Pathology and molecular characterization of recent Leucocytozoon caulleryi cases in layer f l ocks
2016-04-18HaeRimLeeBonSangKooEunOkJeonMooSungHanKyungCheolMinSeungBaekLeeYeonjiBaeInPilMo
Hae Rim Lee,Bon-Sang Koo,Eun-Ok Jeon,Moo-Sung Han,Kyung-Cheol Min,Seung Baek Lee,Yeonji Bae,In-Pil Mo,✉
1Avian Disease Laboratory,College of Veterinary Medicine,Chungbuk National University,Cheongju 28644,Korea;
2Division of Basic Research,Bureau of Ecological Research,National Institute of Ecology,Seocheon 33657,Korea.
Pathology and molecular characterization of recent Leucocytozoon caulleryi cases in layer f l ocks
Hae Rim Lee1,2,Bon-Sang Koo1,Eun-Ok Jeon1,Moo-Sung Han1,Kyung-Cheol Min1,Seung Baek Lee1,Yeonji Bae1,In-Pil Mo1,✉
1Avian Disease Laboratory,College of Veterinary Medicine,Chungbuk National University,Cheongju 28644,Korea;
2Division of Basic Research,Bureau of Ecological Research,National Institute of Ecology,Seocheon 33657,Korea.
Leucocytozoonosis was found in three layer farms in chickens with suspected fatty liver or fatty liver hemorrhagic syndrome in Korea between 2009 and 2011.These layer chicken f l ocks showed both mortality and decreased egg production for one or two weeks when they were between 59 and 82 weeks old.At the necropsy,the most prominent gross lesions were found in the liver,which was enlarged,had a fragile texture,exhibited yellowish discolorations, and had various hemorrhagic lesions.Tissue reactions associated with megaloschizonts specif i c for Leucocytozoon caulleryi were prominent upon microscopic examination of the liver without signif i cant lipidosis.In addition,the ovaries and uterus were the most affected organs for Leucocytozoon caulleryi multiplication,which led to decreased egg productions.Molecular studies with formalin-f i xed,paraff i n-embedded tissues were performed in search of a partial region of the cytochrome b gene for hemosporidian parasites.Based on these results,the causal agent was determined to be closely related to Leucocytozoon caulleryi reported in Japan and Malaysia.In this study,we describe recently re-occurring leucocytozoonosis in layer chickens,which required histopathology for disease diagnosis.To prevent outbreaks and maintain chicken health and egg production,layer chickens need to be monitored for symptoms of leucocytozoonosis.
chicken leucocytozoonos is,Leucocytozoon caulleryi,layer chicken flocks,histopathology,megaloschizont
Introduction
Leucocytozoonosis in chickens is one of the important poultry diseases caused by the parasitic protozoa Hemosporida belonging to the phylum Apicomplexa.Leucocytozoon caulleryi(L.caulleyri) was f i rst reported in Vietnam in 1909,and leucocytozoonosis in chickens has been endemic to south-eastern Asian countries[1–3].In Korea,starting with its f i rst report in 1959,leucocytozoonosis cases had been continuously reported through the late 1990s[4–8]. However,the prevalence of the disease signi fi cantly decreased after the year 2000 due to improved facilities such as windowless housing[9].
The clinical features and the required method of diagnosis of this hemosporidian disease in the chicken fl ock mainly depend on its life cycle,especially whether the parasite is in the stage of schizogony and gametogony.In the stage of schizogony,sporozoites are transmitted from the salivary glands of an insectvector,Culicoides arakawae(C.arakawae),invade the vascular endothelium in various organs of the chickens, and develop into f i rst generation schizonts.The second generation,observable as megaloschizonts,can be detected with histopathology.Subsequently,megaloschizonts release merozoites which invade and develop into gametocytes in erythrocytes,thus marking the gametogony stage.At this point,leucocytozoonosis can be diagnosed with a blood smear.As the disease progresses,chickens suffer from internal hemorrhages and anemia,resulting in increased mortality and decreased egg productions[10–12].
