A Comparative Study on Pattern of Urban Forest Patch and Its Ecological Benefit Evaluation in the Park of Hefei Based on the GIS Technology
2015-12-14LeiZHANGYaliangLI
Lei ZHANG, Yaliang LI
Huainan Normal University, Huainan 232001, China
CITYgreen, applied in land use planning, is a piece of software operated in ARC/View developed by ESRI company, based on GIS, providing statistical analysis,map, and report for ecosystem servicing function. AMERICAN FORESTS develops CITYgreen for the convenience of community planning and management[1-2].Currently,CITYgreen is widely applied in more than 200 cities in the US to formulate environment control planning, land use policy and re-constructing forests.With satellite image increasingly applied, US Forest Service has built a dynamic monitoring system on 12 states,which provides information for analyzing forest changes since 1972. Therefore,CITYgreen is widely applied in analysis of forest ecological benefits in the research area. Recently, ecological analysis function is increasingly strengthening of CITYgreen as multispectral and high-ratio image applied,which makes it possible to conduct ecological benefits analysis covering county, city and even the whole regions[3].
Domestically, many researches have been made on CITYgreen. For example,Hu et al.[4]and Zhu et al.[5]evaluated urban forest ecological benefits in Shenyang with CITYgreen3.0.Zhang et al.[6]evaluated ecological service value of green land in Hangzhou with CITYgreen 5.0.
The research conducted a comparative study on forest ecological benefits of Xiaoyaojin Park and Xinghua Park with CITYgreen in order to analyze ecological benefits of forests in Hefei and provide references for urban forest planning and construction. Meanwhile, the research explored the possibility and method for researching urban forest ecological benefits, providing theory and method of aid-decision making for urban planning,design and management.
Research Areas
The research was conducted based on two parks in Hefei City, An-hui Province. Hefei is located in the north of the Yangtze River and borders Chaohu to the southeast. It is notable that park environment differs little in the same city,with high comparability.
Hefei, at 117°11′-117°22′E and 31°48′-31°58′N, is the capital of Anhui Province in Jianghuai hilly region.Hefei has an area of 596 km2and a population of 1 558 000 inhabitants until the end of 2007. It is the Nationally Designated Garden City , with green coverage ratio of 39.5%and per capita public green area of 10.15 m2.The areas of Xiaoyaojin Park and Xinghua Park area 37.75 and 28.55 hm2, respectively.
Hefei features a humid subtropical climate with four distinct seasons.Its annual average temperature is 15.7℃, with a July average of 28.5 ℃and a January average of -2 ℃. Besides,its annual precipitation is 981.4mm,being heavier from June to August.The frost-free days last for 230 d.Yellow brown soils, with pH of 6.5-7.3,are widely distributed,with heavier soil horizon,and sticky texture.Local vegetations include Pinus massoniana,Dalbergia hupeana, Quercus acutissima, Liquidambar formosana, Maackiaamurensis Rupret Maxim,Celtis sincensis, Ulmus parvifolia, and Ulmus pumila.
Research Methods and Steps
CITYgreen model, data source and registration
The research data were collected from TM data of Landsat on May 3,2009, covering 185 ×185 km2. The wavebands of TM data were 3, 4 and 5.Specifically,the length of waveband 3 is in the range of 0.63-0.96 μm, of waveband 4 is 0.76-0.90 μm, and of waveband 5 is 1.55-1.75 μm.Besides,instantaneous field of view of bands 3,4 and 5 was 30 m. Vegetation in remote sensing image is a kind of direct reflection information. Furthermore,green vegetation is generally of high reflected value near infrared band (the 4th waveband)and low reflected value bear the 3thwaveband. The 5thwaveband of TM shows much sensitive to water content of vegetation, reflecting vegetation growth. Therefore, the research composited image using false color from the 3rd, 4th, and 5thwavebands of Landsat TM in order to highlight vegetations and reduce influences of other factors on vegetation.
After obtaining the images, the research used remote sensing data,followed by image processing with ERDAS IMAGINE and conducted geometric correction on the images by selecting control points, followed by map merging and cutting,and geographical registration.
Classification of landscape composition
According to Chinese Land Use Status and research region, the research classified landscape types of urban park into buildings and hard surface, water surface, urban forest(crown coverage rate over 30% ),greenbelt (crown coverage rate below 30%),farmland,and bare land.
Field survey
The research conducted a field survey on research regions. Specifically, oriented with GPS, the research investigated on the spot and compared urban forest, buildings and hard surface, water surface, greenbelt and farmland with chromatographic surface features in order to reduce influences of different objects in the same image and the same object with different spectra. Meanwhile, the changes of ground objects caused by park constructions should be aware of in different development stages and the field survey should coincide with ground objects in the shooting term in case of construction caused errors.
