血浆N末端B型利钠肽前体水平对非ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者经皮冠状动脉介入术造影剂肾病的早期预测价值研究
2016-06-07王海莹涂晓文
王海莹,涂晓文
·论著·
血浆N末端B型利钠肽前体水平对非ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者经皮冠状动脉介入术造影剂肾病的早期预测价值研究
王海莹,涂晓文
100088北京市,辽宁医学院中国人民解放军第二炮兵总医院研究生培养基地(王海莹);中国人民解放军第二炮兵总医院肾内科(涂晓文)
【摘要】目的探讨术前血浆N末端B型利钠肽前体(NT-proBNP)水平与非ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者经皮冠状动脉介入术(PCI)造影剂肾病(CIN)发生的关系。方法选取2014年1月—2015年7月中国人民解放军第二炮兵总医院行PCI的非ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者244例,根据PCI后是否发生CIN分为CIN组30例和非CIN组214例。记录患者的基本资料,检测实验室检查指标,采用心脏彩超检测左心室射血分数,评估肾小球滤过率(eGFR),记录患者既往史及术前用药情况。采用多因素Logistic回归分析CIN的影响因素,采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评价血浆NT-proBNP水平预测CIN的价值。结果CIN组与非CIN组患者性别、体质指数、收缩压(SBP)、舒张压(DBP)、空腹血糖、血钾、血钙、血磷、血红蛋白、三酰甘油水平、高脂血症、糖尿病、心功能不全检出率、血管紧张素Ⅱ受体阻滞剂(ARB)、血管紧张素转化酶抑制剂(ACEI)、利尿剂、降糖药物、胰岛素、阿司匹林、β-受体阻滞剂使用率、造影剂剂量>200 ml者所占比例、冠状动脉病变>2支或左主干病变者所占比例比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);CIN组与非CIN组患者年龄、糖化血红蛋白、NT-proBNP、超敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)、血尿酸、总胆固醇水平、左心室射血分数、eGFR、高血压检出率、慢性肾脏病检出率、他汀类药物使用率比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。多因素Logistic 回归分析结果显示,年龄、糖化血红蛋白、NT-proBNP、hs-CRP、血尿酸水平、左心室射血分数、eGFR、高血压、慢性肾脏病、使用他汀类药物与CIN有回归关系(P<0.05)。血浆NT-proBNP 水平预测CIN的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.862,95%CI(0.789,0.935),NT-proBNP=770 ng/L时,灵敏度为67.7%,特异度为85.9%。结论CIN的发生与年龄、糖化血红蛋白、hs-CRP、血尿酸水平、左心室射血分数、eGFR、高血压、慢性肾脏病、使用他汀类药物等相关,术前血浆NT-proBNP水平是CIN发生的独立危险因素,可用于非ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者PCI CIN的预测。
【关键词】肾病;造影剂;利钠肽,脑;危险因素;灵敏度;特异度
王海莹,涂晓文 .血浆N末端B型利钠肽前体水平对非ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者经皮冠状动脉介入术造影剂肾病的早期预测价值研究 [J].中国全科医学,2016,19(15):1768-1773.[www.chinagp.net]
Wang HY,Tu XW.Predictive value of NT-proBNP for contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention[J].Chinese General Practice,2016,19(15):1768-1773.
