基于改进HHT的泵站管道工作模态辨识
2016-03-21张建伟朱良欢华北水利水电大学水利学院郑州450011
张建伟,江 琦,朱良欢,王 涛,郭 佳(华北水利水电大学水利学院,郑州 450011)
基于改进HHT的泵站管道工作模态辨识
张建伟,江琦,朱良欢,王涛,郭佳
(华北水利水电大学水利学院,郑州 450011)
摘要:为提高管道工作模态辨识精度,在希尔伯特-黄变换(Hilbert-Huang Transform,HHT)辨识基础上,发展奇异值分解(singular value decomposition,SVD)和经验模态分解(empirical mode decomposition,EMD)联合滤波技术与HHT时频域辨识结合的模态辨识方法。SVD-EMD联合滤除结构振动信号中的强噪声,凸显结构振动特性,有效避免了后期HHT参数辨识过程中虚假模态干扰,提高辨识精度和准确性。将该方法应用于景泰二期工程3泵站2管道的模态参数辨识问题中,建立该管道有限元模型并计算其结构动力特性。对比该文方法辨识结果、随机子空间辨识结果与有限元计算结果,该文方法辨识结果稍小于随机子空间辨识结果,与有限元计算结果更接近,其最大辨识误差为3.6%。研究表明,该方法能准确辨识管道频率,且有效降低管道结构背景强噪声。该研究可为管道安全运行和在线健康监测提供参考。
关键词:振动;有限元法;信号分析;泵站管道;供水;模态参数辨识
张建伟,江琦,朱良欢,王涛,郭佳. 基于改进HHT的泵站管道工作模态辨识[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(2):71-76.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.02.011http://www.tcsae.org
Zhang Jianwei, Jiang Qi, Zhu Lianghuan, Wang Tao, Guo Jia. Modal parameter identification for pipeline of pumping station based on improved Hilbert-Huang transform[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(2): 71-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.02.011 http://www.tcsae.org
Email:zjwcivil@126.com
0 引 言
压力管道在水利、农业、工业等领域的输水输气中广泛应用,特点是规模大、运行时间长,因此管道安全稳定运行尤为重要。振动对于管道是交变动荷载,长期的振动会引起管道和支吊架材料的疲劳破坏,影响与管道相连设备的安全运行[1-3]。尤其在结构应力集中处,疲劳破坏引发管线断裂、水流外泄,造成严重的生产事故。
