CD235a+CD71+细胞在胃癌患者体内表达的临床意义
2015-10-19丁一心张光波赵光耀陈卫昌
丁一心 张光波 赵光耀 陈卫昌★
·论著·
CD235a+CD71+细胞在胃癌患者体内表达的临床意义
丁一心张光波赵光耀陈卫昌★
目的 初步探讨胃癌患者外周血中CD235a+CD71+细胞的表达水平及临床意义。方法 流式细胞仪检测64例胃癌患者及30例健康人外周血中CD235a+CD71+细胞表达水平,初步分析其与胃癌患者临床病理参数之间的关系;qRT-PCR分析胃癌组和健康对照组该群细胞的基因表达差异,初步探究其免疫抑制作用的分子机制。结果 胃癌患者外周血CD235a+CD71+细胞表达显著高于健康人[(30.34±18.29)% vs(22.36±7.86)%,P<0.01],且表达率与胃癌临床分期、淋巴结转移、远处转移和浸润深度密切相关;胃癌患者外周血CD235a+CD71+细胞的Arg1和TNF-α基因表达较健康人明显下调(Foldchange>2.0)。结论 与健康对照组相比,胃癌患者外周血CD235a+CD71+细胞表达水平显著升高,且与胃癌进展相关,其涉及的分子机制可能与Arg1和TNF-α表达下调有关。
胃癌 免疫抑制 CD235a+CD71+细胞
2013年Elahi S等[1]在新生儿脐带血中发现了一群以CD235a+CD71+为特征的新型免疫抑制性细胞群体异常增高,在新生儿感染性疾病中抑制免疫应答反应,是导致新生儿免疫低下的关键因素。然而该群细胞在肿瘤患者外周血中的表达特征、临床意义和生物学功能尚未见报道。本项目利用流式方法检测胃癌患者外周血中CD235a+CD71+细胞的表达,并结合临床资料初步分析该细胞亚群与胃癌临床分期、淋巴转移、远处转移及浸润程度的相关性,初步探讨该群细胞在胃癌发生、发展中的临床意义及可能的分子机制。
1 临床资料
1.1一般资料 观察组64例胃腺癌外周血标本均取自本院2014 年1至6月间初诊手术治疗患者,均未接受放化疗。男44例,女20例;年龄39~82岁,平均57.67岁。以上病例均经手术后病理学检查证实。对照组为健康体检者30例,男20例,女10例;年龄40~80岁,平均56.33岁。
1.2仪器与试剂 FC-500型流式细胞仪(Beckman Coulter公司);FTC2000实时荧光定量PCR仪(Funglyn Biotech公司);荧光标记PE anti-human CD71、PE/Cy7 anti-human CD235a(均为Biolegend 公司)。
1.3流式细胞仪检测CD235a+CD71+细胞表达水平 外周血标本采集均在患者住院后次日清晨,肝素抗凝真空采血管采集胃癌患者静脉血2ml。标本在24 h内进行检测。淋巴细胞分离液分离出外周血中单个核细胞(PBMC),分为空白对照组、CD235a-PE/Cy7组、CD235a-PE/Cy7+CD71-PE组。4℃避光孵育30min,洗涤离心重悬后上流式机检测CD235a+CD71+双阳性细胞表达水平,每例样本均分析3×104个细胞左右。