造影剂肾病(CIN)是指由碘造影剂引起的急性肾功能障碍,是医源性肾衰竭的第三大原因[1]。CIN在普通人群中的发病率为0.6%~2.3%,而在急性心肌梗死(AMI)患者中发病率高达20%,并可能延长住院时间、增加住院费用,且与死亡等远期预后相关[2-3]。目前CIN尚无确切有效的治疗方法,因此CIN重在预防,经皮冠状动脉介入术(PCI)前对危险因素进行评估至关重要。以往研究表明,血浆B型利钠肽(BNP)与心脏手术后发生急性肾损伤(AKI)有关[4]。N末端B型利钠肽前体(NT-proBNP)能够预测AMI患者近期心房颤动发生率[5],NT-proBNP与BNP线性相关,且有较高的临床预测价值[6]。目前对NT-proBNP与CIN的相关性研究甚少,本研究旨在探讨血浆NT-proBNP水平对非ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者PCI CIN的预测价值。
1资料与方法
1.1一般资料选取2014年1月—2015年7月中国人民解放军第二炮兵总医院行PCI的非ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者244例为研究对象,其中男162例,女82例;年龄40~83岁,平均年龄(65±12)岁;体质指数16.4~31.2 kg/m2,平均体质指数(24.8±2.3)kg/m2;合并高血压147例。非ST段抬高型心肌梗死诊断标准:采用2010年中华医学会心血管病学分会制定的标准,同时具备以下3项:(1)缺血性胸痛的临床表现和病史;(2)心电图心肌缺血动态表现;(3)血清心肌损伤标志物水平的动态变化,肌钙蛋白≥0.4 μg/L,血清心肌酶谱升高超过参考值上限2倍以上并呈动态变化[7]。排除标准:(1)对造影剂过敏者;(2)PCI前血肌酐>300 μmol/L,或长期血液透析患者,或肾移植患者;(3)近1个月内有急慢性感染、手术、创伤、自身免疫性疾病、血液系统疾病者;(4)最近1周内接受过其他造影剂检查者;(5)恶性肿瘤患者;(6)术前48 h内使用氨基糖苷类抗生素或其他明显肾毒性药物者。本研究通过中国人民解放军第二炮兵总医院医学伦理委员会批准,患者均签署知情同意书。
1.2分组CIN诊断标准:排除其他因素引起的AKI,PCI后 48~72 h 内血肌酐水平较PCI前升高≥25%以及绝对升高值≥0.5 mg/dl(44 μmol/L)[8]。根据PCI后是否发生CIN将患者分为CIN组30例和非CIN组214例。
1.3PCI按Seldinger′s法穿刺右侧桡动脉,置入6F桡动脉鞘,选用5F TIG多功能导管,按Judkin′s法行冠状动脉造影及介入治疗。造影剂均使用低渗非离子型造影剂碘普罗胺注射液(北京费森尤医药有限公司生产,国药准字H20103246),造影剂限制量(Vmax)=5 ml×体质量(kg)/血肌酐(mg/dl),Vmax不得超过300 ml。所有患者术后进行水化处理,术后常规给予羟乙基淀粉(万汶,拜耳医药保健有限公司生产,国药准字J20130157)500 ml进行水化。
