经改良Judet入路手术治疗肩胛骨骨折的疗效
2015-06-26赵良瑜陈爱民李永川
赵良瑜 陈爱民 李永川
经改良Judet入路手术治疗肩胛骨骨折的疗效
赵良瑜 陈爱民 李永川
目的 介绍改良Judet入路的概念,经该入路治疗部分复杂肩胛骨骨折的手术方法,并经临床随访,分析该方法手术疗效和意义。方法 17例肩胛骨骨折患者进行了改良Judet入路。手术采用Judet切口,从肩胛冈掀起三角肌下缘。自肩胛骨背面和肩胛冈剥离部分冈下肌,向外侧在冈下肌和小圆肌的间隙进行分离,形成两个“窗口”,显露肩胛冈、肩胛颈、肩胛盂背侧、肩胛骨内、外侧缘。对骨折进行复位和充分固定。术后6周、12周、6个月分别进行临床和影像学随访,末次随访时采用美国肩肘外科协会(ASES)评分。结果 17例患者均在6个月的随访期内骨折愈合。并发症包括肺部感染3例、切口皮肤边缘坏死1例、切口浅表感染1例,均治愈,1例患者提前取出内固定材料。ASES评分56~100分,平均为85.9分。结论 改良Judet入路显露充分、易于复位固定、保护肩胛上神经,对于部分复杂肩胛骨骨折具有良好疗效。
改良Judet入路;肩胛骨;骨折;内固定
肩胛骨位于胸廓后面,是一块三角形的不规则骨,通过肩峰、喙突、肩胛盂等结构,与锁骨和肱骨相连接,是上肢和躯干相结合的重要结构。肩胛骨经常由于各种外伤因素造成损伤形成骨折,对上肢的运动造成障碍。以往肩胛骨骨折经常进行保守治疗,近年来,随着外科条件的改善、相关器械和器材的研发和手术技术的改进,越来越多的肩胛骨患者经过手术治疗取得了良好的效果[1]。肩胛骨骨折的手术入路种类较多,包括前方入路、后方直切口入路、Judet入路等,本文重点总结了经改良Judet入路行肩胛骨骨折手术的情况。
对 象 与 方 法
一、一般资料
自2004年7月至2014年7月,本组共进行肩胛骨骨折手术患者71例。其中,有17例患者进行了改良Judet入路,男性16例、女性1例,年龄29~62岁,平均47.1岁。致伤原因:车祸受伤8例,高处坠落摔伤6例,摔倒、运动损伤和其他原因3例。按照部位分型,包括肩胛颈累及肩胛冈或肩胛骨内侧缘骨折13例,累及肩胛盂的骨折3例,肩胛骨合并同侧锁骨骨折1例。41%(7/17)合并有其他部位的各类损伤,包括肋骨骨折6例,颅脑损伤1例,肺挫伤和胸腔积液3例,脊柱骨折5例,颈椎过伸伤1例,上颌窦骨折1例,肱骨近端骨折1例,第一掌骨基底部骨折1例,臂丛神经损伤1例。肩胛骨骨折为双侧者1例。受伤至手术时间2~15 d,平均7.1 d。
二、手术方法
患者取全麻或者臂丛阻滞麻醉。手术采取后方改良Judet入路,切口起自肩胛盂背侧沿肩胛冈向内,经肩胛骨内上角转向下方,沿肩胛骨内缘至肩胛骨下角。分离皮肤皮瓣后,从肩胛冈掀起三角肌下缘。自肩胛骨背面和肩胛冈剥离部分冈下肌,向外侧在冈下肌和小圆肌的间隙进行分离,保留冈下肌在肩胛骨内侧缘和背面的附着,形成两个“窗口”,显露肩胛冈、肩胛颈和肩胛盂背侧、肩胛骨内、外侧缘。注意避免肩胛上神经、腋神经损伤,有时为扩大显露需结扎旋肩胛动脉。切开骨膜显露骨折线,将骨折复位,以克氏针临时固定骨折,透视确认复位良好后,以空心钉、普通实心螺钉或2.7~3.5 mm内固定板进行内固定。复位固定完成后透视确认螺钉没有误穿破肩胛盂关节面,手术台上检查肩关节活动,逐层缝合。
三、手术后治疗
术后早期即可开始主、被动肩关节圆周活动,并逐渐加大活动范围。术后6周内患肢不得持重。术后6周、12周、6个月分别来院复查,拍摄X线检查骨折愈合情况,并指导进一步加强功能锻炼。待骨折端可见有骨痂生长通过骨折线时可逐步进行上肢持重。末次随访时进行肩关节功能评定,以影像学显示骨折线消失,连续性骨痂通过骨折线为骨折愈合标准。功能评定采用美国肩肘外科协会(ASES)评分系统[2],满分为100分。