1.4流式细胞术分选纯化CD235a+CD71+细胞 将分别采集的健康体检者及术前胃癌患者的静脉血,肝素抗凝真空采血管分装。利用上述Ficoll分离液分离出PBMC,滤膜过滤后定容,加入CD235a-PE/Cy7和CD71-PE。4℃避光孵育30min,洗涤离心重悬后上流式细胞分选仪纯化出CD235a+CD71+细胞。
1.5qRT-PCR检测 取纯化CD235a+CD71+细胞的cDNA进行实时定量荧光PCR,鉴定胃癌患者和健康人员该群细胞相关功能因子Arg1、Arg2、IL-10、iNOS、TNF-α、TGF-β、IL-12、IL-6、PGE-2及IL-1β的表达水平。qRT-PCR检测CD235a+CD71+细胞功能基因,DNA表达相对量=2-△ct,△Ct=目的基因Ct-内参基因Ct。Foldchange(差异倍数)=2-△△Ct[△△Ct =(胃癌患者目的基因Ct-内参基因Ct)-(健康人目的基因Ct-内参基因Ct)]。三次重复实验取均值,倍数变化(FoldChange)>2.0为差异具有显著性。1.6 统计学方法 采用SPSS17.0统计软件。计量资料以(x±s)表示,组间比较采用t检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1胃癌患者外周血CD235a+CD71+细胞表达 健康对照组和胃癌组患者外周血中CD235a+CD71+细胞表达情况见图1A。健康对照组CD235a+CD71+细胞表达平均为(22.36±7.86);胃癌组表达平均为(30.34±18.29),两者存在显著差异(P<0.01)(图1B)。

图1 CD235a+CD71+细胞在胃癌患者外周血中表达
2.2胃癌患者外周血CD235a+CD71+细胞表达的临床意义 见表1。
表1 胃癌患者外周血CD235a+CD71+细胞表达率与临床病理因素分析(±s)
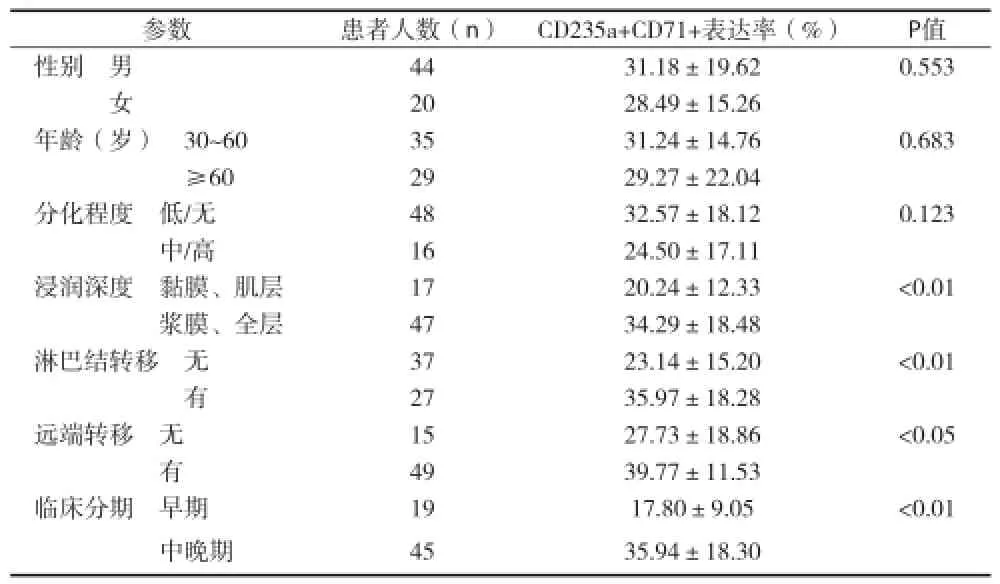
表1 胃癌患者外周血CD235a+CD71+细胞表达率与临床病理因素分析(±s)
参数患者人数(n)CD235a+CD71+表达率(%)P值性别 男4431.18±19.620.553女2028.49±15.26年龄(岁) 30~603531.24±14.760.683≥602929.27±22.04分化程度 低/无4832.57±18.120.123中/高1624.50±17.11浸润深度 黏膜、肌层1720.24±12.33<0.01浆膜、全层4734.29±18.48淋巴结转移 无3723.14±15.20<0.01有2735.97±18.28远端转移 无1527.73±18.86<0.05有4939.77±11.53临床分期 早期1917.80±9.05<0.01中晚期4535.94±18.30
2.3胃癌组与健康组外周血CD235a+CD71+细胞功能基因差异分析 利用qRT-PCR方法初步分析胃癌组与健康组外周血CD235a+CD71+细胞中关键功能因子Ct值,统计分析结果表明胃癌组Arg1和TNF-α基因表达量较健康组明显升高(Foldchange>2.0),见表2。
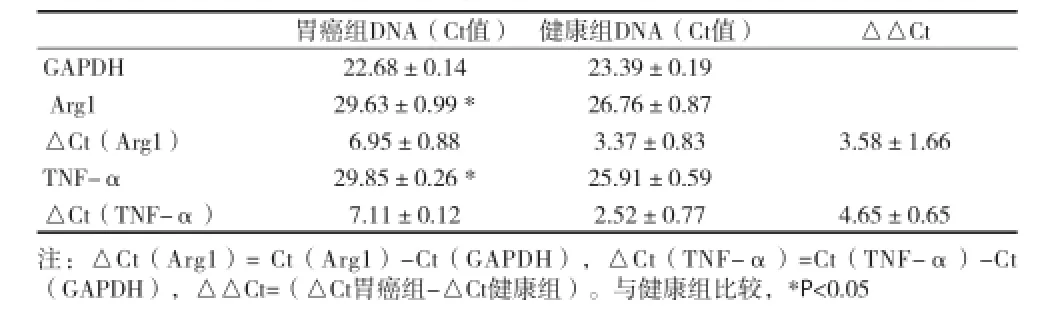