1.4观察指标记录患者入院时基本资料,包括性别、年龄、体质指数,测量血压,检测空腹血糖、血钾、血钙、血磷、血红蛋白、糖化血红蛋白、NT-proBNP、超敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)、血尿酸、总胆固醇、三酰甘油水平,采用心脏彩超检测左心室射血分数,基础估算的肾小球滤过率(eGFR)通过简化的MDRD方程{eGFR〔ml·min-1·(1.73 m2)-1〕=186×(血肌酐)-1.154×(年龄)-0.203×(0.742女性)}计算。记录患者既往史及术前用药情况,包括高血压、高脂血症、糖尿病、慢性肾脏病、心功能不全等既往史及血管紧张素Ⅱ受体阻滞剂(ARB)、血管紧张素转化酶抑制剂(ACEI)、利尿剂、降糖药物、胰岛素、他汀类药物、阿司匹林、β-受体阻滞剂使用情况,造影剂剂量>200 ml、冠状动脉病变>2支或左主干病变发生情况。
2结果
2.1CIN组与非CIN组患者基本资料及实验室检查指标比较CIN组与非CIN组患者性别、体质指数、收缩压(SBP)、舒张压(DBP)、空腹血糖、血钾、血钙、血磷、血红蛋白、三酰甘油水平比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);CIN组与非CIN组患者年龄、糖化血红蛋白、NT-proBNP、hs-CRP、血尿酸、总胆固醇水平、左心室射血分数、eGFR比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05,见表1)。
2.2CIN组与非CIN组患者既往史及术前用药情况比较CIN组与非CIN组患者高脂血症、糖尿病、心功能不全检出率、ARB、ACEI、利尿剂、降糖药物、胰岛素、阿司匹林、β-受体阻滞剂使用率、造影剂剂量>200ml者所占比例、冠状动脉病变>2支或左主干病变者所占比例比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);CIN组与非CIN组患者高血压检出率、慢性肾脏病检出率、他汀类药物使用率比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05,见表2)。

表1 CIN组与非CIN组患者基本资料及实验室检查指标比较
注:CIN=造影剂肾病,SBP=收缩压,DBP=舒张压,NT-proBNP=N末端B型利钠肽前体,hs-CRP=超敏C反应蛋白,eGFR=肾小球滤过率;a为χ2值,b为U值,其他检验统计量值为t值
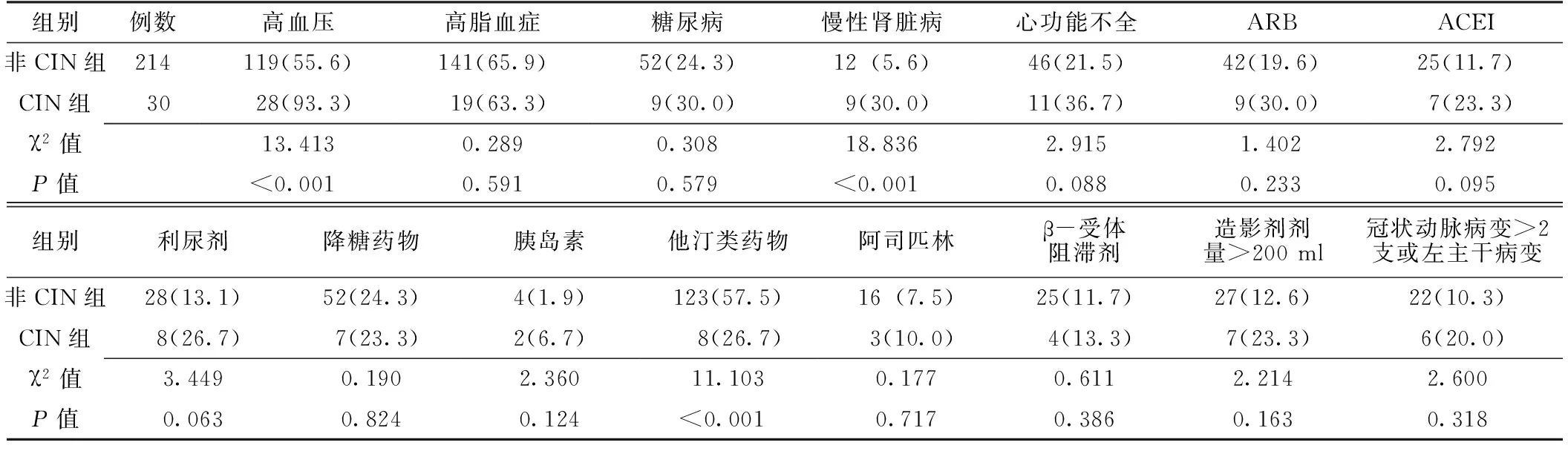
表2 CIN组与非CIN组患者既往史及术前用药情况比较〔n(%)〕
注:ARB=血管紧张素Ⅱ受体阻滞剂,ACEI=血管紧张素转化酶抑制剂
2.3CIN影响因素的多因素Logistic 回归分析以是否发生CIN为因变量,以年龄、糖化血红蛋白、NT-proBNP、hs-CRP、血尿酸、总胆固醇、左心室射血分数、eGFR、高血压、慢性肾脏病、他汀类药物为自变量(赋值见表3),纳入多因素Logistic 回归模型,结果显示,年龄、糖化血红蛋白、NT-proBNP、hs-CRP、血尿酸水平、左心室射血分数、eGFR、高血压、慢性肾脏病、使用他汀类药物与CIN有回归关系(P<0.05,见表4)。