结 果
17例患者完成18侧肩胛骨骨折手术,采用改良Judet入路17侧(1例双侧肩胛骨骨折患者,单侧采取了本入路),占同期肩胛骨手术的24%(17/71)。17侧全部达到解剖复位,12例采用2块内固定板,2例使用3块内固定板,3例经双窗口复位后1块内固定板即达到固定效果。本组17例患者完成全程随访,在6个月的随访期内骨折愈合,未出现骨不连病例。6例患者围手术期发生并发症。其中肺部感染3例,经抗生素治疗痊愈,切口皮肤边缘坏死1例,切口浅表感染1例,经切口换药获得愈合,有1例患者因内固定物突出不适,于骨折出现愈合迹象后提前取出内固定材料。全部病例未发生骨折再移位、内固定装置断裂或者移位、内固定螺钉穿破肩胛盂关节面、神经损伤等并发症。
肩关节功能评分:ASES评分56~100分,平均为85.9分,其中10例未合并其他损伤,单纯肩胛骨骨折患者术后平均评分较高,达90.8分。在评分不足70分的患者中,未按医师指导进行充分的肩关节功能锻炼、肩胛盂粉碎性骨折、合并损伤多、并发症发生导致延长治疗时间是主要影响因素。
讨 论
肩胛骨与锁骨一起,形成了将人体上肢悬吊于身体躯干两侧的悬臂,并通过肩胛盂关节面,与肱骨头构成了肩关节的主要部分,肩胛骨类似上肢的“骨盆”。既往多采取保守治疗[3],然而,单纯采取保守治疗,肩关节不能及时进行功能锻炼,容易发生粘连和僵硬,导致肩关节活动障碍,移位的肩胛骨骨折如果发生畸形愈合,将发生肩胛颈短缩、肩胛盂关节面角度改变从而丧失与肱骨头的正常对合关系。愈合不良的肩胛冈、喙突等部位也会产生症状影响肩关节的活动[4-5]。因此手术主要针对重建肩关节的正常活动与稳定性,手术指征主要包括:(1)累及肩胛盂关节面的骨折;(2)肩胛颈骨折短缩移位超过1 cm或者成角超过40°,肩胛骨体部或者突起部粉碎性骨折和移位较大的骨折;(3)以及肩胛骨合并同侧锁骨骨折,经锁骨骨折切开复位内固定仍不能达到肩关节稳定以及肩胛颈恢复良好角度者。
肩胛骨形状不规则,相关解剖复杂。经典Judet入路(图1)需将冈下肌自起点切开剥离,向外侧掀开,形成以肩胛上神经血管为蒂的肌瓣,对肩胛骨背面、肩胛颈、肩胛盂背侧进行充分显露。此种方法虽然显露较为充分和广泛,然而对肌肉组织剥离多,创伤面积大,不利于术后及时进行功能锻炼。
2000年Braun 等[6]学者对Judet入路尝试进行改良,然而他们的方法对冈下肌的剥离仍然较大,具有一定损伤。2004年Obremskey等[7]学者对Judet入路进行了较为科学的改良,即在冈下肌与小圆肌之间、以及在冈下肌在肩胛冈的附着点进行分离,治疗了部分肩胛骨骨折,发现可减少肌肉组织的剥离,尤其对肩袖的功能增加保护。然而他们并未阐述该入路的适应证范围以及结果评价。2006年周东生等[8]学者对Judet入路进行了不同的变化,进行了多种手术入路的组合,取得了良好的临床效果。本组对17例复杂肩胛骨骨折患者进行了单一的、标准化的改良Judet入路,即不剥离冈下肌在肩胛骨背面内侧缘的起点,仅仅剥离冈下肌在肩胛冈上的部分起点,以及在外侧的冈下肌和小圆肌间隙进行分离,进而形成冈下肌上缘与肩胛冈、冈下肌外下缘与小圆肌两个“窗口”。两者可以在冈下肌深面连通,同样可对肩胛冈、肩胛颈和肩胛盂背侧进行充分显露(图2~4)。对冈下肌、三角肌起点进行剥离时应做好标记,手术缝合切口时应将其重建于肩胛骨冈下窝以及肩胛冈。本组17例患者均为肩胛颈/肩胛盂/肩胛骨外侧缘+肩胛冈骨折,单纯采用外侧直切口,无法对肩胛颈和肩胛盂背侧尤其是肩胛冈外缘进行充分显露,无法对肩胛上神经进行显露和松解,损伤该神经的风险较大,采用改良Judet入路则均达到了对复杂骨折的充分显露,实现了良好复位和内固定,并保护了肩胛上神经。本组患者随访时均未发现肩胛上神经医源性损伤。