美国OakRidge国家实验室开发的电磁超声应力腐蚀裂纹检测系统成功应用在天然气长输管道中[4];Questar公司推出ITI视频内窥镜检测管道损伤情况,之后又推出无损检测方法辨识管道结构损伤状况[5-6],无损检测多采用超声导波技术、磁场探测技术及X射线探伤等方法。上述方法及检测仪器虽然先进,但检测对象有局限性,价格昂贵,专用性强[7],且不能实现实时在线健康监测。随着神经网络、小波等现代信息处理技术发展[8-10],潘虹等[11]提出利用小波包处理管道振动信号得到结构动力特性,进而判别损伤程度,但小波包分析局限于高频信号辨识,导致辨识结果不完整。泵站输水管道主要受水力激振和外界环境激励影响,振动信号属于非线性非平稳低信噪比信号,结构振动特性淹没在低频水流脉动噪声中,故寻找高效的现代化管道安全健康检测方法成为研究热点[12]。
基于环境激励下模态参数辨识方法是近几年快速发展的结构健康损伤辨识方法,该方法辨识结果能真实反映结构正常运行状态下动力特性,且辨识精度高,在诸多领域广泛应用[13-18]。Huang N E[19]提出的希尔伯特-黄变换(Hilbert-Huang Transform,HHT)适用于非线性非平稳信号,具有自适应性、且不需要“先验”知识等优点而广受瞩目。国内诸多学者提出利用HHT辨识不同领域结构模态参数。薛延刚等[20]将HHT方法引入到水轮发电机组空化信号特征提取中,提取出具有明确物理意义的水轮机空化模式分量信号;单德山等[21]采用改进的HHT方法有效地识别桥梁结构的频率、阻尼等模态参数;李成业等[22]采用HHT方法辨识高拱坝泄流结构模态参数。
因此,为提高管道模态参数辨识准确性和精度,结合奇异值分解(singular value decomposition,SVD)和经验模态分解(empirical mode decomposition,EMD)联合滤波技术(简写为SVD-EMD)的优越性,提出基于改进HHT的泵站管道工作模态辨识方法,以期为管道安全运行和在线健康监测提供参考。
1 SVD-EMD联合滤波技术
奇异值分解是利用矩阵奇异值分解理论处理信号的数据驱动方法。其降噪本质在于信号相空间重构矩阵后,经奇异值分解得到的矩阵奇异值是唯一的,同时奇异值具有稳定性、比例不变形等性质,使得奇异值作为一种有效描述信号内在属性的代数特征应用于信号处理中。SVD具有很强的滤除高频随机白噪声的能力,但其实质属于低通滤波[23],无法滤除低频水流噪声,因此,需要对SVD降噪后信号进一步进行低频水流噪声处理。EMD根据信号自身特性自适应分解成一系列从高频到低频的固态模量(intrinsic mode function,IMF),每一阶IMF都能反映一定的物理意义,可通过分析每一阶固态模量频谱特性进行信号降噪重构。
结合SVD和EMD的降噪特点,针对含高频白噪声和低频水流噪声的低信噪比信号进行SVD-EMD联合的滤波降噪。首先,利用SVD滤除高频白噪声,其次,对SVD降噪后信号再进行EMD处理,滤除低频水流噪声,最后,得到反映结构振动特性的信号。SVD-EMD联合滤波降噪流程图如图1所示。

图1 SVD-EMD联合滤波方法流程图Fig.1 Flow chart of combined singular value decomposition and empirical mode decomposition filtering method
2 工作模态参数辨识方法
2.1自然激励技术
实际工程应用中脉冲响应获取十分困难,因此,利用系统脉冲响应函数进行结构模态辨识受到限制。美国SADIA国家实验室提出环境激励下的自然激励技术(natural excitation technique,NExT),该方法利用白噪声环境激励下结构两点间互相关或自相关函数代替脉冲响应函数进行模态参数辨识[24]。
