任意大初值等温相对论欧拉方程组的奇性形成问题
2015-11-17耿永才
耿永才, 刘 健
(上海应用技术学院理学院,上海 201418)
任意大初值等温相对论欧拉方程组的奇性形成问题
耿永才, 刘 健
(上海应用技术学院理学院,上海 201418)
主要证明了当初始值受到挤压以及初始流体向外流出时等温相对论欧拉方程组光滑解的奇性形成问题.通过引入与解有关的泛函,证明该泛函满足适当的微分不等式,同时证明该微分不等式的解会发生奇性,继而得到等温相对论欧拉方程组解的奇性形成结果.
等温相对论欧拉方程组;光滑解;奇性形成
1 简介
考虑等温相对论欧拉方程组[1-3],

式中:ρ,v分别表示流体的质能密度和速度,c表示光速,p表示压力.式(1)中第1个方程表示动量守恒方程,第2个方程表示能量守恒方程.有关式(1)最早数学方面系统的研究始于Smoller-Temple,在文献[4]中证明了式(1)的整体弱解存在性.随后Lu-Ukai在文献[5]中讨论了熵解的整体相对论极限问题.对不同的状态方程,文献[6-9]中证明了式(1)的整体熵界存在性和黎曼解的稳定性.
由于双曲守恒律系统本身的特点,不管初值怎样光滑,随着时间的发展,光滑解都将会出现奇性,故人们更加关注解的奇性形成问题.对一维流体光滑解的奇性形成问题,多采用特征线法[10-11]进行分析,但是对于高维情形,特征就不再那么明晰,Sideris[12-13]引入了泛函方法.该方法主要是在积分意义下考虑解的性质,避免了逐点讨论.由于结构的复杂性,有关相对论流体的奇性形成问题结果还不是很多.对于式(1)的三维情形,Pan-Smoller在文献[14]中证明了初始能量充分大和初始能量有限的两种情形下解的奇形性问题,但没有考虑任意大初值下式(1)解的奇性形成问题.
为简单起见,引入两个记号

式(1)可写成

初始条件为
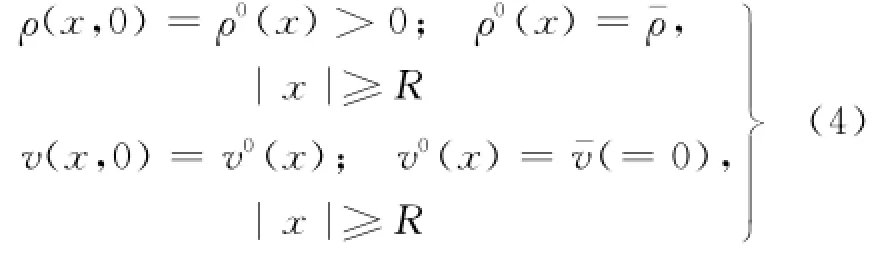
式中,R表示一个正常数.
式(1)有两个方程,但是有3个未知数,故还需要另外一个方程.本文试图纯粹从数学角度来考虑式(1)光滑解的奇性形成问题,假设状态方程为

2 方程组(1)光滑解的奇性形成问题
假设
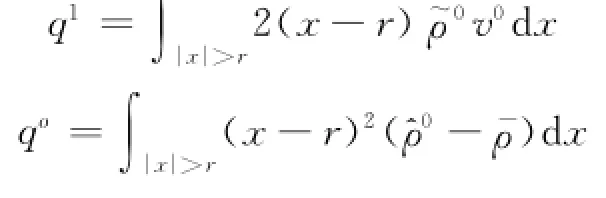
本文的主要结果如下:
定理1 假设(ρ(x,t),v(x,t))是式(1)和(4)的光滑解,若存在常数R0,满足0<R0<R,且R0<r<R,有

则式(1)和(4)光滑解的生命跨度T是有限的.其中R0为常数.T<∞表示光滑解的最大存在区间,即当时间t→T时,解本身的范数或者其梯度的范数就会出现奇性.
为证明定理1,需要一个重要的性质,即光滑解具有有限传播速度.
命题1[12]假如(ρ0,v0)满足初始条件(4),则对0≤t≤T,式(1)和(4)的光滑解(ρ,v)存在于D(t)上.其中为常数状态处的声速.
定理1证明如下.
证明 定义泛函
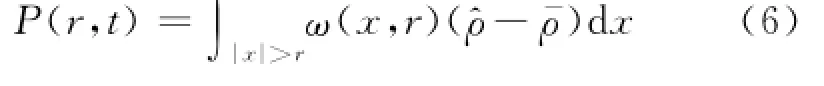
式中,权函数ω=(x-r)2.易计算得

通过计算P(r,t)关于r的导数并且利用式(6),可得

求P(r,t)关于t的导数,并且利用命题1和式(6),可得
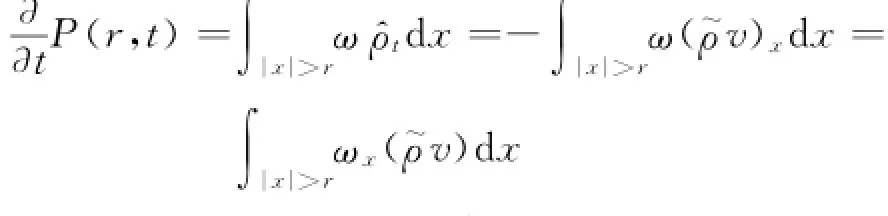
对上式再次关于时间求导

