Effects of-glucosidase lnhibitors on the Function of Mulberry Leaf Extract as an Additive in Feedstuff
2015-11-18HongZHANGQingfangWANGBoSUNChaoXlONGZhongxuSONGInstituteofEconomicCropsHubeiAcademyofAgriculturalSciencesWuhan430064ChinaInstituteofAnimalHusbandryandVeterinaryScienceHubeiAcademyofAgriculturalSciencesWuhan430064China
Hong ZHANG,Qingfang WANG,Bo SUN,Chao XlONG,Zhongxu SONG.Institute of Economic Crops,Hubei Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Wuhan 430064,China;.Institute of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Science,Hubei Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Wuhan 430064,China
Hong ZHANG1*,Qingfang WANG1,Bo SUN1,Chao XlONG1,Zhongxu SONG2
1.Institute of Economic Crops,Hubei Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Wuhan 430064,China;
2.Institute of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Science,Hubei Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Wuhan 430064,China
The mulberry juice contains high concentrations of α-glucosidase inhibitors that affect glycometabolism and cause diarrhea in animals,thereby affecting the development and application of mulberry(Morus alba L.)as feedstuff resources.In this study,the effects of mulberry leaf extract with and without removal of mulberry juice on starch metabolism were analyzed and compared.The results showed that mulberry leaf extract with removal of mulberry juice exhibited significantly lower inhibition rate on starch metabolism compared with mulberry leaf extract without removal of mulberry juice.In animal feeding trials,piglet feedstuff was added with 10%mulberry leaf powder;compared with mulberry leaf powder without removal of mulberry juice,experimental piglets fed with mulberry leaf powder with removal of mulberry juice exhibited significantly improved weight gain and significantyl reduced diarrhea rate.
Mulberry(Morus alba L.);α-glucosidase inhibitors;Feeding function
I n recent years,the proportion of feed grains accounting for food consumption has maintained a rapid growth in China.Feed grain supply has become one of the most important issue and key factor of food security.It is necessary to develop"nonfood"feed and focus on the development and utilization of unconventional feed resources.
Mulberry (Morus alba L.)is a perennial deep-rooted species with strong adaptability and high resistance to barren and drought,which can be cultivated in barren hills and slopes,with the total planting area of approximately one million hm2in China.Currently,mulberry has become one of the most high-yielding woody plants,but the peasants have only used mulberry leaves as silkworm feed.With the development of breeding industry,using mulberry as a broad-spectrum feed has attracted increasingly attention.Moreover,mulberry contains more abundant nutrients than other pasture species,which can be prepared into an ideal unconventional feed source.In addition,mulberry has rare diseases and insect pests,which can be planted with pesticide-free techniques to provide green feed sources with no pesticide residues.
Generally,mulberry branches and leaves are harvested by artificial or mechanical stumping,cut into 1-2 cm segments using a mechanical guillotine,dried,mechanically crushed into powder,and added into normal feedstuffs.
However,the content of mulberry powder is usually below 6%in chicken diets and below 10%in pig diets[2].Excessively high concentrations of mulberry powder in feedstuffs will affect the growth of livestock,mainly causing diarrhea.So far,studies of mulberry feedstuffs are mainly focused on the recommended dosage and their improving effect on animal quality,but little information is available on the reason why the dosage can not be raised. Previous studies show that alkaloids are the main factors causing diarrheain animals.A certain amount of alkaloids exhibit a positive effect on the growth and development of pigs,but overdose will lead to diarrhea.Morus plants are characterized by juice secretion,which ooze juice after being damaged.Mulberry juice contains three kinds of alkaloids:1,4-dideoxy-1,4--imino-d-arabinitol(D-AB1),1-deoxynojirimycin(DNJ)and 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-D-ribitol[3],which all belong to α-glucosidase inhibitors that can inhibit sugar degradation in animal intestines and affect normal glucose metabolism. Alkaloids are soluble in water,and the percentage of alkaloids in mulberry juice accounts for about 2.4%of the wet weight,which is 100 times of that in other issues[4].In this study,the effects of of mulberry leaf extract with and without removal of mulberry juice on starch metabolism were analyzed and compared,aiming at providing the basis for the promotion and utilization of mulberry feedstuffs.
Materials and Methods
Materials
Mulberry leaves Mulberry leaves were collected from Husang 32 plants cultivated in the mulberry germplasm nursery of Institute of Economic Crops,Hubei Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
Experimental animals Local 3-month-old broilers with consistent weight (500 g);Dabai piglets with consistent weight(approximately 25 kg).