2.2基于奇异熵增量的结构工作模态定阶
利用输出响应识别结构模态参数,结构的模态阶次是一个重要的参数。由于结构系统未知,通常在模态辨识中会假定系统阶次,这种人为主观假设必定导致结果不准确,无法真实反映结构运行健康状况。为解决这一难题,采用奇异熵增量概念对系统定阶。
奇异熵增量理论定阶思想是[25]:对于同一脉冲响应信号,无论其受到的噪声干扰程度如何,完整提取其有效特征信息所需的奇异谱阶次是一定的,即结构系统阶次一定。故可选取奇异熵增量开始降低到渐近值时的对应阶次作为系统模态阶次。
2.3希尔伯特-黄变换模态参数辨识
根据NExT理论,选择受迫振动量较小的测点作为参考点,计算同工况下其它测点与参考点之间的互相关函数,将之作为脉冲响应函数进行EMD分解,得到的各阶IMF分量即为结构的自由衰减响应,其函数表达式为

式中x(t)为脉冲响应信号;A0表示与荷载强度、结构质量和频率特性等有关的常数;ξ表示相对阻尼系数;ω0为结构系统的无阻尼固有圆频率,Hz;x0为初始位移,m;ωd为有阻尼固有圆频率,Hz;t为时间,s;φ0为初始相位角,(°)。
对式(1)进行Hilbert变换,得到x(t)的解析信号
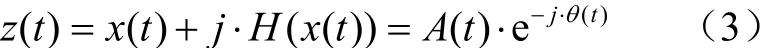
在阻尼较小、频率较高情况下,式(3)幅值及相位可表示为
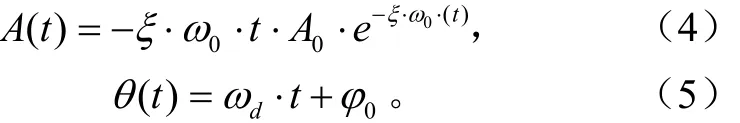
对式(4)和式(5)分别取对数并进行微分
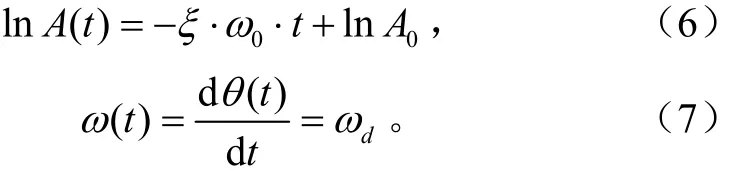
由式(7)可得到ωd,则系统的固有圆频率ω0和阻尼比ξ可通过式(2)求得。
对于管道振动信号,为提高模态辨识精度,减少虚假模态干扰,结合SVD-EMD联合降噪优势,提出基于改进HHT的泵站管道工作模态辨识方法。首先对现场采集振动信号进行SVD-EMD联合滤波前处理,减少强噪声干扰,利用奇异熵增量理论确定系统模态阶次,然后采用HHT辨识降噪后信号获得结构振动动力特性。
3 工程实例应用
3.1景泰工程实例
甘肃景泰电力提灌工程(简称景泰工程)是一项高扬程、大流量、多梯级电力提水灌溉工程。以二期3泵站工程的2号压力管道为研究对象进行工作模态参数识别。2号管道(4号、5号机组)布置型式为多机单管,3个拾振器作为一组,分别沿管道的径向、轴向和铅垂方向布置。试验采用中国地震局工程力学研究所研制的891-2型拾振器,该拾振器设有小速度、中速度、大速度和加速度4档,具有体积小、质量小、使用方便、动态范围大和一机多用的特点,根据管道的工作振动特点,选用中速度档位,该档位下12个水平拾振器的灵敏度范围在7.394~7.543 V·s/m之间,6个垂直拾振器的灵敏度范围在6.729~6.920 V·s/m之间。现场测点布置和压力管道测点具体布置见图2。
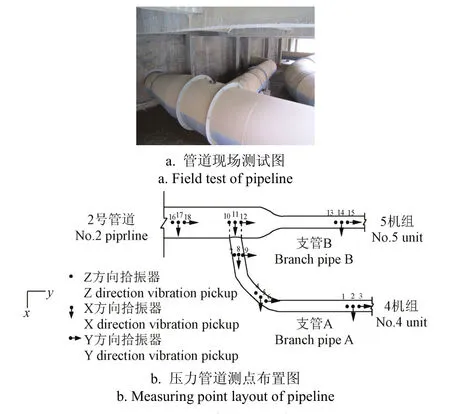
图2 景泰3泵站2号管道现场测试和测点平面布置图Fig.2 Field test and measuring point layout of 3pumping station 2pipeline in Jingtai
