某社区中青年人椎管形态学MRI观察
2016-06-03李晓东胡振顺崔国庆李艳捧
李晓东,胡振顺,崔国庆,张 斌,李艳捧
(河北北方学院附属第一医院磁共振科,河北 张家口 075000)
某社区中青年人椎管形态学MRI观察
李晓东,胡振顺,崔国庆,张斌,李艳捧
(河北北方学院附属第一医院磁共振科,河北 张家口 075000)
摘要:目的探讨长青路社区中青年人MRI C3~C7椎体矢状径、椎管矢状径、颈髓矢状径、Torg比值及SAC大小变化。方法50例长青路社区健康中青年人分为男女两组,男21人,女29人,均行颈椎MRI检查。矢状位T2WI测量C3~C7节段椎体矢状、椎管及脊髓矢状径,计算相应节段Torg比值和脊髓缓冲空间(SAC)。结果男性组C3~C7椎体矢状径大于女性椎体矢状径,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。C3~C7椎管矢状径、脊髓矢状径男女两组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。C3~C7节段Torg比值范围男性0.62~1.19,女性0.82~1.34,女性Torg比值大于男性,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。C3~C7 SAC值男女两组差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。受试者Torg比值与椎体矢状径、脊髓矢状径的皮尔逊相关系数为-0.676、0.153。SAC值与椎体矢状径、脊髓矢状径、椎管矢状径的皮尔逊相关系数为0.241、-0.324、0.869。结论C3~C7椎体矢状径存在性别差异,椎管矢状径无性别差异,单纯以Torg比值作为椎管狭窄的诊断指标会加大男性椎管狭窄的误诊率。与Torg比值相比,SAC值的变化与椎管矢状径大小明显相关,较Torg比值更能反映椎管狭窄情况。
关键词:发育性椎管狭窄;Torg比值;脊髓缓冲空间(SAC);MRI
椎管大小不仅与脊髓损伤密切相关,而且还是颈髓型颈椎病发生和发展的病理基础,对外伤及退行性病变的预后具有重要影响[1]。Torg比值法测量椎管大小避免了X线放大所产生的误差,被视为诊断椎管狭窄最可靠的指标。但X线只能显示骨质结构,不能全面评价椎管及内容物的变化,而MRI凭借其出色的组织分辨力,能够精确测量椎管、脊髓及其它软组织的大小[2-3]。本研究旨在利用MRI探讨正常人群C3~C7椎体矢状径、椎管矢状径、颈髓矢状径、Torg比值及SAC的大小变化。
1资料与方法
1.1一般资料
2014-11—2015-12月河北北方学院附属第一医院附近长青路社区健康志愿者50例,其中男21人,女29人;年龄21~40岁,平均(29.4±6.07)岁;两组体重指数无差异。排除脊柱外伤、感染、肿瘤及先天性疾病。
1.2图像获取与数据测量
采用Philips Ingenia 3.0T核磁对每位志愿者均行颈椎MRI检查,图像包括FSE-T1WI、FSE-T2WI,FS-FSE-T2WI。FOV=180 mm×222 mm,层厚=3 mm,NSA=1~3。矢状位T2WI测量C3~C7节段椎体矢状径、椎管矢状径及脊髓矢状径,计算相应节段Torg比值和有效脊髓空间值(SAC)。测量及计算方法:椎体前后缘中点连线为椎体矢状径;以椎体后缘中点至椎板结合部之间最短的连线为椎管矢状径,同时于相应水平测量脊髓矢状径(图1)。Torg比值=椎管矢状径/椎体矢状径;SAC=椎管矢状径-脊髓矢状径。数据由1名高年资主治医师测量3次,结果取平均值。
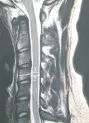
图1C4椎体水平测量椎体矢状径(线1)、椎管矢状径(线2)及脊髓矢状径(线3)
1.3统计学方法
SPSS 11.0处理数据,行配对t检验、方差分析及相关性分析,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2结果
50名志愿者均完成颈椎MRI检查,获得清晰图像。男性组C3~C7椎体矢状径大于女性,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。C3~C7节段椎管矢状径男女两组差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。C3~C7节段脊髓矢状径男女两组差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。C3~C7节段Torg比值范围男性0.62~1.19,女性0.82~1.34;Torg比值平均值男性0.89±0.09,女性1.1±0.11;女性Torg比值大于男性,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。受试者Torg比值与椎体矢状径、脊髓矢状径的皮尔逊相关系数为-0.676、0.153。男性志愿者Torg比值<0.80,多发生在C4和C5节段;在测量29名女性的203个节段中,仅有1处Torg比值<0.80。C3~C7节段SAC值范围男性4.82~12.36 mm,女性5.15~11.5 mm,两组SAC最大值均为C7节段,最小值均为C4节段,C3~C7节段SAC值男女两组差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)(表1)。