Methods
Feeding trials of broilers with mulberry juice Accurately 0.1 g of mulberry juice was added into 10 g of feedstuff(per day)and fed to each broiler for five consecutive days;the defecation of broilers was observed to calculate watery excrement rate(on average).
Watery excrement rate=Watery excrements/Total excrements×100%.
Feeding trials of piglets with mulberry leaf powder Dabai piglets were divided into two groups.Group A: normal feedstuff was added with 10% mulberry leaf powder with removal of mulberry juice;group B:normal feedstuff was added with 10%mulberry leaf powder without removal of mulberry juice.Experimental piglets were reared in pens for a week and then fed with feedstuffs containing 10%mulberry leaf powder.The dietary preference and adaptability to mulberry leaf powder and diarrhea situation in piglets was observed.After feeding for 12 d,each piglet was weighed(on average).
Extraction of mulberry leaf extract Accurately 200 mg of mulberry leaf powder with and without removal of mulberry juice were weighed,added with 1 ml of 0.05 mol/L HCl solution,mixed with a vortex for 1 min,processed by ultrasonic treatment for 40 min,evaporated at 60℃ for 30 min to remove HCl,and centrifuged at 12 000 r/min for 10 min.The supernatant was collected separately to obtain two different mulberry leaf extracts.
lnhibitory effects of mulberry leaf extract on starch metabolism The efficiency of starch degradation into glucose was determined with p-nitrophenol method that involves amylase and glucosidase.In accordance with the introductions of amylase assay kit(Wuhan Life Origin Biotech Co.,Ltd.),100 U of enzyme was added into 250滋l enzymatic reaction system and added with 30滋l of mulberry leaf extract,with 30滋l of distilled water as a control(original enzyme activity assay).Each treatment was repeated three times and the determined values were averaged to calculate the inhibition rate of mulberry leaf extract on starch metabolism.
Inhibition rate=(Original enzyme activity-Enzyme activity in samples)/ Original enzyme activity×100%.
Determination of 1-deoxynojirimycin(alkaloid)content in mulberry leaves By using ultraviolet reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography[5],the content of 1-deoxynojirimycin in mulberry leaves with and without removal of mulberry juice was determined.Each treatment was repeated twice and the determined values were averaged.
Results and Analysis
Feeding trials of broilers with mulberry juice
Broilers were fed with 10 g of normal feedstuff containing 0.1 g of mulberry juice.Results showed that the loose stool rate of broilers increased significantly from 10.2%to 21.2%during the experimental period,which indicated that mulberry juice could cause diarrhea in broilers(Table 1).
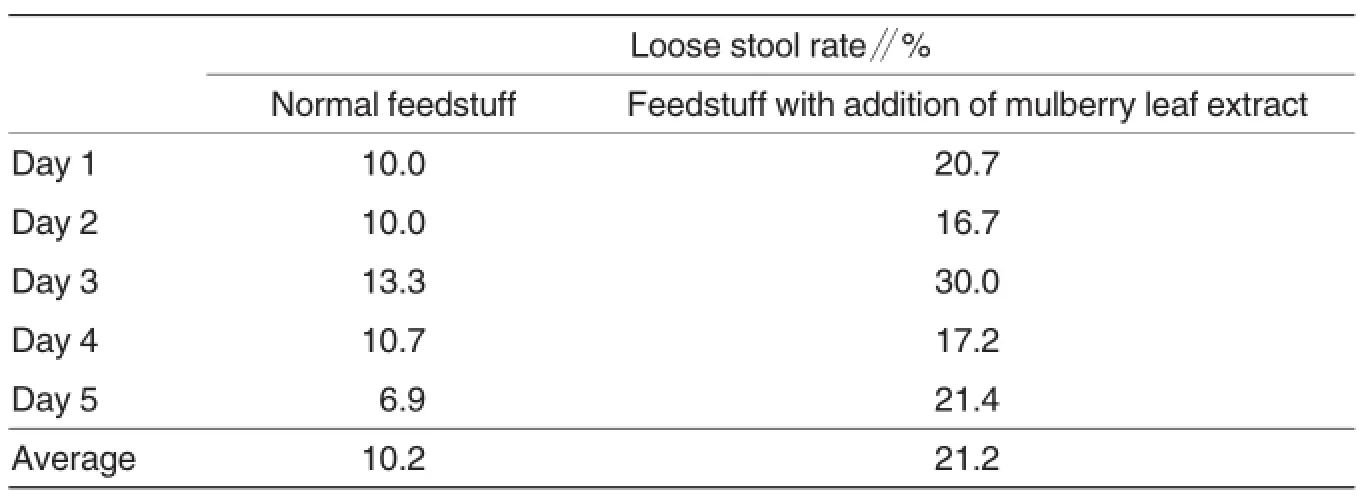
Table 1 Effects of different feedstuffs on defecation in broilers
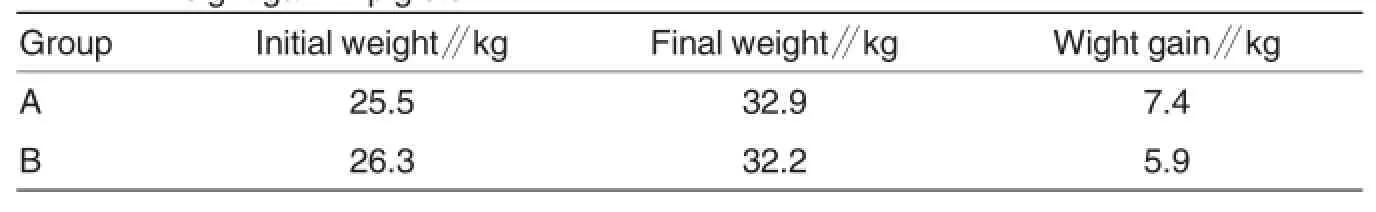