以4号、5号机组正常运行为实测工况,测试采样频率204.8 Hz,采样时间为1 500 s。为全面反映主管和支管间耦合作用的整体振动情况、保证辨识结果的准确性,分别选择铅垂z方向13#和16#测点数据、水平x方向8# 和17#测点数据和水平y方向6#和9#测点数据。该6个测点分别位于2号主管端部和A、B支管的端部和中部,其中z方向和x方向测点可反映主管和支管B的耦合振动作用,y方向测点可反映主管和支管A的耦合振动作用。
以z方向13#和16#测点为例说明本文方法辨识管道结构工作模态参数过程。首先,对13#和16#测点采用SVD-EMD联合滤波方法得到降噪后信号,降噪前后信号时程线如图3所示。

图3 13#和16#点信号降噪前后时程Fig.3 Time history curves of original signal and de-noised signal at points13# and 16#
其次,对降噪后信号进行HHT模态参数辨识。对13# 和16#测点滤波降噪后信号进行NExT处理得到两点间互相关函数,互相关函数如图4所示。由图4可知函数逐渐衰减最后收敛成一条直线,表明两测点通过SVD-EMD联合降噪处理基本滤除环境强噪声,可利用互相关函数代替脉冲响应函数进行HHT模态参数辨识。结合奇异熵增量随奇异谱阶次变化曲线确定模态阶次,如图5所示,当奇异谱阶次为12阶时,对应的奇异熵增量开始逐渐趋于平稳,剔除系统非模态项和共轭项之后,得到管道系统有效振动阶次为6阶。
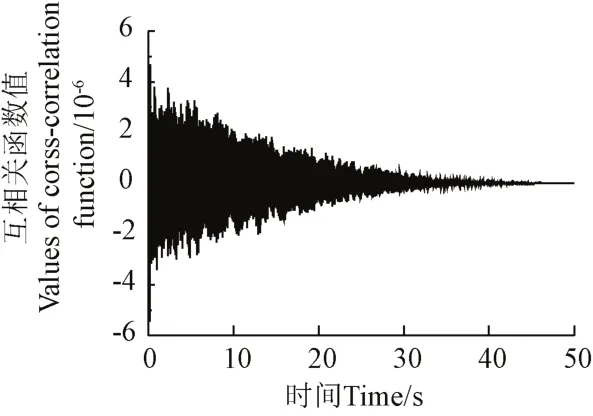
图4 13#和16#测点降噪后互相关函数图Fig.4 Cross-correlation function of de-noised signal between 13# and 16#
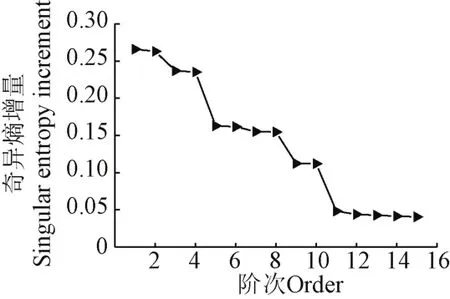
图5 奇异熵增量随奇异谱阶次变化曲线Fig.5 Curve between increment of singular entropy and order
确定互相关函数和结构系统阶次后,对互相关函数进行EMD分解获得每一阶IMF分量,采取适时剔除序列两端数据的方法抑制端点效应、提高分解质量。之后将每一阶IMF分量进行Hilbert变换,根据式(6)和式(7)分别求出幅值对数曲线和相位曲线,利用最小二乘法分别拟合两曲线中间部分得到拟合直线并求出拟合直线斜率。第一阶模态对数幅值曲线及其拟合直线如图6a所示,第一阶相位函数曲线及其拟合直线如图6b所示。将求得的拟合直线的斜率数值代入式(2)求得结构固有圆频率ω0和阻尼比ξ。
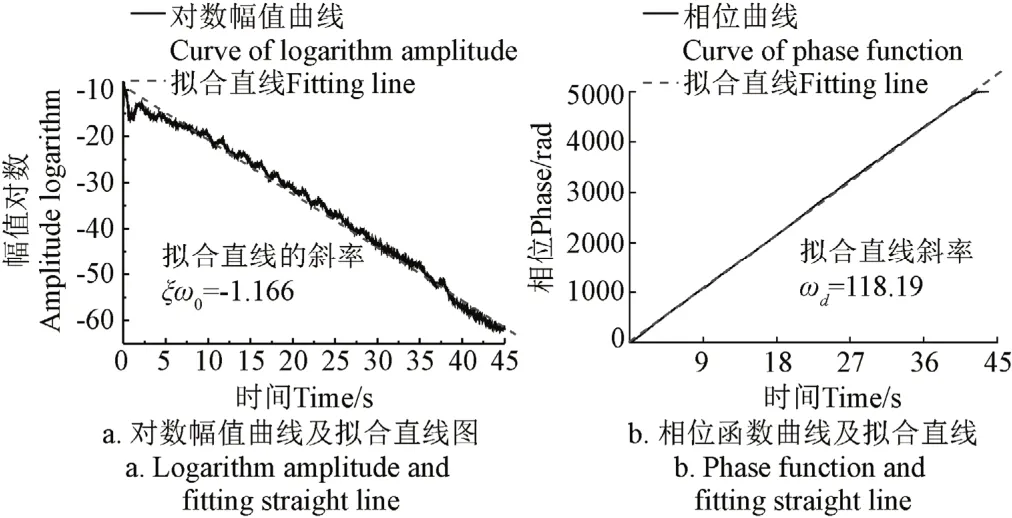
图6 模态参数识别过程图Fig.6 Process of modal parameters identification
为避免某一时间段内数据计算结果的偶然性,对同工况下实测的1 500 s数据,每隔100 s选取50 s数据采用本文方法计算管道结构模态参数,共得10组模态辨识结果,每一组数据分别计算得到前6阶模态频率,利用稳定图法对这10组计算结果求每一阶频率均值。稳定图横坐标为频率,纵坐标为试验组数,在稳定图中标记每一组模态识别得到的前6阶频率,将10组模态辨识结果依次标记完成,频率稳定图如图7所示。根据图7标记的10组试验的前6阶频率结果,计算每一阶频率均值作为管道结构最终结果,前6阶频率均值计算结果见表1。