表3CIN影响因素的多因素Logistic 回归分析赋值
Table 3Assignment of multivariate Logistic regression analysis of influencing factors for CIN
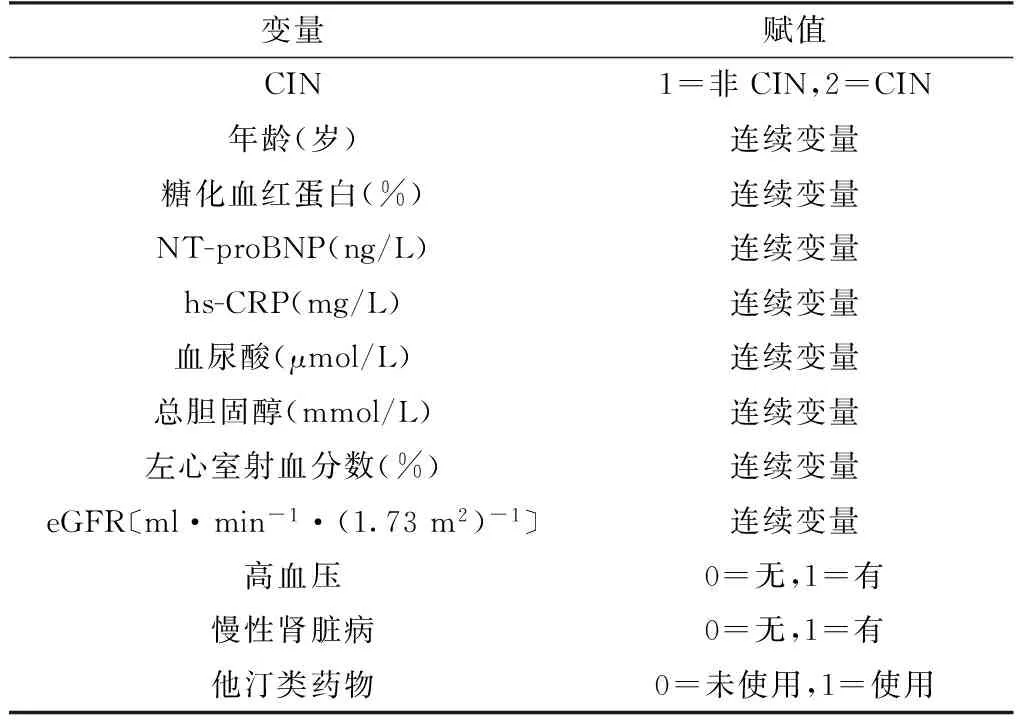
变量赋值CIN1=非CIN,2=CIN年龄(岁)连续变量糖化血红蛋白(%)连续变量NT-proBNP(ng/L)连续变量hs-CRP(mg/L)连续变量血尿酸(μmol/L)连续变量总胆固醇(mmol/L)连续变量左心室射血分数(%)连续变量eGFR〔ml·min-1·(1.73m2)-1〕连续变量高血压0=无,1=有慢性肾脏病0=无,1=有他汀类药物0=未使用,1=使用
表4CIN影响因素的多因素Logistic 回归分析
Table 4Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of influencing factors for CIN
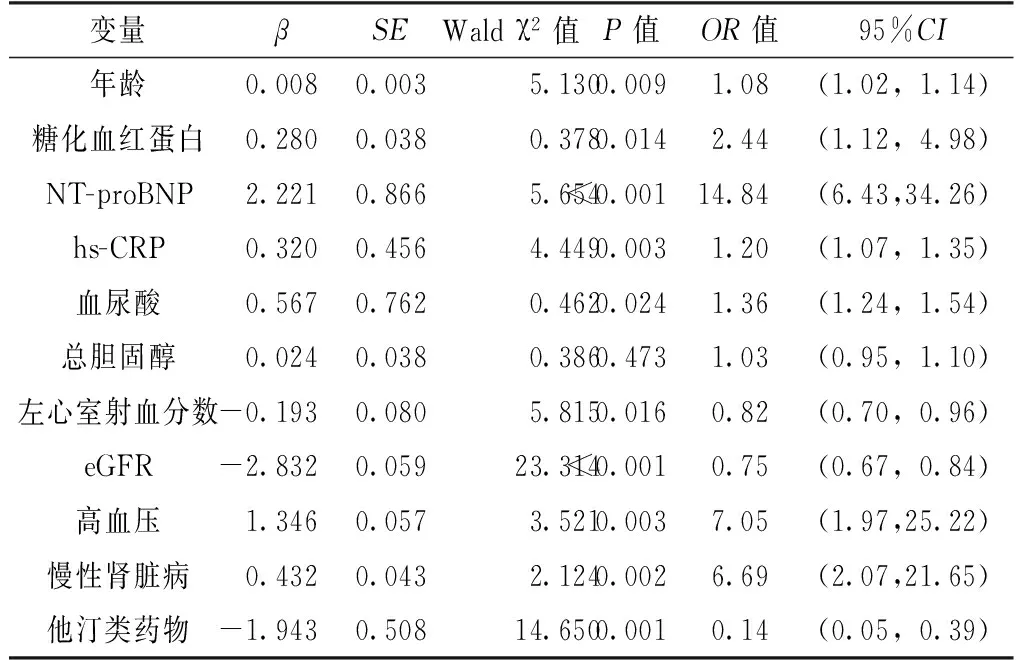
变量βSEWaldχ2值P值OR值95%CI年龄0.0080.0035.1300.0091.08(1.02,1.14)糖化血红蛋白0.2800.0380.3780.0142.44(1.12,4.98)NT-proBNP2.2210.8665.654<0.00114.84(6.43,34.26)hs-CRP0.3200.4564.4490.0031.20(1.07,1.35)血尿酸0.5670.7620.4620.0241.36(1.24,1.54)总胆固醇0.0240.0380.3860.4731.03(0.95,1.10)左心室射血分数-0.1930.0805.8150.0160.82(0.70,0.96)eGFR-2.8320.05923.314<0.0010.75(0.67,0.84)高血压1.3460.0573.5210.0037.05(1.97,25.22)慢性肾脏病0.4320.0432.1240.0026.69(2.07,21.65)他汀类药物-1.9430.50814.6500.0010.14(0.05,0.39)
2.4血浆NT-proBNP 水平预测CIN的价值绘制血浆NT-proBNP 水平预测CIN的ROC曲线,ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.862,95%CI(0.789,0.935),NT-proBNP=770 ng/L时,灵敏度为67.7%,特异度为85.9%(见图1)。

图1 血浆NT-proBNP 水平预测CIN的ROC曲线
Figure 1ROC curve of plasma NT-proBNP level predicting CIN
3讨论