表2 胃癌组与健康组外周血CD235a+CD71+细胞功能因子Arg1、TNF-α Ct值(x±s)
3 讨论
免疫抑制性细胞群体在肿瘤免疫逃逸中发挥着重要的作用[2~5]。CD235a+CD71+细胞作为一类新发现的免疫抑制性细胞亚群,在肿瘤外周血中的表达特征和临床意义尚未见报道[6,7]。本项目初步检测了胃癌患者外周血中该细胞的表达水平,并结合临床资料初步分析其在胃癌发生、发展中的临床意义。
通过检测胃癌患者外周血CD235a+CD71+细胞,发现其表达水平显著高于健康对照组。进一步统计分析显示,与早期胃癌组相比,中晚期胃癌组CD235a+CD71+细胞水平显著升高;而且在不同肿瘤浸润程度、有无淋巴结转移、有无远处转移的患者之间,该亚群的表达也存在明显差异。因此,检测CD235a+CD71+细胞水平可能有助于评估胃癌进展的程度。
Elahi S等[1]通过体外共培养实验发现CD235a+CD71+细胞阻碍CD8+T细胞活化,抑制TNF-α表达进而发挥免疫抑制功能;利用特异性阻滞剂阻断精氨酸酶(Arg)通路,发现该群细胞对成年脾脏免疫细胞的抑制作用显著增强。这表明CD235a+CD71+细胞可能通过精氨酸酶通路来抑制免疫细胞活化,维持机体免疫抑制状态。为初步探讨CD235a+CD71+细胞在胃癌进展中可能的分子机制,选择Arg、TNF-α、iNOS等功能因子做相关分析。结果发现,胃癌患者来源的CD235a+CD71+细胞Arg1和TNF-α的mRNA表达均显著低于健康对照组。Arg1是一类三聚体双核含锰金属酶,该分子表达下调可导致精氨酸蓄积,促进癌细胞浸润、微血管形成和向周围组织转移[8,9];在缺乏精氨酸的内环境中,肿瘤细胞增殖受到了显著抑制[10,11]。因此推测CD235a+CD71+细胞 Arg1表达下调,可以通过精氨酸蓄积促进胃癌细胞增殖、浸润[12,13]。TNF-α是CD235a+CD71+细胞发挥生物学功能的关键分子[1],本资料发现胃癌患者外周血中该细胞TNF-α的mRNA表达水平较对照组显著降低。TNF-α表达上调并与其受体结合可以诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡,促进免疫细胞增殖分化,发挥抗肿瘤效应;TNF-α也可提高肿瘤血管内皮细胞通透性,抗肿瘤新生血管形成。所以TNF-α表达下调可能促进了胃癌的侵袭转移。这可能是CD235a+CD71+细胞在胃癌进展中发挥作用的机制,其确切的分子机制需要进一步的实验来证实。
综上所述,本项目初步发现CD235a+CD71+细胞表达水平与胃癌的临床分期、淋巴结转移、远处转移和浸润程度相关。但该群细胞确切的临床意义和生物学机制尚需扩大样本数量进一步探索。
1 Elahi S, Ertelt JM, Kinder JM ,et al. Immunosuppressive CD71+ erythroid cells compromise neonatal host defence against infection. Nature,2013,504(7478):159~162.