Although leucocytozoonosis has characteristic clinical signs and pathological lesions,this disease can be confused with other hepatic disorders,such as fatty liver or fatty liver hemorrhagic syndrome(FLHS). Indeed,these hepatic diseases usually occur in the summer,and lead to similar clinical symptoms including a decrease in egg production and mortality,and similar hepatic lesions,such as fragile hepatic tissue texture and hepatic hemorrhages[11–16].However, histopathological examination can clearly differentiate these two hepatic diseases in that chicken leucocytozoonosis shows characteristic megaloschizonts and associated tissue reactions in various organs including the liver[11–12,14–15].Moreover,fatty liver and FLHS lead to fatty vacuoles in hepatocytes,and FLHS additionally presents with reticulolysis and vein degenerative changes[14,17].
In this study,we report the recent occurrence of chicken leucocytozoonosis in layer chicken f l ocks suspected of having fatty liver or FLHS.Gross and microscopic examinations and molecular studies were used to characterize chicken leucocytozoonosis cases. In addition,we emphasize the importance of histopathological diagnosis of poultry diseases in order to control the reoccurrence of this protozoal disease for the health and egg productivity of chickens.
Materials and methods
Case history
Three necropsy cases from different layer farms of four chickens per farm were submitted to the Avian Disease Laboratory in Chungbuk National University between 2009 and 2011.They were 82 weeks old from Kangwon in 2009(farm A),59 weeks old from Kyunggi in 2011(farm B),and 72 weeks old from Chungbuk in 2011(farm C).All of them were reared in conventional cages in windowless houses,and the farms experienced egg production losses for one or two weeks during late summer from the middle of August to September and less than one percent weekly mortality.
Necropsy and laboratory examinations
Necropsy on each case was performed following the standard procedures.Bacteriological examinations were performed with liver culture.Routine screening of avian inf l uenza virus(AIV)were performed for virus isolation and molecular detection with trachea and cecal tonsil samples[18],and PCR for fowl adenovirus serotype-4 (FAdV-4)was performed with liver tissues[19].The organs with gross lesions were f i xed in 10%neutralized formalin,and processed tissues were trimmed, embedded in paraff i n,sectioned at 4 mm,and stained with HE.Microscopic examination was performed with a light microscope.
Molecular analysis with formalin-f i xed paraff i n-embedded tissues
Polymerase chain reaction(PCR)was performed on a partial region of malarial parasites'cytochrome b(cyt b) gene of the mitochondrial genome with formalin-f i xed, paraff i n-embedded(FFPE)tissues with specif i c lesions containing L.caulleryi megaloschizonts.Samples of 4 mm-sectioned FFPE tissues were de-paraff i nized with xylene,and DNA was extracted using RecoverAll™Total Nucleic Acid Isolation Kit(Life Technologies Corporation,Carlsbad,CA,USA).To conf i rm gene extraction eff i cacy,housekeeping genes glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and beta-actin were also amplif i ed[20].Partial cyt b gene of Leucocytozoon spp.was amplif i ed using nested PCR as described by Hellgren et al.(2004)[21],and nucleotide(nt)sequences of PCR products were analyzed with BigDye®Terminator v 3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit and Applied Biosystems 3730xl DNA Analyzer(Applied Biosystems,Foster City,CA,USA).Phylogenetic analysis was performed on the 476 bp sequences of the cyt b gene by the maximum-likelihood method in the Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis(MEGA)software package,version 7.0.14,and comparative sequences used for phylogeny were obtained from GenBank™. The phylogenetic tree was constructed after 1,000 bootstrap replications,and the Kimura two-parameter model was used to estimate the evolutionary distances.
Results
Gross lesions and laboratory examinations
At necropsy,the layer chickens from the three different farms commonly showed friable hepatic lobes,splenomegaly,degenerated ovaries and oviducts, and excessive abdominal fat.Layers in farm A had ruptured livers covered with resultant blood clots over the entire lobe,and there were subcapsular hemorrhageson the margins of both lobes(Fig.1A).Chickens from farm B had yellowish friable livers that showed hemorrhages underneath the capsule as well as pinpoint hemorrhages on the lobes and margins(Fig.1B). Chickens from farm C had hepatomegaly and petechial or necrotic lesions on the lobes(Fig.1C).Spleens were enlarged with hypertrophied white foci,and ovarian follicles were atrophied and misshapen,which is associated with yolk peritonitis or f i brous peritonitis (Fig.1D,E).Other lesions observed in some birds were petechiae in the kidney,enteritis,perihepatitis,an irregular surface of an oviduct,andexcessive abdominal fat(Fig.1F).