既往研究显示,PCI后发生CIN的主要危险因素包括:慢性肾功能不全、糖尿病、血容量不足、高血压、心力衰竭、贫血、使用肾毒性药物、低清蛋白血症等[9],本研究结果与之基本一致。本研究多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示:糖化血红蛋白、hs-CRP、血尿酸水平是CIN发生的独立危险因素。糖化血红蛋白可以反映患者最近2~3个月机体糖代谢状态及血糖水平控制情况,可作为评估早期肾脏功能损害的重要指标,其主要通过改变红细胞对氧的亲和力,使组织与细胞缺氧,导致肾脏出现微血管并发症[10]。PCI后造影剂的高渗作用可引起肾脏血流动力学改变,在糖化血红蛋白水平升高的基础上,更易发生CIN[11]。He等[12]研究220例行PCI的ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者血浆hs-CRP水平与CIN的关系,术后21例(9.5%)发生CIN,采用ROC曲线评估血浆hs-CRP水平预测CIN的价值,当血浆hs-CRP水平取16.85 mg/L时,灵敏度为81.0%,特异度为61.8%,AUC为0.748。炎性机制在CIN的发生发展中的作用已经得到了共识,本研究结果显示,CIN组患者hs-CRP水平较非CIN组升高,进一步证实了炎症在CIN发生中的作用。血尿酸水平与eGFR相关,Lytvyn等[13]观察188例1型糖尿病青少年患者发现,血尿酸与eGFR呈负相关(r=-0.48,P<0.001)。血尿酸可能通过激活肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统以及增强氧化反应,刺激血管平滑肌细胞增殖,引起肾血管持续强烈收缩,导致肾脏缺血,增加CIN的发生风险[14-15]。Barbieri等[16]观察1 950例接受PCI的患者(所有患者肌酐清除率均<90 ml/min),251例(12.9%)发生CIN,多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,血尿酸是CIN发生的独立危险因素〔OR=1.42,95%CI(1.04,1.93),P=0.026〕。他汀类药物对CIN的作用,临床上尚存在争议,本研究中他汀类药物对CIN有一定的保护作用。
NT-proBNP是BNP分裂后无活性的N-末端片段,主要来自心室肌细胞,当心室肌细胞受到压力和容量负荷的调控时而释放,具有括血管、利尿、排钠,抑制交感神经系统、肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统等生物学效应[17]。NT-proBNP主要经肾脏清除,t1/2长,体外稳定时间长,测定方法统一,较BNP灵敏度高[18]。Goussot等[19]进行的一项多中心、前瞻性研究的1 243例患者均诊断为急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死,均行PCI,其中130例(10.5%)发生CIN;CIN组患者NT-proBNP水平较非CIN组升高〔1 275(3 587)pg/ml与247(907)pg/ml,P<0.001〕,住院病死率也显著升高(6.9%与1.1%,P<0.001),多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,NT-proBNP是CIN的预测因子,对CIN的预测价值较年龄、高血压、糖尿病、吸烟、脑卒中、基础肾疾病、C反应蛋白、eGFR等大。