外侧直切口是肩胛骨后侧另一个常用重要入路,该入路经冈下肌和小圆肌间隙进行显露,这个切口损伤范围相对较小,因此与Jones等[9]不同,我们对于发生于后侧的骨折,包括大部分肩胛骨体部、外侧缘、肩胛颈和肩胛盂后、下方以及肩胛冈骨折,并不需要进行改良Judet入路,仅仅进行外侧直切口入路即可。而对于骨折范围较广、需广泛显露的病例,可采用Judet入路,即采用后侧弧形切口,剥离三角肌后侧以及部分乃至全部冈下肌。这些病例包括肩胛冈合并肩胛骨外缘和肩胛颈骨折、肩胛颈和肩胛骨外缘骨折,单纯外侧固定无法稳定肩胛颈者,以及肩胛冈、肩胛颈骨折损伤肩胛上神经,需要充分显露和松解者。
肩胛骨骨折的复位,应以点状复位钳小心夹持,配合克氏针临时固定,必要时在肩胛骨背面钻孔,容纳点状复位钳的尖端。固定器材可采用空心钉、2.7~3.5 mm板等。对于骨质条件好的患者,普通板足以完成固定,而骨质疏松患者,可采用锁定板,对粉碎的骨折块可采用2.7 mm螺钉和板等小型内固定器材固定[9]。3.5 mm空心钉在固定喙突、肩胛盂等部位的骨折时,有使用方便的优点,但应注意防止较细的导针在骨内弯折,空心钻扩孔时导致导针折断。采用经典或者改良Judet入路,可以在肩胛骨外侧及肩胛盂/肩胛颈背侧、或者肩胛冈安放内固定板,放置内固定的空间较为充分,一般均可放置至少2块内固定板(图5)。本组患者中14例使用2块及以上内固定板,固定充分,术后均达到早期功能锻炼的效果。
肩胛骨骨折术后的随访和功能锻炼极为重要,其目标是在骨折愈合的同时,获得活动良好、无痛、稳定的肩关节。手术完成复位和固定后,医师需“个体化”地指导患者,在康复训练师的协助下循序渐进地进行功能锻炼以达到最大的功能效果[10]。一方面应防止过度锻炼引起骨折和内固定移位;另一方面需防止大多数患者的畏惧锻炼引起肩关节僵硬。一般来讲,经良好复位固定的患者,6周内应在不持重状态下进行肩关节活动范围的锻炼;6~12周达到肩关节最大范围的活动;12周后,经拍片发现骨折愈合迹象后,逐步增加上肢持重。患者最终的肩关节功能评分,主要受到骨折的类型和复杂程度、手术复位和固定的质量以及有无并发症、功能锻炼的依从性的影响。
[1] Cole PA,Dubin JR,Freeman G.Operative techniques in the management of scapular fractures[J].Orthop Clin North Am,2013,44(3):331-343.
[2] Richards RR,An KN,Bigliani LU,et al.A standardized method for the assessment of shoulder function[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,1994,3(6):347-352.
[3] Bartonícek J,Cronier P.History of the treatment of scapula fractures[J].Arch Orthop Trauma Surg,2010,130(1):83-92.
[4] Hill BW,Jacobson AR,Anavian J,et al.Surgical management of coracoid fractures:technical tricks and clinical experience[J].J Orthop Trauma,2014,28(5):E114-E122.