Routine screening of AIV had negative results for both biologic and molecular examinations.For hepatic lesions,any bacterial colonies were not isolated from the liver cultures,and FAdV-4 was not detected in the liver samples by PCR.
Microscopic lesions
On the microscopic examination,megaloschizonts specif i c for L.caulleryi were found in various organs examined including the liver,spleen,kidney,heart, lung,pancreas,and reproductive organs,the ovary and oviduct.Each of the L.caulleryi megaloschizonts contained numerous basophilic schizonts in round unilocular structures surrounded by well-def i ned capsular walls,which were eosinophilic-stained,of various sizes,and in either solitary or aggregated forms (Fig.2A).There were various degenerating stages from intact to highly degenerated in the various tissues (Fig.2).Developing megaloschizonts consisted of fulf i lled schizonts in an intact capsule,and some of the schizonts had started to rupture,liberating merozoites from the defective schizonts(Fig.2B).Partially or mostly depleted schizonts had irregular capsules and amorphous structures;the normal structure was hard to recognize after the tissue reactions(Fig.2C,D). Protozoal degeneration induced various tissue reactions in the host.Released merozoites and defective capsules induced inf i ltration with lymphocytes,heterophils, foreign-body giant cells,and macrophages around the periphery of the schizonts(Fig.2C,D).
In livers,each f l ock showed different patterns in regard to histopathologic lesions for parasitism and associated tissue reactions.Chickens from farm A exhibited a multifocal area of coagulative necrosis, where the normal structure of hepatic cords was lost, and foreign-body giant cells were formed around amorphous eosinophilic areas,which were composed of degenerated megaloschizont capsules(Fig.3A). Central and hepatic veins were severely congested and showed lymphocytic venous phlebitis.In farm B,livers showed a group of aggregated megaloschizonts,which ranged from being intact to empty due to liberation of merozoites,which induced foreign-body giant cell formation.In addition,pleomorphic lymphocytes inf i ltrated into almost all the veins,leading to venous phlebitis and periphlebitis(Fig.3B).Lipidosis coverage was less than ten percent in all tissues.In farm C,livers showed multifocal architectural disruptions where eosinophilic matrix with erythrocytes replaced hepatic cords as well as the presence of aggregated forms of parasitism(Fig.3C).
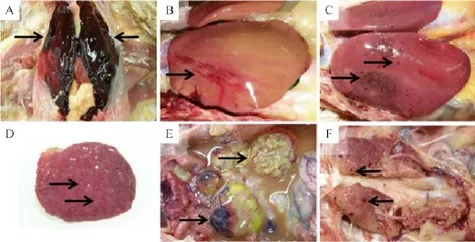
Fig.1 Gross lesions of chicken leucocytozoonosis cases suspected of fatty liver or fatty liver hemorrhagic syndrome in three chicken layer f l ocks between 2009 and 2011.A:The liver lobes from farm A were covered with blood clots(arrows).B:Liver from farm B was yellowish in color,and a subcapsular hemorrhagic region was present(arrow).C:Liver lobes from farm C were enlarged and had multifocal petechiae(arrows).D:The spleen from three f l ocks commonly showed enlargement and white mottling(arrows).E:The ovarian follicles were misshapen,atrophied,and congested(arrows).F:The kidney had multiple pin-point hemorrhages(arrows).
