Economic analysis in product design—A case study of a TCM dietary supplement
2016-05-29YuenShanChengKaYipFungKaMingNgChristiantoWibowo
Yuen Shan Cheng ,Ka Yip Fung ,Ka Ming Ng ,*,Christianto Wibowo
1 Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering,The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology,Clear Water Bay,Hong Kong,China
2 Clear Water Bay Technology,Inc.,4000 W.Valley Blvd.Suite 100,Pomona,CA 91789,USA
1.Introduction
The development of methods for chemical product design has been widely advocated in the chemical engineering community in the past decade.Many research papers[1-4],review articles[5-7],textbooks[8,9],and monographs[10-12]have contributed to various aspects of product design,and provided case studies to define and substantiate this nascent research area.Ulrich and Eppinger[13]summarized the activities involved in the design of mechanical products.Along the same line,Cheng et al.[14]proposed an integrated approach for product design and development considering both technical and management issues.The activities are grouped into five job functions-management,sales and marketing,research and design,manufacturing,and finance and economics-in three development phases,namely product conceptualization,detail design and prototyping,and product manufacturing and launch.Each activity such as studying competing products,identifying product form,and performing make-buy analysis is referred to as a unit task(Fig.1).The italicized activities are those that can benefit from the input of a chemical engineer.This approach generalizes the concept of unit operations in process design,the present mainstay of chemical engineering,to unit tasks that include not only the ‘hardware’such as equipment selection and sizing in unit operations,but also the‘software’such as the procedure for gathering and analyzing the marketing information in accomplishing a task in product design.The details of some aspects of this integrated approach-setting product development objective-time chart,choosing ingredients and base-case formula,prototyping,product performance tests,and synthesizing the manufacture processes for chemical products such as sunscreen cream[14]and trans dermal patch[15]-were discussed.
Another important aspect of product design is finance and economics.No product could ever succeed in the market without sound economic decisions.Bagajewicz[16]pioneered the integration of finance and economics into chemical product design,providing a framework for balancing consumers' preferences and willingness to pay for the desired product.The final product quality is selected by maximizing the pro fit as illustrated by the case studies of making an insect repellent[16],a carpet deodorizer/disinfectant[17],and wine[18].
In this study,w e aim to investigate the activities involved in market study,product design,feasibility study,and economic analysis highlighted in red in Fig.1.There are two focuses.First,while the decision of“w hat to make”,as pointed out by Bagajewicz and co-workers,is made by considering both product quality and economic bene fits at the early stage of product design,the business objectives will be expanded to include capture of market share,and minimization of investment[19],etc.Second,w e will investigate issues in make-buy analysis,which is critical to saving cost and time to market.A number of generic methods for make-buy analysis such as the Multi-Attribute Decision-Making methodology are available in the literature[20].Such an analysis calls for the identification of the alternatives to manufacturing and demands in-depth know ledge of the value chain of the chemical product under consideration.
A class of products that is sensitive to such economic factors is traditional Chinese medicinal(TCM)dietary supplement.A case study of designing a Ganoderma lucidum(GL)dietary supplement product is used to illustrate the related activities in this approach.
1.1.Background of the TCM Market and GL
TCMs are w idely accepted in the market due to their long history of treating and preventing ailments and research results in recent years have proved their efficacy on treating various diseases such as cancer and hepatitis[21-24].TCMs are customarily delivered in liquid form by boiling a single herb or multiple herbs in water according to a traditional recipe,while most modern TCMs,particularly dietary supplements,are delivered in solid or liquid form after extracting the bioactive ingredients from the herbal decoction.Proper processing is therefore crucial to control the product quality[25-28].With the increasing popularity of TCM dietary supplements in Asian and Western countries[29],many small and medium-sized enterprises enter into this competitive market.These companies contract out part of the manufacturing process or purchase some of the bioactive ingredients from other manufacturers in order to save capital investment.In fact,some companiesonly engage in dosage form preparation by purchasing all herbal extracts from other manufacturers.In that case,reliableherbal extract suppliers are important to produce product with consistent quality.
G.lucidum(GL),also know n as Lingzhi,is a w ell-know n and widely used medicinal fungus that possesses antitumor and immunomodulatory properties[30,31].It has been proven that GL prevents and treats a variety of ailments,including hypertension,diabetes,hepatitis,and cancers[32,33].Both the GL fruit body(Fig.2(a))and thespores(Fig.2(b))contain bioactive components such as polysaccharides,triterpenes,nucleosides,steroids,fatty acids,alkaloids,peptides,amino acids.The sporescontain higher concentrations of polysaccharides and triterpenes such as ganoderic acids A,B,C,and E;and ganosporic acid A is only found in spores[34].In most commercial products,the hard cell w all of spores,sporoderm,is broken during processing to release the bioactive ingredients(Fig.2(c)).
Table1 presents a survey of twelve GLdietary supplements obtained from different companies in Hong Kong and China markets.Brand 1 contains slices of the raw fruit body.The other eleven products are extracts from different parts of GL prepared in different dosage forms.Fruit body extract products can be found in the market in the form of hard gel capsules(Brands 2 and 3),granules(Brands 4 and 5),and oral drinks(Brand 6).Broken spores are in the form of hard gel capsules(Brands7 and 8).Soft gel capsules containing concentrated spore oil extract(Brands 9 and 10)are intended for ailments that require high dosage intake.Mixtures of fruit body extract and broken spores(Brands 11 and 12)also exist in the market.The number of units per pack,w eight per unit,the amount of active ingredients listed by the manufacturer,and the selling price of one bottle are also listed in Table 1 for all twelve brands.The active ingredients in raw fruit body refer to the water soluble substances,which are assumed to be about 5 w t%of raw herb.The product prices vary considerably but can be compared based on the monthly dose of GLfruit body extract and GLs poresrequired for general health protection,which are recommended by the product suppliers and the Chinese Pharmacopeia[35]to be 14.4 g and 18 g,respectively.This case study considers the economic analysis of designing a GL dietary supplement product made up of either fruit body extract or spores.For simplicity,products that contain a mixture of fruit body extract and spores,and spore oil extract in soft gel capsules are not considered.

Fig.2.Pictures of(a)Ganoderma lucidum.(b)Ganoderma lucidum spores and c)sporoderm-broken spores.
2.Product Conceptualization and Economic Analysis
Fig.3 show s an overview of the activities needed to relate overall product quality to economic analysis for business decision-making.It begins with a market study to collect information on w hat the customers would like to buy in terms of product qualities and the price that they are willing to pay(the buying price)for a specific product.The former can be expressed by a number of product quality factors with different weighting factors.These quality factors include parameters relating to product form,key ingredients selection,physico chemical and sensorial properties,as w ell as other technical specifications.The buying price in conjunction with the selling price of the product the company decides to offer lead to a predicted demand and the corresponding plant capacity using a pricing model.The manufacturing process for the desired quality factors and the plant capacity is then designed based on input information such as experimental data,design heuristics,technical know-how,and product formula.A different combination of product qualities,pricing and demand/capacity would lead to different capital investment and manufacturing cost,and thus different economic return.All of the product candidates are then ranked by criteria including product quality,pro fit,desired market share,and amount of initial investment.Other considerations such as project risks,social responsibility,core competency,and company strategy,while important,are not considered in this study.


