分化型甲状腺癌131I治疗前刺激性Tg动态变化与远处转移的关系
2015-12-21李田军李从心林岩松
赵 腾,梁 军,李田军,李从心,丛 慧,杨 珂,李 方,林岩松
1中国医科院学院 北京协和医学院 北京协和医院核医学科,北京1007302青岛大学附属医院肿瘤科,山东青岛266003
分化型甲状腺癌131I治疗前刺激性Tg动态变化与远处转移的关系
赵 腾1,梁 军2,李田军2,李从心1,丛 慧2,杨 珂1,李 方1,林岩松1
1中国医科院学院 北京协和医学院 北京协和医院核医学科,北京1007302青岛大学附属医院肿瘤科,山东青岛266003
目的 探讨分化型甲状腺癌(DTC)131I治疗前未服或停服甲状腺激素状态下测定的刺激性甲状腺球蛋白(sTg)的动态变化及其与远处转移的关系。方法 远处转移组(M1)38例和非远处转移组(M0)130例。动态监测131I治疗前sTg及相应促甲状腺激素(TSH)值(首次记为Tg1、TSH1,末次记为Tg2、TSH2)。比较两组Tg1、Tg2、sTg变化值(ΔTg)及sTg随TSH变化比值(ΔTg/ΔTSH)有无差异。用ROC曲线及最佳诊断界值点(DCP)评估以上指标对远处转移的预测价值。结果 M1组Tg1和Tg2均显著高于M0组(P均<0.001),ROC曲线下面积分别为0.921和0.942,其中Tg2对远处转移预测准确性更高,达85.71%(DCP=24.30 ng/ml,灵敏度92.11%,特异度83.85%)。两组间ΔTg及ΔTg/ΔTSH差异均有统计学意义(P均<0.01);△Tg/△TSH对远处转移预测准确性及特异度均优于Tg2(分别为87.50% 和86.92%)。结论131I治疗前动态监测sTg有助于提高DTC远处转移预测的准确性和特异度,△Tg/△TSH所反映的sTg 随TSH变化比值可作为DTC远处转移有效的预测指标。
分化型甲状腺癌;甲状腺球蛋白;131I治疗;外科治疗
甲状腺癌是最常见的内分泌恶性肿瘤,近年发病率逐年上升[1]。甲状腺癌中约90%为分化型甲状腺癌(differentiated thyroid cancer,DTC),其中约1%~23%诊断时已发生远处转移(distant metastasis,DM)[2-4]。甲状腺球蛋白(thyroglobulin,Tg)是DTC131I治疗后长期随访重要指标[5-7]。对于131I治疗前刺激性甲状腺球蛋白(stimulated thyroglobulin,sTg),由于受残余甲状腺组织影响,其在病情评估方面意义尚待探讨[8]。目前研究主要侧重于sTg与 DTC缓解与复发的关系[9-11],本课题组前期研究显示131I治疗前sTg水平对DM亦有预测价值[12],但尚未有报道关注其动态变化在病情评估方面的意义。本研究探讨了DTC根治术后131I治疗前sTg的动态监测与DM的关系。
对象和方法
对象及分组 2012年3月至2014年6月在北京协和医院就诊DTC患者168例,其中,男60例,女108例,平均年龄(41.0±11.9)岁,所有患者均行甲状腺全切或次全切术及131I治疗,术后病理确诊为DTC。根据影像学及病理资料综合判断是否存在DM,分为DM组(M1,n=38)和非DM组(M0,n=130)。
