时延异构多自主体系统的群一致性分析
2016-05-14李向军刘成林刘飞
李向军 刘成林 刘飞


摘要:针对由一阶自主体和二阶自主体构成的异构多自主体系统的静态群一致性问题,分别提出了在固定连接拓扑和切换连接拓扑结构下的静态群一致性算法。通过构造LyapunovKrasovskii 函数,得到了系统在具有相同时变通信时延的群一致性算法作用下渐近收敛群一致的充分条件,并以线性矩阵不等式表示。最后,仿真结果表明, 所提算法在满足一定条件下能使时延异构多自主体系统渐近收敛群一致。
关键词:异构多自主体系统;群一致性;时变通信时延;切换拓扑
中图分类号:TP273 文献标志码:A
Abstract:Concerning the stationary group consensus problem for the heterogeneous multiAgent systems, which are composed of firstorder Agents and secondorder Agents, two stationary group consensus protocols were proposed under fixed interconnection topology and switching interconnection topologies respectively. By constructing LyapunovKrasovskii functions, the sufficient conditions, which are formulated as linear matrix inequalities, were obtained for the system converging to the group consensus asymptotically under the group consensus algorithm with identical timevarying communication delay. Finally, the simulation results show that the heterogeneous multiAgent systems with time delay converg to the group consensus asymptotically under certain conditions.
Key words:heterogeneous multiAgent systems; group consensus; timevarying communication delay; switching topologies
0 引言
近年来,由于在多无人机/无人车系统的协调编队、传感器网络的时钟同步、卫星姿态协调同步等领域的广泛应用,多自主体系统的一致性问题引起了众多领域学者的深入研究,包括物理学、计算机学科、自动控制学科等。
作为多自主体系统协调控制研究中最基本和最主要的问题之一,一致性问题是指多个自主体通过局部协调耦合来实现所有自主体的状态趋于相同。结合图论和矩阵论等,文献[1-4]研究了一阶多自主体系统渐近达到一致的分布式协调算法及其收敛条件。利用频域分析法,Yu等[5]得到了二阶多自主体系统在相同输入时延(或视为同步匹配通信时延)约束下实现动态一致性收敛的充要条件。文献[6-7]考察了具有不同通信时延和输入时延的二阶多自主体系统在静态一致性算法作用下的一致性收敛问题,分别利用频域分析法和Lyapunov函数法得到了一致性收敛的充分条件。此外,自主体动态为一般线性时不变模型[8-9]和非线性模型[10-11]的多自主体系统的一致性问题也得到了广泛关注,利用图论、随机矩阵理论等方法完成了一致性算法设计与收敛性分析。