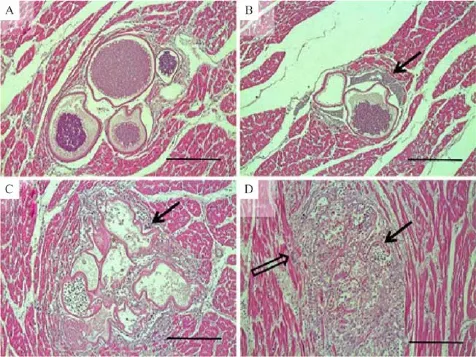
Fig.2 Different stages of Leucocytozoon caulleryi megaloschizont degeneration observed in the heart.A:The intact forms of L.caulleryi megaloschizonts were observed as round,unilocular structures f i lled with numerous basophilic schizonts and surrounded by an eosinophilic capsular wall.These were observed in an aggregated form.B:Here,degenerating megaloschizonts had started to rupture,and merozoites were liberated from the defective schizonts(arrow).C:Partially or mostly depleted schizonts exhibited irregular capsules,and induced inf l ammatory cells and foreign-body giant cells(arrow)surrounded the defective structures.D:Capsular structures became more amorphous(arrow)and induced severe inf l ammatory reactions caused by lymphocytes,heterophils,foreign-body giant cells(open arrow),and macrophages inf i ltrating the periphery of the schizonts.HE staining.Bar=50 mm(A),100 mm(B),50 mm(C),and 100 mm(D).
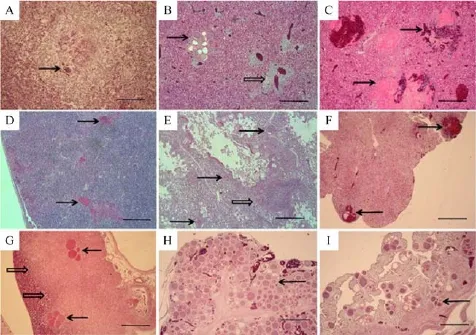
Fig.3 Histopathological f i ndings in the liver,spleen,lung,heart,kidney,pancreas,oviduct,and ovary from three cases of chicken leucocytozoonosis in different chicken layer farms between 2009 and 2011.A:Liver from farm A showed severe coagulative necrosis and eosinophilic amorphous residues of megaloschizont capsules of Leucocytozoon caulleryi surrounded by multi-nucleated giant cells(arrow). B:Liver from farm B showed a group of megaloschizonts specif i c for L.caulleryi,illustrating different degenerate stages(arrow)and pleomorphic lymphocytes inf i ltrated around hepatic veins(open arrow).C:Liver from f l ock C showed multifocal hemorrhages(arrows).D:The spleen showed lymphocytic depletion and eosinophilic residues of degenerating megaloschizonts(arrows).E:In the lung,megaloschizonts were found mostly in solitary forms in both the respiratory lobules and interlobular connective tissues(arrows),and defective schizonts induced mild pneumonitis(open arrow).F:In the kidney,there were hemorrhages(arrows)and interstitial nephritis associated with leucocytozoonosis.G:In the pancreas,the large areas of zymogen depletion in the exocrine cells were found around the groups of megaloschizonts(arrows)and were marginated from unaffected exocrine glands(open arrows).H:In the ovary,a considerable number of schizonts(arrow)multiplied and replaced the normal structure of the ovary.I:In the oviduct,numerous developing megaloschizonts were observed within the lamina propria of the gland, some of which invaded the muscularis layers.HE staining.Bar=200 mm(A)and 500 mm(from(B)to(I)).
Other organs were also affected by Leucocytozoon infections.In the spleen,lymphoid cells were depleted, and irregular eosinophilic structures were found,which resulted from degenerate megaloschizonts(Fig.3D).In the lung,megaloschizonts were found mostly in solitary forms in both the respiratory lobules and interlobularconnective tissues where merozoite-laden alveolar macrophages were found.Defective schizonts induced mild lymphocytic pneumonia(Fig.3E).In the heart,the severity of tissue reactions ranged from no inf l ammatory reactions or reaction only adjacent to the heart to destructive schizonts in the myocardium.However,in other cases,marked accumulation of mononuclear cells was found within the epicardium that extended to the myocardium (Fig.2).In the kidney,there were prominent hemorrhages associated with the degeneration of schizonts,and interstitial lymphocytic inf i ltrations were found(Fig.3F).In the pancreas,zymogen depletion in the exocrine cells was observed in a large area of all the sections around groups of megaloschizonts(Fig.3G).