Table 2 Effects of mulberry leaf powder with and without removal of mulberry juice on weight gain in piglets
Feeding trials of piglets with mulberry leaf powder
Piglets weighing 25 kg were selected for feeding trials because they are more sensitive to diets than adult pigs.Experimental piglets were fed with feedstuff containing 10%mulberry leaf powder for 12 d.According to the observation results, experimental piglets exhibited higher dietary preference to mulberry leaf powder with removal of mulberry juice (treatment A)than to mulberry leaf powder without removal of mulberry juice(treatment B);after feeding,the diarrhea rate in group A was significantly lower than that in group B;weight gain in group A was significantly higher than that in group B;to be specific,the weight of piglets in group A increased averagelyby 7.4 kg and that in group B increased averagely by 5.9 kg(Table 2).
Determination of 1-deoxynojirimycin(alkaloid)content in mulberry leaves
Mulberry juice contains various alkaloids,including 1-deoxynojirimycin. The variation of 1-deoxynojirimycin content in mulberry samples with and without removal of mulberry juice reflects the effects of different treatment measures on alkaloid content in samples.According to the determination results,1-deoxynojirimycin content in mulberry samples without removal of mulberry juice was 0.19%;1-deoxynojirimycin content in mulberry leaves with removal of mulberry juice was 0.15%that was reduced by 21% compared with untreated mulberry leaves.
lnhibitory effects of different mulberry leaf extracts on starch hydrolysis
α-glucosidase is required for starch hydrolysis,and alkaloids in mulberry leaves are α-glucosidase inhibitors.In this study,the effects of mulberry leaf extract with and without removal of mulberry juice on starch hydrolysis in vitro were analyzed.According to the results,the original enzyme activity was 0.053;after the addition of extract A (mulberry leaf extract with removal of mulberry juice),the enzyme activity (represented by the changes in absorbance value)reached 0.046 and the inhibition rate on starch metabolism was 13.2%;after the addition of extract B(mulberry leaf extract without removal of mulberry juice),the enzyme activity reached 0.035 and the inhibition rate on starch metabolism was 34.0%,which indicated that mulberry leaf extract without removal of mulberry juice exhibited significantly higher inhibitory effects on starch metabolism than mulberry leaf extract with removal of mulberry juice.
Conclusion and Discussion
Alkaloids in mulberry juice are αglucosidase inhibitors.α-glucosidase can act on glycosides or oligosaccharides to hydrolyze glucosidic bonds into glucose.Excess α-glucosidase inhibitors in the feedstuff will inhibit the hydrolysis of carbohydrates in animals. Mulberry leaf extracts exhibit significantly strong inhibitory effects on the hydrolysis process of starch into glucose.