现有的一致性问题研究主要考察所有自主体最终达到一个相同的一致性状态,但是环境、状况以及合作任务等改变要求自主体对未知状况或变化作出相应的反应,从而整个多自主体系统会出现收敛多个最终一致状态,此现象称为群一致性问题。群一致性问题是指:一个网络中的自主体被划分为不同的子群,在信息交换同时存在于群内自主体和群间自主体的条件下,同一个子群的自主体状态达到一致,不同子群的一致性状态可以不同[12-16]。利用矩阵理论和Lyapunov稳定性理论,Yu等[12]得到了具有固定连接拓扑的一阶多自主体系统达到群平均一致的充分条件,并在文献[13]中采用双树型变换分析了具有切换拓扑结构的一阶多自主体系统在切换拓扑在通信时延约束下的群一致性收敛条件。根据代数图论和矩阵理论,文献[15]给出了二阶多自主体系统在固定连接拓扑下渐近达到群一致的充要条件。Xie等[16]分别用Lyapunov第一法和Hopf分岔法讨论了定常时延对二阶多自主体系统群一致性收敛的影响,并得到了时延相关一致性条件。
在实际的工程应用中,由于外界影响或者通信受限,各自主体通常具有不同的动态,所以针对由不同动态的自主体构成的异构多自主体系统的一致性问题研究更有实际意义[17-19]。根据圆盘定理和Lyapunov稳定性理论,宋运忠等[17]给出了混合一阶和二阶多自主体系统在无向动态切换拓扑结构下渐近达到一致的充要条件。Liu等[18]利用非负矩阵理论得到了具有不同通信时延的混合一阶和二阶多自主体系统在动态切换连接拓扑下一致性收敛的充分条件。根据Lyapunov稳定性理论,梁有明等[19]得到了异构多自主体系统在具有时变输入时延的一致性算法作用下渐进收敛一致的时延相关充分条件,并表示为线性矩阵不等式。根据代数图论和Barbalat引理,Hu等[20]讨论了由参数不确定的欧拉拉格朗日系统和二阶积分器构成的异构多自主体系统的群一致性问题,并给出了系统渐近收敛群一致的充分条件。
考虑到自主体之间信息交换不可避免地会产生通信时延,本文研究了由一阶和二阶自主体组成的异构多自主体系统在时变通信时延约束下的群一致性问题,并根据Lyapunov稳定性理论得到了异构多自主体系统分别在无向固定连接拓扑和无向切换连接拓扑下渐近收敛群一致的充分条件,所得条件均可转化为线性矩阵不等式进行求解。
与文献[12]相似,本文作如下假设:
假设1[12]各自主体与群间邻居自主体的连接权值之和为零。
注1 在本文中,因为允许连接权值为负值,所以Laplacian矩阵并不是对角占优矩阵。与现有文献[1-10]不同,不能保证Laplacian矩阵所有非零特征值均具有正实部。当连接拓扑连通且每个子群都连通时,Yi等[21]给出子群数目与Laplacian矩阵的关系,即子群数目与Laplacian矩阵零特征根的重数相同。
针对Laplacian矩阵,本文将用到如下假设:
假设2 L有且仅有两个零特征值且其余特征值均具有正实部。
2.2 切换连接拓扑
选取N个对应不同连接拓扑图的时间段,在每个时间段上对V(t)求导,并利用引理1和引理2进行放大,其过程与定理1的证明过程类似,从略, 因此,若不等式组(13)和不等式(14)成立,则系统(12)渐近稳定,即异构多自主体系统(11)将渐近收敛至群一致状态。
注2 若通信时延τ(t)满足假设4,即通信时延导数上限大于1或者未知时,能用和推论1相同的方法得到异构多自主体系统在切换拓扑结构下渐近收敛群一致的充分条件。
3 仿真结果
本章利用MaltabSimulink仿真平台,构建自主体动态模型、自主体之间连接,以及引入时变通信时延,完成时延异构多自主体系统的一致性问题的数值仿真研究。
例1 固定拓扑结构下的群一致性收敛。
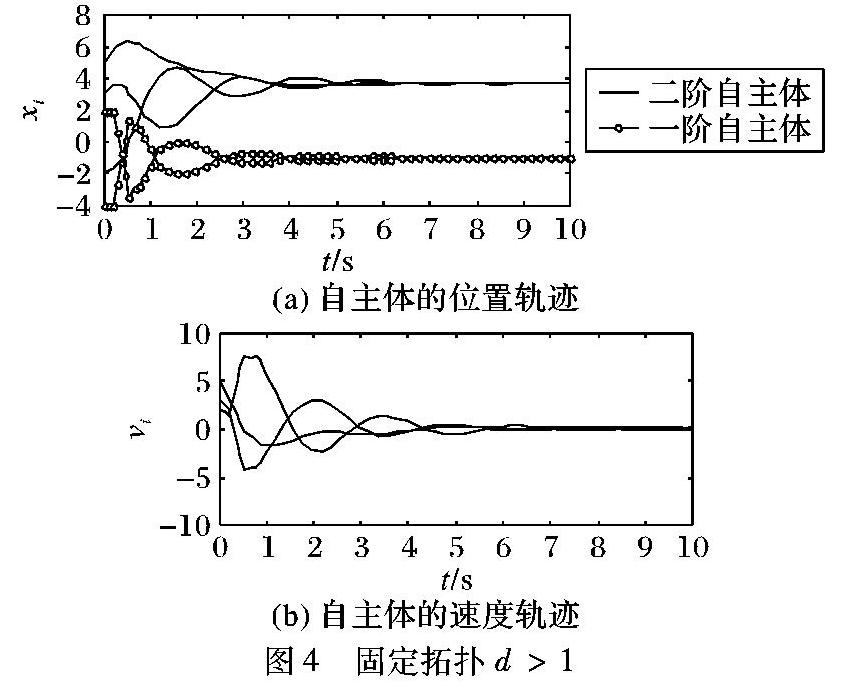
考察5个自主体构成的异构多自主体系统(4),假设含有两个子群,其中二阶自主体1、2、3组成一个子群,一阶自主体4和5组成一个子群。各自主体的初始状态随机产生。 连接拓扑图G如图2所示,连接权值为a12=3,a13=1,a14=-1,a15=1,a24=1,a25=-1,a45=2,则系统的Laplacian矩阵L的特征值为:0,0,1.2984,3,7.7016,进而假设1和2满足。在群一致性算法(3)中,选择控制增益为k=1,通信时延为τ(t)=0.3|sin (t)|,其满足假设3,即通信时延导数小于1。通过用Matlab中的线性矩阵不等式工具箱验证,存在正定矩阵P、Q、R、Z满足线性矩阵不等式(6)和(7),其Simulink仿真结果如图3所示。选择通信时延:τ(t)=0.3|sin (10t)|,其满足假设4,即时延导数上限大于1或者未知,其Simulink仿真结果如图4所示。