Patel等[20]关于PCI后AKI与血浆BNP水平相关性的研究中,1 139例患者按PCI后血肌酐水平分为轻度AKI〔407例(35.7%)〕、重度AKI〔58例(5.1%)〕;血浆BNP水平预测轻度AKI的OR=1.87〔95%CI(1.40,2.49)〕、预测重度AKI的OR=3.17〔95%CI(1.06,9.48)〕,预测轻度AKI的AUC的95%CI(0.67,0.69)(P=0.02)、预测重度AKI的AUC的95%CI(0.73,0.75)(P=0.11),血浆BNP水平可以预测AKI。本研究结果显示,血浆NT-proBNP水平预测CIN的OR=14.84〔95%CI(6.43,34.26),P<0.001〕,AUC为0.862,95%CI(0.789,0.935),NT-proBNP=770 ng/L时,灵敏度为67.7%,特异度为85.9%。
NT-proBNP水平与CIN发生机制的关系目前尚未明确,可能是由于心室肌细胞受到容量负荷、缺氧、缺血刺激而大量释放,左心室射血分数降低、血流动力学改变,肾血流量重新分布,肾髓质血流量降低,加重了造影剂对肾小管的毒性作用[21]。NT-proBNP水平受年龄、糖尿病、慢性肾脏病等多种因素的影响,这些因素同时也是CIN发生的危险因素[22],采用NT-proBNP预测CIN发病机制有待进一步的研究与探讨。NT-proBNP主要经肾脏清除,其水平的升高与肾功能受损情况相关[23],本研究结果也印证了这一观点。NT-proBNP水平与PCI CIN的发生相关,为PCI前评估以及PCI后治疗提供简便可靠的理论基础。Liu等[24]最近进行的一项关于2 248例行PCI患者的回顾性分析将NT-proBNP水平预测CIN与Mehran评分进行比较,同时采用NT-proBNP水平预测术后病死率,其结果表明,NT-proBNP水平预测CIN与Mehran评分一致,NT-proBNP水平>682 ng/L也可用于预测PCI后病死率,本文尚需进一步研究进行证实。
本研究存在以下不足:(1)单中心、样本量少,回顾性分析;(2)未能对血浆NT-proBNP水平进行动态监测。血浆NT-proBNP水平对CIN的预测,还需要多中心、大规模、长时间随访的临床研究来进一步证实。
作者贡献:王海莹进行试验设计与实施、资料收集整理、撰写论文、成文并对文章负责;王海莹、涂晓文进行试验实施、评估、资料收集;涂晓文进行质量控制及审校。
本文无利益冲突。
参考文献
[1]Chong E,Poh KK,Liang S,et al.Risk factors and clinical outcomes for contrast-induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with normal serum creatinine[J].Ann Acad Med Singapore,2010,39(5):374-380.