Digitization
After registration, field survey and classification,TM images were digitalized on ArcView to construct relationship between image spatial characteristics and attribute data. Besides, the relationship should be constructed of ground objects in different colors with relevant properties. For example, dark green represents urban forests, and an attribute database can be established with an attribute table.
Value assessment
Value assessment on carbon fixation efficiency According to Carbon Tax Law, carbons are charged as per discharge of CO2. Specifically, carbon tax rate of Sweden in China Biodiversity Research Report[7],150 U.S.dollar would be charged if 1 ton carbon is discharged,converted into 1 148 yuan/t,so that economic values of carbon in storage and absorbing can be computed of trees.
Value assessment of purifying atmospheric pollutants Middle true value[8-9]of every pollutant of the US was used, as follows: NO2of 51.6 yuan/kg,PM10 of 34.4 yuan/kg,SO2of 12.6 yuan/kg, CO of 7.3 yuan/kg, and O3of 51.6 yuan/kg and O3of 51.6 yuan/kg.
Value assessment on reducing rainstorm-induced runoff The data of annual mean precipitation and maximal precipitation models (24 h)were collected from Hefei Meteorological Service. The management and construction rate of rainstorm on ground runoff in the US were adopted and converted into RMB of 540.6 yuan/m3[10].
Results and Analysis
Analysis on landscape composition
As shown in Table 1, Xiaoyaojin Park has an area of 35.75 hm2,covering 18.82 hm2urban forests, representing 52.62%,and water and greenbelt areas taking up to 15.20% and 9.54%, respectively. It is an ancient battlefield in the Three Kingdoms, with a long history, where many trees are grown, such as arbors. Therefore, the beautiful environment and clean airs are contributed by high coverage of forest(Fig.1a).
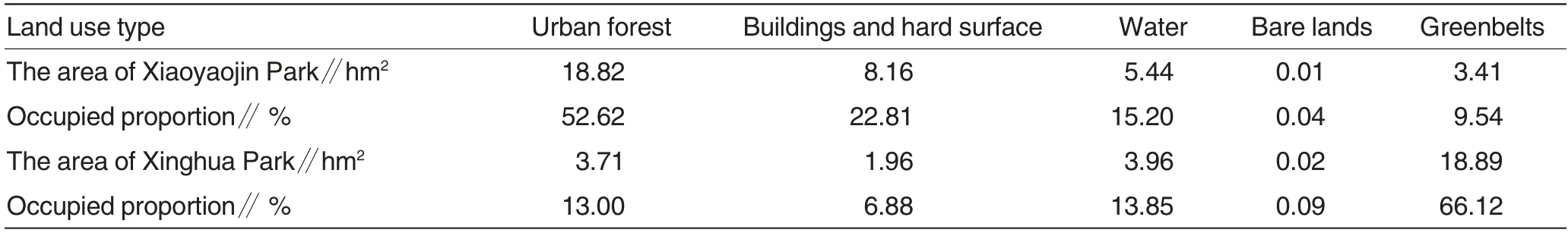
Table 1 Landscape composition of Xiaoyaojin Park and Xinghua Park
Xinghua Park has an area of 28.55 hm2, including 18.89 hm2greenbelts, representing 66.12%, followed by 3.96 hm2water, representing 13.85%. Besides, urban forest area reaches 3.71 hm2, taking up to 13.00%.The Park is situated in roundcity-park belts in Hefei, where largescale lawns are distributed and arbors are planted recently(Fig.1 b).
In conclusion, forests, a kind of substrate, hold the highest proportion in Xiaoyaojin Park, influencing landscapes in the whole areas. In Xinghua Park, however, the proportion of greenbelts keeps higher, and lawns are substrates in the region.
Analysis on carbon storage and absorbing of forests in parks
Carbon fixation efficiency of urban forests can be concluded with CITYgreen according to landscape distributions in the parks (Table 2). As shown in Table 2, the total stored amount of carbon was 1 999.94 tons and annual absorbed carbon reached 15.57 tons in Xiaoyaojin Park,converting into 2.312 7 million yuan. In contrast,the amount of stored carbons totaled 394.68 tons and annual absorbed carbons reached 3.07 tons in Xinghua Park,which can be converted into 456 400 yuan. The two parks are both located in downtown of Hefei.Forests in Xiaoyaojin Park make contribution to reduction of CO2 content in surrounding areas as well as relieving of heat island effect, supplemented by lawns in Xinghua Park.