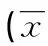
表1 两组志愿者椎体矢状径、椎管矢状径、脊髓矢状径、Torg比值及SAC比较±s)
注:与男性组比较*P<0.05,**P<0.01
SAC值与椎体矢状径、脊髓矢状径、椎管矢状径的皮尔逊相关系数分别为0.241,-0.324,0.869。
3讨论
形态学研究表明,不仅不同性别、不同年龄者椎管矢状径存在差异,不同种族人群间亦存在差异,印度人群椎管矢状径远小于其他人种[4-5]。Tierney等[6]采用MRI测得正常人椎管矢状径为(13.28±1.47) mm,椎体矢状径为(17.7±2.18) mm。Lee[7]在尸体标本上测得C3~C7平均椎管矢状径为(14.1±1.6) mm,且男性椎管直径在各脊髓节段均远大于女性。Morishita等[8]通过MRI测得C3~C7椎管平均直径为(13.73±1.37)mm。MRI测量数据体现了软组织结构对形态参数的影响。本研究男女两组C3~C7椎体矢状径差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),男性C3~C7椎体矢状径大于女性,Torg比值与椎体矢状径存在负相关,即Torg比值与性别有关。研究中多数男性受试者至少有一个椎体节段其Torg比值小于0.80,因此用Torg比值作为诊断椎管狭窄的指标并不可靠。Lim等[9]指出,女性各个椎体水平的椎管矢状径、椎体矢状径均较小,男性椎体矢状径比女性大,因此男性Torg比值反而较小。
Miyazaki等[10]认为脊髓大小与椎管大小无明显相关,在人群中相对恒定,本研究结果与之相同。李艳捧[2]测得C3~C7颈髓SAC值(3.97±0.97)~(5.57±1.04)mm,C3的SAC值最小。本组C4的SAC值最小,SAC值与椎管矢状径存在较强正相关,SAC值可更客观地反映椎管大小,对预测椎管狭窄的发展具有重要提示作用,对预防和指导诸如运动员或其他有脊髓损伤职业风险的人群避免可能的损伤有着重要意义。此外,SAC值较小的患者更易受到诸如椎间盘突出、椎管骨质增生、黄韧带或关节面肥厚引起的脊髓压迫,其症状较常人更重。
Boden等[11]用MRI检测了无症状受试者的椎管改变情况:40岁以上的受试者中有28%颈椎存在异常改变,而40以下的受试者中仅有14%存在异常。本研究受试者年龄较小(21~40)岁,减小了颈椎退行性变对测量结果的影响。采用3.0T磁共振获得的图像信噪比、图像分辨率均较高,减小了测量误差。本研究也存在样本量较小等局限性。
综上,MRI可精确测量椎体矢状径、椎管矢状径、颈髓矢状径、Torg比值及SAC。Torg比值受性别影响较大,不能十分准确反映椎管狭窄情况。SAC值与椎管矢状径具有明显相关性,能够较为客观地反映椎管的大小,有必要扩大样本进一步深入研究。
参考文献:[1]Takao T,Morishita Y,Okada S,etal.Clinical relationship between cervical spinal canal stenosis and traumatic cervical spinal cord injury without major fracture or dislocation[J].Eur Spine J,2013,22(10):2228-2231.[2]李艳捧,杜晓猛,胡振顺,等.发育性颈椎椎管狭窄脊髓缓冲空间的MRI研究[J].颈腰痛杂志,2015,36(6):479-481.[3]Endo K,Suzuki H,Nishimura H,et al. Kinematic analysis of the cervical cord and cervical canal by dynamic neck motion[J].Asian Spine J,2014,8(6):747-752.[4]Matveeva N,Janevski P,Nakeva N,et al.Morphometric analysis of the cervical spinal canal on MRI[J].Prilozi,2013,34(2):97-103.