The reproductive organs,specif i cally the ovaries and oviducts,were the most actively proliferating tissues for L.caulleryi.In the ovary,the parenchymal zone was fi lled with considerable numbers of second-generation schizonts and,as a result,normal ovarian follicles were lost(Fig.3H).Numerous developing megaloschizonts were observed within the lamina propria of the oviduct gland,some groups of which invaded the muscularis layers.Pressure atrophy of the glandular structure in the oviduct was caused by severe parasitism and edema (Fig.3I).However,in fl ammatory cellular in fi ltration was seldom observed despite the release of merozoites or disrupted capsules in both the ovaries and the oviducts.
The organs that exhibited aggregates of L.caulleryi megaloschizonts were identif i ed during the microscopic examinations and studied on a molecular level with FFPE tissues.PCR was used to detect the presence of the partial region of the cyt b gene and was successfully identif i ed in the FFPE tissue from one case.A phylogenetic analysis was performed based on the partial gene of mitochondrial DNA for Leucocytozoon spp.,and we showed that the hematoprotozoa in this study belonged to the L.caulleryi strain.The strain in this study(KX398011)was closely related to the strains reported in Japan in 2008(AB302215.1)and in Malaysia in 2015(KT290933.1)(Fig.4).
Discussion
In Korea,leucocytozoonosis had been problematic in commercial chicken layers since the f i rst report in 1959[5-6],but there have been much fewer reports since 2000.In this study,using histopathology and molecular studies,we conf i rmed the recent occurrences of leucocytozoonosis in layer chicken cases that were suspected to have fatty liver or FLHS.As such,we emphasize the importance of histopathological diagnosis for hepatic diseases in poultry for controlling as well as preventing the re-occurrence of chicken leucocytozoonosis.
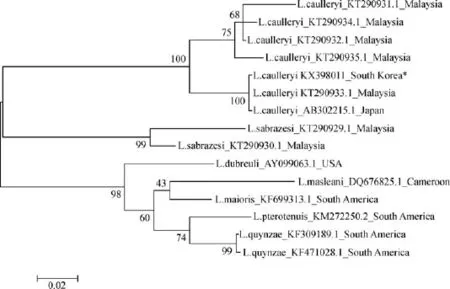
Fig.4 A maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree based on the partial Cytochrome b gene of various Leucocytozoon species in this study (asterisk)and those obtained from GenBank.All strains are indicated by the Leucocytozoon species name,the accession number,and the country where the agent was reported.Bootstrap values(>50%)are listed as percentages after 1,000 replications,and the genetic distances were calculated by the Kimura-two method.The scale bar indicates the number of substitutions per site.
Three cases in this study showed prominent gross lesions on the liver associated with fragile hepatic texture,hepatic hemorrhages,splenomegaly,regressive reproductive organs,and excessive abdominal fat. Unfortunately,these characteristic gross f i ndings could also indicate fatty liver or FLHS.Moreover,in the summer season,laying hens frequently suffer from fatty liver or FLHS,especially those reared in conventional battery cages[13-14,22-23].In addition,other hepatic diseases,such as salmonellosis or inclusion body hepatitis by FAdV-4,could co-occur[24-25],so careful diagnosis is needed so that other hepatic diseases are not overlooked.
Microscopic examinations provide def i nitive diagnosis tools for chicken leucocytozoonosis even though there was lack of molecular evidence for L.caulleryi infections[11,15].Histopathologically,L.caulleyri presents its characteristic megaloschizonts in the vascular endothelium of various organs[8,10,15],which is distinctive from other avian hemosprodians including Leucocytozoon spp.infective for other avian hosts, such as L.simondi for duck leucocytozoonosis[2,26].In this study,all of the three cases were diagnosed as L. caulleryi infection because they were infected with histopathologically identical pathogens characteristic for L.caulleryi,one of which was phylogenetically belonged to L.caulleryi.
In addition,histopathological examination afforded the evidence of co-occurred infection.In the case of farm B,livers of chickens showed intense venous phlebitis and periphlebitis,where veins were inf i ltrated with lymphocytes that showed pleomorphism,indicative for Marek’s disease[27].However,there was not prominent evidence of hepatic lipidosis in any of the three cases,which meant that the hepatic lesions were not largely due to lipidosis or FLHS.For the possible co-occurred infections of hepatic diseases,there were no evidence of bacterial infection and FAdV-4 infection from the laboratory examination.