Fig.3.The overview of activities in connecting the product quality and the economic bene fits for business decision making.
2.1.Product quality
The overall product quality,QFov,is a function of different quality factors,QFi,that would elicit customers' delight.These quality factors could be functional,sensorial or simply a perception of the user about a specific aspect of the product.Examples include effectiveness,taste and smell,aesthetic appearance,touch and feel,ease of use,and stability.Not all quality factors carry the same weight in the overall product quality and a linear model can be used to relate these quality factors to the overall product quality.A different weighting factor,wi,can be assigned to each quality factor:

These quality factors have to be translated into product attributes,choice of materials,and technical specifications,xi,

For example,afunctional quality factor of a medicinal product can be its potency for a specific ailment,represented as a function of the active ingredient concentration.The sensorial quality factor of a skin cream can be the touch and feel which depends on the type and concentration of emollients,and its microstructure.The ease of use of a medical device such as a transdermal patch can be a major concern.The corresponding quality factor may depend on the devicecon figuration and the materials selection in order to deliver the active ingredients to the target site conveniently.Sometimes,consumers select a product based on the perception on a particular product attribute.For instance,the public may accept the notion that a food product made of“organic”ingredients to be more natural and healthy,and this label may weigh heavily on the overall quality factor.The product quality of the GL dietary supplement is discussed below.
2.1.1.Product quality of GL dietary supplement
Although the studies in the literature[29,36]are not an official market survey,it reflects to a large extent the customers' preferences related to TCM dietary supplements.The quality factors used in this case study are efficacy,safety,ease of use,ease of carrying,taste,smell and the key ingredients used in the product.
Efficacy is a crucial quality factor that has to be supported by scientific and clinical trial data.As mentioned,the recommended daily dose for GL fruit body extract and spores for general health protection are 480 mg and 600 mg,respectively.In the absence of better information,the efficacy is assumed to be met by using the recommended dose for the proposed GLproducts.Similarly,safety of herbal products isacrucial quality factor[36].While GL is reported to be non-toxic,toxicity arising from heavy metals and pesticides may originate from polluted soils at the cultivation sites[37,38]or from contaminantsin the manufacturing process[39].The concentrations of the secontaminants should bemaintained below the allow able limits[40].Protocols for strict control and monitoring of the entire production cycle,from growth of herbs to packaging(Good Agricultural Practice,Good Laboratory Practice and Good Manufacturing Practice),have been established[41,42].Safety is assumed to be acceptable for the GL products in this case study.
Thus,the overall quality of our new product varies with the changes of other five quality factors:ease of use(QF1),ease of carrying(QF2),smell(QF3),taste(QF4),and the key ingredients(QF5).Ease of carrying is the most important because consumers tend to take the product along as they travel.Since dietary supplements are for long term daily use,ease of use is also important.The choice of key ingredients is also deemed important.In the local market,the advertisements stating that spores are superior to fruit body have influenced the consumers' perception of quality and their buying preferences,regardless of whether or not this claim has been verified scientifically.