[5]Papinutto N,Schlaeger R,Panara V,et al.Age,gender and normalization covariates for spinal cord gray matter and total cross-sectional areas at cervical and thoracic levels:A 2D phase sensitive inversion recovery imaging study[J].PLoS One,2015,10(3):e0118576.
[6]Tierney T R,Maldjian C,Mattacola G C,etal.Cervical spine stenosis measures in normal subjects[J].Athl Train,2002,37(2):190-193.
[7]Lee M J,Cassinelli E H,Riew K D.Prevalence of cervical spine stenosis:Anatomic study in cadavers[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,2007,89(2):376-380.
[8]Morishita Y,Naito M,Hymanson H,etal.The relationship between the cervical spinal canal diameter and the pathological changes in the cervical spine[J].Eur Spine J,2009,18(6):877-883.
[9]Lim J K,Wong H K.Variations of the cervical spinal Torg ratio with gender and ethnicity[J].Spine J,2004,4(4):396-401.
[10]Miyazaki M,Takita C,Yoshiiwa T,et al.Morphological analysis of the cervical pedicles,lateral masses,and laminae in developmental canal stenosis[J].Spine(Phila Pa 1976),2010,15;35(24):E1381-1385.
[11]Boden S D,McCowin P R,Davis D O,etal.Abnormal magnetic-resonance scans of the cervical spine in asymptomatic subjects:A prospective investigation[J].J Bone Joint Surg Am,1990,72(8):1178-1184.
[责任编辑:李蓟龙英文编辑:刘彦哲]
MRI Observation of Spinal Canal Morphology in Young and Middle-aged People in Changqing Road Community
LI Xiao-dong,HU Zhen-shun,CUI Guo-qing,ZHANG Bin,LI Yan-peng
(Magnetic Resonance Imaging Center,The First Affiliate Hospital of Hebei North University,Zhangjiakou,Hebei 075000,China)
Abstract:ObjectiveTo study the changes of C3 to C7 vertebral sagittal diameter,canal sagittal diameter,spinal cord sagittal diameter,Torg ratio and SAC of the young and middle-aged people in Changqing Road community.MethodsFifty young and middle-aged volunteers from Changqing Road community were divided into two groups of men(21)and women(29).Everyone underwent cervical spine MRI.We measured their vertebral sagittal diameter,canal sagittal diameter and spinal cord sagittal diameter and calculated the corresponding segmental Torg ratio and SAC on the sagittal T2WI.ResultsVertebral sagittal diameter from C3 to C7 in men was significantly larger than that in women(P<0.05).Canal sagittal diameter and spinal cord sagittal diameter had no difference between two groups.The Torg ratio in men ranged from 0.62 to 1.19,and 0.82 to 1.34 in women.The Torg ratio in women was significantly larger than that in men(P<0.01).SAC from C3 to C7 was of no statistical significance between two groups. All volunteers’ Pearson correlation coefficients in Torg ratio and vertebral sagittal diameter,and spinal cord sagittal diameter were 0.676 and 0.153,respectively.Pearson correlation coefficients in SAC and spinal cord,vertebral sagittal diameter,and canal sagittal diameter were 0.241,0.324 and 0.241,respectively.ConclusionVertebral sagittal diameters from C3 to C7 were different according to gender,and canal sagittal diameters were of no difference between two groups.The misdiagnosis rate of canal stenosis in men would be increased only by Torg ratio.Compared with Torg,SAC changes were significantly correlated with the size of the canal sagittal diameter,and so the SAC could reflect stenosis more exactly.
Key words:developmental canal stenosis;Torg ratio;space available for the cord(SAC);magnetic resonance imaging
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-1492.2016.04.002
中图分类号:R 445.2
文献标识码:A
作者简介:李晓东(1969-),男,河北张家口人,副主任医师,研究方向:骨关节疾病的MRI诊断。
来稿日期:20160303