2 Kollmann TR ,Levy O ,Montgomery RR, et al. Innate immune function by Toll-like receptors: distinct responses in newborns and the elderly.Immunity,2012,37(5):771~783.
3 PrabhuDas M, Adkins B, Gans H, et al. Challenges in infant immunity:implications for responses to infection and vaccines. Nature Immunol,2011, 12(3):189~194.
4 Zaghouani H, Hoeman CM , Adkins B. Neonatal immunity: faulty T-helpers and the shortcomings of dendritic cells. Trends Immunol,2009,30(12):585~591.
5 Kollmann TR, Crabtree J, Rein-Weston A, et al. Neonatal innate TLR-mediated responses are distinct from those of adults. Immunol,2009,183(11):7150~7160.
6 Wheatley DN, Campbell E. Arginine deprivation, growth inhibition and tumour cell death:Deficient utilisation of citrulline by malignant cells.Br J Cancer, 2003, 89(3):573~576.
7 Derek K,Geraldine S, Yu H. An Effective Marker for erythroid Precursors in Bone Marrow Biopsy Specimens.Hematopathology,2010,134(3): 429~435.
8 Bronte V, Zanovello P. Regulation of immune responses by L-arginine metabolism. Nature Rev. Immunol,2005,5(8): 641~654.
9 Cheng PN,Lam TL,Lam WM,et al.Pegylated recombinant human arginase inhibits in vitro and in vivo proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma through arginine depletion.Cancer Res,2007, 67(1): 309~317.
10 Liu Q, Zhang C, Sun A, et al. Tumor-educated CD11b regulatory dendritic cells suppress T cell response through arginase-I.Immunol,2009,182(10):6207~6216.
11 Sun MH, Han XC, Jia MK, et al.Expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase and matrix metalloproteinase-9 and their effects on angiogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gas troenterol,2005,11(38):5931~5937.
12 ChungDJ,RossiM,Romano E,et al.Indoleamine 2, 32dioxygenase2 expressing mature human monocyte2derived dendritic cells expand potent autologous regulatory T cells. Blood,2009,114(3):555~563.
13 Feun L, You M, Wu CJ, et al. Arginine deprivation as a targeted therapy for cancer.Curr Pharm Des,2008,14(11):1049~1057.
Objective To explore the expression level and clinical signifi cance of CD235a+CD71+cells among the peripheral blood in gastric cancer patients. Methods A total of 64 gastric cancer patients and 30 controls patients were prospectively enrolled in this study. The expression level of CD235a+CD71+cells from peripheral blood was measured by fl ow cytometry in gastric cancer patients and healthy controls,and then the relationship between the two cell subsets and clinical pathology of gastric cancer was further explored. The differences of gene expression of the cell subsets from gastric cancer patients and healthy controls were evaluated by qRT-PCR to explore molecular mechanism of this cell subset's immunosuppression. Results The expression level of CD235a+CD71+cells from the peripheral blood in gastric cancer was signifi cantly higher than which in healthy controls[(30.34± 18.29)% vs.(22.36±7.86)%,P<0.01],and was positively correlated with clinical staging,lymphatic metastasis rate,distant metastasis rate and invasion depth of gastric cancers. The gene expression levels of Arg1 and TNF-α in CD235a+CD71+cell from the peripheral blood of gastric cancer patients were signifi cantly lower than that of healthy controls(Foldchange>2.0).Conclusion CD235a+CD71+cell among the peripheral blood in gastric cancer is associated with clinical pathology of cancer,which is able to act as an effective indicator to evaluate the state of gastric cancer patients.
Gastric cancer Immunosuppression CD235a+CD71+cell
国家自然科学基金项目(81272737)
215006 苏州大学附属第一医院