Table2 summarizes the list of quality factors from customers' preferences and their corresponding weighting factors,as well as product attributes and technical specifications related to each quality factor.The first three quality factors(ease of use,ease of carrying,smell)are related to the selection of dosage forms that are common in the market such as hard gel capsules,granules,and oral drinks.The customers' preference scores on these three quality factors for different dosage forms are presented in Table 3.Hard gel capsule is a common dosage form for TCM extract products and is w ell accepted in the market because of its ease to use(QF1)and ease of carrying for travel(QF2),and thus have a relatively high score of 90 and 95,respectively.Granules require dissolution in water be foread ministration and scores slightly lower in both QF1and QF2than those for hard gel capsules.For most TCM oral drinks,the concentrated liquid extract is held in a glass vial,this gives a perfect preference score on its ease of use.How ever,as a glass vial may break w hen it is carried around,it has a low er score(QF2=80)in ease of carrying.For smell(QF3),an easy w ay to mask the unpleasant smell of the ingredients is to prepare the dietary supplement in the form of a capsule,and hence results in a high score of 95 in QF3for hard gel capsules.Granules can be coated to minimize the smell,but it is still released w hen the granules are dissolved in water before drinking.Thus,it has a low preference score of 65 in QF3,and similarly for oral drinks.
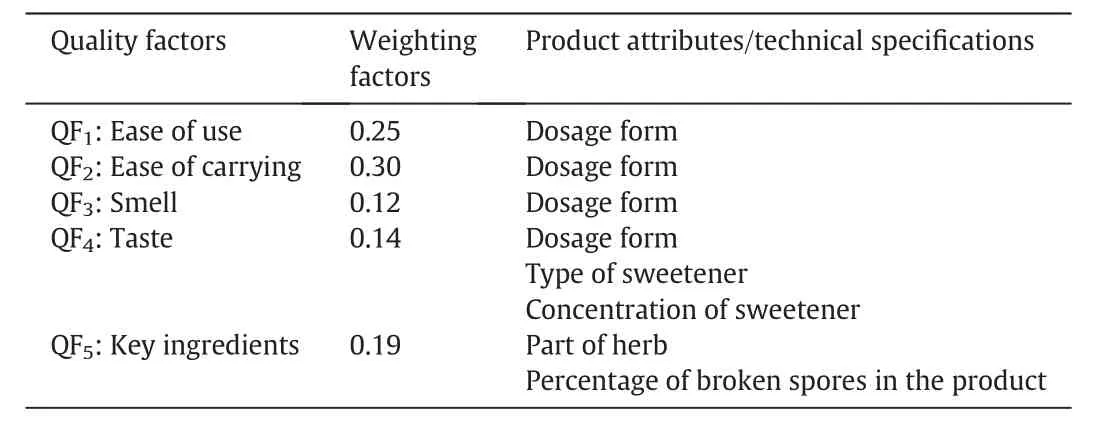
Table 2 List of quality factors and the corresponding product attributes/technical specifications
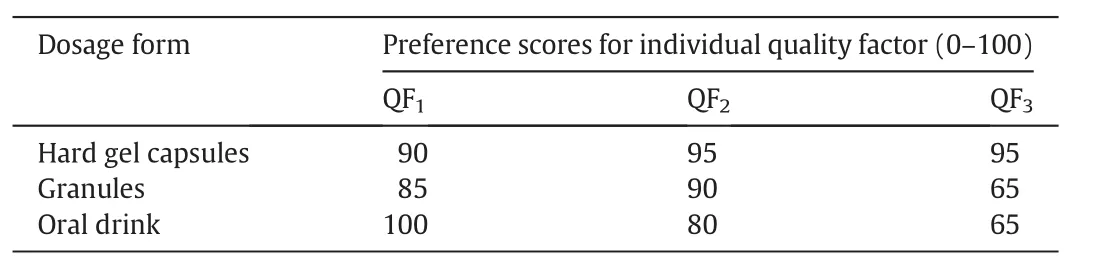
Table 3 Preference scores for ease of usage(QF1),ease of carrying(QF2),and smell(QF3)for different dosage forms
Triterpene in GL extract is w here the bitter taste comes from.This bitter taste can be masked by adding a sweetener to the granules and oral drinks formulation,while hard gel capsules do not require such addition as the gel capsule acts as a barrier to block the unpleasant taste.Sugar,mannitol,or honey is the common sweetener that can be selected,and its concentration used in the formulation has to be specified.Fig.4 show s the dependence of taste(QF4)on sweetener concentration,represented by the mass ratio of a sweetener to GL body extract or spores.All curves exhibit a maximum reflecting that unsweet or too sweet product is not preferred by the customers.Sugar is the sweetest,while honey and mannitol have a sweetness of 97%[43]and 50%[44]that of sugar,respectively.Therefore,mannitol hasto be added at a larger concentration to obtain the sames core or taste.Table4 shows the dependence of the QF4score on the dosage form and taste/level of sweetness.The bitter taste is blocked by the hard gel capsules so that it has a high score of 95 for QF4.For granules and oral drinks,the level of sweetness/bitterness is classified as bitter,slightly bitter,slightly sweet,sweet and too sweet,corresponding to different concentrations of sweetener,and each level gets a different score of QF4.
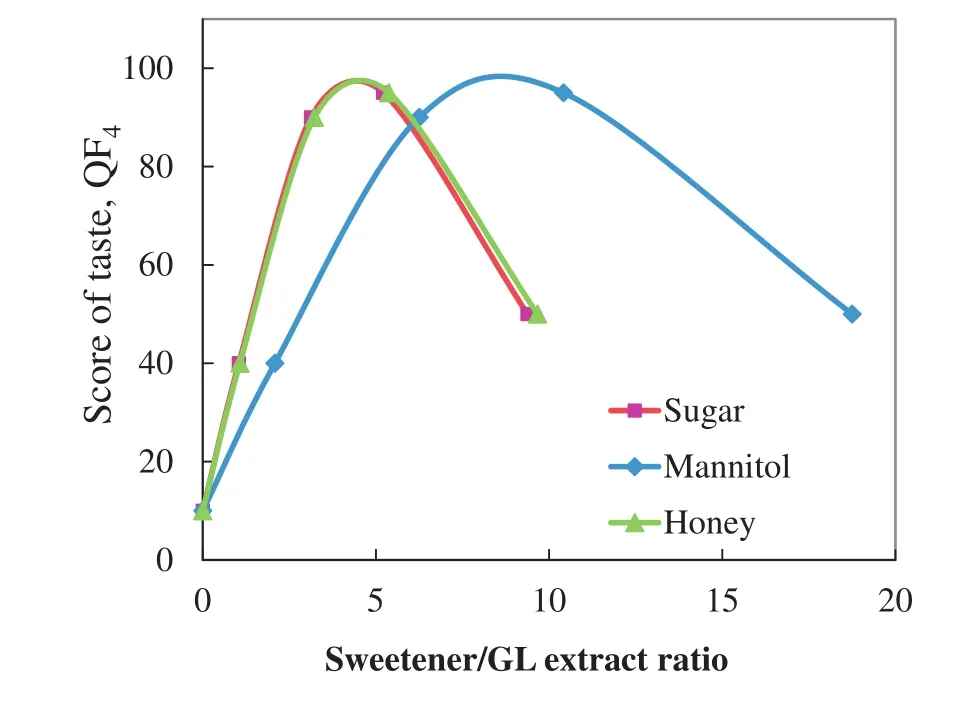
Fig.4.The relationship between score of taste,QF4,and massratio of sweetener/GLextract ratio for three sweeteners of sugar,mannitol,and honey.
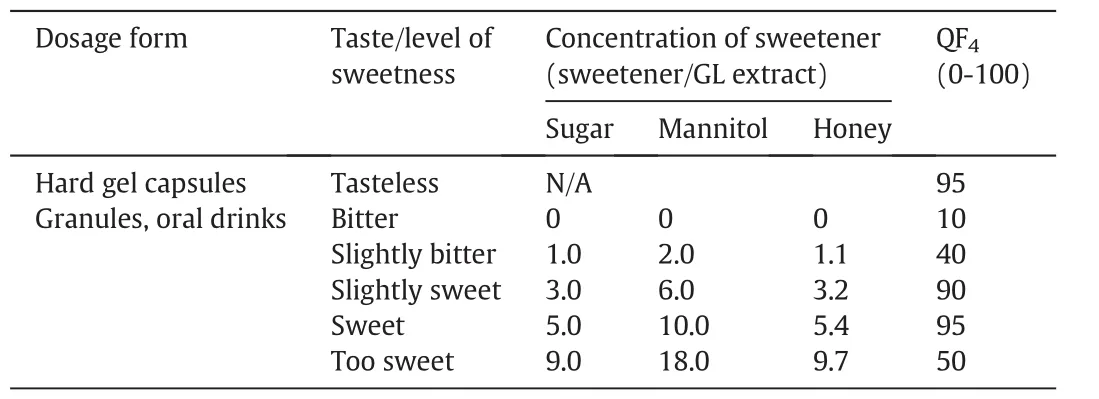
Table 4 Preference scores for taste on different dosage forms,types and concentrations of sw eeteners used in the formulation
Another important quality factor of customers' preference,influenced by advertisements,is their perception of the key ingredient used in the product.Table 5 shows the preference scores which depend on the part of the herb(fruit body or spores)and the percentage of broken spores(only applicable to spore products).In general,consumers prefer spores over fruit body and a high percentage of broken spores in the spore products.In the local market,products with broken spores below 80%are considered unacceptable.

