Anti-tumor effect of LTA combined with 5-FU on H22 tumor bearing mice
2015-12-23BinWangChangJiangLeiRongWuLeiLiChunMeiDengWenXiaChenFuRongHuHaoChengLongZeZhangTaoChengZengJianBinHuangChunZhouChenDeFaRen
Bin Wang, Chang-Jiang Lei, Rong Wu, Lei Li, Chun-Mei Deng, Wen-Xia Chen, Fu-Rong Hu, Hao-Cheng Long, Ze-Zhang Tao, Cheng Zeng, Jian-Bin Huang, Chun-Zhou Chen, De-Fa Ren
1Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China
2Department of General surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Jianghan University, Wuhan 430050, Hubei Province, China
3Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, The Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical College, Zhanjiang 524001, Guangdong Province, China
Anti-tumor effect of LTA combined with 5-FU on H22 tumor bearing mice
Bin Wang1#, Chang-Jiang Lei2#, Rong Wu2#, Lei Li2, Chun-Mei Deng3, Wen-Xia Chen3, Fu-Rong Hu2, Hao-Cheng Long2, Ze-Zhang Tao1*, Cheng Zeng2, Jian-Bin Huang2, Chun-Zhou Chen2, De-Fa Ren2
1Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China
2Department of General surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Jianghan University, Wuhan 430050, Hubei Province, China
3Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, The Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical College, Zhanjiang 524001, Guangdong Province, China
ARTICLE INFO
Article history:
Received 15 April 2015
Received in revised form 20 May 2015
Accepted 15 June 2015
Available online 20 July 2015
Cancer bearing mice
LTA
5-FU
Tumor inhibition rate
Caspase-3
综上所述,在农村中学开展校园足球能够很好地提高学生对足球的学习兴趣,促进学生全面发展,丰富农村学校大课间活动和课外活动内容,提升农村学校文化内涵,进而有效促进农村中学体育教学的发展。
EGFR
TGF-αα
Objective: To study the effect of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) and 5-FU on the expression of caspase-3, EGFR, TGF-αα proteins of tumor tissue of H22 cancer bearing mice and its antitumor mechanism. Methods: A total of 40 SPF grade Kunming mice were selected to establish H22 liver cancer model, and then the mice were divided into 4 groups at random with ten mice in each group. Group A was given saline lavage treatment, Group B was treated with 5-FU by intraperitomeal injection, Group C was treated with LTA by lump body injection; Group D was treated with LTA by lump body injection and 5-FU by intraperitomeal injection. Two weeks after the treatment, the mice in each group were executed and the tumor tissue was stripping and weighted, and the tumor growth inhibition ratio was calculated. Then the tumor tissue was processed for conventional embedding, sectioned to observe the expression of caspase-3, EGFR, TGF-αα by immunohistochemical staining method. Results: The tumor inhibitory rate o f Group D was significantly higher than Groups B and C (P<0.05); B, the tumor inhibitory rate o f Group B had no statistical difference compared with Group C (P>0.05). The IDO values of TGF -αα, EGFR proteins in Groups B, C, D mice tumor tissue were significantly lower than that in group A (P<0.05); while IDO value of caspase-3 in Groups B, C, D group mice tumor tissue was significantly higher than that in Group A (P<0.05). The IDO value of TGF-αα, EGFR in Group D mice tumor tissue were significantly lower than that in Groups B and C; While IDO value of aspase-3 in Group D was significantly higher than that in Groups B and C (P<0.05). Conclusions: LTA combined with 5-FU can effectively inhibit the tumorigenesis of H22 tumor bearing mice, increase the caspase-3 protein expression, inhibit TGF –αα and EGFR protein expression, further promote tumor cell apoptosis and play a synergistic antitumor effect.