式中,

对于第2项,可得
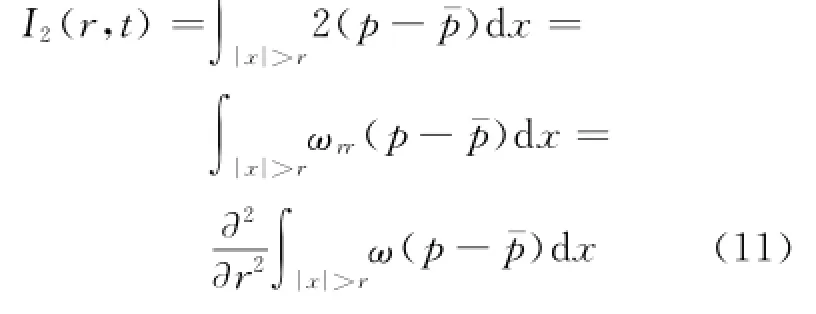
利用式(9),(10)易计算得

由状态方程(5),得
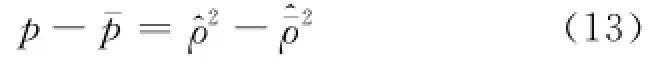
和

将式(13)、(14)代入式(12),可得


式中,
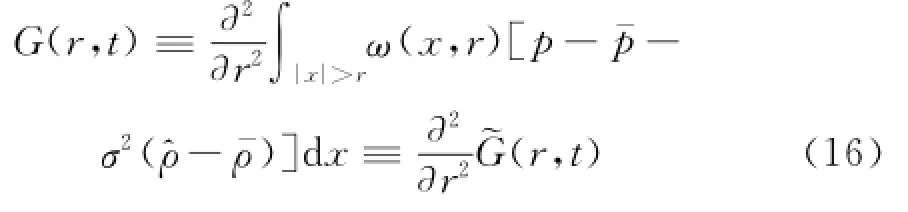
式中,

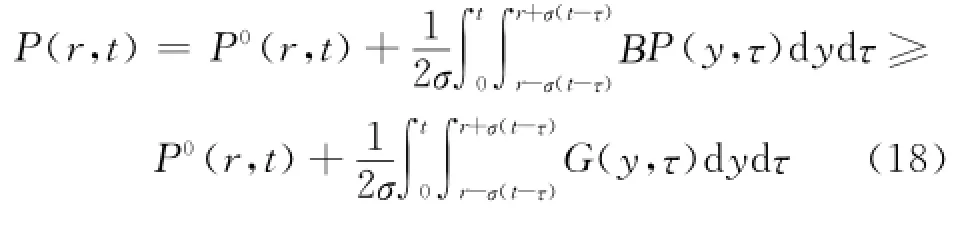
式中,

定义泛函
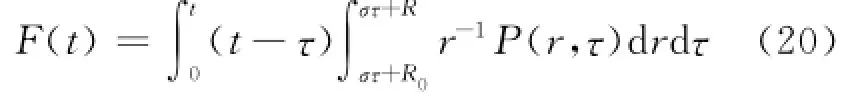
容易看出F(t)关于时间t是C2的,故有

式中,

通过定理1中的假设,在R0<r<R上,q0(r)>0和q1(r)>0,故
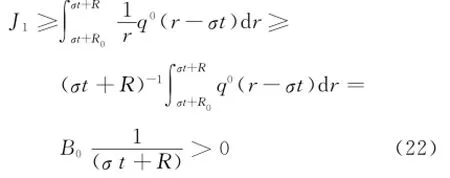
式中,

改变J2的积分顺序,利用G(y,t)在集合{y≤σt+R}上是紧支的,发现

在t≥R1=(R-R0)/2的假设下.最内层的积分可由下式控制[12],即
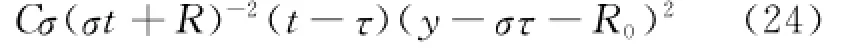
由G(y,t)>0,有
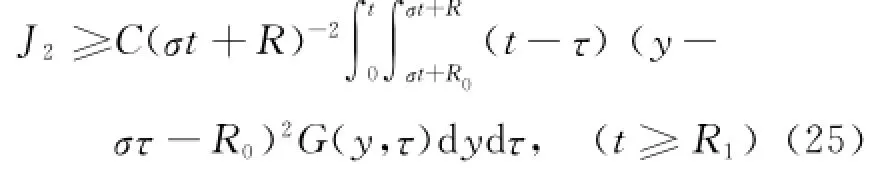
并且注意到~G(y,τ)在y>στ+R为零,利用式(16),对式(25)分部积分,得
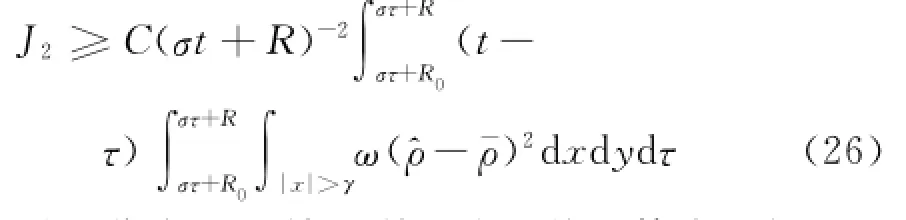
记内层积分为J4,并且利用施瓦兹不等式可得:

令J5表示式(27)中的积分项,估计如下:
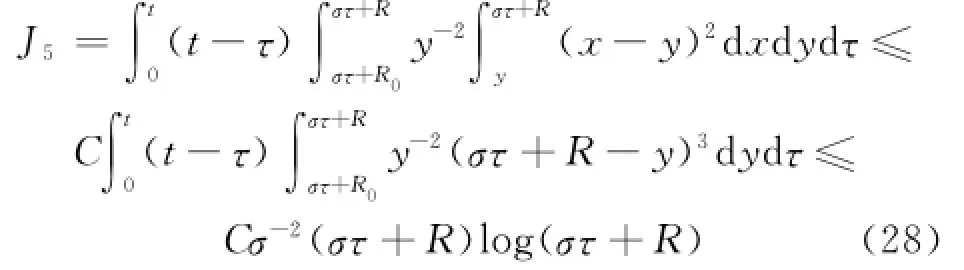
结合式(21)、(27)、(28),得

利用文献[13]中的方法就可得到时间t≤C(常数),式(29)才有意义,其中,C只和初始条件相关.故式(1)和(4)的光滑解在有限时间内会发生爆破,从而得到定理1的证明.
[1] Anile A M.Relativistic fluids and magneto-fluids[M].New York,Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics:Cambridge University Press,1989:80-82.
[2] Landau L D,Lifchitz M.Fluid mechnics[M].2nd ed.Oxford:Pergamon,1987:505-512.
[3] Li T,Qin T.Physics and parital differential Equations[M].2nd ed.Beijing:Higher Eudcation Press,2005:183-196.
[4] Smoller J,Temple B.Global solutions of the relativistic Euller equation[J].Commun Math Phys,1993,156:67-99.
[5] Lu Min,Ukai S.Non-relativistic global limits of weak solutions of the relativistic Euler equation[J].J Math Kyoto Univ,1998,38(3):525-537.
[6] Chen G Q,Li Y C.Relativistic Euler equations for isentropic fluids:Stability of Riemann solutions with large oscillation[J].Z Angew Math Phys,2004,55(6):903-926.
[7] Li Y C,Feng D,Wang Z.Global entropy solutions to the relativistic Euler equations for a class of large initial data[J].Z Angew Math Phys,2005,56(2):239-253.
[8] Chen J.Conservation Laws for the relativistic p-system[J].Commu Partial Diff Eqs,1995,20(9/10):1605-1646.
[9] Chen G Q,Li Y C.Stability of Riemann solutions with large oscillation for the relativistic Euler equations[J].J Diff Eqs,2004,202(2):332-353.
[10] Lax P D.Hyperbolic systems of conservation laws and the mathematical theory of shock waves[M]. New York:Society for Industrial and Appl Math Philadelphia,1973.33-38.
[11] Ruan L,Zhu C.Existence of global smooth to the relativistic Euler equations[J].Nonl Anal,2005,60(6):993-1001.
[12] Sideris T.Global behavior of solutions to nonlinear wave equations in three space dimensions[J].Comm Partial Differ Equations,1983,8:1291-1323.
[13] Sideris T C.Formation of singularities in three-dimensional compressible fluids[J].Comm Math Phys,1985,101:475-485.
[14] Pan R,Smoller J.Blowup of smooth solutions for relativistic Euler equations[J].Comm Math Phys,2006,262(3):729-755.
(编辑 吕丹)
Singularities Formation to the lsothermal Relativistic Euler Equations with Arbitrary lnitial Data
GENG Yong-cai, LIU Jian
(School of Sciences,Shanghai Institute of Technology,Shanghai 201418,China)
The singularities formation of the isothermal relativistic Euler equations was testified in the condition of the compression of the initial data and the external flow of the initial fluid.By introducing proper functionals coming from the smooth solutions,it was proved that the functionals would match the differential inequalities,and the singularities would occur in the solutions of the differential inequalities. Thus,the singularities formation results were obtained.
isothermal relativistic Euler equations;smooth solutions;singularities formation
O 29
A
1671-7333(2015)01-0095-04
10.3969/j.issn.1671-7333.2015.01.017
2014-07-09
国家自然科学基金资助项目(11201308);上海市创新基金资助项目(13ZZ136);上海市优秀青年基金资助项目(ZZyyy12025)
耿永才(1979-),女,讲师,博士,主要研究方向为偏微分方程.E-mail:ycgengjj@sit.edu.cn