Table 5 Preference scores for perception on different parts of herb and percentage of broken spores in the spore products
Different combinations of product attributes and technical specifications would lead to products with different overall product quality scores.In this case study,fruit body extract and spore products are considered.For fruit body extract,three dosage forms,hard gel capsules,granules and oral drinks,are considered.For granules,either sugar or mannitol can be added as the sweetener to provide five levels of sweetness.For oral drinks,all three sweeteners,sugar,mannitol or honey,can be used,again,to provide five levels of sweetness.For spore products,only hard gel capsules with 80%-90%and 90%-100%of broken spores are considered.There are altogether 28 potential candidates,resulting from different combinations of these parameters(Table 6).They are scored using the scoring systems described earlier in this section.For example,candidate no.1,a fruit body extract in hard gel capsule,scores 90,95,95,and 95 for ease of use(QF1),ease of carrying(QF2),smell(QF3),and taste(QF4),respectively,but has a relatively low score of 85 for QF5due to customers' perception on the choice of key ingredient.The overall product quality score QFov,calculated by Eq.(1)using the corresponding weighting factors listed in Table 2,is 91.85.With the overall product quality score for all candidates available,their estimated market share and demand are determined next.

Table 6 Lists of potential product candidates with combinations of various parts of herb,product forms,sources of herb,type and concentration of sweetener
2.2.Pricing and demand

such that Y≥p1d1+p2d2w here Y is the consumer budget for buying this kind of product;d1and d2(p1and p2)are the demands(prices)of the new and existing products,respectively;α represents how much the consumer is aware of the superiority of the new product;β is the consumer preference coefficient,which is a measure of how much more the consumer prefers product 2 over product 1;and ρ is a model parameter(related to elasticity of the utility function).Assuming a w ell established market for a product,this model predicts the relationship between the price of the new product and the corresponding demand.While multiple competitors can be considered[17],a single competitor model is used in this case study.It is assumed that the consumer preference coefficient,β,is equal to the ratio of the quality of the competing product to that of the new product,that is,QFov2/QFov1.The demand of a new product of a know n quality can then be predicted using the pricing model(Eq.(3)).The market share of the new product is calculated as follow s:
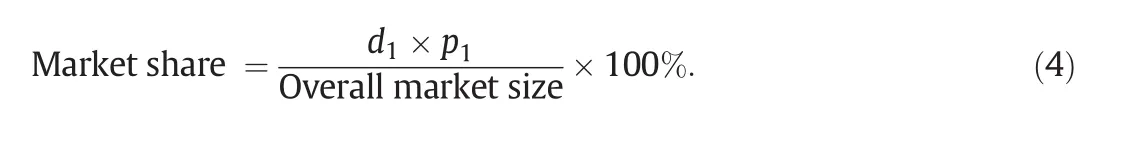
2.2.1.Pricing and demand of GL dietary supplement
In this case study,the pricing model is used to predict the relationship between prices,product quality,and predicted demands of the new and competing products for a specified customers' budget.Here,Brand 2 product in Table 1 is selected as the competing product which has a selling price of 64.05 USD/monthly dose,and an overall quality score of 92.8 based on the scoring system developed in Tables 3-5.Assuming that the current demand of the existing product is 7000 units of monthly dose/month,the consumer budget,Y,is 64.05×7000=448350 USD per month.To compete with this product in the market,the target price of the new product is set 10%below that of the competing product.An α value of 0.8 is used,implying that customers have nearly the same know ledge and aw areness of the new product compared with that of the competing product.The value of ρ is set at 0.7,to be consistent with the available information on price,quality,and demand of another product in the local market having a similar consumer awareness compared with the competing product.With an overall market size of GLproduct to be 4.5 million USD per month,the market share of the new product is calculated by Eq.(4).These results will be described later in this article.
2.2.2.Capital investment and total product cost for GL dietary supplement
A superstructure for manufacturing GL hard gel capsules,granules,and oral drinks is show n in Fig.5.It is developed based on the generic manufacturing process for natural products suggested by Harjo et al.[26].The manufacturing process for the GL products involves four main sections—feed preparation,extraction,dosage form preparation,and bottling and packaging.Manufacturing routes for different dosage forms and using different parts of herb are captured in the superstructure.The routes for fruit body extract products and spore products are represented by thin red lines and thick blue lines,respectively.Dashed lines in the diagram represent alternative routes using intermediates purchased from vendors instead of making it in the company's plant.The dosage form and the part of the herb used in the product may substantially impact the capital investment since they involve different manufacturing processes.
For the fruit body extract product(thin red line routes in Fig.5),the raw GL fruit body enters the feed preparation section which contains washing,drying,and cutting/grinding steps.Water is used to rinse off the soils on the surface of GL.It is then dried at a temperature of about 30-50°C,and ground into pow ders using a cutting mill in order to increase the surface area for enhancing the extraction efficiency.In the past,the pileus of the herbs is considered to be the only useful part and the stipe is removed before extraction.Since it has recently been show n that the extract from the stipe of GL performs better on antitumor and immunomodulate activities than that of pileus[45],the stipe is also used for extraction.The extraction section includes extraction, filtration,and concentration units.Water is conventionally employed as the extraction solvent at a mass ratio of GL/water of 1:12 at 100°C for 1 h,the extraction is repeated for three times[46].Excess water is removed in a concentration unit and the concentrated extract is sent to the dosage form preparation section.The manufacturing process of hard gel capsules and granules is designed based on the procedure developed by Fung and Ng[3].For hard gel capsules,the concentrated extract solution ismixed with starch,which acts as a filler,and spray dried,before entering the capsule filling unit.For granules product,the concentrated GL extract solution from the extraction section is mixed with dextrin and sweetener before entering thew et granulation machine.The resulting granules are dried and sieved.For oral drinks,theconcentrated GL extract is mixed with sw eetener,dispersing agent,preservatives and additional water if necessary to make up the final product.All dosage forms are then either bottled or packaged.
Thesporeproduct(thick bluelineroutesin Fig.5)issporepowder in hard gel capsules.Common sporoderm-breaking methods used in feed preparation are ultra- fine grinding,micronization,high pressure homogenization,and enzyme hydrolysis[47,48].It is common to use either a single or a combination of the above techniques for sporodermbreaking in industry.For example,enzyme hydrolysis can be used to obtain broken sporesonly up to a certain point sinceover-hydrolysiscauses decomposition of the active ingredients.This is follow ed by a mechanical technique to further increase the amount of broken spores.These broken spores are then sent directly to the dosage form preparation section.
The capital cost and the total product cost,which includes manufacturing cost and general expenses,have to be estimated.The capital cost for products with given product attributes and technical specifications is calculated using the capacity predicted by the pricing model.It includes all the initial investment of the manufacturing process,such as land and building,facilities,purchased equipment and installation,instrumentation and control,and other start up expenses.The manufacturing cost includes the costs for the raw materials,manpower,utilities,waste treatment and disposal,maintenance and repairs,depreciation,and plant overhead.General expenses include the office operating cost,and sales and marketing expenses.The formulations for various fruit body extract and spore products are summarized in Table 7,while the input information for the calculation of the capital and total product costs are listed in Tables 8 and 9,respectively.
2015年,欧米茄携手瑞士联邦计量研究院 (METAS)推出至臻天文台认证程序,星座系列尊霸腕表成为全球首款获得该认证的腕表。自此以来,越来越多的欧米茄机械腕表通过METAS核准的严苛测试,成为获得至臻天文台认证的腕表。
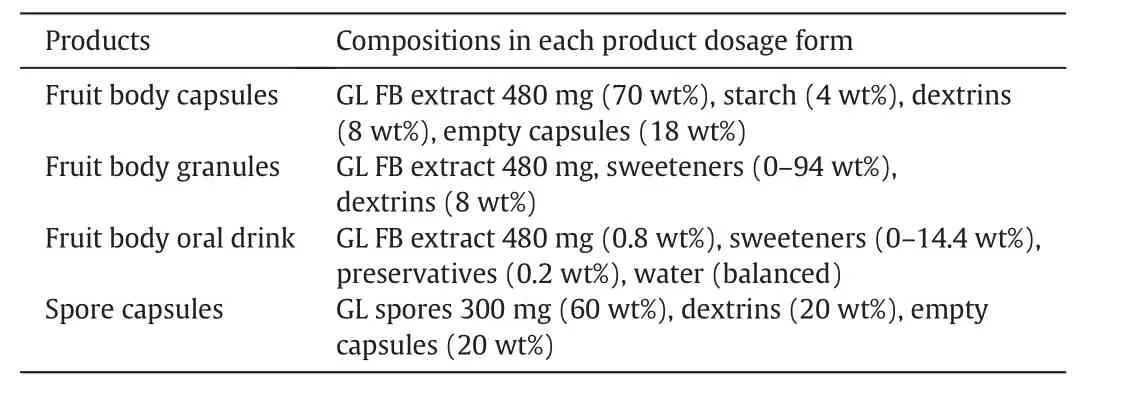
Table 7 Formulations of GL fruit body extract and spores products

Fig.5.A superstructure of the manufacturing process for GL fruit body extract and spores products in the forms of capsules,granules,and,oral drink.