Even though the histopathology for L.caulleryi was the def i nitive tool for diagnosis,recent occurrence of chicken leucocytozoonosis is so rare that gross and microscopic lesions of this protozoal disease could be overlooked and unrecognized.In this study,three cases were undiagnosed and left as unknown cases,and only formalin-f i xed or FFPE tissues were kept for the longperiod storage.Fortunately,FFPE tissues have advantages that we could target the exact locations of the undiagnosed agents on microscopy and take samples for molecular characterization in the absence of fresh or refrigerated tissues.However,PCR with FFPE tissues need to be careful because it could fail to react due to the preservation status[28].
Molecular studies on a partial region of hemoprotozoal cyt b gene suggested that the strain in this study was closely related to L.caulleryi reported in Japan and Malaysia,where chicken leucocytozoonosis was endemic.As a vector-borne disease,the occurrence of chicken leucocytozoonosis is strongly associated with the distribution of its insect vector,C.arakawae[29]. Culicoides spp.has been an abundant fauna among hematophagous insects and has been reported in various regions of Asia where the climate,land use,and vegetation meet the demand for survival and reproduction for these disease-vector insects[30].The large distribution of C.arakawae throughout Asian countries could predispose the transmission and circulation of L. caulleryi,and strong winds and typhoons that occur in the summer could promote the prevalence of chicken leucocytozoonosis in late summer or early fall[31].
通过诊断性评价、 形成性评价、总结性评价构建出了在SPOC模式下ERP课程的评价体系,从理论层面有效保障了课程教学目标与学生学习目标的达成。
C.arakawae is a species that prefers an avian host, and a greater population of C.arakawae were captured near chicken farms than livestock farms[30,32].In this sense,biosecurity is important for preventing this ornithophilic insect from contacting chickens.The introduction of windowless houses was attributed to a decrease in the occurrence of chicken leucocytozoonosis in the early 2000s in Japan[9,30].However,the chickens from the farms in this study were infected with chicken leucocytozoonosis despite being reared in windowless houses.This means that Culicoides inf i ltrated the physical biosecurity barrier and contacted the chickens.Moreover,as the demand for the organic products and the interest in animal welfare are increasing[33-34],there are more open area farms and more chances for chickens to come into contact with insect vectors.Thus,there is currently a greater opportunity for outbreaks of chicken leucocytozoonosis[9,22,29,35].
Importantly,farmers and veterinarians need to be cognizant of the symptoms of chicken leucocytozoonosis and need to be aware that is a possible egg production-related disease in layer chickens in Korea, especially in the summer.In this study,the pathogenesis of egg production losses was histopathologically observed in the ovary and oviduct.Considerable numbers of megaloschizonts were found in the ovary and in the uterus,which resulted in malfunction of ovum production and oviductural secretion.The importance of controlling and preventing leucocytozoonosis in egg-laying hens has been reported in Japan where chicken leucocytozoonosis has continually been a problem[11-12].
In this sense,when poor health or egg production problems arise in layer chicken in Korea,chicken leucocytozoonosis needs to be considered as a possiblecause.Histopathologic examinations are an important tool for accurately diagnosing poultry diseases,especially in liver diseases,as leucocytozoonosis can easily be confused with fatty liver or FLHS and can occur in spite of windowless houses.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the veterinarians involved for their cooperation and help in the sample collection. Funding for this research was provided by the project of National Institute of Environment Research(No. 2015080777).
[1] Mathis C,Léger M.Trypanosome de la poule[J].C R Seances Soc Biol Fil,1909,67:452–454.
[2] McDougald L.Protozoal Infections[A].In:Swayne D,Glisson J,McDougald L,Nolan L,Suarez D,Nair V,(eds.).Diseases of Poultry[M].13 ed.Aimes:Wiley-Blackwell;2013.1147–1201.
[3] Morii T,Shiihara T,Lee YC,et al.Seroimmunological and parasitological surveys of Leucocytozoon caulleryi infection in chickens in several Asian countries[J].Int J Parasitol,1981,11 (3):187–190.
