过表达 TRAIL 联合特异性沉默 Eag 1 的协同抗骨肉瘤作用
2016-03-18曾文容陈志达刘庆军林斌吴欣宇吴进
曾文容 陈志达 刘庆军 林斌 吴欣宇 吴进
过表达 TRAIL 联合特异性沉默 Eag 1 的协同抗骨肉瘤作用
曾文容 陈志达 刘庆军 林斌 吴欣宇 吴进
【摘要】目的 检测过表达肿瘤坏死因子相关凋亡诱导配体 ( TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand,TRAIL) 联合特异性沉默 Ethergo-go 1 ( Eag 1) 基因对骨肉瘤的影响。方法 分别构建名为 Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. siEag、CRAd5. TRAIL 和 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 的腺病毒载体并检测其抗骨肉瘤的作用。结果Ad5. eGFP 对 MG-63 细胞中的 Eag 1 和 TRAIL 表达无明显影响,CRAd5. siEag 仅可抑制 Eag 1 的表达,CRAd5. TRAIL 仅可过表达 TRAIL,而 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 既能沉默 Eag 1 又能过表达 TRAIL。细胞增殖实验结果显示:CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 比 Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. TRAIL 或 CRAd5. siEag1 能更有效地抑制骨肉瘤细胞增殖。同时,对人成骨细胞 hFOB 1.19 无明显细胞毒性。CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 组 Caspase-3 / 7 活性为 ( 39693.33±1922.96) RLU,Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. siEag1 和 CRAd5. TRAIL 组 Caspase-3 / 7 活性分别为:( 2832.83±375.99)、( 3242.50±329.97) 和 ( 15583.17±698.54) RLU。统计学分析显示 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 组 Caspase-3 / 7活性明显高于其它三组 ( P<0.001)。此外,CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 还可有效地诱导 MG-63 细胞中 PARP 裂解物表达。局部注射第 8 天,CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 组裸鼠肿瘤的体积为 ( 231.19±25.96) mm3,Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. siEag1 和 CRAd5. TRAIL 组裸鼠肿瘤体积分别为:( 504.68±102.32)、( 365.85±47.60) 和 ( 355.48±35.34) mm3,CRAd5. TRAIL 组裸鼠肿瘤体积与其它三组相比差异均有统计学意义 ( P<0.05)。第 10、12 和14 天,CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 组裸鼠肿瘤的体积分别为:( 367.82±39.52)、( 470.18±60.11) 和 ( 631.52±61.22) mm3,Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. siEag1 和 CRAd5. TRAIL 组裸鼠肿瘤体积分别为:( 826.57±130.60)、( 1284.69±243.50) 和 ( 1762.06±180.36) mm3,( 552.12±64.39)、( 721.82±108.20) 和 ( 949.20±124.70) mm3,( 524.03±43.47)、( 653.54±56.22)、( 896.44±93.64) mm3。与其它三组相比,CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 可更有效地抑制裸鼠骨肉瘤生长。TUNEL 实验结果显示:CRAd5.TRAIL / siEag1 的凋亡指数为 ( 27.33±2.07) %,而Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. siEag1 和 CRAd5. TRAIL 组的凋亡指数分别为 ( 2.68±0.64) %,( 8.49±1.06) % 和 ( 15.99±1.94) %,CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 组与其它三组相比可有效地促进骨肉瘤凋亡 ( P<0.001)。结论 过表达 TRAIL联合特异性沉默 Eag 1 基因可产生协同抗骨肉瘤作用,因此 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 腺病毒载体可作为一个有效的骨肉瘤基因治疗工具。