[2]Kim JH,Yang JH,Choi SH,et al.Predictors of outcomes of contrast-induced acute kidney injury after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with chronic kidney disease[J].Am J Cardiol,2014,114(12):1830-1835.
[3]Senoo T,Motohiro M,Kamihata H,et al.Contrast-induced nephropathy in patients undergoing emergency percutaneous coronary intervention for acute coronary syndrome[J].Am J Cardiol,2010,105(5):624-628.
[4]Akgul O,Uyarel H,Pusuroglu H,et al.High BNP level as risk factor for acute kidney injury and predictor of all-cause mortality in STEMI patients[J].Herz,2014,39(4):507-514.
[5]Dorje T,Wang X,Shao M,et al.Plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide levels predict new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with acute myocardial infarction[J].Int J Cardiol,2013,168(3):3135-3137.
[6]Sakai H,Tsutamoto T,Ishikawa C,et al.Direct comparison of brain natriuretic peptide(BNP) and N-terminal pro-BNP secretion and extent of coronary artery stenosis in patients with stable coronary artery disease[J].Circ J,2007,71(4):499-505.
[7]中华医学会心血管病学分会,中华心血管病杂志编辑委员会.急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死诊断和治疗指南[J].中华心血管病杂志,2010,38(8):675-690.
[8]Ad-hoc working group of ERBP,Fliser D,Laville M,et al.A European Renal Best Practice(ERBP) position statement on the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes(KDIGO) clinical practice guidelines on acute kidney injury:part 1:definitions,conservative management and contrast-induced nephropathy[J].Nephrol Dial Transplant,2012,27(12):4263-4272.
[9]Aurelio A,Durante A.Contrast-induced nephropathy in percutaneous coronary interventions:pathogenesis,risk factors,outcome,prevention and treatment [J].Cardiology,2014,128(1):62-72.
[10]Naruse H,Ishii J,Hashimoto T,et al.Pre-procedual glucose levels and the risk for contrast-induced acute kidney injury in patients undergoing emergency coronary intervention[J].Circ J,2012,76(8):1848-1855.
[11]Kuo IC,Lin HY,Niu SW,et al.Glycated hemoglobin and outcomes in patients with advanced diabetic chronic kidney disease[J].Sci Rep,2016,6:20028.
[12]He YT,Tan N,Liu YH,et al.Association between high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and contrast-induced nephropathy after primary percutaneous coronary intervention[J].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi,2013,41(5):394-398.
[13]Lytvyn Y,Mahmud FH,Daneman D,et al.Association between plasma uric acid levels and cardiorenal function in adolescents with type 1 diabetes[J].Diabetes Care,2016.[Epub ahead of print].
[14]Xu W,Huang Y,Li L,et al.Hyperuricemia induces hypertension through activation of renal epithelial sodium channel(ENaC)[J].Metabolism,2016,65(3):73-83.
[15]Uedono H,Tsuda A,Ishimura E,et al.Relationship between serum uric acid levels and intrarenal hemodynamic parameters[J].Kidney Blood Press Res,2015,40(3):315-322.
[16]Barbieri L,Verdoia M,Schaffer A,et al.Uric acid levels and the risk of contrast induced nephropathy in patients undergoing coronary angiography or PCI[J].Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis,2015,25(2):181-186.
[17]Struthers AD,George J.High B-type natriuretic peptide hypertensives at target blood pressure:potential role of β-blockers to reduce their elevated risk[J] Hypertension,2015,66(5):927-932.
[18]Hernández-Leiva E,Dennis R,Isaza D,et al.Hemoglobin and B-type natriuretic peptide preoperative values but not inflammatory markers,are associated with postoperative morbidity in cardiac surgery:a prospective cohort analytic study[J].J Cardiothorac Surg,2013,8:170.
[19]Goussot S,Mousson C,Guenancia C,et al.N-terminal fragment of pro B-type natriuretic peptide as a marker of contrast-induced nephropathy after primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction[J].Am J Cardiol,2015,116(6):865-871.