Table 8 Assumptions and input information for calculating the capital cost for GL products including aspects of land and building,facilities,instruments and control,startup expenses,purchased equipment and installation
2.3.Shortlisting product candidates
Many factors and measures can be used to select a product to market.These include pro fit,initial investment,market share,marketing channels,material sources,regulatory restrictions,company mission,and environmental impact,among others.In this paper,three are selected for consideration—market share,initial investment,and pro fit.Capturing market share is an important consideration in a highly competitive market such as the GL dietary supplement.For small and medium-sized enterprises,the amount of initial investment is a sensitive issue because of the potential difficulty in managing the cash flow of the company.Common financial metrics to evaluate an investment are net present value,internal rate of return,and return on investment(ROI).Only ROI is used to illustrate the approach and is defined as the net annual pro fit,the difference between the annual sales revenue and the product cost before tax,divided by the total capital investment.

For this calculation,sales volume(demand),selling price of the product,total product cost,and capital investment as a function of product qualities are required.Complications such as leveraging manufacturing cost for multiple products are not considered.
2.3.1.Shortlisting GL product candidates
The 28 product candidates in Table 6 are reduced to a manageable number by ranking them based on certain criteria.Since customers'preferences on overall quality are deemed important,only products with a QFovscore of 85 or above are accepted.Based on this quality cut-off,eleven candidates are shortlisted(Table 10).As expected,the market share increases with the overall product quality,in agreement with the prediction of the pricing model that a product of higher quality hasa higher demand.Clearly,candidate nos.1,27 and 28 are better than the other options although all three have relatively high initial investment.The top candidate is a spores in hard gel capsule product containing 90%-100%broken spores,which has a QFovscore of 93.75 and an ROI of 13.98%.The other spore product also has an ROI>13%due to a relatively low total product cost.Since the product cost and the initial investment could change by contracting out part of the process,make-buy options are considered next.
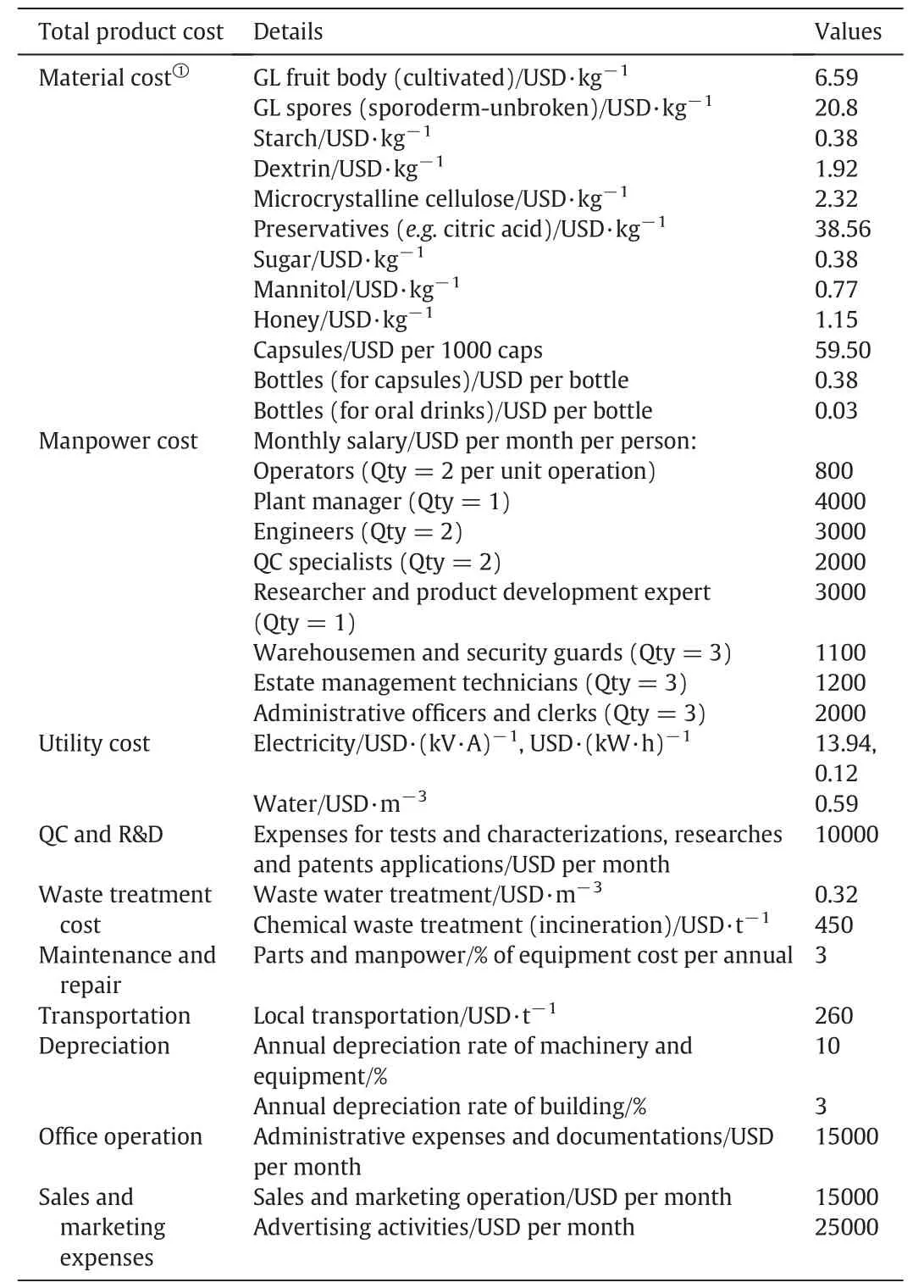
Table 9 Assumptions and input information for calculating the total product cost for GL products including aspects of materials,manpower,utility,QC and R&D,waste treatment,maintenance and repair,transportation,depreciation,office operation,and sales and marketing
2.4.Make-buy analysis
A variety of reasons would trigger make-buy considerations including in-house manufacturing technology,resources availability,intellectual properties,economic bene fits,quality assurance,regulatory restrictions,and company strategic plan.Table 11 summarizes situations that would either favor make or buy options.For instance,a company may consider out-sourcing part of the manufacturing process to vendors in order to save capital investment and time,instead of setting up its ow n facilities.Another reason is the superiority of vendors' technology or regulatory restrictions.How ever,if the manufacturingtechnique is critical to the success of the product and/or the design secrecy is important,it is preferable to keep the process in-house.
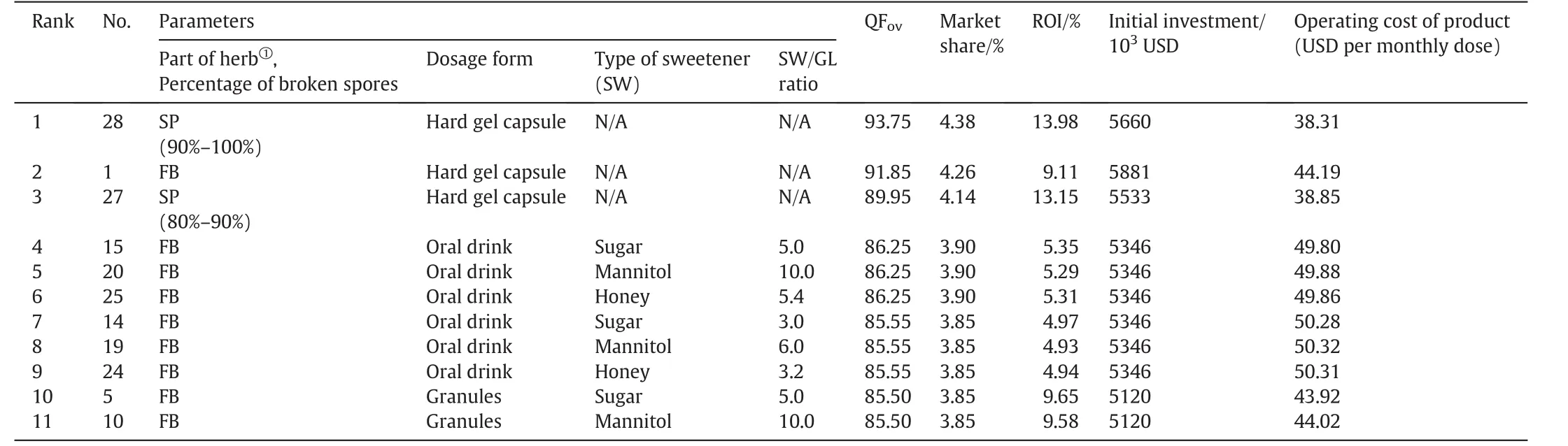
Table 10 Shortlisted product candidates ranked by product quality
Fig.6 depicts the proposed flow of activities involved in the make-buy analysis for chemical products design.To begin,an all make base case for manufacturing a desired product is developed,assuming that all the manufacturing steps are performed in-house.The base case is checked with the guidelines for make-buy decision listed in Table 11.If some buy alternatives are deemed necessary,internal information including the desired time-to-market,capital budget range,manufacturing experiences,and technical knowhow,is used to identify the preliminary buy options.Such internal information is collected from various departments of the company such as production,engineering,research and development,technical support,logistics, finances,human resources,and purchasing.Many combinations of make-buy options can be generated.At this point,external information such as quotations from an identified vendor,location and capabilities of the vendor is obtained.The preliminary buy options become con firmed buy options if the availability and acceptability of such options can be con firmed.Simultaneously,evaluation criteria based on the importance of situations listed in Table 11 should be developed.All con firmed make-buy options are then evaluated and scored based on these criteria.
2.4.1.Make-buy analysis for GL dietary supplement
Only candidate no.28,the top candidate in Table 10,is used to illustrate the make-buy analysis process.The product is a hard gel capsule containing over 90%broken spores.The manufacturing process consists of three sections,feed preparation,capsule filling,and product packaging(Fig.7).The feed preparation section contains the key technology to control the product quality.The spores first go through the sporoderm breaking step by enzymatic treatment at 38°C to obtain 80%broken spores.The spores are then filtered out and part of the filtrate is recycled.The spores are washed with water to remove the remaining enzyme solution.The suspension of spores in water is further processed using micronization technique to further increase the percentage of broken spores to over 90%.Then,the dried spores are sent to a capsule filling machine,w here the quantity of broken spores in each capsule is precisely controlled.The bottling and packaging section includes bottle sterilization,capsule counting,bottle filling,labeling,as w ell as final bottle sealing.This all-make base case leads to an initialinvestment,including equipment cost and building of a plant site,of 5.66 million USD.The management w ants to reduce this amount by considering out-sourcing part of the process.