Clinical studies have shown that blood sugar levels in patients with type II diabetes can be reduced effectively by 20 mg/d DNJ[6].In this study,results show that high concentrations of alkaloids affect carbohydrate metabolism and cause diarrhea in animals.Due to lack of hydrolase or other reasons,some carbohydrates can not be absorbed by the intestinal mucosa,forming hypertonic intestinal contents to absorb large amounts of water,thus causing hypertonic diarrhea.In the present study,10% mulberry leaf powder was added into piglet diets,which significantly declined the growth rate of piglets;however,after removal of partial DNJ in mulberry leaves,diarrhea situation in piglets was reduced significantly and weight gain increased remarkably.
High concentrations of α-glucosidase inhibitors restrict the feeding function of mulberry.However,China is rich in mulberry resources.Mulberry varieties with relatively low content of α-glucosidase inhibitors and high protein content can be selected to accommodate feedstuff needs of mulberry industry.
References
[1]AL-KIRSHI R,et al.Utilization of mulberry leaf meal(Morus alba)as protein supplement in diets for laying hens[J].I-talian Journal of Animal Science,2010,9(3):265-267.
[2]LI YG(李有贵),ZHANG L(张雷),ZHONG S(钟石),et al.Effects of dietary mulberry leaf on growth performance,fat metabolism and meat quality of finishing pigs(饲粮中添加桑叶对育肥猪生长性能、脂肪代谢和肉品质的影响)[J]. Acta Zoonutrimenta Sinica(动物营养学报),2012,24(9):1805-1811
[3]KONNO K,et al.Mulberry latex rich in antidiabetic sugar-mimic alkaloids forces dieting on caterpillars[J].PNAS,2006,103(5):1337-1341.
[4]ASANO N,et al.Polyhydroxylated alkaloids isolated from mulberry trees(Morus alba L.)and silkworms(Bombyx mori L.)[J].J.Agric.Food Chem.,2001,49:4208-4213.
[5]SHI XQ(施新琴),CUI WZ(崔为正),QIU LQ (裘立群),et al.Determination of 1-deoxynojirimycin content by ultraviolet reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography(用反相高效液相色谱-紫外检测法测定1-脱氧野尻霉素的含量)[J].Science of Sericulture(蚕业科学),2006,32(1):146-149.
[6]OK HM,et al.The effect of aqueous mulberry leaf extract on glucose metabolism in subjects with impaired fasting glucose[J].The FASEB Journal,2012,26:440-448.
Responsible editor:Xiaohui FAN
Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
Copyright Authorization Statement
Should the article be accepted and published by Agricultural Science&Technology,the author hereby grants exclusively to the editorial department of Agricultural Science&Technology the digital reproduction,distribution,compilation and information network transmission rights.
桑树中α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂对桑饲料功能的影响
张 鸿1*,王晴芳1,孙 波1,熊 超1,宋忠旭2(湖北省农业科学院经济作物研究所,湖北武汉 430064;湖北省农业科学院.畜牧兽医研究所,湖北武汉 430064)
桑(Morus)汁中含有极高的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂,高含量α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂可影响动物的糖代谢,导致动物腹泻,影响桑树作为饲料资源的开发和利用。试验对去除桑汁和未去除桑汁的桑叶提取物对淀粉代谢的影响进行了分析比较。结果表明,去除桑汁的桑叶提取物对淀粉代谢的抑制率明显低于未去除桑汁的桑叶提取物。在饲养试验中,以10%的比例添加到仔猪饲料中,去除桑汁的桑叶提取物组与未去除桑汁的桑叶提取物组相比,仔猪增重明显增加,腹泻程度明显下降。
桑 (Morus);α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂;饲料功能
张鸿(1968-),女,湖北武汉人,助理研究员,博士,主要从事桑树生理研究,E-mail:1844454772@qq.com。。
2014-12-30
2015-02-12
.E-mail:1844454772@qq.com
December 30,2014Accepted:February 12,2015
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Characteristics of Pollen Germination and Storage of Zygocactus truncates
- lnfluence of a New Nano-PE-film on the Greenhouse Environmental Factors
- Effects of Penicillium spp.and Trichoderma spp. on Pleurotus ostreatus Growth and Screening of Effective Disinfectants
- Study on Photosynthetic and Physiological Effects of a Novel Adaxially-Rolled Character in Rice(Oryza sativa L.)
- Effects of Mutagenesis by UV lrradiation and60Co-γ lrradiation on Fermentation of Xylose to Ethanol by Pichia stipitis
- Genetic Variation Analysis of 3D Gene and Molecular Detection of Porcine Kobuvirus in 2013-2014