方法 根据计算机断层扫描(computed tomography,CT)、131I诊断性全身显像(diagnostic wholebody scintigraphy,DxWBS)或治疗后全身显像(posttreatment whole-body scintigraphy,RxWBS)、2-氟-2-脱氧-D-葡萄糖(18F-FDG)正电子发射断层成像、全身骨显像结合病理检查综合判断患者是否存在DM,并通过术后DxWBS或RxWBS判断残余甲状腺情况。131I治疗前常规检查包括胸部CT、颈部超声,术后未服甲状腺激素或停药后促甲状腺激素(thyrotropin,TSH)升高(>30 μU/ml)状态下测定的刺激性Tg(stimulated thyroglobulin,sTg)及相应TSH、TgAb水平的动态监测(首次测量值分别记为Tg1、TSH1、TgAb1,末次记为Tg2、TSH2、TgAb2)。所有患者131I治疗准备均参照美国甲状腺协会(American Thyroid Association,ATA)相应指南[8]。为排除TgAb对Tg测量值干扰,TgAb测量值高于参考值范围上限(>115 U/ml)或未监测相应TgAb水平者不纳入本研究。Tg和TgAb测定采用电化学发光免疫分析法(electrochemiluminescence immunoassay,ECLIA)(美国罗氏公司,E170),检测范围分别为0.1000~1000.0000 ng/ml和10~4000 U/ml。TSH测定采用化学发光免疫分析法(chemiluminescence immunoassay,CLIA) 法(德国拜耳公司,ADVIA CENTAVRXP),检测范围为0.004~150.000 μU/ml。Tg和TSH测量值若超过其测定范围则分别记为1000 ng/ml和150 μU/ml。
统计学处理 采用SPSS 18.0统计软件,首先采用t检验、χ2检验和Mann-Whitney秩和检验分别比较两组患者的年龄、性别及残余甲状腺情况等特征差异;采用 Mann-Whitney秩和检验分析两组间 Tg1、Tg2、sTg变化值(ΔTg=Tg2-Tg1)和sTg随TSH变化比值 [ΔTg/ΔTSH= (Tg2-Tg1)/(TSH2-TSH1)]的差异,并建立其与DM关系的ROC曲线,获得最佳诊断界值点;比较以上指标在预测DM方面的灵敏度、特异度、准确性、阳性预测值(positive predictive value,PPV)和阴性预测值(negative predictive value,NPV);P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结果
一般资料 两组患者在年龄(t=-1.35、P= 0.179)、性别(χ2=1.74,P=0.19)和残余甲状腺情况(U=2067,P=0.056)方面差异均无统计学意义(表1)。
不同时间sTg测量值与DM的关系 M1组Tg1 及Tg2水平均显著高于M0组(P均<0.001)(表2)。Tg1和 Tg2的 AUC分别为0.921(95%CI:0.864~0.978)和0.942(95%CI:0.906~0.977),约登指数最大值分别为0.732和0.760,对应的最佳诊断界值点分别为12.35 ng/ml和24.30 ng/ml(图1)。其中,当Tg2以24.30 ng/ml为界值时约登指数最大,对应的灵敏度、特异度分别为92.11%和83.85%,预测DM的准确性、PPV、NPV分别为85.71%、62.50% 和97.32%(表3)。