Table 11 A list of situations initiating the concerns for make-buy decision

Fig.6.Activities involved in the make-buy analysis process for product design and development.
The company has been in the business of manufacturing TCM tincture products for over 10 years,but has no experience in handling GLrelated products and solid dosage form preparation.The in-house TCM experts in the company have sufficient knowledge of the feed preparation for the GL spores process.Strategically,the company intends to develop a family of GL products in the future and hopes that the first GL product reaches market within 24 months.The feed preparation section is considered as the key process affecting product quality,so that the company prefers to keep this section in-house.The internal information related to the GL process is summarized in Table 12.
Also show n in Table 12 is the collected external information indicating that vendors supplying broken spores powder or capsules are available,but most are of uncertain quality and consistency.As show n in the manufacturing process(Fig.7),buying the broken spores powder eliminates the feed preparation step.Buying the broken spore capsules can take out both feed preparation and capsule- filling sections.There are also reliable OEM(original equipment manufacturer)services in the local market that can handle the capsule- filling,and bottling and packaging steps.
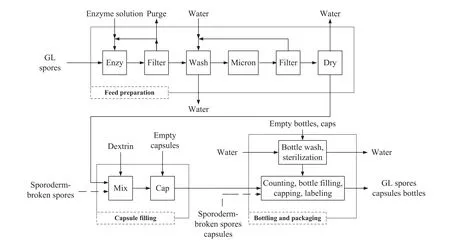
Fig.7.The manufacturing process for the production of GL spore capsules that is composed of feed preparation,capsule filling,and bottling and packaging sections.