[4] Chung KT,Choi HJ,Shin JB,et al.Survey of Slaughtered Chicken Leucocytozoon Infection Rate in Pusan,Gyeongnam Area[J].Korean J Vet Serv.,1990,13:189–195.
[5] Jang DW.Protozoan infection of the domestic animals and poultry in Korea[J].Kisaengchunghak Chapchi,1975,13(1): 1–6.
[6] Lee KP.Chicken hemoprotozoa[J].J Korean Vet Med Assoc., 1963,7:20–30.
[7] Lee YH,Park KS,Oh SJ.Studies on Epidemiological Survey of Infectious Disease of Chicken in Korea[J].Korean J Poult Sci., 1989,16:175–192.
[8] Rim BM,Suh IS,Rhee JK,et al.Studies on leucocytozoonosis of chickens in Honam districts[J].Korean J Vet Res.,1994,34: 135–139.
[9] Sakai T.Current status and countermeasures of chicken leucocytozoonosis in Japan[J].Journal of Animal Protozooses (Japan),2007,22:14–21.
[10]Nakamura K,Mitarai Y,Tanimura N,et al.Pathogenesis of reduced egg production and soft-shelled eggs in laying hens associated with Leucocytozoon caulleryi infection[J].J Parasitol,1997,83(2):325–327.
[11]Nakamura K,Ogiso M,Shibahara T,et al.Pathogenicity of Leucocytozoon caulleryi for specif i c pathogen-free laying hens [J].J Parasitol,2001,87(5):1202–1204.
[12]Valkiunas G.Avian Malaria Parasites and other Haemosporidia [M].1 ed.Boca Raton,Florida:CDC Press;2004.
[13]Butler EJ.Fatty liver diseases in the domestic fowl—a review [J].Avian Pathol,1976,5(1):1–14.
[14]Crespo R,Shivaprasad H.Developmental,Metabolic,and Other Noninfectious Disorders[A].In:Swayne D,Glisson J, McDougald L,Nolan L,Suarez D,Nair V,(eds.).Diseases of poultry[M].13 ed.Aimes:Wiley-Blackwell;2013.1233–1270.
[15]Miura S,Oshima K,Itakura C,et al.A histopathological study on leucocytozoonosis in young hens[J].Nihon Juigaku Zasshi, 1973,35(3):175–181.
[16]Squires EJ,Leeson S.Aetiology of fatty liver syndrome in laying hens[J].Br Vet J,1988,144(6):602–609.
[17]Martland MF,Butler EJ,Fenwick GR.Rapeseed induced liver haemorrhage,reticulolysis and biochemical changes in laying hens:the effects of feeding highand low glucosinolate meals[J]. Res Vet Sci,1984,36(3):298–309.
[18]Swayne DE,Halvorson DA.6.Inf l uenza.In:Swayne D, Glisson J,McDougald L,Nolan L,Suarez D,Nair V,(eds.)[J]. Diseases of Poultry.13ed.Aimes:Wiley-Blackwell;2013, 181–218.
[19]Meulemans G,Boschmans M,Berg TP,et al.Polymerase chain reaction combined with restriction enzyme analysis for detection and differentiation of fowl adenoviruses[J].Avian Pathol,2001,30(6):655–660.
[20]De Boever S,Vangestel C,De Backer P,et al.Identif i cation and validation of housekeeping genes as internal control for gene expression in an intravenous LPS inf l ammation model in chickens[J].Vet Immunol Immunopathol,2008,122(3-4):312–317.
[21]Hellgren O,Waldenström J,Bensch S.A new PCR assay for simultaneous studies of Leucocytozoon,Plasmodium,and Haemoproteus from avian blood[J].J Parasitol,2004,90(4): 797–802.
[22]Fossum O,Jansson DS,Etterlin PE,et al.Causes of mortality in laying hens in different housing systems in 2001 to 2004[J]. Acta Vet Scand,2009,51:3.
[23]Trott KA,Giannitti F,Rimoldi G,et al.Fatty liver hemorrhagic syndrome in the backyard chicken:a retrospective histopathologic case series[J].Vet Pathol,2014,51(4):787–795.