【关键词】骨肉瘤;细胞增殖;细胞凋亡;基因;TNF 相关凋亡诱导配体;Eag 1 基因
骨肉瘤是一种好发于青少年的骨原发性恶性肿瘤[1-2]。即使采用手术联合化疗的治疗方案,患者 5 年生存率也仅为 55%~60%,而并发肺转移者2 年生存率不到 40%[3]。因此开发针对骨肉瘤的新型疗法迫在眉睫。研究表明,Eag 1 基因不仅参与了多种肿瘤细胞增殖和周期的过程,还可能成为一个新兴的肿瘤治疗靶点[4-5]。Eag 1 基因在骨肉瘤发生发展中的作用、机制及其是否可成为骨肉瘤基因治疗靶点,仍需进一步研究。TRAIL 是肿瘤坏死因子( tumor necrosis factor,TNF) 家族的成员。近年来,因其可选择性的诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡并对正常细胞无明显副作用而成了一个新兴的肿瘤治疗基因[6]。但TRAIL 结构的不稳定性及某些肿瘤细胞对 TRAIL 抵抗仍是其临床运用的主要障碍[7]。
本研究构建了一种新型的重组腺病毒载体并将其命名为 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1。该载体可同时过表达 TRAIL 并沉默 Eag 1,本研究利用其感染骨肉瘤 MG-63 细胞并检测其抗骨肉瘤的作用。
材料与方法
一、原料、试剂和仪器
人骨肉瘤 MG-63 细胞 ( CRL-1427)、人胚肾 293 细胞 ( CRL-1573) 和人成骨细胞 hFOB 1.19 ( CRL-11372) 购自美国 ATCC 公司;MEM 培养基( 11095-027)、RPMI-1640 培养基 ( 11875-119)、DMEM / F12 培养基 ( 11039-021) 及胎牛血清( 10437-077) 购自美国 Gibco 公司;细胞培养板( M5811)、二甲基亚砜 ( DMSO,W387520) 和 MTT 试剂盒 ( M2128) 购自美国 Sigma 公司;辣根过氧化物酶偶联山羊抗兔 IgG 抗体 ( sc-45101) 和 Eag 1 siRNA ( sc-146362) 购自美国 Santa Cruz 公司;Eag l 单克隆抗体 ( APC-104) 购自以色列 Alomone 公司,Caspase-3 / 7 检测试剂盒 ( G7792) 购自美国Apo-ONE®公司,TUNEL 工具包 ( C10618) 购自美国Invitrogen 公司。PCR 仪 ( T100) 和 Luminometer 化学发光酶标仪均购自美国 Bio-rad 公司。
二、实验方法
1. 各种载体质粒的构建:通过 PCR 扩增人 TRAIL 的 cDNA,并将其克隆到 pcDNA 上形成 pcDNA-CMV-TRAIL。根据序列 5’-AGC CAT CTT GGT CCC TTA TAA-3’ 构建 Eag 1 shRNA。将 hU6-shEag1 片段引入 pcDNA-CMV-TRAIL,成为 pcDNA-CMV-TRAIL-hU6-shEag1。再将 CMV-TRAIL-hU6-shEag1 片段亚克隆于 pAdeno-X 骨架上,从而形成合并的 pCRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 质粒。按照上述方法分别构建 CRAd5. TRAIL ( 过表达TRAIL),CRAd5. siEag1 ( 沉默 Eag 1) 和 Ad5. eGFP ( 对照) 质粒。在人胚肾 293 细胞用 260 nm 吸光度和噬斑试验检测病毒准备质粒效价。
2. 细胞培养及感染:人骨肉瘤 MG-63 细胞株、人胚肾 293 细胞株和人成骨 hOFB 1.19 细胞株分别常规培养于 MEM 培养基、RPMI-1640 培养基、DMEM / F12 ( 都含 10% 小牛血清和 1% 青霉素-链霉素) 培养液中,置于 37 ℃、5% CO2恒温孵育箱孵育传代。感染腺病毒前 1 天将细胞接种到 24 孔板中,培养后 24 h,细胞密度达到 80%~90%。分别感染不同腺病毒,实验分为:Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. siEag1、CRAd5. TRAIL 和 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 组。
3. MTT 检测细胞增殖:100 μl 细胞悬液 ( 1× 105/ ml) 均匀分布于 96 孔培养板中,在 37 ℃、5% CO2条件下培养后 24 h 孔中分别感染不同的腺病毒。继续培养后 48 h,加入 20 μl MTT 溶液 ( 5 mg / ml),继续孵育 4 h,终止培养。弃种植孔内清液,每孔加 150 μl DMSO,振荡 10 min。选择 490 nm 波长,在酶联免疫监测仪 ( 美国 Bio-Rad 公司) 上测定各孔光吸收值。为提高实验结果的准确性,每组至少设置 3 个复孔。按照公式:细胞存活率=实验组吸光值 / 阳性对照吸光值×100% 计算增殖率。设平行对照组,加细胞、培养基不加抑制剂的组为阳性对照组;只加培养基不加细胞的孔设置为空白对照组,比色时空白对照组调零。
4. 细胞凋亡实验:96 孔板每孔中加入 20 μl 细胞悬液 ( 1×105/ ml) 并在 37 ℃、5% CO2条件下培养箱过夜,随后感染不同的腺病毒,相同量的Apo-ONE Caspase-3 / 7 试剂加入 96 孔板,室温孵育1 h。每组至少设置 3 个复孔,在 Luminometer 化学发光酶标仪上测定各孔光吸收值。