1. Introduction
Primary liver cancer is one of clinical common malignant tumors, the morbidity showed a rising trend year by year in recent years[1]. According to statistics[2], about 42% of global new liver cancer patients are in China. Liver cancer has become the second leading cause of death in China's tumor patients with serious damage to their life and health. As continuous research on liver cancer diagnosis, treatment and prognosis conducted by many modern scholars, the therapeutic schedule has transformed from a single surgery treatment mode to mode of surgery supplemented with part treatment and combination with a variety of methods[3]. Chemotherapy is an important mean to prolong the life of patients with liver cancer and has curative effect. But liver cancer has a low sensitivity for most of chemotherapeutic drugs, poor effect of chemotherapy alone, and the larger toxic and adverse reaction, moreover, it has no obvious effectfor improving survival time and quality of life of patients with liver cancer. Bifidobacteria are important physiologic bacteria in human intestinal and the major effective component is lipoteichoic acid (LTA). Studies have confirmed that[4], LTA can significantly inhibit tumor cell proliferation, promote apoptosis, improve the immune function of body on the tumor, and has significant inhibitory effect on a wide variety of tumor cells. 5-FU, clinical commonly used chemotherapy drugs, has become the main chemotherapy drug for digestive system tumor and has the curative effect. In this study to explore the tumor suppression effect of LTA combined with 5-FU, SD mice were selected to establish H22 liver cancer model, then treated with LTA and 5-FU, and the tumor suppression effect and mechanism of action was observed for providing clinical laboratory data for its clinical application.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Experimental animals
Forty SPF kunming mice aged between 8 to 12 weeks, weighting 18- 22 g, were selected, provided by Beijing Huafukang Biological Technology co., LTD. The mice received food and water ad libitum under the temperature of (23±3) ℃. The experimental process strictly followed the Regulations on the Administration of Experimental Animals to deal with experimental animals.
2.2. Experimental drugs and instruments
LTA was isolated and purified from bifidobacteria adolescentis passage in Balb/c mice for breeding according to the method of literature[5]. 5-FU injection, provided by Nanjing Jiancheng Biological Engineering Institute, was prepared with normal saline into 3 mg/mL, stored for future use. H22 tumor strains were obtained from the cell bank of Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Rabbit anti-mouse caspase 3, EGFR, TGF-αα ready-to-use monoclonal antibody and DAB chromogenic liquid were purchased from Beijing Zhongshan Company. BL420 multichannel physiologic recorder, BI-2000 immunohistochemical analysis system (Chengdu), Olympus BH-type 2 microscope (Japan) were used.
2.3. Establishment of H22 tumor cancer mice model
2.4. Observation items
Groups of mice were executed on the next day after the treatment. Stripped intact tumor tissue and blotted up with filter paper, weighted and calculated average weight and area of tumor tissue, and tumor inhibitory rate. After weighing, the tumor issue was conventional embedding, sectioning, immunohistochemical staining to observe the expression of caspase 3, EGFR and TGF-αα proteins. The results judgment[6]: caspase 3 protein positive expression shows yellow or brown granules, mainly expressed in the cytoplasm; EGFR protein expression shows yellow and brown granules, mainly expressed in the cytoplasm and cell membrane; TGF-αα protein positive expression shows yellow and brown granules, mainly expressed in the cytoplasm and cell membrane.
2.5. Statistical analysis
Data was analyzed by SPSS 10.0 software, and expressed as mean ± SD. They were analyzed by using the One-way ANOVA among groups. P<0.05 was considered as statistically significant difference.
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of tumor inhibitory rate among groups mice
Tumor volume and weight of Groups B, C, D was significantly lower than that of Group A (P<0.05). Tumor volume and weight of Groups B, D was significantly lower than that of Group C (P<0.05). Tumor volume of Group D was significantly lower than that of Group B (P<0.05), while tumor weight was significantly higher than group B (P<0.05). Tumor inhibitory rate of Group D was significantly higher than that of Groups B and C (P<0.05). The results were shown in Table 1.

Table 1 Comparison of tumor inhibitory rate among groups mice.
3.2. Expression of caspase-3, EGFR, TGF-α proteins in tumor issue
The expression of caspase 3 protein in the tumor tissue of Groups B, C, D mice was significantly higher than that in Group A (P<0.05), while the expression of EGFR and TGF-αα proteins in Groups B, C, D was significantly lower than that in Group A (P<0.05). Caspase3 protein expression in Groups B and D was significantly higher than that in Group C (P<0.05), while the expression of EGFR and TGF-αα was significantly lower than that in Group C (P<0.05). Expression of caspase 3 protein in Group D was significantly higher than in Group B (P<0.05), while EGFR, TGF-αα expression was significantly lower than in Group B (P<0.05). The results were shown in Table 2.