△Tg、△Tg/△TSH与DM的关系 M1组的△Tg(P=0.002)及△Tg/△TSH(P<0.001)水平均显著高于 M0组(表2)。△Tg、△Tg/△TSH>0(变化呈升高趋势)时 ROC的 AUC分别为 0.884(95%CI:0.807~0.961)和0.903(95%CI:0.829~0.977),约登指数最大值分别为0.604和0.783,预测DM的最佳临界值分别为21.55 ng/ml和0.44 ng/μU;当△Tg、△Tg/△TSH<0(变化呈降低趋势)时ROC 的AUC分别为0.800(95%CI:0.629~0.971)和0.867(95%CI:0.000~1.000),约登指数最大值分别为0.551和0.721,对应的最佳诊断界值点分别为-10.50 ng/ml和-0.40 ng/μU(图1)。其中,△Tg/ △TSH以-0.40~0.44 ng/μU为界值时约登指数最大,对应灵敏度、特异度分别为89.47%和86.92%,预测DM的准确性、PPV和NPV分别为87.50%、66.67%和96.58%(表3)。
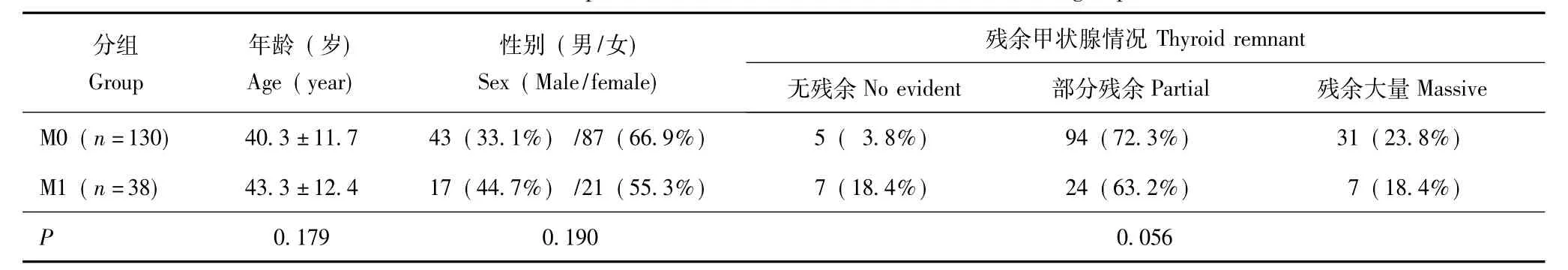
表1 两组患者临床特征的比较Table 1 Comparison of clinical characteristics between two groups
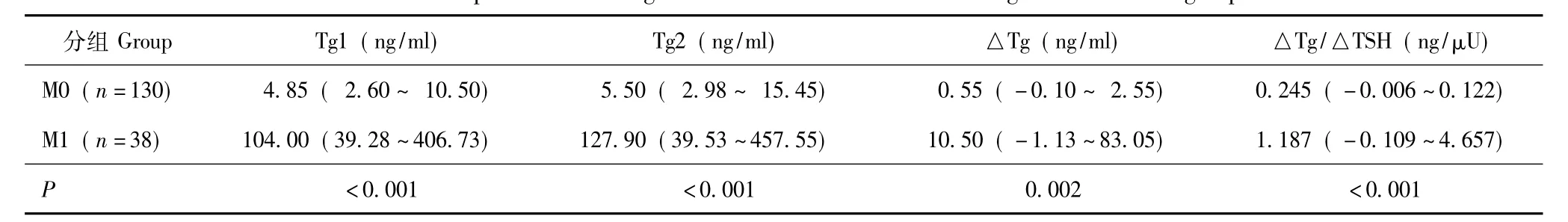
表2 两组患者血清学特征及其变化指标的比较Table 2 Comparison of serological characteristics and their changes between two groups
讨论
Tg是甲状腺产生的特异性蛋白,主要由甲状腺滤泡上皮细胞分泌。DTC来源于甲状腺滤泡细胞,Tg分泌活跃。目前对术后已行131I治疗清除甲状腺组织(简称清甲)的DTC患者,血清Tg变化情况是随访过程中监测患者是否存在肿瘤残留或复发的重要手段[13]。TSH刺激后(通过停服L-T4或应用重组人TSH使血清TSH升高至>30 μU/ml)Tg水平对于DTC患者术后清甲治疗后病情监测具有较高敏感性和特异度[14]。
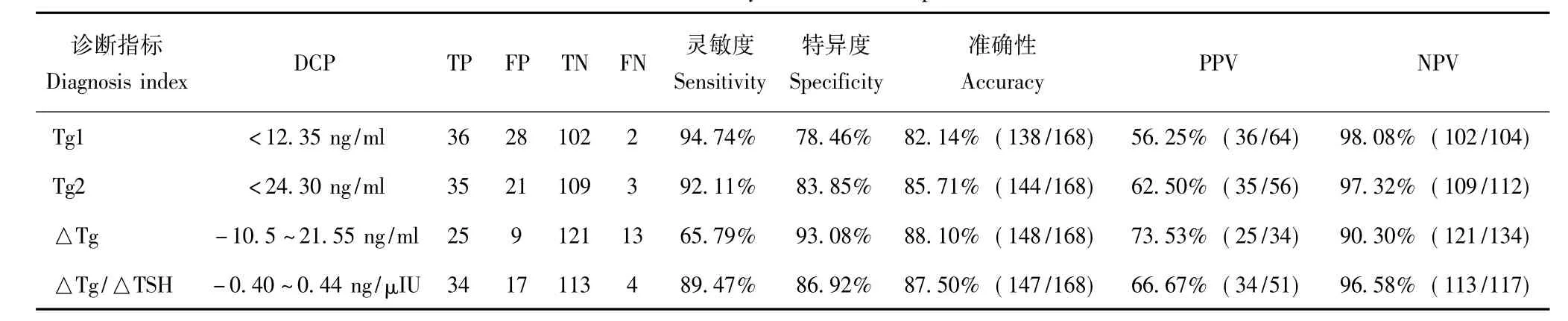
表3 131I治疗前血清学指标及其变化特征对DTC远处转移诊断价值的比较Table 3 Serological characteristics and their changes before radioiodine therapy in judging distant metastasis of differentiated thyroid carcinoma patients
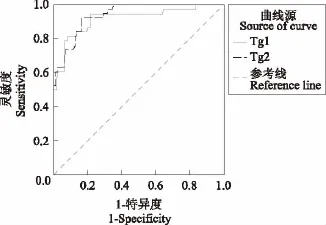
图1 DTC患者Tg1、Tg2与远处转移关系的ROC曲线Fig 1 The ROC curves of Tg1 and Tg2 in predicting distant metastasis in DTC patients