5. Western Blot 分析 ( WB):收集 5~6×107个细胞,提取细胞蛋白,将 4 ℃ 预冷的细胞裂解缓冲液 ( 10 mmol / L EDTA,10 mmol / L Tris-HCl,150 mmol / L NaCl,0.4% SDS,pH 7.4) 裂解细胞,在 4 ℃ 下 15 000 转 / 分离心约 10 min,吸取上清液,用 BCA 比色法测定蛋白浓度后,把样品置于沸水浴中 5~8 min,然后进行 10% SDS- 聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳 ( SDS-polyacrylamidegel electrophoresis,SDS-PAGE) 在 80 伏特电流下电泳 30 h,120 伏50 min 分离蛋白,用电转膜仪 100 V,230 mA 湿法转膜过夜 ( 转膜前 PVDF 膜用甲醇活化 1 min)。用含5% 脱脂奶粉的 TBST 室温封闭 1 h,倒掉封闭液,然后在室温下用兔抗人 Eag 1、PARP 多克隆抗体孵育,置于 4 ℃ 冰箱过夜;用 PBST 洗涤 3 次,每次10 min,加入二抗室温孵育 1.5 h,1∶1000 稀释;用PBST 洗涤 3 次,每次 10 min;采用 DAB 显色法检测 Eag 1、PARP,内参照为 GAPDH,用 Touching 凝胶成像分析软件分析条带净灰度,用各组目的蛋白的灰度值除以内参 GAPDH 的灰度值以校正误差,所得结果为目的蛋白的相对含量,表示目的蛋白的表达水平。
6. 裸鼠骨肉瘤模型的构建:从中国医学科学院购买 BALB / c 裸鼠 ( 雌性,年龄 6~8 周)。实验过程中对动物处置符合科学技术部 2006 年“关于善待实验动物的指导性意见”的要求。按照文献的方法构建骨肉瘤移植瘤模型[8]:将 150 μl MG-63 细胞悬液 ( 1.5×106/ ml) 注射裸鼠右侧后腿皮下。模型建成后 1 周,长出肉眼可见的肿瘤。之后将裸鼠随机分为 4 组 ( 每组 6 只),分别每隔 1 天瘤内注射 Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. siEag1、CRAd5. TRAIL 或 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 ( 1×107pfu / 50 μl),共注射 7 次。用ab2 / 2 ( a 代表长度和 b 代表宽度) 公式来测定肿瘤体积。
7. 末端标记法 ( TUNEL) 检测凋亡:瘤内注射14 天后处死裸鼠。处理离体的右侧后腿肿瘤,碎块用 3.7% 甲醛固定。随后多聚甲醛 ( 4%,pH 7.4) 室温固定 30 min。4% PBS 室温清洗 30 min,冰上用0.1% Tritons X-100 in 0.1% 柠檬酸钠透化重悬。凋亡指数计算使用公式:凋亡指数=( 凋亡细胞总数 / 细胞总数)×100%。
三、统计学分析方法
结 果
一、CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 效能的检测
在人骨肉瘤 MG-63 细胞中,为了获得沉默Eag 1 和过表达 TRAIL 最大转染效率,本研究构建了四种腺病毒载体:Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. siEag1、CRAd5. TRAIL 和 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1。为比较沉默 Eag 1 和过表达 TRAIL 效率,WB 分别检测了不同腺病毒载体感染后 Eag 1 和 TRAIL 的表达水平。如图 1 所示,感染 CRAd5. siEag1 或 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1,均可显著减少 Eag 1 表达。相比而言,感染Ad5. eGFP 或 CRAd5. TRAIL,Eag 1 表达水平无明显变化。另一方面,感染 CRAd5. TRAIL 或 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1,TRAIL 表达水平明显上升,而感染Ad5. eGFP 或 CRAd5. siEag1 则未见上述情况。结果显示 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 既能沉默 Eag 1 又能过表达 TRAIL。
二、CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 对骨肉瘤细胞生长和凋亡的影响
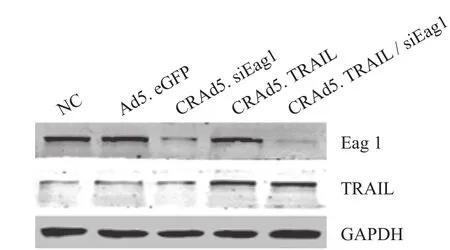
