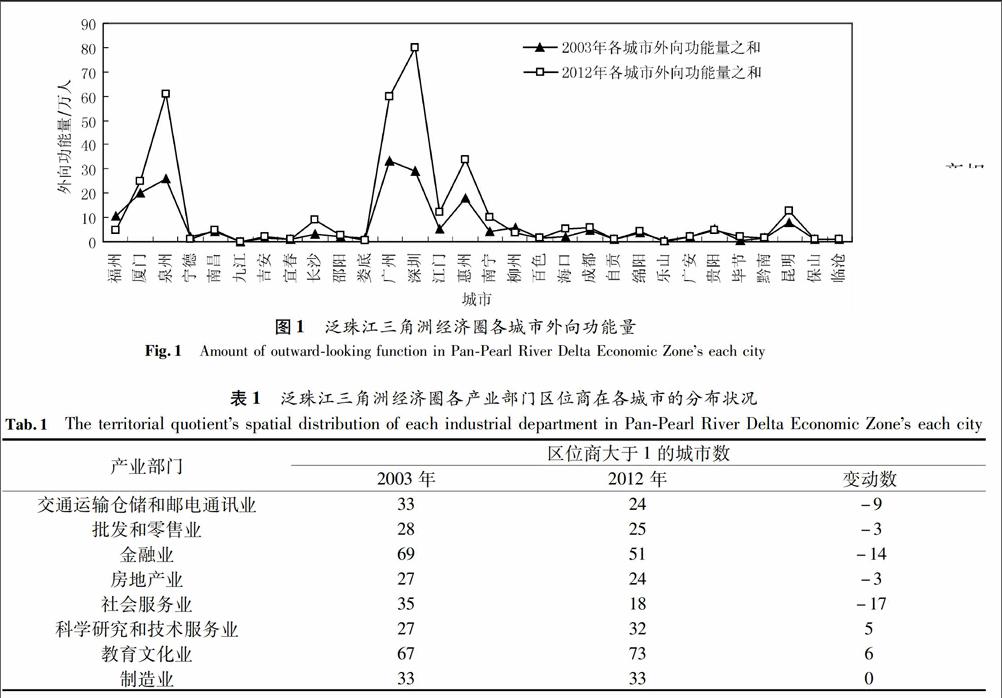
基于城市流视角的泛珠江三角洲经济圈空间联系分析
2015-10-20张磊武友德李君
张磊 武友德 李君
摘要基于城市流强度理论模型,对泛珠江三角洲经济圈117个地级市2003年和2012年的城市流强度和结构特征进行测算,并依此对经济圈的空间联系进行分析.结果表明,经济圈城市流强度值偏小的城市数量多于75个,城市间的空间联系偏弱,城市流强度存在明显的区域差异.主要原因是区域发展不均衡,综合经济实力较弱的城市数量超过65个,产业的外向服务能力不足.第二产业对经济圈城市流强度影响大于第三产业,第三产业对城市流强度的影响逐渐增强.随时间发展,经济圈城市流强度由受第二产业主导变为二、三产业共同影响.泛珠江三角洲经济圈仍处于工业化发展阶段,未来城市空间联系的格局和演化还可基于城市职能及发展要素的空间分布关系等方面进行调控.
关键词空间联系;城市流强度;泛珠江三角洲经济圈
中图分类号F290文献标识码A文章编号10002537(2015)05000107
Analysis on the Urban Space Contact of PanPearl River
Delta Economic Zone Based on Urban Flow
ZHANG Leia, WU Youdeb*, LI Junc
(a.School of Tourism and Geographic Science; b.Yunnan Chinese Language and Culture College;
c.School of economics and management, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming 650500, China)
AbstractBased on the theory model of urban flow, the intensity and structure of urban flow in 117 cities of PanPearl River Delta Economic Zone in both 2003 and 2012 are calculated and analyzed, and thereby the space relation of economic circle is analyzed as well. The results showed that more than 75 cities have a smaller intensity of urban flow and a smaller space relation and there exists significant regional differences in the intensity of the urban flow owe to uneven regional development. More than 65 cities have a smaller economy power and a smaller outward service function.The intensity of urban flow still obtains a lager benefit from the secondary industry than from the tertiary industry, the impact of the tertiary industry in urban traffic intensity gradually increased. With time going on, the intensity of urban flow has been affected by both the secondary and tertiary industries from dominated by the secondary industry. The PanPearl River Delta Economic Zone is still in the development stage of industrialization, future structure and evolution of urban spatial linkages could be regulated based on both urban function and spatial distribution of development elements.
Key wordsspace relation; intensity of urban flow; PanPearl River Delta Economic Zone
在区域协作与发展日益一体化的背景下,城市的规模与结构日益完善,在区域发展中的作用和区域经济中的地位日益突出[1].随着时间演进,城市间空间联系的内容与方式日趋改变,对区域间功能互补以及生产要素的空间配置效率影响明显,已成为经济地理学研究的热点与核心之一[2].
基于空间联系的内容、方式、深度以及广度等方面,国内外学者进行了较为系统的研究.早在上世纪三、四十年代Reilly[3]和Harris[4]等国外学者就基于区域间的空间联系强度运用引力模型等方法进行了定量的测度与模拟.20世纪五、六十年代,国外学者频繁运用定量分析法对城市间的空间联系和相互作用进行研究,其中以Ullman[5]和Haggett[6]为代表.近年来,国外学者对区域间空间联系分析的重点逐步向定性描述方向转变,实证性的应用分析逐步减少,具有代表性的是Sara[7]和Shaw[8]分别基于加强区域间联系措施以及人口迁移流动特征,从不同方面对城市流强度模型进行的分析.国内学者朱英明[9]、曹红阳[10]、蔡坚[11]、薛宗保[12]、高超[13]等也分别利用城市流强度模型对我国不同区域及城市间的空间联系进行了相关研究.国内外学者关于城市间相互作用研究的方向、尺度与阶段差异明显,国外学者从宏观尺度上将城市流强度模型与其他理论模型相结合,倾向于对理论模型的定性分析与扩展运用,而国内学者则侧重于中观尺度上对城市流强度模型与其他模型的对比实证分析.