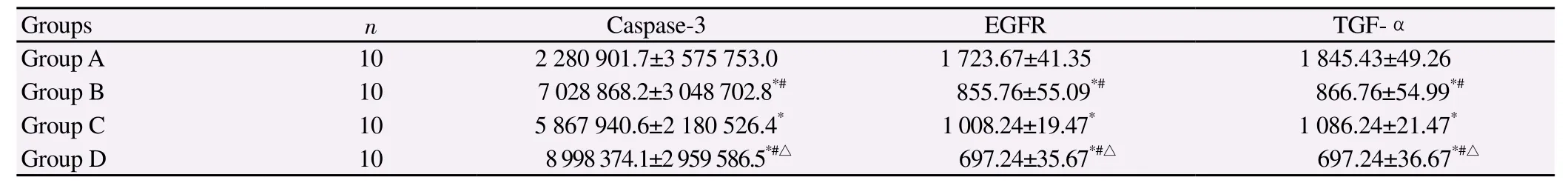
Table 2 Expression of caspase-3, EGFR, TGF-αα proteins in tumor issue of groups mice (IOD value).
3.3. Microscopic observation of caspase-3, EGFR, TGF-α proteins expression in tumor issue biopsies
Microscopically, caspase-3 was more expression in the cytoplasm, which in group D expressed the highest; EGFR, TGF-αα was expression in the cytoplasm and cell membrane, and mainly in cell membrane expression, expression of Groups C, B and D were significantly lower than that of Group A. The results were presented in Figure 1.
4. Discussion
Liver cancer is a clinically common malignant tumor, and the average age attacked by this disease was 44. It has a high malignant degree, developed fast, if not treated in time, the average survival time was only half a year, seriously affect the quality of life of patients[7]. The early stage of liver cancer has no obvious symptoms, once found, about one third of patients have been in advanced stage[8]. Liver cancer should be treated individualized with comprehensive treatment according to different stages of liver cancer. Surgery is the first choice for liver cancer treatment. For cancer cannot be removed by surgery after surgical exploration, or as follow-up treatment of a tumor palliative resection, comprehensive treatment with radiation as the major one can be used. But the solution has larger toxic and adverse reactions and greatly influent the patient’s life[9]. Therefore, it is a clinically urgent issue to be solved that looks for an effective treatment schedule to improve the quality of life and survival time of the patients.
5-FU is a pyrimidine class antagonists, also is the main chemotherapy regimens drug for digestive system tumor. It has an obvious effect on the proliferation of tumor cells, but it has limited targeting property, the sensitivity declines after repeatedly use and lager side effects, which limit its use for a long time[10-13]. LTA, isolated and purified from bifidobacteria adolescentis, is a kind of linear glycerol phosphate amphoteric polymer related to the adhesion[14]. Studies have confirmed that[15-17], LTA can inhibit the growth of a variety of tumor cells. It is safe with non-toxic side effects and can be long-term use. At present, the main anti-tumor mechanism focused on two aspects, i.e. direct tumor suppression and improving the antitumor immunity of patients. In this study, after the treatment the tumor weight and volume in Groups B and C was significantly lower than that in Group A (P<0.05). It proved that both the two drugs have a certain tumor suppression effect. No statistical difference was found in the inhibitory rate these two groups (P<0.05), it indicated that both the two drugs has similar tumor suppression effect. After treatment inhibitory rate of tumor issue in Group D mice was significantly higher than in Groups B and C (P<0.05), suggesting that the curative effect of combination of LTA and 5-FU in tumor suppression is significantly better than alone.