图1 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 载体效能的检测 [ MG-63 细胞分别感染四种腺病毒:Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. siEag1、CRAd5. TRAIL 和 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 ( 感染复数为 10,单位 pfu / 细胞个数);48 h 后,WB 检测 Eag 1 和 TRAIL 表达水平;NC:negative control 即阴性对照组 ( 无病毒感染) ]Fig.1 Characterization of CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 adenoviral vector [ MG-63 cells were infected with different adenoviruses Ad5. eGFP, CRAd5. siEag1, CRAd5. TRAIL or CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 at MOI ( multiplicity of infection, calculated as pfu / cell numbers) of 10, respectively. After 48 h, the relative expression levels of Eag 1 and TRAIL were examined by Western blot analysis. NC, negative control ( cells without infection) ]
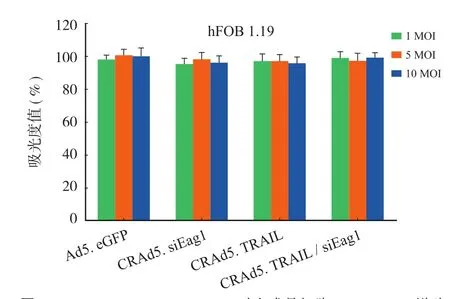
图3 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 对人成骨细胞 hFOB 1.19 增殖无明显影响 [ hFOB 1.19 细胞分别感染 1、5、10 MOI 浓度的Ad5. eGFP,CRAd5. siEag1,CRAd5. TRAIL or CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1,48 h 后行 MTT 检测细胞增殖情况 ( n = 6) ]Fig.3 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 had no effects on the proliferation of hFOB 1.19 cells [ hFOB 1.19 cells were infected with Ad5. eGFP, CRAd5. siEag1, CRAd5. TRAIL or CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 at MOI of 1, 5, 10, respectively. After 48 h the cells were harvested for MTT assay ( n = 6) ]
CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 比 Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. TRAIL 或 CRAd5. siEag1 能更有效地抑制骨肉瘤细胞增殖 ( 图 2)。同时,对人成骨细胞 hFOB 1.19 无明显细胞毒性 ( 图 3)。凋亡实验结果显示:CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 组中 Caspase-3 / 7 值明显高于其它组 ( 图 4)。聚腺苷二磷酸-核糖聚合酶 [ poly ( ADP-ribose) polymerase,PARP ] 在细胞凋亡时期被Caspase 分割成大小为 89 kDa 和 24 kDa 的碎片,因此PARP 裂解物 ( Cleaved PARP) 被认定是一种 Caspase依赖凋亡的经典特征。WB 示,CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 可有效诱导 Cleaved PARP 表达 ( 图 5)。上述结果提示,沉默 Eag 1 联合过表达 TRAIL 能有效的抑制 MG-63 细胞生长抑制并诱导凋亡。
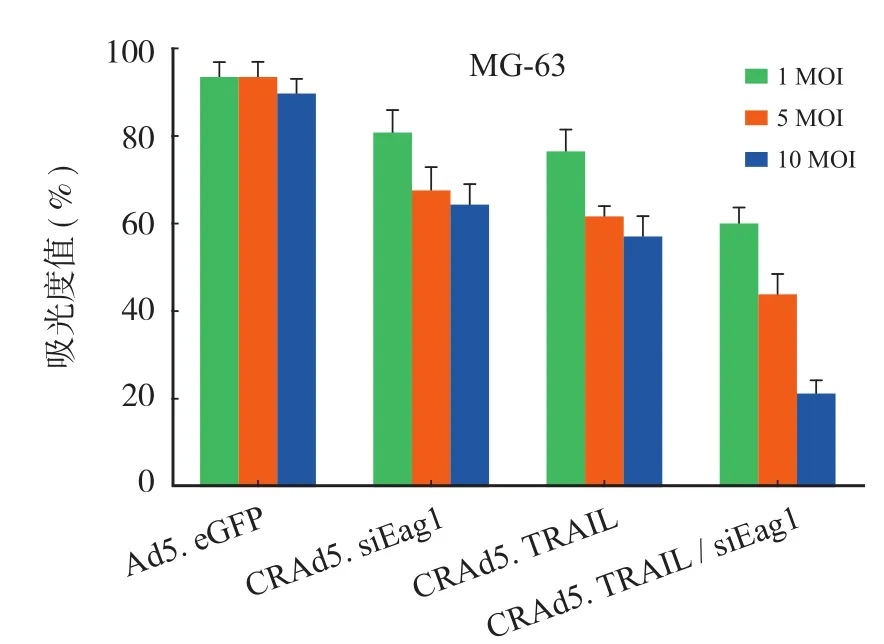
图2 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 能有效抑制 MG-63 细胞增殖[ MG-63 细胞分别感染 1、5、10 MOI 浓度的 Ad5. eGFP,CRAd5. siEag1,CRAd5. TRAIL or CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1,48 h后行 MTT 检测细胞增殖情况 ( n = 6) ]Fig.2 Strong induction of cell growth arrest of MG-63 by CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 [ MG-63 cells were infected with Ad5. eGFP, CRAd5. siEag1, CRAd5. TRAIL or CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 at MOI of 1, 5, 10, respectively. After 48 h the cells were harvested for MTT assay ( n = 6) ]