[24]Fitzgerald SD.Adenovirus Infections[A].In:Swayne D, Glisson J,McDougald L,Nolan L,Suarez D,Nair V,(eds.). Diseases of Poultry[M].13 ed.Aimes:Wiley-Blackwell;2013, 289–331.
[25]Gast RK.Salmonella Infections[A].In:Swayne D,Glisson J, McDougald L,Nolan L,Suarez D,Nair V,(eds.).Diseases of Poultry[M].13 ed.Aimes:Wiley-Blackwell;2013,677–736.
[26]Gardiner CH,Fayer R,Dubey J.An atlas of protozoan parasites in animal tissues[J].Washington:US Department of Agriculture,Agricultural Research Service;1988,72–75
[27]Nair V.Neoplastic Diseases[A].In:Swayne D,Glisson J, McDougald L,Nolan L,Suarez D,Nair V,(eds.).Diseases of Poultry[M].13ed.Aimes:Wiley-Blackwell;2013,513–673.
[28]Ludyga N,GrünwaldB,Azimzadeh O,et al.Nucleic acids from long-term preserved FFPE tissues are suitable for downstream analyses[J].Virchows Arch,2012,460(2):131–140.
[29]Yu CY,Wang JS,Yeh CC.Culicoides arakawae(Diptera: Ceratopogonidae)population succession in relation to leucocytozoonosis prevalence on a chicken farm in Taiwan[J].Vet Parasitol,2000,93(2):113–120.
[30]Wirth WW,Hubert AA.The Culicoides of Southeast Asia (Diptera:Ceratopogonidae)[J].Washinton DC:Walter Reed Army Inst of Research,1989.
[31]Sellers RF.Weather,host and vector—their interplay in the spread of insect-borne animal virus diseases[J].J Hyg(Lond), 1980,85(1):65–102.
[32]Cho HC,Chong CS.Notes on biting midges of the genus Culicoides from South Korea-with special reference to unrecorded species and distribution[J].Kisaengchunghak Chapchi,1974,12(1):45–75.
[33]Hughner RS,McDonagh P,Prothero A,et al.Who are organic food consumers?A compilation and review of why people purchase organic food[J].J Consum Behav,2007,6:94–110.
[34]Yiridoe EK,Bonti-Ankomah S,Martin RC.Comparison of consumer perceptions and preference toward organic versus conventionally produced foods:a review and update of the literature[J].Renew Agric Food Syst,2005,20:193–205.
[35]Uslu U,Dik B.Chemical characteristics of breeding sites of Culicoides species(Diptera:Ceratopogonidae)[J].Vet Parasitol,2010,169(1-2):178–184.
CLINICAL TRIAL REGISTRATION
The Journal requires investigators to register their clinical trials in a public trials registry for publication of reports of clinical trials in the Journal.Information on requirements and acceptable registries is available at www.icmje.org/faq_clinical.html.
✉Corresponding author:In-Pil Mo,Avian Disease Laboratory, College of Veterinary Medicine,Chungbuk National University, Cheongju,Chungbuk 28644,Republic of Korea,Fax:+82-43-261-3356/+82-43-267-3150;Email:moip@cbu.ac.kr.
©2016 by the Journal of Biomedical Research.All rights reserved
Received 2 May 2016,Revised 17 June 2016,Accepted 1 July 2016, Epub 20 August 2016
R183,Document code:A
The authors reported no conf l ict of interests.
10.7555/JBR.30.2016K0017
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
THE JOURNAL OF BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH的其它文章
- Modified methods for isolation of pancreatic stellate cells from human and rodent pancreas
- Retrograde traff i cking of VMAT2 and its role in protein stability in non-neuronal cells
- Protein inhibitor of activated STAT 4(PIAS4)regulates liver fi brosis through modulating SMAD3 activity
- Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces cardiac inf l ammation and dysfunction in a rat obstructive sleep apnea model
- Assessment of atrial electromechanical interval using echocardiography after catheter ablation in patients with persistent atrial f i brillation
- Elevated thyroid stimulating hormone levels are associated with metabolic syndrome in a Chinese community-based population of euthyroid people aged 40 years and older