[20]Patel UD,Garg AX,Krumholz HM,et al.Preoperative serum brain natriuretic peptide and risk of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery[J].Circulation,2012,125(11):1347-1355.
[21]Liu YH,Liu Y,Zhou YL,et al.Association of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide with contrast-induced nephropathy and long-term outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease and relative preserved left ventricular function[J].Medicine(Baltimore),2015,94(13):e358.
[22]Andreucci M,Faga T,Pisani A,et al.Prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy through a knowledge of its pathogenesis and risk factors[J].Scientific World Journal,2014,2014:823169.
[23]Yoshitomi R,Nakayama M,Sakoh T,et al.Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide concentration is independently associated with kidney function decline in Japanese patients with chronic kidney disease[J].J Hypertens,2016,34(4):753-761.
[24]Liu Y,He YT,Tan N,et al.Preprocedural N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide(NT-proBNP) is similar to the Mehran contrast-induced nephropathy(CIN) score in predicting CIN following elective coronary angiography[J].J Am Heart Assoc,2015,4(4):e001410.
(本文编辑:陈素芳)
Predictive Value of NT-proBNP for Contrast-induced Nephropathy in Patients With Non-ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
WANGHai-ying,TUXiao-wen.
LiaoningMedicalPostgraduateTrainingBase,GeneralHospitaloftheSecondArtilleryofPLA,Beijing100088,China
【Abstract】ObjectiveTo study the association between preoperative plasma NT-proBNP and the incidence of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction(NSTEMI) after percutaneous coronary intervention(PCI).MethodsWe collected 244 NSTEMI patients who underwent PCI in the General Hospital of the Second Artillery of PLA from January 2014 to July 2015.According to whether CIN happened after PCI,the patients were assigned into CIN group(n=30) and non-CIN group(n=214).We recorded the patients′ basic information,measured laboratory indexes,recorded left ventricular ejection fraction by echocardiography,estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and recorded patients′ medical history and the usage of medication before operation.The influencing factors for CIN were analyzed by multivariate Logistic regression analysis.The predictive value of plasma NT-proBNP level for CIN was evaluated by ROC curves.ResultsCIN group and non-CIN group were not significantly different in gender,BMI,SBP,DBP,the levels of FBG,blood potassium,blood calcium,blood phosphorus,hemoglobin,triacylglycerol,the detection rates of hyperlipemia,diabetes mellitus and cardiac fuctional insufficiency,the usuage rates of ARB,ACEI,diuretic,hypoglycemic agent,insulin,aspirin and β-receptor blocker,the proportions of patients using contrast agent dose >200 ml,patients with >2 lesion coronary arteries or with lesion in left main coronary artery (P>0.05);CIN group and non-CIN group were significantly different in age,the levels of glycosylated hemoglobin,NT-proBNP,hs-CRP,blood uric acid and total cholesterol,left ventricular ejection fraction,eGFR,the detection rates of hypertension and chronic renal failure and the usage rate of statins (P<0.05).Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that age,the levels of glycosylated hemoglobin,NT-proBNP,hs-CRP and blood uric acid,left ventricular ejection fraction,eGFR,hypertension,chronic renal failure and the usage of statins had regression relation with CIN (P<0.05).The AUC of NT-proBNP level predicting CIN was 0.862 with a 95%CI(0.789,0.935),and the sensitivity and specificity were 67.7% and 85.9% respectively when NT-proBNP=770 ng/L.ConclusionThe occurrence of CIN has correlation with age,the levels of glycosylated hemoglobin,hs-CRP and blood uric acid,left ventricular ejection fraction,eGFR,hypertension,chronic renal failure and the usage of statins.Preoperative NT-proBNP is an independent risk factor for the occurrence of CIN and can be used in the prediction of CIN in NSTEMI patients after PCI.
【Key words】Nephrosis;Contrast media;Natriuretic peptide,brain;Risk factors;Sensitivity;Specificity
通信作者:涂晓文,100088北京市,中国人民解放军第二炮兵总医院肾内科;E-mail:xiaowentu@126.com
【中图分类号】R 692
【文献标识码】A
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2016.15.007
(收稿日期:2015-09-26;修回日期:2016-03-04)