Table 12 Current internal and external situations for the case study
Table13 lists the six criteria and the corresponding weighting factors for evaluating the make-buy options.The evaluation,some qualitative and some quantitative,is scored on a five point scale.The first criterion is concerned with product quality.This new product is the company's first TCM dietary supplement product,product quality assurance and control is essential to gain customers' confidence.If the process is fully monitored and the QC is performed every step of the w ay,the score is 5.Reduction of initial investment is important to minimize the investment risk.The initial investment is calculated for all make-buy options under consideration,and 5 is assigned to an option with over 60%reduction.Similarly,5 is assigned to the criterion on total product cost if it can be reduced by over 20%.Another criterion is time-to-market.The shorter the time,the higher the score.Market demand and customers' preference may change with time.It is highly desirable that the plant is sufficiently flexible to meet changing demands and product specifications.The last criterion has to do with logistics in any buy option w here part of the manufacturing is done off-site.
If one considers replacing one or more of the manufacturing sections of the plant by a buy option,there are altogether 8 make-buy options,as listed in Table 14.Option 1 is the all-make base case,while Option 8 is the all-buy option.Options 2 to 7 contain different make-buy combinations.Since external information indicates that no reliable vendors can be found to supply broken spores,the feed preparation section is a must.Also,four OEM companies for both capsule filling and bottling are within 30 min of the company plant site.Thus,Options 1,3,4 and 6 can be con firmed to be realizable.
For each con firmed option,the initial capital investment and operating cost are calculated.With the external information and judgment,the overall score for each con firmed make-buy option is determined(Table14).Option 6 with the highest score of 3.60 provides the best balance among all the evaluation criteria.It offers reasonable flexibility for adjusting process parameters to meet the changes in demand and product specifications.The weak point of this option is its relatively long time-to-market because of the lead time for ordering and installing the necessary equipment.The procedure can be repeated for other candidate products to obtain a more comprehensive analysis,but this is not attempted in this article.The top-scored option,including their advantages and potential risks,would be presented to the management for final decision.
3.Conclusions
An approach for the economic analysis of chemical product design is proposed.It takes into account of customers' preference on product quality and economic considerations.The emphasis is put on the connection between customer preference,product quality,corresponding product attributes/technical specifications,as well as the economic benefits such as product pricing,product sales pro fit,predicted market share,initial capital investment,and operating cost.For TCM dietary supplement,quality is considered as the most important criterion,those products reaching a certain level in the overall quality score are shortlisted.The related pro fit,capital investment,and market share should also be compared.With a shortlist of product candidates and an all-make base case manufacturing process,make-buy analysis can be performed.Many aspects such as manufacturing technology,resources,IP issues,economic benefits,quality assurance,regulatory restrictions,and company strategic plan trigger make-buy considerations.The decision should balance all selection criteria based on the company's situations.Designing both w hat to make and how to make are finally a business decision,company will also need to consider other decision criteria such as stability of supplying raw materials,sales channels and company strategy.
The analysis can continue by further investigating the sensitivity of the target price of the new product on economic returns.As a key element in overall product design and development,the proposed economic analysis in this study would assist,or sometimes alter,the decision on both what to make and how to make.This study proposes the major economic analyses and related activities to be carried out atthe early stage of product development.This analysis can actually be repeated along the development process whenever a critical change in market situation and/or company strategy is observed.

Table 13 Weighting factors and five-point scales for each judgment criteria for make-buy analysis for the GL spore capsule product
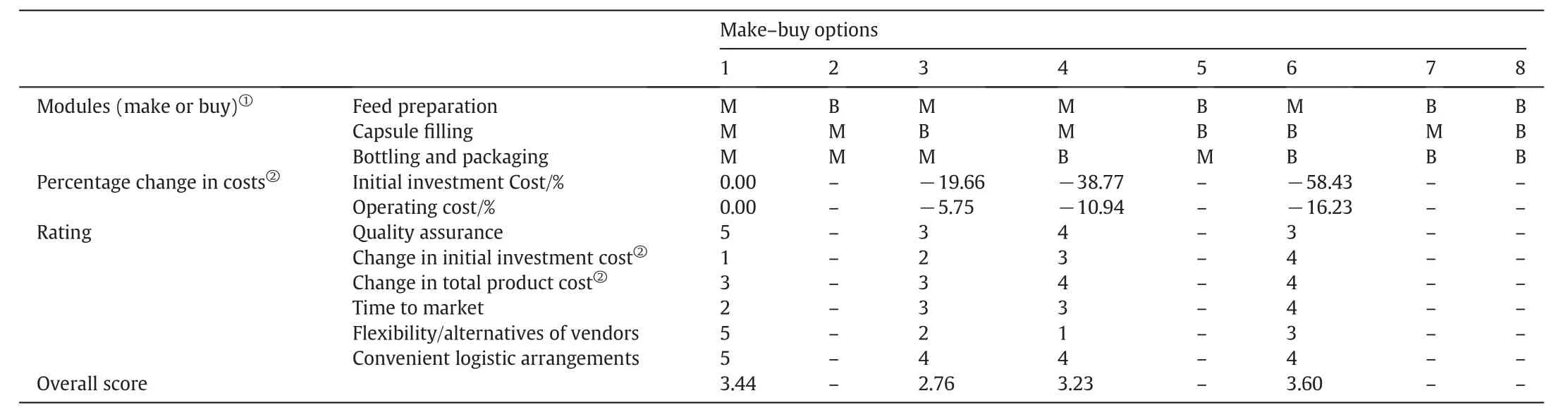
Table 14 Eight make-buy options and their corresponding scores on each judgment criteria
Nomenclature