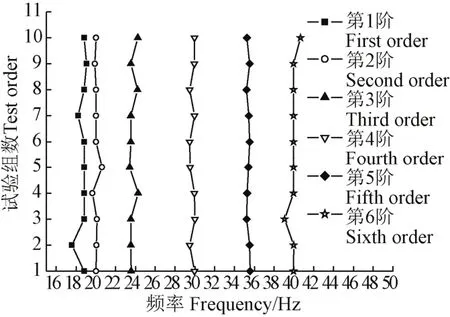
图7 管道模态频率稳定图Fig.7 Stabilization diagram of modal frequency of pipe
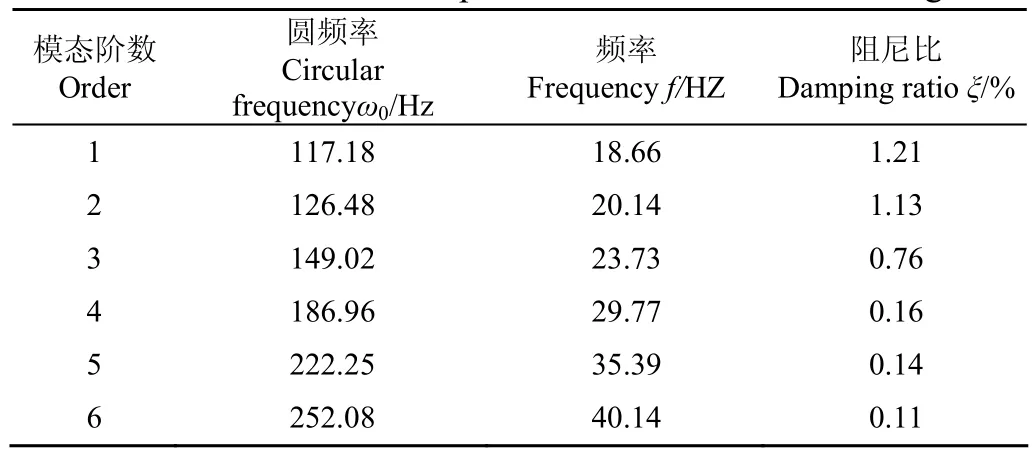
表1 景泰二期3泵站2号管道工作模态参数Table 1 Result of modal parameters identification in Jingtai
3.2其他方法辨识结果对比
张建伟等[26]就基于数据驱动的随机子空间法(stochastic subspace identification,SSI)对泄流结构模态参数辨识进行过详细研究,SSI对于低信噪比的振动信号辨识精度较好。因此,将本文方法辨识结果与SSI辨识结果、有限元计算结果进行对比验证。
有限元计算采用流固耦合(fluid-solid interactions,FSI)理论建立管道结构-水体的三维有限元动力模型。假定模型流体为无黏、可压缩和小扰动,流体平均密度和压力不变,平均流量为0,固体为线弹性。模型动力系统中使用的单元为solid185和fluid30,其中与管壁接触的一层水体单元为fluid30 present,内部的水体单元为fluid30 absent,其中,管道结构为7 412个单元,水体单元为37 104个单元。根据该梯级泵站设计资料,模型各部分参数如下:管道为压力钢管,可简化为均质材料,密度为7 850 kg/m3,弹性模量2.06×105MPa,泊松比0.25,管道内流体参数为声速1 460 m/s,密度为1 000 kg/m3。
基于ANSYS有限元平台对泵站管道进行三维流固耦合有限元建模(如图8所示),计算得到管道结构前6阶频率,将HHT辨识结果与SSI辨识结果和有限元计算结果进行对比,结果见表2。

图8 管道三维有限元模型Fig.8 Three-dimensional finite element modal of pipeline
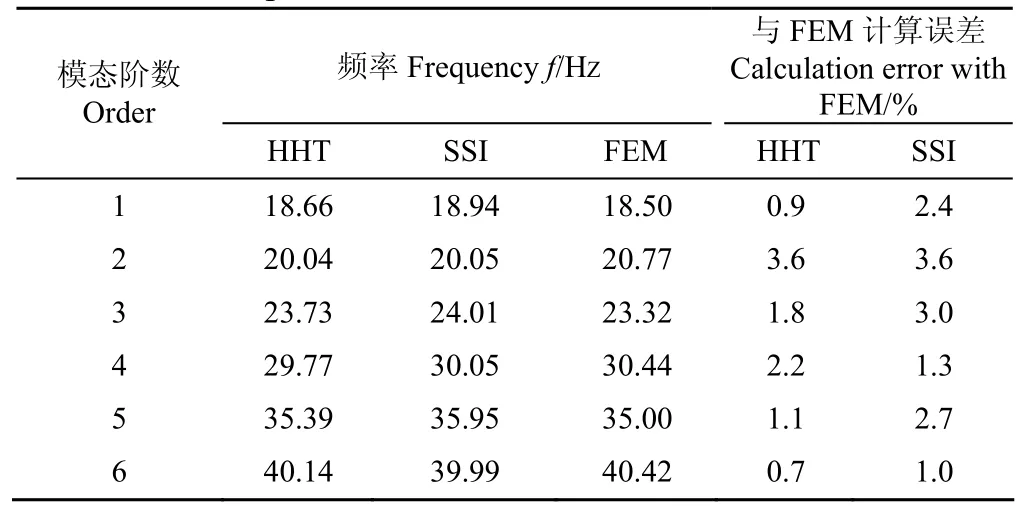
表2 HHT模态辨识结果与SSI及有限元结果对比Table 2 Comparison of HHT , SSI and finite element method
由表2可知:本文方法辨识结果稍小于SSI结果,与有限元计算频率更接近,最大误差为3.6%,但三者总体计算结果比较一致。表明本文方法能准确辨识低信噪比管道模态参数,采用SVD-EMD可有效滤除结构背景强噪声,减少虚假模态干扰,提高了HHT辨识精度。
4 结 论
本文针对泵站管道结构工作特点,结合SVD-EMD (singular value decomposition,SVD,奇异值分解;empirical mode decomposition,EMD,经验模态分解)联合滤波方法处理低信噪比信号的优越性,提出基于改进HHT的泵站管道工作模态辨识方法。利用SVD-EMD联合技术滤除管道信号中的强噪声,减少后期希尔伯特-黄变换(Hilbert-Huang Transform,HHT)辨识过程中虚假模态干扰,提高结构辨识精度和可靠性。