In recent years, the relationship between the incidence of liver cancer and the cytokines has become the research focus, but research reports on TGF-αα are relatively few[18]. TGF-αα is a polypeptide composed of 50 amino acid, played a special role in regulating the growth of normal cells and the transformation of abnormal cells[19]. EGFR is the expression product of proto-oncogene c-erbB-1. It is widely distributed in mammalian epithelial cell membrane and vascular tissue, and plays an important role in regulating cell proliferation and activation[20]. Studies have found that[21], TGF-α, EGFR can express in liver cancer tissues at the same time. Moreover, the excessive expression closely associated with the onset of cancerof the liver, and there is a significant positive correlation between these two expressions. The results of this study showed that the expression of EGFR and TGF-αα proteins in Groups B, C, D after treatment was significantly lower than that in Group A (P<0.05); EGFR, TGF-α expression in Group D was significantly lower than in Groups B and C (P<0.05). This manifested that combined treatment can effectively inhibit the over expression of TGF-ααand EGFR, inhibit tumor cell proliferation, thus achieve the therapeutic effect of tumor suppression. Caspase, according to its role in cell apoptosis, can be divided into two kinds, enzymes for initiating and effective enzymes, which is the great discovery in the research of apoptosis in molecular biology in recent years[22]. In caspase, caspase 3 is an important effective protein lyase, and plays an important role in the process of tumor cell apoptosis[23-24]. The results of this study showed that after the treatment the expression of caspase 3 in Group D was significantly higher than the other three (P<0.05), suggesting that the LTA combined with 5-FU can improve the expression of caspase 3, promote tumor cell apoptosis, and thus play a synergistic antitumor effect.
According to the results of this study LTA combined with 5-FU can inhibit the over expression of TGF-αα and EGFR expression, improve the expression of caspase 3, thus inhibit tumor cell proliferation and promote tumor cell apoptosis. Therefore, LTA combined with 5-FU has remarkable synergistic antitumor effects.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
[1] Zhang ZM, Li LQ, Liu JY, Yuan WP, Wu FX, Xiang BD, et al. Curative effect and safety analysis of Sorafenib for the treatment of advanced primary liver cancer. J Clin Oncol 2010; 15(4): 352 -354.
[2] Jiang CL, Wang GJ, Li FW. The curative effect of perfusion chemotherapy on middle-late hepatic cancer and metastatic liver cancer. Chin J Coal Industry Med 2008; 11(8): 1160-1161.
[3] Liu B, Liu QG, Yue TQ, Yang SH, Li X. Evaluation on curative effect of interventional chemotherapy perfusion and embolization on primary liver. Modern Med & Health 2010; 26(16): 2469-2470.
[4] Cong Y, Xiang M. The antitumor progress of mushroom polysaccharide in basic research and clinical application. J Dalian Med Univ 2010; 32(4): 465-469.
[5] Sutcliffe IC, Hogg SD. Extraction of lipoteichoic acid from Streptococcus mutans with the non-ionic detergent TritonX- 114. J Microbiol Methods 1993; 17(3): 215-225.
[6] Ma Q, Mu JQ, Yu LL, Zhang ZP. Effect of extract of purple mushroom from Helan mountain on antioxidant capacity of H22 mice. Sci Technol Food Industry 2013; 34(14): 342-345.
[7] Ngo DH, Vo TS, Ngo DN, Wijesekara I, Kim SK. Biological activities and potential health benefits of bioactive peptides derived from marine organisms. Int J Biol Macromolecules 2012; 51(4): 378-383.
[8] Rameshkumar G, Ravichandran S, Kaliyavarathan G. Antimicrobial peptide from the crab, Thalamita crenata (Latreille, 1829). World J Fish Marine Sci 2009; 1(2): 74-79.
[9] Gerlinger M, Swanton C. How Darwinian models form therapeutic failure initiated by clonal heterogeniety in cancer medicine. Br JCancer 2010; 103(11): 39-43.
[10] Hoefl B, Linseisen J, Beckmann L, Muller-Decker K, Canzian F, Husing A, et al. Polymorphisms in fatty acid metabolism related genes are associated with eoloreetal cancer risk. Carcinogenesis 2010; 31(3): 466-472.
[11] Kantoff PW, Higano CS, Shore ND, Berger ER, Small EJ, Penson DF, et al. Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration resistant prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2010; 363(4): 411-422.