[1]C.Wibow o,K.M.Ng,Product-oriented process synthesis and development:Creams and pastes,AIChE J.47(2001)2746-2767.
[2]C.Wibowo,K.M.Ng,Product-centered processing:manufacture of chemical-based consumer products,AIChE J.48(2002)1212-1230.
[3]K.Y.Fung,K.M.Ng,Product-centered processing:pharmaceutical tablets and capsules,AIChE J.49(2003)1193-1215.
[4]U.Brockel,C.Hahn,Product design of solid fertilizers,Chem.Eng.Res.Des.82(2004)1453-1457.
[5]K.Wintermantel,Process and product engineering-achievements,present and future challenges,Chem.Eng.Sci.54(1999)1601-1620.
[6]R.Gani,Chemical product design:challenges and opportunities,Comput.Chem.Eng.28(2004)2441-2457.
[7]M.Hill,Product and process design for structured products,AIChE J.50(2004)1656-1661.
[8]E.L.Cussler,G.D.Moggridge,Chemical Product Design,Cambridge University Press,Cambridge,2001.
[9]W.D.Seider,J.D.Seader,D.R.Lewin,Product and Process Design Principles:Synthesis,Analysis,and Evaluation,John Wiley&Sons,New York,N.Y.,2009
[10]U.Bröckel,W.Meier,G.Wagner,Product Design and Engineering:Best Practice,Wiley-VCH,Weinheim;[Chichester],2007.
[11]K.M.Ng,R.Gani,K.Dam-Johansen(Eds.),Chemical Product Design:Tow ard a Perspective Through Case Studies,Elsevier,Amsterdam,2007.
[12]K.M.Ng,R.Gani,K.Dam-Johansen,Special issue on chemical products:from conceptualization to commercialization preface,Comput.Chem.Eng.33(2009)929-929.
[13]K.T.Ulrich,S.D.Eppinger,Product Design and Development,McGraw-Hill/Irw in,Boston,2004.
[14]Y.S.Cheng,K.W.Lam,K.M.Ng,C.Wibowo,An integrative approach to product development—a skin-care cream,Comput.Chem.Eng.33(2009)1097-1113.
[15]Y.S.Cheng,K.M.Ng,C.Wibow o,Prod uct design:A transd ermal patch containing a traditional Chinese medicinal tincture,Ind.Eng.Chem.Res.49(2010)4904-4913.
[16]M.J.Bagajew icz,On the role of microeconomics,planning,and finances in product design,AIChE J 53(2007)3155-3170.
[17]C.Street,J.Wood y,J.Ard ila,M.Bagajew icz,Prod uct design:A case stud y of slow-release carpet deodorizers/disinfectants,Ind.Eng.Chem.Res.47(2008)1192-1200.
[18]C.Whitnack,A.Heller,M.T.Frow,S.Kerr,M.J.Bagajewicz,Financial risk management in the design of products under uncertainty,Comput.Chem.Eng.33(2009)1056-1066.
[19]J.J.Lerou,K.M.Ng,Chemical reaction engineering:A multiscale approach to a multiobjective task,Chem.Eng.Sci.51(1996)1595-1614.
[20]University of Cambridge,Institute for Manufacturing,Industrial make-or-buy decisions[Online]http://w w w.ifm.eng.cam.ac.uk/csp/projects/mvb.htmlJuly 24 2010.
[21]P.Leung,A practical way of research in Chinese medicine,Ann.Acad.Med.Singap.35(2006)770-772.
[22]J.M.Luk,X.Wang,P.Liu,K.Wong,K.Chan,Y.Tong,C.Hui,G.K.Lau,S.Fan,Traditional Chinese herbal medicines for treatment of liver fibrosis and cancer:from laboratory discovery to clinical evaluation,Liver Int.27(2007)879-890.
[23]I.K.Y.Tsang,Establishing the efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine,Nat.Clin.Pract.Rheumatol.3(2007)60-61.
[24]H.L.Tian,T.Yu,N.N.Xu,C.Feng,L.Y.Zhou,H.W.Luo,D.C.Chang,S.F.Le,K.Q.Luo,A novel com pound modified from tanshinone inhibits tumor grow th in vivo via activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway,Cancer Lett.297(2010)18-30.
[25]K.M.Ko,K.M.Ng,Processing control of Chinese herbal products:An ultimate approach for quality assurance,APBM 8(2004)1338-1341.
[26]B.Harjo,C.Wibow o,K.M.Ng,Development of natural prod uct manufacturing processes:phytochemicals,Chem.Eng.Res.Des.82(2004)1010-1028.
[27]B.Harjo,C.Wibow o,E.J.N.Zhang,K.Q.Luo,K.M.Ng,Development of process alternatives for separation and purification of is oflavones,Ind.Eng.Chem.Res.46(2007)181-189.
[28]K.F.Luk,K.M.Ko,K.M.Ng,Separation and purification of schisandrin B from Fructus schisandrae,Ind.Eng.Chem.Res.47(2008)4193-4201.
[29]E.L.Archer,D.K.Boyle,Herb and supplement use among the retail population of an independent,urban herb store,J.Holist.Nurs.26(2008)27-35.
[30]Z.B.Lin,H.N.Zhang,Anti-tumor and immunoregulatory activities of Ganoderma lucidum and its possible mechanisms,Acta Pharmacol.Sin.25(2004)1387-1395.
[31]Y.Q.Zhou,X.T.Yang,Q.Yang,Recent advances on triterpenes from Ganoderma mushroom,Food Rev.Int.22(2006)259-273.
[32]S.C.Jong,J.M.Birmingham,Medicinal benefits of the mushroom Ganoderma,Adv.Appl.Microbiol.37(1992)101-134.
[33]C.W.Huie,X.Di,Chromatographic and electrophoretic methodsfor Lingzhipharmacologically active components,J.Chromatogr.B 812(2004)241-257.
[34]Z.B.Lin,P.Y.Wang,The pharmacological study of Ganoderma spores and their active components,J.Peking Univ.Health Sci.38(2006)541-547.
[35]Chinese-Pharmacopoeia(Ed.),The 8th Edition of Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China,Chemical Industry Press,China,2005.
[36]C.B.Eliason,Dietary supplement users:Demographics,product use,and medical system interaction,J.Am.Board Fam.Pract.10(4)(1997)265-271.
[37]B.Tang,X.Q.Liu,Determination of 5 elements in Ganoderma by ICP-OES,Sino TCM 8(2006)19-21.
[38]Y.Z.Wang,Y.G.Zhu,Y.Z.Huang,A survey on heavy metals in Ganoderma lucidum(LingZhi)and its preliminary health risk assessment,Asian J.Ecotoxicol.1(2006)316-322.
[39]H.L.Koh,S.O.Woo,Chinese proprietary medicine in Singapore—regulatory control of toxic heavy metals and undeclared drugs,Drug Saf.23(2000)351-362.
[40]Chinese Medicine Council of Hong Kong,Technical guidelines—product safety documents(Appendices)Retrieved from http://www.cmchk.org.hk/pcm/eng/idx_down.htm 2004.
[41]S.Melethil,Proposed rule:“Current good manufacturing practice in manufacturing,packing,or holding dietary ingredients and dietary supplements”,Life Sci.78(2006)2049-2053.
[42]V.H.Frankos,Review of FDA's current good manufacturing practices for dietary supplements regulations,dealing with herbal-botanical substances,and the global scope of industry,Planta Med.74(2008)322-322.
[43]W.H.Brow n,C.S.Foote,B.L.Iverson,E.V.Anslyn,Organic Chemistry,Brook/Cole Cengage Learning,Belmont,2009.
[44]M.W.Kearsley,R.C.Deis,Sorbitol and Mannitol,in:H.Mitchell(Ed.),Sweeteners and Sugar Alternatives in Food Technology,Blackw ell Publishing Ltd,Oxford,Ames,Iowa,2006.
[45]G.G.L.Yue,K.Fung,P.Leung,C.B.S.Lau,Comparative studies on the immunomodulatory and antitumor activities of the different parts of fruiting body of Ganoderma lucidum and Ganoderma spores,Phytother.Res.22(2008)1282-1291.
[46]Z.X.Yan,Q.B.Yan,J.X.Liu(Eds.),Ling Zhi Yu Fu Ling,Gui Zhou Ke Ji Chu Ban She,Gui Yang Shi,2002.
[47]J.H.Ni,B.S.Song,H.B.Li,Y.S.Xie,Breaking of the sporoderm of Ganoderma lucidum and its effect on the extraction yield of polysaccharides,Chin.Tradit.Herb.Drugs 33(2002)422.
[48]W.Zhang,Y.S.Zeng,Progress in research on Ganoderma lucidum spore,J.Chin.Integr.Med.2(2004)463-465.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- Effect of ionic liquids on stability of O/W miniemulsion for application of low emission coating products☆
- Characterization and adsorption behaviors of a novel synthesized mesoporous silica coated carbon composite☆
- Experiment and simulation of foaming injection molding of polypropylene/nano-calcium carbonate composites by supercritical carbon dioxide☆
- Salt-free reactive dyeing of betaine-modified cationic cotton fabrics with enhanced dye fixation☆
- A computational analysis of the impact of mass transport and shear on three-dimensional stem cell cultures in perfused micro-bioreactors
- Production and characterization of exopolysaccharides in mycelial culture of Cordyceps sinensis fungus Cs-HK1 with different carbon sources☆