由数值仿真发现:在异构多自主体系统渐进收敛群一致过程中,通信时延导数的增大将导致各自主体相对于其一致性状态的超调量增大,这必然会增加各子群渐近收敛至一致的时间,但并不影响多自主体系统最终收敛群一致。
例2 切换拓扑结构下的群一致性收敛。
假设异构多自主体系统(11)由5个自主体组成,其含有两个子群,其中二阶自主体1、2、3组成一个子群,一阶自主体4和5组成一个子群,且各自主体的初始状态随机产生。 不失一般性,考虑异构多自主体系统(11)的连接拓扑在图2和图5中的G、G1之间周期切换,切换周期T=1s。连接拓扑G1的连接权值为:a12=3,a13=1,a14=2,a15=-2,a24=-1,a25=1,a34=-1,a35=1,a45=3,则系统的Laplace矩阵L的特征值为:0,0,0.9050,3.4297,9.6653,假设1和2条件满足。选择控制增益k=1,通信时延选为τ(t)=0.5|sin (t)|,其满足假设3,即通信时延导数小于1。通过用Matlab中的线性矩阵不等式工具箱验证,存在正定矩阵P、Q、R、Z满足线性矩阵不等式组(13)和(14),其Simulink仿真结果如图6所示。选择通信时延:τ(t)=0.5|sin (10t)|,其满足假设 4,即时延导数上限大于1或者未知,其Simulink仿真结果如图7所示,将切换周期改为T=0.1s,其Simulink仿真结果如图8所示。
4 结语
本文研究了由一阶自主体和二阶自主体构成的异构多自主体系统的群一致性问题。通过变量代换,异构多自主体系统的群一致性问题被转化为等价误差系统的渐近稳定性问题。在假设各自主体与群间邻居自主体连接权值之和为零的前提下,利用LyapunovKrasovskii稳定性定理分别得到了具有相同时变通信时延的异构多自主体系统在固定连接拓扑和切换连接拓扑下的群一致性充分条件。值得注意的是:同一子群自主体将渐近趋于一致,不同子群自主体的一致性状态可以不同;一致性收敛可以对通信时延的变化快慢具有鲁棒性,但时延的变化快慢会影响群一致性的收敛速度;同时,一致性收敛对切换拓扑结构的切换频率具有鲁棒性,群一致性收敛不受切换周期大小的影响。
参考文献:
[1]OLFATISABER R, MURR R M. Consensus problems in networks of Agents with switching topology and timedelays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2004, 49(9): 1520-1533.
[2]OLFATISABER R, ALEX FAX J, MURRAY R M. Consensus and cooperation in networked multiAgent systems[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2007, 95(1): 215-233.
[3]LEWIS F L, ZHANG H, HENGSTERMOVRIC K, et al. Cooperative control of multiAgent systemsoptimal and adaptive design approaches[M]. London: SpringerVerlag, 2014:23-43.
[4]ZHANG Y, TIAN Y P. Consentability and protocol design of multiAgent systems with stochastic switching topology[J]. Automatica, 2009, 45(5): 1195-1201.