由于绝大多数DTC患者术后仍存在残余甲状腺组织,多数研究者认为首次131I治疗前sTg水平易受残余甲状腺影响,在发现DTC残留或复发方面敏感性和特异性均不高[15-16],区分正常甲状腺组织和肿瘤组织的界值不详[8],在病情评估方面意义仍不明确。近期研究主要侧重于131I治疗前sTg水平与DTC缓解与复发之间的关系[9-11],例如,González等[9]研究发现DTC术后、首次131I治疗前的基线sTg<8.55 ng/ml对治疗后18~24个月内疾病缓解有预测作用,而Kim等[10]认为131I治疗前sTg预测疾病缓解的界值为sTg<3.3 ng/ml。此外也有研究发现停药后sTg>28 ng/ml(或人重组TSH下sTg>2.8 ng/ml)时即与疾病复发或持续状态有关[11]。本课题组前期研究显示,首次131I治疗前sTg水平对DM亦有预测作用[12]。上述研究均仅以单次静止sTg测量值为观察点,尚未有研究探讨sTg随停药时间及TSH的动态变化,以及这种动态变化在DTC131I治疗前评估及治疗决策中的意义。
本研究通过对伴有DM的DTC患者131I治疗前sTg水平动态观察发现,131I治疗前末次sTg测量值较其首次测量值对DM具有更高预测价值,本研究得到Tg2的最佳诊断界值点为24.30 ng/ml,这一数值低于本课题组一项针对术后131I清甲治疗前sTg的前期研究得到的界值(52.75 μg/L)[12],笔者认为这可能与本研究纳入了部分已成功行131I清甲治疗的患者,避开了残余甲状腺组织多少对sTg的影响有关[15,17],因此本研究得到的Tg2界值可能更适合于DTC131I治疗后长期随诊过程中对DM的监测;另外,两个研究纳入的患者不完全相同,sTg测量值对应的TSH水平不同也是导致sTg水平差异的原因。
本研究首次从动态监测角度进一步探究了131I治疗前sTg动态变化与DM的关系,发现131I治疗前sTg变化值(△Tg)预测DM的准确性、特异度优于末次sTg,但其灵敏度仍较低(65.79%)。根据131I治疗前sTg的升高和降低趋势不同,将反应Tg变化的△Tg分为>0(sTg升高)和<0(sTg降低)两种情况,在升高者,DM组△Tg较非DM组高,且TSH均呈升高趋势,提示这部分患者的远处转移灶在TSH不断增高的刺激下Tg合成增加;而在降低者,DM组较非DM组△Tg的绝对值更大,分析这部分患者的远处转移灶在TSH不断增高的刺激下Tg合成减少,笔者认为这可能主要与远处转移灶产生内源性甲状腺激素反馈抑制TSH导致sTg水平相应下降有关。
由于TSH是正常甲状腺或DTC细胞产生和释放Tg最重要的刺激因子[18-20],多数患者TSH水平随着术后未服或停服甲状腺激素时间的延长而升高,不同TSH水平可对sTg测量值产生较大影响。为校正TSH水平对sTg的影响,本研究进一步探讨了△Tg/△TSH作为sTg变化指标的意义,结果显示,△Tg/△TSH在预测DM方面兼顾了较高的准确性、灵敏度及特异度,其准确性、特异度均优于末次 sTg;其灵敏度高达89.47%,显著高于△Tg,这提示△Tg/△TSH对临床DM的判断更有价值。
综上,本研究动态观察了sTg变化及其与DTC患者是否存在DM之间的关系。结果表明,与单次sTg测量值相比,动态监测sTg有助于提高其在判断DM的准确性和特异性,△Tg/△TSH所反映的sTg随TSH变化比值可作为DM有效的预测指标。
[1]National Cancer Institute.SEER Cancer Statistics Factsheets: Thyroid Cancer[R/OL].[2014-09-15].http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/thyro.html.