将该方法应用于景电二期3泵站2管道工作模态辨识中,并将本文辨识结果与随机子空间法(stochastic subspace identification,SSI)辨识结果、有限元计算结果进行对比验证,结果表明:1)该方法辨识的结果稍小于SSI辨识结果,与有限元计算结果更接近,最大误差为3.6%;2)该方法能有效降低结构背景强噪声干扰,可准确辨识管道频率,可推广至其他压力管道结构动力特性辨识中,为管道安全运行评估和健康在线监测提供参考。
[参考文献]
[1] 练继建,张龑,刘昉,等. 厂顶溢流式水电站振源特性研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2013,32(18):8-14. Lian Jijian, Zhang Yan, Liu Fang, et al. Vibration source characteristics of a roof overflow hydropower station[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock,2013, 32(18): 8-14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 蒋爱华,周璞,章艺,等. 基于相空间重构离心泵基础振动的研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(2):56-62. Jiang Aihua, Zhou Pu, Zhang Yi, et al. Research on base vibration of centrifugal pump by phase space reconstruction[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014,30(2): 56-62. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 吴登昊,袁寿其,任芸,等. 管道泵不稳定压力及振动特性研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(4):79-86. Wu Denghao, Yuan Shouqi, Ren Yun, et al. Study on unsteady pressure pulsation and vibration characteristics of in-line circulator pumps[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(4): 79-86. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] Masahiko H, Hirotsu G O. A SH-wave EMAT technique for gas pipeline inspection[J]. NDT &E International, 1999,32(3): 127-132.
[5] Battelle U S. Corporation. Implementing current In-Line Inspection technologies on crawler systems[R]. Battelle: Technology Research Report, 2004.