Xiaoyaojin Park performs better in ecological function than Xinghua Park,because arbors in the former make higher contribution in carbon fixation than lawns in the latter.
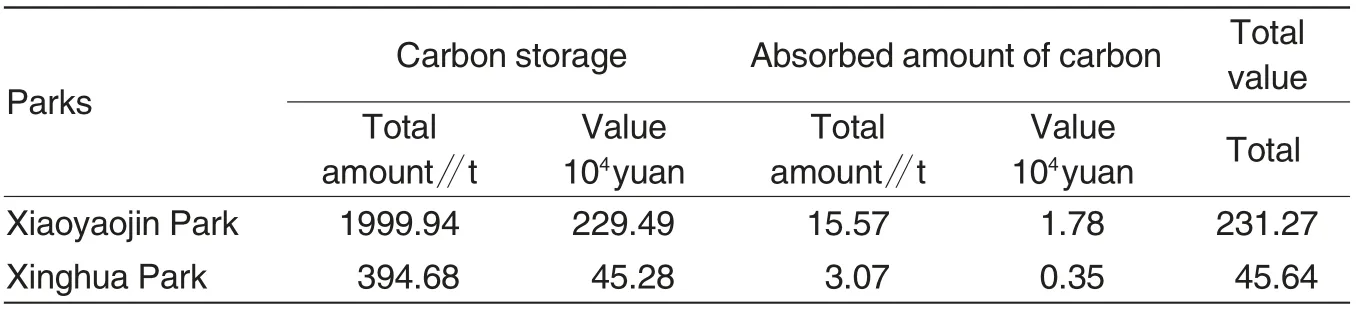
Table 2 Carbon fixation efficiency of urban forests in Xiaoyaojin Park and Xinghua Park
Analysis on air purification by park forests
As shown in Fig.1 and Table 3,annual absorbed O3,SO2,NO2and CO and cleaned PM10 were 701.4, 297.7,698.0,137.3 and 665.9kg, respectively,converted into 99 800 yuan of forests in Xiaoyaojin Park. In contrast,annual absorbed O3,SO2,NO2and CO and cleaned PM10 were 138.4, 58.7,137.8,27.1 and 131.4 kg,respectively,converted into 19 700 yuan of forests in Xinghua Park. Such differences actually coincide with forest areas in two parks.

Table 3 Comparisons of air purification of urban forests in Xiaoyaojin Park and Xinghua Park

Table 4 Comparisons of efficiencies of park forests in cutting rainstorm-induced runoff
Analysis on efficiencies of park forests in cutting rainstorm-induced runoff
As shown in Fig.1 and Table 4,the effectively-cut amounts of rainstorm-induced runoff were 5 064.25 and 1 624.49 m3in Xiaoyaojin Park and Xinghua Park, converted into2.737 7 and 0.878 100 million yuan,accordingly. In terms of forest coverage and non-forest coverage, the differences of curve index reflect the effects of landscape composition changes on reducing rainstorm-induced runoff and the higher the differences, the higher the effects. For instance, curve index changes of Xiaoyaojin Park and Xinghua Park were 8 and 2,respectively,showing that Xiaoyaojin Park curve changed the most dramatically. Therefore, the Park performed better in cutting rainstorm-induced runoff, with higher eco-importance.On the contrary, the cutting effects would be affected severely if forests here are destroyed. As for surface runoff and maximal runoff, Xiaoyaojin Park and Xinghua Park achieved 1.68 and 0.35, and 64.72 and 9.32, accordingly, indicating that Xiaoyaojin made higher contribution,in reducing the runoffs.