[2]Sampson E,Brierley JD,Le LW,et al.Clinical management and outcome of papillary and follicular(differentiated) thyroid cancer presenting with distant metastasis at diagnosis [J].Cancer,2007,110(7):1451-1456.
[3]Nixon IJ,Whitcher M,Palmer FL,et al.The impact of distant metastases at presentation on prognosis in patients with differentiated carcinoma of the thyroid gland[J].Thyroid,2012,22(9):884-889.
[4]Lee J,Soh EY.Differentiated thyroid carcinoma presenting with distant metastasis at initial diagnosis clinical outcomes and prognostic factors[J].Ann Surg,2010,251(1):114-119.
[5]Tuttle RM,Leboeuf R.Follow up approaches in thyroid cancer: a risk adapted paradigm[J].Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am,2008,37(2):419-435.
[6]Mazzaferri EL,Robbins RJ,Spencer CA,et al.A consensus report of the role of serum thyroglobulin as a monitoring method for low-risk patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma [J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2003,88(4):1433-1441.
[7]Eustatia-Rutten CFA,Smit JWA,Romijn JA,et al.Diagnostic value of serum thyroglobulin measurements in the follow-up of differentiated thyroid carcinoma,a structured metaanalysis[J].Clin Endocrinol,2004,61(1):61-74.
[8]Cooper DS,Doherty GM,Haugen BR,et al.Revised American Thyroid Association management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer[J].Thyroid,2009,19(11):1167-1214.
[9]González C,Aulinas A,Colom C,et al.Thyroglobulin as early prognostic marker to predict remission at 18-24 months in differentiated thyroid carcinoma[J].Clin Endocrinol,2014,80(2):301-306.
[10]Kim H,Kim SJ,Kim IJ,et al.Limited clinical value of periablative changes of serum markers in the prediction of biochemical remission in patients with papillary thyroid cancer [J].Nucl Med Mol Imaging,2013,47(4):268-272.
[11]Ciappuccini R,Hardouin J,Heutte N,et al.Stimulated thyroglobulin level at ablation in differentiated thyroid cancer: the impact of treatment preparation modalities and tumor burden[J].Eur J Endocrinol,2014,171(2):247-252.
[12]李田军,林岩松,梁军,等.131I治疗前刺激性Tg对乳头状甲状腺癌远处转移的预测价值[J].中华核医学与分子影像杂志,2012,32(3):189-191.
[13]中华医学会内分泌学分会,中华医学会外科学分会内分泌学组,中国抗癌协会头颈肿瘤专业委员会,中华医学会核医学分会.甲状腺结节和分化型甲状腺癌诊治指南[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2012,28(10):779-797.
[14]Eustatia-Rutten CF,Smit JW,Romijn JA,et al.Diagnostic value of serum thyroglobulin measurements in the follow-up of differentiated thyroid carcinoma,a structured meta-analysis [J].Clin Endocrinol(Oxf),2007,61(1):61-74.
[15]Phan HT,Jager PL,van der Wal JE,et al.The follow-up of patients with differentiated thyroid cancer and undetectable thymglobulin(Tg)and Tg antibodies during ablation[J].Eur J Endocrinol,2008,158(1):77-83.