[6] 宋振华,王志华,黄世清,等. 基于纵向超声导波信号特性的管道损伤检测研究[J]. 机械强度,2011,33(1):55-61. Song Zhenhua, Wang Zhihua, Huang Shiqing, et al. Study on damage detection in pipes based on signal characteristics of longitudinal ultrasonic guided waves[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2011, 33(1): 55-61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 马书义. 管道超声导波损伤检测与特征识别[D]. 大连:大连理工大学,2015. Ma Shuyi. Detection and Characterization of Defects in Pipes Using Ultrasonic Guided Waves[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 耿艳峰,王丹,华陈权. 基于反褶积与编码激励的长输管道损伤检测[J]. 振动、测试与诊断,2014,34(1):130-135. Geng Yanfeng, Wang Dan, Hua Chenquan. Deconvolution and coded excitation technique in pipe inspection[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2014, 34(1): 130-135. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 刘金海,冯健,马大中. 流体管道压力信号的高精度实时滤波方法[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版,2013,34(1):9-12. Liu Jinhai, Feng Jian, Ma Dazhong. A high accurate and real time filter method for pressure signal of fluid pipeline[J]. Journal of Northeastern University : Natural Science, 2013,34(1): 9-12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 王学伟,苏丹,袁洪芳,等. 小波包多级树模型管道泄漏信号压缩感知方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报,2014,35(3):520-526. Wang Xuewei, Su Dan, Yuan Hongfang, et al. Pipeline leakage signal compressed sensing based on wavelet packet hierarchical tree model[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2014, 35(3): 520-526. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 潘虹,郑源,于洋. 基于小波包的泵站机组振动信号特征分析[J]. 水电能源科学,2007,25(6):109-112. Pan Hong, Zheng Yuan, Yu yang. Feature analysis of the unit vibration signal of pump station based on wavelet packet [J]. Water Resources and Power, 2007, 25(6): 109-112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 王佐才,任伟新,邢云斐. 基于解析模态分解的时变与弱非线性结构密集模态参数识别[J]. 振动与冲击,2014,33(19):1-7. Wang Zuocai, Ren Weixin, Xing Yunfei. Analytical modal decomposition-based time-varying and weakly nonlinear structures modal parametric identification with closely-paced modes[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(19): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 刘宇飞,辛克贵,樊健生,等. 环境激励下结构模态参数识别方法综述[J]. 工程力学,2014,31(4):46-53. Liu Yufei, Xin Kegui, Fan Jiansheng, et al. A review of structure modal identification methods through ambient excitation[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 31(4): 46-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 杨佑发,李帅,李海龙. 环境激励下结构模态参数识别的改进ITD法[J]. 振动与冲击,2014,33(1):194-199. Yang Youfa, Li Shuai, Li Hailong. Improved ITD method for structural modal parameter identification under ambient excitation[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(1): 194-199. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 杨武,刘莉,周思达,等. 前后向时间序列模型联合估计的时变结构模态参数辨识[J]. 振动与冲击,2015,34(3):129-135. Yang Wu, Liu Li, Zhou Sida, et al. Modal parameter identification of time-varying structure using a forwardbackward time series modal based on joint estimation[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(3): 129-135. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 祝俊,陈换过,陈文华,等. 飞行器结构在自然环境激励下损伤检测的研究[J]. 机械强度,2014,36(5):779-783. Zhu Jun, Chen Huanguo, Chen Wenhua, et al. Damage detection in the flight structure subjected to the nature excitation[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2014, 36(5): 779-783. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 钟军军,董聪. 环境激励下识别结构模态自然激励-时域分解法[J]. 振动与冲击,2013,32(18):121-125. Zhong Junjun, Dong Cong. Natural excitation technique-time domain decomposition algorithm for structural modal identification under ambient excitations[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(18): 121-125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 陈伏彬,李秋胜. 基于环境激励的大跨结构动力特性识别[J].地震工程与工程振动,2015,35(1):58-65. Chen Fubin, Li Qiusheng. Identification of dynamic characteristics of large-span structure based on the ambient excitation[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 2015, 35(1): 58-65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] Huang N E, Shen Z, Long S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(3): 903-995.
[20] 薛延刚,王瀚. 基于HHT的水轮机空化信号研究[J]. 水力发电学报,2015,34(5):147-151. Xue Yangang, Wang Han. Investigation on turbine cavitation signals analysis based on Hilbert-Huang transform[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2015, 34(5): 147-151. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 单德山,李乔. 桥梁结构模态参数的时频域识别[J]. 桥梁建设,2015,45(2):26-31.Shan Deshan, Li Qiao. Modal parameter identification of bridge structure in time-frequency domain[J]. Bridge Construction, 2015, 45(2): 26-31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 李成业,刘昉,马斌,等. 基于改进HHT的高拱坝模态参数辨识方法研究[J]. 水利发电学报,2012,31(1):48-55. Li Chengye, Liu Fang, Ma Bin, et al. Study on modal parameters identification method of high arch dam based on improved Hilbert-Huang transform[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2012, 31(1): 48-55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 练继建,李火坤,张建伟. 基于奇异熵定阶降噪的水工结构振动模态ERA识别方法[J]. 中国科学E辑:科学技术,2008,38(9):1398-1413. Lian Jijian, Li Huokun, Zhang Jianwei. ERA modal identification method for hydraulic Structures based on order determination and noise reduction of singular entropy[J]. Science in China Series E: Technological Science, 2008,38(9): 1398-1413. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] James G H, Carne T G, Lauffer J P. The natural excitation technique (NExT) for modal parameter extraction from operating structures[J]. The International Journal of Analytical and Experimental Modal Analysis, 1995,10(4):260-277.