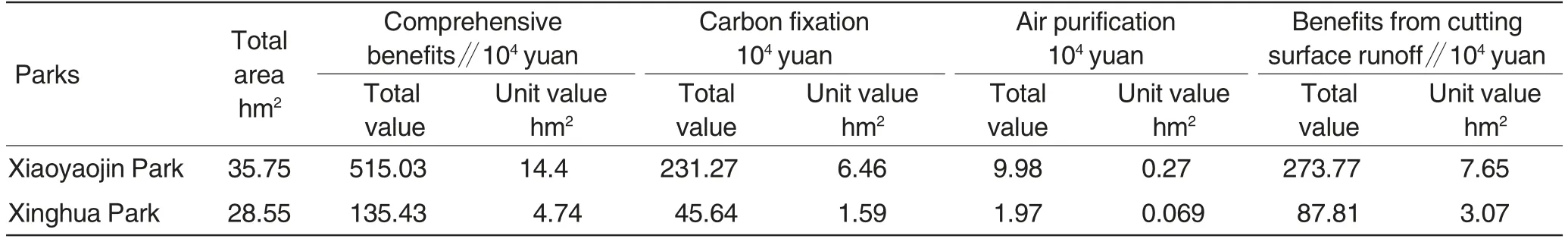
Table 5 Comparisons of comprehensive ecological benefits of park forests
Comparisons of comprehensive ecological benefits of park forests
As shown in Fig.1 and Table 5,comprehensive ecological benefits of Xiaoyaojin Park and Xinghua Park were 5.150 3 and 1.354 3 million yuan,respectively and per unit area ecobenefits were 144 000 and 47 400 yuan,accordingly.Because Xiaoyaojin Park area is larger,the comprehensive ecological benefits prove higher, as well as per unit area eco-benefits. On the other hand, vegetations in the two parks play key roles.For example,Xiaoyaojin Park is dominated by arbors,with a high coverage rate, and Xinghua Park dominated by lawns,with young trees.
Conclusion
Xiaoyaojin Park and Xinghua Park are both located within the 1stRing Road and key sections of round-citypark greenbelts. However, the two parks differ significantly in forest landscape pattern, leading to large variations of eco-benefits. It can be concluded that eco-benefits of Xiaoyaojin Park are higher, because it’s forest coverage rate keeps higher. Xiaoyaojin Park is dominated by arbors influencing environment by photosynthesis and transpiration, as well as selfgrowth in terms of increasing air humidity and absorbing harmful gas.Xinghua Park, in contrast, is dominated by lawns,having little effects on semi-climate and rainstorm-induced runoff.Therefore,comprehensive ecobenefits of Xinghua Park are lower.
In conclusion, construction of public greenbelts should take both landscape effects of laws and ecological benefits from ecology aspect in order to improve urban environment based on forest functions. Meanwhile,it is necessary to local conditions,such as terrain and landform, are also crucial in constructing urban forest parks,which should not be ignored.
[1]OHSAWA, M. DA LJ. Integrated Studies in Urban Ecosystemsas the Basis of Urban Planning III). Chiba: Chiba University,1988:137-142.
[2]ROWNTREE, RA. Forest cover and land use in four Eastern United States cities.Urban Ecol,1984,8:55-67.
[3]American Forests. CITYgreen5.0 User Manual. Washington DC: American Forests,2002:6-12.
[4]HU ZB(胡志斌),HE XY(何兴元),CHEN W (陈玮), et al. Urban forest structure and benefit analysis in Shenyang City(沈阳市城市森林结构与效益分析)[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报),2003,14(12):2108-2112.
[5]ZHU WQ (朱文泉), HE XY (何兴元),CHEN W ( 陈玮), et al. Quantitative analysis of urban forest structure: A case study on Shenyang arboretum (城市森林结构的量化研究——以沈阳树木园森林群落为例)[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报),2002,14(12):2090-2094.
[6]ZHANG K (张侃),ZHANG JY (张建英).Urban greenbelt eco-service value of Hangzhou city under effects of land use change: an evaluation with CITYgreen model(基于土地利用变化的杭州市绿地生态服务价值CITY-green 模型评价)[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (应用生态学报),2006,17(10):1918-1922.
[7]National Environmental Protection Bureau(国家环境保护局). China biodiversity reports(中国生物多样性国情研究报告) [M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press(北京:中国环境科学出版社),1998.
[8]NOWAK D J,CRANE D E,STEVENS J C. Air pollution removal by urban trees and shrubs in the United States. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2006, 4:115-123.
[9]WU ZM (吴泽民), MCBRIDE J R,NOWAK D J, et al. Effects of Urban Forest on Air Pollution in Hefei City (合肥城市森林减少大气污染的效果)[J].Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry(中国城市林业),2003,1(1):39-43.
[10]American forests organizations. Urban ecosystem analysis, town of flower mound,TX[R/OL].(2006-08-23).http://www.americanforests.org/resources/urbanforests/analysis.php
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Evaluation on Suitability of Camellia sinensis Planting Based on GIS
- Light Quality-controlled Phytochemicals Biosynthesis in Vegetables and Fruits
- Cloning and Characterization of Phytochrome A Gene FaPHYA from Tall Fescue
- Genetic Analysis of Embryo Production Frequency in Wheat×Maize Cross
- The Application Effects of Truly Biodegradable Mulch in Potato Farmlands
- The Analysis and Prospect of Development of Fresh Cut Flower Industry Based on the Patent Analysis