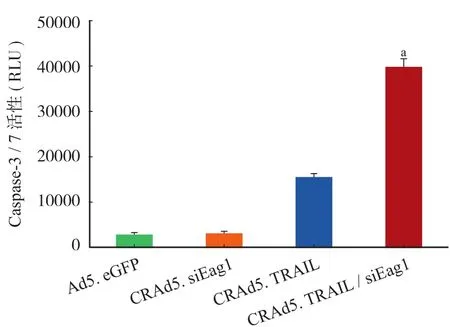
图4 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 能显著诱导 Caspase-3 / 7 活性( CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 组中 Caspase-3 / 7 的活性明显高于其它载体感染组。aP < 0.001,n = 6)Fig.4 Higher Caspase-3 / 7 activity induced by CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 ( The level of activated Caspase-3 / 7 was higher in CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 infected cells than in other adenoviral vectors infected cells.aP < 0.001, compared with Ad5. eGFP, CRAd5. siEag1 or CRAd5. TRAIL n = 6)

图5 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 可有效诱导 Cleaved PARP 表达( CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 感染组中 PARP 裂解产物表达水平明显高于其它组)Fig.5 The higher expression of cleaved PARP induced by CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 ( The level of cleaved PARP was higher in CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 infected cells than in other adenoviral vectors infected cells)
三、CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 对裸鼠骨肉瘤生长和凋亡的影响
体内实验结果显示:相比注射 Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. siEag1 或 CRAd5. TRAIL,注射 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 的裸鼠肿瘤体积显著减小 ( 图 5,6),显示 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 在活体水平可有效抑制肿瘤生长。TUNEL 实验结果显示:CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 的凋亡指数为 ( 27.33±2.07) % ( 凋亡指数,即从 6 个随机视野 TUNEL 阳性细胞平均百分比),明显高于其它组。Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. siEag1 和 CRAd5. TRAIL 组的凋亡指数分别为 ( 2.68±0.64) %,( 8.49±1.06) % 和 ( 15.99±1.94) % ( 图 7)。
讨 论
1969 年,Kaplan 等[9]在 Genetics 杂志上首次报道了一种可以使成年雄性黑腹果蝇腿部在麻醉状态下发生缓慢而规律运动的基因,人们将其命名为Ethergo-go ( Eag),其性质为一种电压门控性钾离子通道。之后的研究证实 Eag 亚族包括两个成员:Eag 1 和 Eag 2。1999 年,Pardo 等[10]在 EMBO J 杂志上发表了里程碑式的文章,首次证实了 Eag 1 与肿瘤密切相关。进一步的研究表明 Eag 1 在多种人类肿瘤细胞系和肿瘤组织中高表达,而在相应来源的正常细胞和组织中不表达或低表达 ( 主要表达于脑组织,短暂性表达于胎盘和肌原细胞)[5]。一些致癌因素,如 HPV 感染、雌激素和致癌物等均可诱导其高表达,提示 Eag 1 具有致癌潜能并可作为潜在的肿瘤标志物[10]。应用 Eag 1 非特异性阻滞剂如丙咪嗪( 一种抗抑郁药物) 和阿司咪唑 ( 一种抗过敏药物)或特异性阻滞剂小干扰 RNA ( small interfering,siRNA) 和抗体均可达到抑制 Eag 1 活性和肿瘤增殖的效果[11-12],提示 Eag 1 可作为一个有效的肿瘤治疗靶点。但针对 Eag 1 的治疗是否会损伤正常组织尤其是脑组织?尽管丙咪嗪和阿司咪唑在临床上已广泛运用且对脑组织的功能无明显影响,但仍缺乏直接的实验证据消除上述顾虑。近期一项的研究结果从一定程度上消除了上述顾虑:敲除小鼠脑组织内正常表达的 Eag 1 对小鼠的认知、行为和生命并无明显影响[13],这也进一步证实了 Eag 1 作为肿瘤有效治疗靶点的潜能。此外,已有研究破解了小鼠Eag 1 依赖于电压的钾通道的两个细胞内域的 X 射线晶体结构,证实了上述结构域通过直接相互作用来发挥调控作用[14],为进一步研究奠定了基础。