[12] de Bono JS, Oudard S,Ozguroglu M, Hansen S, Machiels JP, Kocak I, et al. Prednisone plus cabazitaxel or mitoxantrone for metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer progressing after docetaxel treatment: a randomised open label trial. Lancet 2010; 376(11): 1l47-1154.
[13] Gerlinger M, Swanton C. How Darwinian models form therapeutic failure initiated by clonal heterogeniety in cancer medicine. Br J Cancer 2010; 103(11): 39-43.
[14] Pu R, Zhang SZ, Zhang DC. Nano-sized Fe3O4-Lipoteichoic acid to relieve ulcerative colitis. Chin J Microecol 2012; 24(1): 1- 5.
[15] Czaja AJ. Promising pharmacological, molecular and cellular treatments of autoimmune hepatitis. Curr Pharm Des 2011; 17(29): 3120-3140.
[16] Yu SL, Han B, Zhang R, Du ZY, Wu XB, Wu W, et al. Isolation of rat liver cells by improved collagenase perfusion digestion method though abdominal aorta. J Clin Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Res 2010; 14(44): 8253-8256.
[17] Wang HX, Liu M, Weng SY, Li JJ, Xie C, He HL, et al. Immune mechanisms of concanavalin A model of autoimmune hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(2): 119-125.
[18] Wang Y, Paszek P, Horton CA, Yue H, White MR, Kell DB, et al. A systematic survey of the response of a model NF-κB signalling pathway to TNF-α stimulation. J Theor Biol 2012; 297: 137- 147.
[19] Seki S, Nakashima H, Nakashima M. Antitumor immunity produced by the liver Kupffer cells,NK cells,NKT cells, and CD8+CD122+T cells. Clin Dev Immunol 2011. doi:10.1155 /2011 /868345.
[20] Zhou HY, Zhou GH. Research progress of mechanism of nitric oxide and endotoxin and intervention effect of probiotic in cirrhosis complications incidence. J Difficult Complicated Cases 2011; 10(7): 560-562.
[21] Xie N, Guo B, Wang Y, Liu MF, Fang DC. The in-vivo effect of bifi dobacterium fat teichoic acid combined with 5 - fluorouracil on tumor cell apoptosis. Chinese J Microecol 2009; 21(12): 1090-1094.
[22] Zhang YY, Fang ZQ, Wang YM. The comparison of different treatments on H22 liver cancer bearing mice. Acta Chin Experimental Animals 2014; 22(3): 67-77.
[23] Liang HF, Pu R, Chen S, Xiang HG, Zhang DC. Study of antiproliferation and promoting apoptosis of bifidobacterium fat teichoic acid on colon cancer cells. Chin J Microecol 2013; 25(3): 269-271.
[24] Qin WL, Zhang J, Dou JF. Effect of bifidobacterium fat teichoic acid on tumor necrosis factor α and levels of nitric oxide of liver cells of sword bean A protein activated mice. J Xinxiang Medi College 2013; 30(5): 353-355.
#Co-first author.
*Corresponding author: Ze-Zhang Tao, M.D., Doctor Tutor, Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China.
E-mail: taozezhang@hotmail.com
Foundation project: This paper was supported by Applied Basic Research Program, Science and Technology Bureau of Wuhan City, (No. 2013062301010823), Medical Care and Science Research Project of Health and Family Planning Commission of Wuhan (No. WX14A11, WX15D26), and The third group of “Hanyang Talents’ Plan”.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine的其它文章
- Andrographolide effect on both Plasmodium falciparum infected and non infected RBCs membranes
- Immunogenicity and efficacy of recombinant 78 kDa antigen of Leishmania donovani formulated in various adjuvants against murine visceral leishmaniasis
- Oral administration of Sauce llorón extract to growing lambs to control gastrointestinal nematodes and Moniezia spp.
- Hepatoprotective and proapoptotic effect of Ecballium elaterium on CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in rats
- Evaluation of protective effect of cactus pear seed oil (Opuntia ficusincida L. MILL.) against alloxan-induced diabetes in mice
- Antimicrobial activity and synergism of Sami-Hyanglyun-Hwan with ciprofloxacin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