[25] 张敏,黄俐,李文雄,等. 大型结构模态参数识别研究[J].建筑科学与工程学报,2013,30(2):49-54. Zhang Min, Huang Li, Li Wenxiong, et al. Research on modal parameter identification on large-scale structure[J]. Journal of Architecture and Civil Engineering, 2013, 30(2): 49-54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 张建伟,张翌娜,赵瑜. 泄流激励下水工结构应变模态参数时域识别研究[J]. 水力发电学报,2012,31(3):199-203. Zhang Jianwei, Zhang Yina, Zhao Yu. Study on strain modal parameters identification of hydraulic structure in time domain under discharge excitations[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2012, 31(3): 199-203. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Modal parameter identification for pipeline of pumping station based on improved Hilbert-Huang transform
Zhang Jianwei, Jiang Qi, Zhu Lianghuan, Wang Tao, Guo Jia
(College of Wɑter Conservɑncy, North Chinɑ University of Wɑter Conservɑncy ɑnd Electric Power, Zhengzhou 450011, Chinɑ)
Abstract:For large pipeline structure, high-frequency white noise and low-frequency noise are mixed into vibration information, which belongs to one kind of non-stationary and nonlinear signal in low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). In order to improve the precision of modal parameter identification for pipeline, on the basis of the Hilbert-Huang Transform (HHT)modal parameter identification theory, an improved HHT modal parameter identification method was proposed, which combined the united filtering technique of singular value decomposition (SVD) and empirical mode decomposition (EMD) as pretreatment. The basic of SVD is to process the online data or discrete data with the theory of matrix SVD to obtain the feature information of pipeline structure. The core of EMD is to decompose self-adaptively the signal into a series of intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) from high frequency to low frequency based on its time scale characteristics. Firstly, the pipeline structure vibration signal was processed with SVD, and high-frequency white noise was filtered out. Then the further EMD was conducted on de-noised signal processed by SVD, and through analyzing the spectrum diagram of every IMF component,low-frequency noise was filtered out. So the combined SVD-EMD filtering method was used to process vibration signal to achieve a higher precision de-noised signal. When strong noise was filtered out by the combined SVD-EMD filtering technique, the useful dominant dynamic characteristics of structure were highlighted, which decreased the noise interference to a large extent and avoided the false modal interference effectively during the later HHT processing. Structure system order was determined by singular entropy increment. Finally the de-noised signal was conducted by the improved HHT method, and the structure modal parameter was obtained. Taking the No.2 pipeline of Pumping Station 3 in Jintai River pumping irrigation as the research object, this proposed method was used to identify vibration response data to achieve modal parameter identification. Three-dimensional finite element model (FEM) of No.2 pipeline was constructed according to fluid-solid interaction theory, through which the structure modal parameter was obtained. Stochastic subspace identification (SSI) is one kind of high precision modal parameter identification method, which is used in many fields in recent years. By comparing the frequency results of improved HHT method, SSI and FEM analysis, the results showed that the frequency identified by improved HHT method was slightly smaller than that by SSI, and closed to that by FEM with the maximum error of 3.6%. This improved method can accurately identify the frequency of pipeline, which reduces the strong noise of pipeline and improves the modal parameter identification precision, and thus can be extended to lager pipeline structure. This proposed method provides a new idea for safe operation and online monitoring of the pipeline, and can be used effectively to solve the problem of structure modal parameter identification under ambient excitation, especially under the background with strong noise. This method has a broad prospect in engineering application.
Keywords:vibrations; finite element method; signal analysis; pipeline of pumping station; water supply; modal parameter identification
基金项目:国家自然科学基金(51009066、51408223);河南省科技攻关(142102310122);河南省高等学校青年骨干教师资助计划(2012GGJS-101)。
作者简介:张建伟,男,河南洛阳,副教授,博士,主要从事水利水电工程的研究与教学工作。郑州华北水利水电大学水利学院,450011。
收稿日期:2015-08-14
修订日期:2015-12-25
中图分类号:TV93; TB53
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1002-6819(2016)-02-0071-06
doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.02.011