[5]YU W W, CHEN G R, CAO M. Some necessary and sufficient conditions for secondorder consensus in multiAgent dynamical systems[J]. Automatica, 2010, 46(6): 1089-1095.
[6]LIU C L, LIU F. Consensus problem of secondorder dynamic Agents with heterogeneous input and communication delays[J]. International Journal of Computers, Communications and Control, 2010, 5(3): 325-335.
[7]林茜, 吴晓锋. 时滞多智能体系统关于参考状态的信息一致性[J]. 系统工程学报, 2010, 25(6): 840-846.(LIN Q, WU X F. Consensus in multiAgent systems with delayed communication and reference state[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering, 2010, 25(6): 840-846.)
[8]程龙. 具有复杂动力学的多智能体系统一致性控制及其应用[D]. 北京:中国科学院自动化研究所, 2009. (CHENG L. Consensus control and its application for complex dynamic multiAgent systems[D]. Beijing: Institute of Automation of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2009.)
[9]YOU K Y, LI Z K, XIE L H. Consensus condition for linear multiAgent systems over randomly switching topologies[J]. Automatica, 2013, 49(10): 3125-3132.
[10]LIU Z X. Consensus of a group of mobile Agents in three dimensions[J]. Automatica, 2014, 50(6): 1684-1690.
[11]李韬, 孟扬, 张纪峰. 多自主体量化趋同与有限数据率趋同综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2013,39(11): 1805-1811.(LI T, MENG Y, ZHANG J F. An overview on quantized consensus and consensus with limited data rate of multiAgent systems[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(11): 1805-1811.)
[12]YU J Y, WANG L. Group consensus of multiAgent systems with undirected communication graphs[C]// Proceedings of the 7th Asian Control Conference. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE 2009: 27-29.
[13]YU J Y, WANG L. Group consensus in multiAgent systems with switching topologies and communication delays[J]. Systems & Control Letters, 2010, 59(6): 340-348.
[14]YU J Y, WANG L. Group consensus of multiAgent systems with directed information exchange[J]. International Journal of Systems Science, 2012, 43(2): 334-348.
[15]FENG Y Z, XU S Y, ZHANG B Y. Group consensus control for doubleintegrator dynamic multiAgent systems with fixed communication topology[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2014, 24(3): 532-547.
[16]XIE D M, LING T. Secondorder group consensus for multiAgent systems with time delays[J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 153(4): 133-139.
[17]宋运忠, 谷明琴. 混合阶多智能体无向网络的拟平均一致性[J]. 控制工程, 2009, 16(2): 220-223.(SONG Y Z, GU M Q. Quasiaverage consensus in undirected networks of multiAgents with mixed order integrators[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2009, 16(2): 220-223.)
[18]LIU C L, LIU F. Stationary consensus of heterogeneous multiAgent systems with bounded communication delays[J]. Automatica, 2011, 47(9): 2130-2133.
[19]梁有明, 刘成林, 刘飞. 异质多自主体系统的一致性[J]. 系统工程学报, 2012, 27(5): 583-592.(LIANG Y M, LIU C L, LIU F. Consensus of heterogeneous multiAgent systems[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering, 2012, 27(5): 583-592.)
[20]HU H X, YU W W, XUAN Q, et al. Group consensus for heterogeneous multiAgent systems with parametric uncertainties[J]. Neurocomputing, 2014, 142: 383-392.
[21]YI J W, WANG Y W, XIAO J W. Reaching cluster consensus in multiAgent systems[C]// Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2011: 569-573.
[22]GU K. An integral inequality in the stability problem of timedelay systems[C]// Proceedings of the 39th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2000: 2805-2810.
[23]HE Y, WANG Q G, XIE L, et al. Further improvement of freeweighting matrices technique for systems with timevarying delay[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2007, 52(2): 293-299.
Background
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61473138, 61104092, 61134007), the National Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province(BK20151130).
LI Xiangjun, born in 1989, M. S. candidate. His research interest includes couplegroup consensus control of multiAgent systems.
LIU Chenglin, born in 1981, Ph. D., associate professor. His research interests include decentralized coordinated control of multiAgent systems, nonlinear control.
LIU Fei, born in 1965, Ph. D., professor. His research interests include advanced control, integrated automation industrial process.