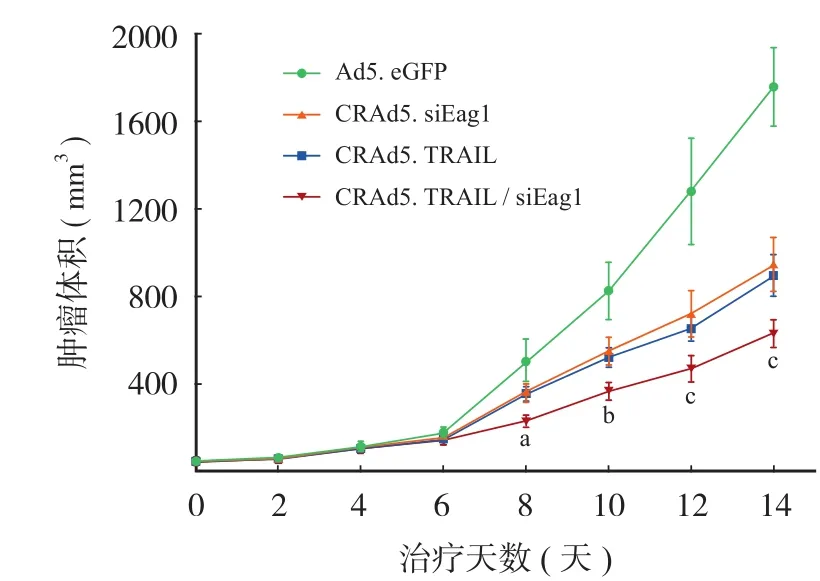
图6 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 可有效抑制裸鼠骨肉瘤生长 ( 在14 天的观察期中,瘤内注射 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 可有效抑制裸鼠骨肉瘤的生长。分别与 Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. siEag1 和CRAd5. TRAIL 组相比,aP < 0.05、bP < 0.01、cP < 0.001,n = 6)Fig.6 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 significantly inhibited the growth of MG-63 cells in nude mice ( Intra-tumor injection of CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 significantly reduced the size of MG-63 derived tumor implanted subcutaneously in nude mice during the 14-day follow-up period.aP < 0.05,bP < 0.01 andcP < 0.001, compared with Ad5. eGFP, CRAd5. siEag1 or CRAd5. TRAIL, respectively n = 6)
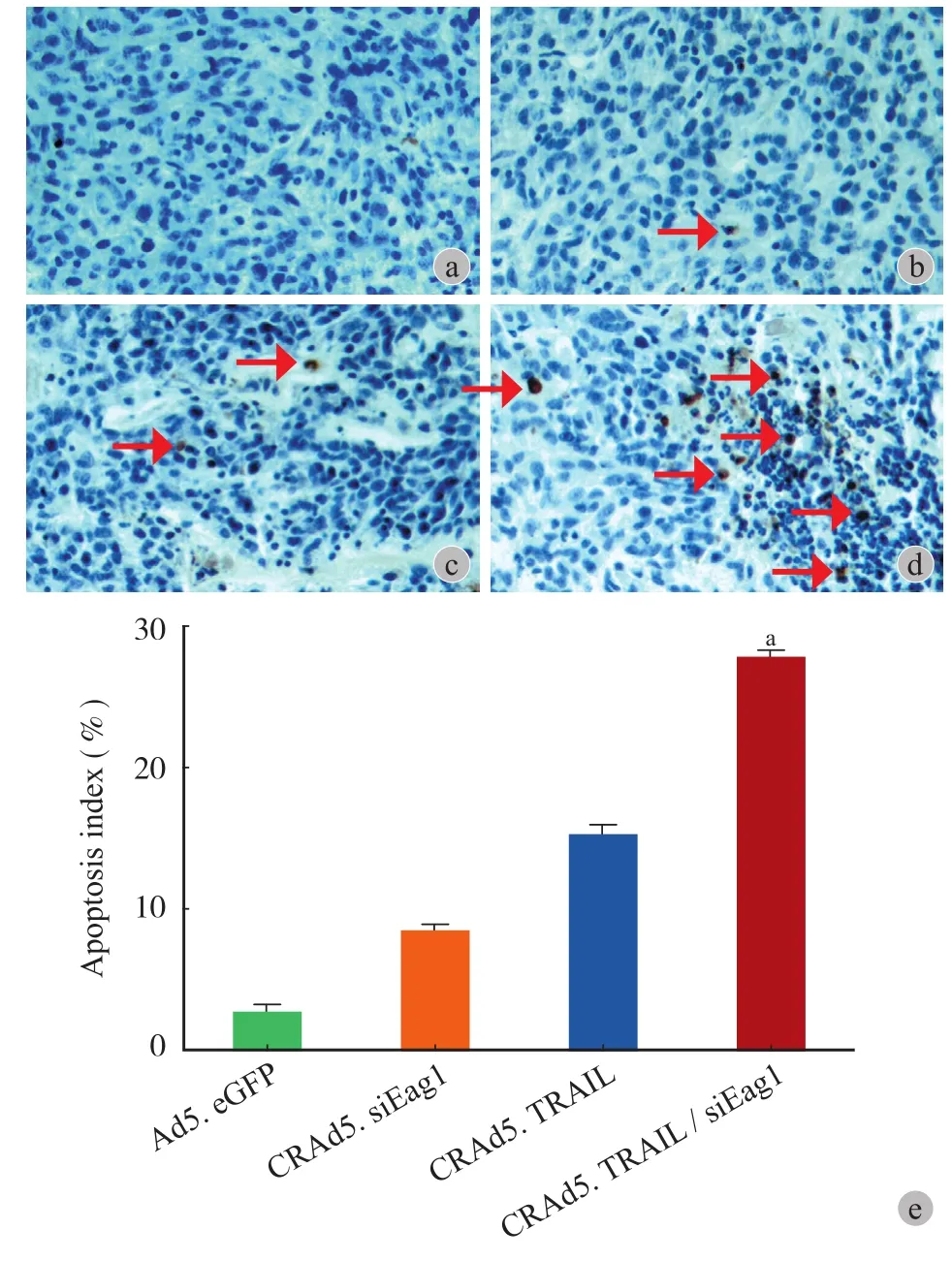
图7 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 可有效诱导裸鼠骨肉瘤凋亡( a~e:TUNEL 法分别检测 Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. siEag1、CRAd5. TRAIL 和 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 组的凋亡指数。表示凋亡的细胞。×400,分别与 Ad5. eGFP、CRAd5. siEag1、CRAd5. TRAIL组相比,aP < 0.001,n = 6)Fig.7 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 significantly induced the apoptosis of MG-63 cells in nude mice [ a - e: Apoptosis index of MG-63 xenograft tumors in nude mice treated with Ad5. eGFP, CRAd5. siEag1, CRAd5. TRAIL or CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 was calculated based on TUNEL assay ( n = 6). The apoptotic cells were indicated by arrows (). Original magnification, × 400.aP < 0.001, compared with Ad5. eGFP, CRAd5. siEag1 or CRAd5. TRAIL, respectively ]
TRAIL 能诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡,而对正常组织无明显副作用。因此,TRAIL 也可作为一个有效的肿瘤治疗靶点。然而,TRAIL 如何诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡的机制尚未完全明确。TRAIL 包含两种死亡受体:死亡受体 4 ( DR4,TRAIL-R1) 和死亡受体 5 ( DR5,TRAIL-R2)[15]。DR4 和 DR5 受体能与 FAS死亡相关结构域结合从激活 Caspase 依赖的凋亡信号通路。然而,一些肿瘤细胞对于 TRAIL 具有抵抗作用是其临床运用的主要障碍。近年来,TRAIL与其它因子联合治疗给肿瘤治疗带来新的模式。Hartung 等[16]设计出一种新型抗 Eag 1 联合 TRAIL单链抗体,它可诱导 Eag 1 阳性表达的肿瘤细胞凋亡并对 Eag 1 阴性表达的肿瘤细胞产生旁观效应,提示 Eag 1 和 TRAIL 联合具有协同抗肿瘤作用。目前,关于肿瘤细胞对 TRAIL 抵抗的可能机制尚无明确的结论。一些基因,如 cFLIP 等[17]均可能参与了肿瘤细胞对 TRAIL 抵抗的过程。本研究探讨了过表达 TRAIL 联合特异性沉默 Eag 1 的协同抗骨肉瘤作用。体外研究显示 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 腺病毒介导的 siRNA 能有效沉默 Eag 1 的表达和并诱导 TRAIL 表达且对于人成骨细胞 hFOB 1.19 细胞无明显毒性。之后的体内实验显示 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 比单纯 CRAd5. siEag1 或 CRAd5. TRAIL 能更有效地抑制骨肉瘤生长,同时诱导其凋亡。可能的机制为:CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 介导的 Eag 1 沉默可增强骨肉瘤细胞对 TRAIL 的敏感性并激活信号通路。而笔者前期的研究已证实了 Eag 1 在骨肉瘤中的异常高表达[8]。因此,本研究的结果为针对 TRAIL的骨肉瘤基因治疗提供了一个新思路。
