731, China
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have been the subject of intense research for use in biomedicine over the past couple of decades. AuNPs, also referred to as colloidal gold, possess some astounding optical and physical properties that have earned them a prime spot among the new promising tools for medical applications. Today, AuNPs are offered to provide the clinical laboratory with more sensitive, faster, and simpler assays, which are also cost-effective. AuNPs can be used to develop point-of-care tests and novel testing strategies such as in drug targeting, disease detection, molecular recognition, and biological labels. The typical structure of AuNPs is spherical nano-sized gold particles, but they can also be composed of a thin gold shell surrounding a dielectric core, such as silica (gold nanoshells). their size range from 0.8 to 250 nm and are characterized by high absorption coefficients. AuNPs have some unique optical properties, such as enhanced absorption and scattering, where the absorption cross-section of AuNPs is 4~5 orders of magnitude greater than that of rhodamine 6G. When AuNPs aggregate, interaction of locally adjacent AuNPs (plasmon-plasmon interaction) shifts their color to blue. Thus, the binding of AuNP-labeled entities to their respective target would lead to aggregation of the nanoparticles and a detectable shift in the optical signal. The strong absorption of AuNPs can also be used in colorimetric detection of analytes by measuring changes in the refractive index of the AuNP’s environment caused by adsorption of the target analytes. However, a large number of surface atoms of nanoparticles have huge surplus bonding ability, because of surface effect of gold nanoparticles, result in reuniting and sinking among the nanoparticles which make them unstable. In order to detect traces of carcinoembryonic antigen, one of the tumor targets, a new kind of gold nanoparticle with hyperchormic effect and fluorescence sensitization effect material needs to be prepared. In this paper, novel mercaptan derivative of nanogold particles are prepared and studied using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), ultraviolet-visible absorption spectra (UV-Vis), fluorescence emission (FE) spectrum and infrared spectrum (IR) methods. The UV-Vis and FE results show the presence of new ligands mercaptan, more electrons from the orbit of ligand which can excite to the central ion related orbits and increase fluorescence of gold. Fluorescence sensitization effect was observed when mercaptan derivatives of nanogold interacted with carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and no fluorescence sensitization effect was found when nanogold interacted with carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). The study of CEA hyperchromic mechanism of mercaptan derivatives nanogold and the CEA by the method of infrared spectrum, shows that the randomized OH bonds in the Au-protein interaction, showed more on the outside of the plane of bending vibration after the interaction with the mercaptan derivative nanogold, making the energy transfer from mercaptan derivatives nanogold to protein easy; leading to its fluorescence sensitization effect.
Nanogold; Mercaptan derivatives nanogold particles; Carcinoembryonic antigen; Hyperchromic effect; Fluorescence sensitization effect
Sep. 9, 2014; accepted Jan. 25, 2015)
2014-09-09,
2015-01-25
国家自然科学基金项目(61071026)资助
曾红娟,女, 1968年生, 电子科技大学生命科学与技术学院副教授 e-mail: zenghj@uestc.edu.cn
O657.3
A
10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2016)02-0478-04