[16]Salvatori M,Raffaelli M,Castaldi P,et al.Evaluation of the surgical completeness after total thyroidectomy for differentiated thyroid carcinoma[J].Eur J Surg Oncol,2007,33(5):648-654.
[17]Suh I,Vriens MR,Guerrero MA,et al.Serum thyruglobulin is a poor diagnostic biomarker of malignancy in follicular and Hurthle-cell neoplasms of the thyroid[J].Am J Surg,2010,200(1):41-46.
[18]Spencer CA,LoPresti JS,Fatemi S,et al.Detection of residual and recurrent differentiated thyroid carcinoma by serum thyroglobulin measurement[J].Thyroid,1999,9(5): 435-441.
[19]Schlumberger M,Baudin E.Serum thyroglobulin determination in the follow-up of patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma[J].Eur J Endocrinol,1998,138(3):249-252.
[20]Baloch Z,Carayon P,Conte-Devolx B,et al.Laboratory medicine practice guidelines.Laboratory support for the diagnosis and monitoring of thyroid disease[J].Thyroid,2003,13(1):3-126.
Relationship between Variation of Pre-ablation Stimulated Thyroglobulin and Distant Metastasis in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
ZHAO Teng1,LIANG Jun2,LI Tian-jun2,LI Cong-xin1,CONG Hui2,YANG Ke1,LI Fang1,LIN Yan-song1
1Department of Nuclear Medicine,PUMC Hospital,CAMS and PUMC,Beijing 100730,China
2Department of Oncology,the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University,Qingdao,Shandong 266003,China
Objective To investigate the relationship between the dynamic variation of pre-ablation stimulated thyroglobulin(sTg)and distant metastasis in patietns with differentiated thyroid cancer(DTC).Methods DTC patients after total or near total thyroidectomy were divided into two groups as M1 group(n= 38)and M0 group(n=130)according to the presence of distant metastases or not.Clinical data including preablation sTg and the corresponding thyrotropin(TSH)values were dynamically measured.The pre-ablation sTg and corresponding TSH collected at the first time were defined as Tg1 and TSH1,while as Tg2 and TSH2 at thelast time.χ2test was used to compare the variation tendency of sTg between these two groups.Tg1,Tg2,preablation sTg variation(ΔTg),and ΔTg/ΔTSH ratio between M0 and M1 were compared by Mann-Whitney ranksum test.The receiver operating characteristic(ROC)curves and diagnostic critical point(DCP)were employed to evaluate the predictive values of the above indicators.Results Both Tg1 and Tg2 of M1 were significantly higher than those of M0(the Mann-Whitney rank-sum test:Tg1 P<0.001,Tg2 P<0.001).The corresponding areas under the ROC curve(AUC)to differentiate the two groups were 0.921 and 0.942,respectively.The cut-off value of Tg2,which was more accurate in predicting distant metastasis,was 24.3 ng/ml with a sensitivity of 92.11%and a specificity of 83.85%.Both ΔTg and ΔTg/ΔTSH between these two groups were significantly different(the Mann-Whitney rank-sum test:ΔTg P=0.002,ΔTg/ΔTSH P<0.001).ΔTg/ΔTSH worked better than Tg2 in predicting distant metastasis with both higher accuracy(87.50%)and higher specificity(86.92%).Conclusions Dynamically tracing pre-ablation sTg may improve the accuracy and specificity of distant metastases prediction in DTC patients.ΔTg/ΔTSH,which means the ratio of sTg variation to TSH variation,may be a useful diagnostic marker for predicting distant metastases in DTC.
differentiated thyroid cancer;thyroglobulin;radioiodine therapy;surgical therapy Acta Acad Med Sin,2015,37(3):315-319
LIN Yan-song Tel:010-69155610,E-mail:linys@pumch.cn
R736.1
A
1000-503X(2015)03-0315-05
10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2015.03.013
2014-09-30)
林岩松 电话:010-69155610,电子邮件:linys@pumch.cn
国家自然科学基金(30970850)和卫生部行业科研专项项目(201202012)Supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China(30970850)and the Ministry of Health Industry Special Scientific Research Projects(201202012);第一、二位作者对本文贡献一致The first two authors contributed equally to this article