综上所述,过表达 TRAIL 联合特异性沉默 Eag 1基因可产生协同抗骨肉瘤作用,而 CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 则能成为一个有效的骨肉瘤基因治疗工具。
参 考 文 献
[1] Schwab JH, Springfield DS, Raskin KA, et al. What’s new in primary bone tumors. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2012, 94(20): 1913-1919.
[2] Endo-Munoz L, Evdokiou A, Saunders NA. The role of osteoclasts and tumour-associated macrophages in osteosarcoma metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2012, 1826(2):434-442.
[3] Lutetke A, Meyers PA, Lewis I, et al. Osteosarcoma treatment-Where do we stand? A state of the art review. Cancer Treat Rev, 2013, pii S0305-7372(13):259-264.
[4] Pardo LA, Sühmer W. Eag1 as a cancer target. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2008, 12(7):837-843.
[5] Pardo LA, Sühmer W. The roles of K (+) channels in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 2014, 14(1):39-48.
[6] Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, et al. Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med, 1999, 5(2):157-163.
[7] Seol JY, Park KH, Hwang CI, et al. Adenovirus-TRAIL can overcome TRAIL resistance and induce a bystander effect. Cancer Gene Ther, 2003, 10(7):540-547.
[8] Wu J, Wu X, Zhong D, et al. Short hairpin RNA (shRNA) Ether à go-go1 (Eag1) inhibition of human osteosarcoma angiogenesis via VEGF/PI3K/AKT signaling. Int J Mol Sci, 2012, 13(10):12573-12583.
[9] Kaplan WD, Trout WE 3rd. The behavior of four neurological mutants of Drosophila. Genetics, 1969, 61(2):399-409.
[10] Pardo LA, del Camino D, Sánchez A, et al. Oncogenic potential of EAG K(+) channels. EMBO J, 1999, 18(20):5540-5547.
[11] Gómez-Varela D, Zwick-Wallasch E, Knötgen H, et al. Monoclonal antibody blockade of the human Eag1 potassium channel function exerts antitumor activity. Cancer Res, 2007, 67(15):7343-7349.
[12] Asher V, Sowter H, Shaw R, et al. Eag and HERG potassium channels as novel therapeutic targets in cancer. World J Surg Onco, 2010, 8:113.
[13] Ufartes R, Schneider T, Mortensen LS, et al. Behavioural and functional characterization of Kv10.1 (Eag1) konckout mice. Hum Mol Genet, 2013, 22(11):2247-2262.
[14] Haitin Y, Carlson AE, Zagotta WN. The structural mechanism of KCNH-channel regulation by the eag domain. Nature, 2013, 501(7467):444-448.
[15] Pan G, O’Rourke K, Chinnaiyan AM, et al. The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. Science, 1997, 276(5309):111-113.
[16] Hartung F, Stühmer W, Pardo LA. Tumor cell-selective apoptosis induction through targeting of K (V) 10.1 via bifunctional TRAIL antiboy. Mol Cancer, 2011, 10:109.
[17] Griffith TS, Chin WA, Jackson GC, et al. Intracellular regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells. J Immunol, 1998, 161(16):2833-2840.
( 本文编辑:李贵存)
. 论著 Original article .
Synergistic anti-osteosarcoma effects of TRAIL overexpression in combination with Ether à go-go 1 silence ZENG Wen-rong, CHEN Zhi-da, LIU Qing-jun, LIN Bin, WU Xin-yu, WU Jin. Department of Orthopaedics, the Affiliated Southeast Hospital of Xiamen University, Zhangzhou, Fujian, 363000, PRC
【Abstract】Objective To evaluate effects of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand ( TRAIL) overexpression in combination with Ether à go-go 1 ( Eag 1) silence on osteosarcoma. Methods Several adenoviral vectors named Ad5. eGFP, CRAd5. siEag, CRAd5. TRAIL and CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 were generated and their anti-tumor effects on osteosarcoma were investigated. Results Ad5. eGFP had no effects on the expression of Eag 1 and TRAIL in MG-63 cells, while CRAd5. siEag knocked down the expression of Eag 1, CRAd5. TRAIL over expressed the TRAIL expression and CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 permitted simultaneous overexpression of TRAIL and knockdown of Eag 1.book=124,ebook=49Results of cell proliferation showed that CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 induced growth arrest in a more efficient manner than CRAd5. TRAIL or CRAd5. siEag1, and had no effects on human osteoblastic hFOB 1.19 cells. The amount of activated Caspase-3 / 7 was ( 39693.33 ±1922.96), ( 2832.83 ±375.99), ( 3242.50 ±329.97) and ( 15583.17 ±698.54) RLU in CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1, Ad5. eGFP, CRAd5. siEag and CRAd5. TRAIL group respectively. Results showed that the amount of activated Caspase-3 / 7 was significantly higher in CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 infected cells than in other adenoviral vectors infected cells ( P < 0.001). Moreover, the amount of cleaved PARP was also significantly higher in CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 infected cells than in other adenoviral vectors infected cells. At 8 day after local injection, the tumor volume in CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 was ( 231.19 ±25.96) mm3, which was significantly smaller than the volumes in Ad5. eGFP ( 504.68 ±102.32) mm3, CRAd5. siEag ( 365.85 ±47.60) mm3or CRAd5. TRAIL ( 355.48 ±35.34) mm3group ( P < 0.05). At 10 th, 12 th and 14 th day after local injection, the tumor volumes in CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 group were ( 367.82 ±39.52), ( 470.18 ±60.11) and ( 631.52 ±61.22) mm3, while the tumor volumes in Ad5. eGFP group were ( 826.57 ±130.60), ( 1284.69 ±243.50) and ( 1762.06 ±180.36) mm3, in CRAd5. siEag group were ( 552.12 ±64.39), ( 721.82 ±108.20) and ( 949.20 ±124.70) mm3and in CRAd5. TRAIL group were ( 524.03 ±43.47), ( 653.54 ±56.22) and ( 896.44 ±93.64) mm3. Results showed that the tumor volume was significantly smaller in CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 injected animals compared with Ad5. eGFP, CRAd5. siEag1 or CRAd5. TRAIL injected animals. The tumors from the mice injected with CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 demonstrated extensive apoptosis ( 27.33 ±2.07) %, compared with the group treated with Ad5. eGFP, CRAd5. siEag1 or CRAd5. TRAIL. The apoptotic index were ( 2.68 ±0.64) %, ( 8.49 ±1.06) % and ( 15.99 ±1.94) % in Ad5. eGFP, CRAd5. siEag1 and CRAd5. TRAIL, respectively. The differences were significant ( P < 0.001). Conclusions CRAd5. TRAIL / siEag1 can represent an effective strategy for osteosarcoma gene therapy due to the synergistic anti-tumor effects of Eag 1 knockdown and TRAIL overexpression.
【Key words】Osteosarcoma; Cell proliferation; Apoptosis; Genes; Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosisinducing ligand; Ether à go-go1
( 收稿日期:2015-05-23)
Corresponding author:WU Jin, Email: wu215@iupui.edu
通信作者:吴进,Email: wu215@iupui.edu
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目 ( 81402217)
作者单位:363000 福建,漳州市厦门大学附属东南医院骨科 ( 曾文容、陈志达、刘庆军、林斌、吴进),神经内科 ( 吴欣宇)
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-252X.2016.02.011
中图分类号:R738.1