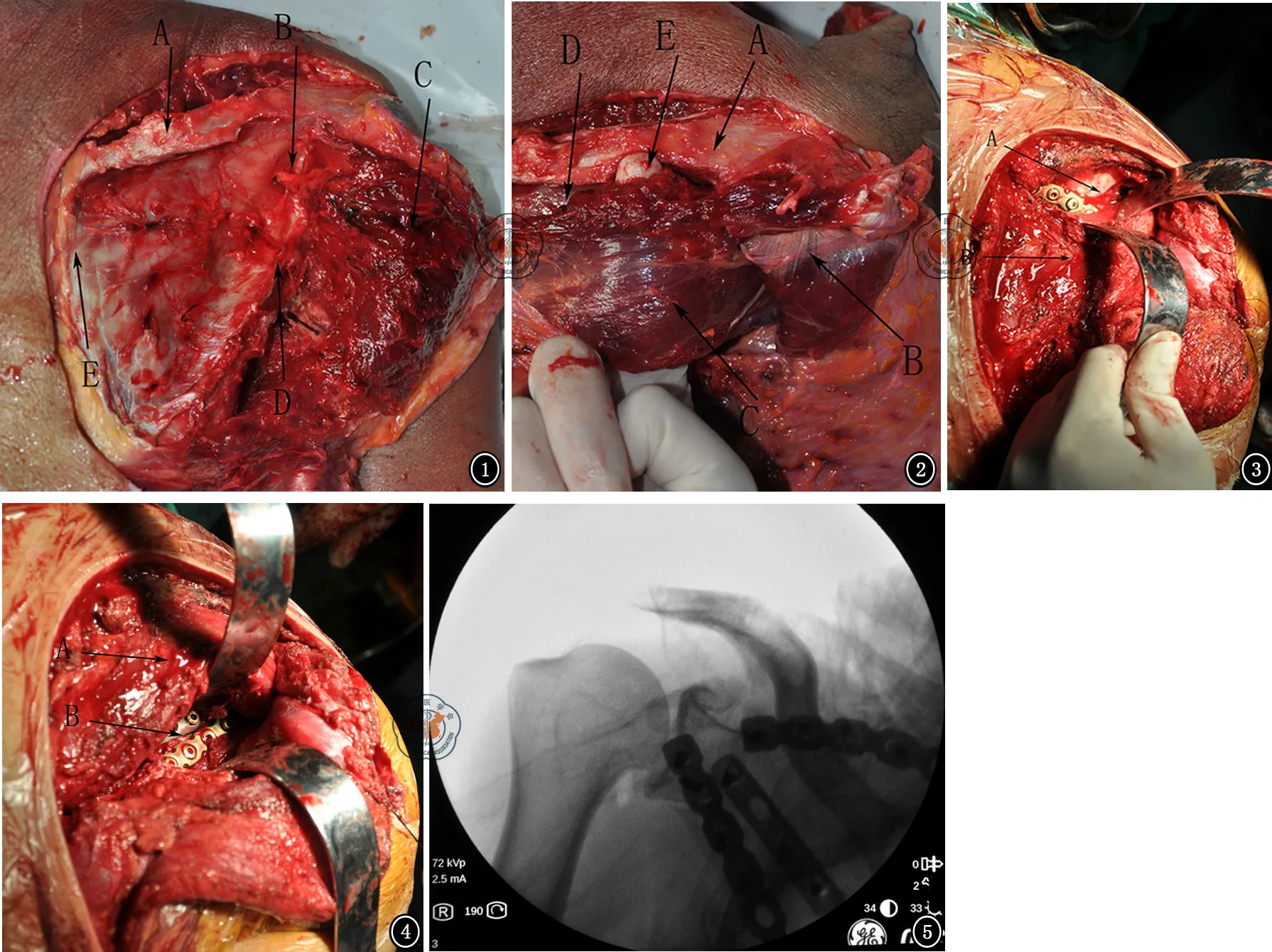
图1 尸体解剖图,示经典Judet入路,右肩。A.肩胛冈;B.肩胛上神经;C.冈下肌;D.肩胛骨外缘;E.肩胛骨内缘 图2 尸体解剖图,示改良Judet入路,右肩。A.肩胛冈外侧份;B .从肩胛冈掀起的三角肌;C .冈下肌;D .冈下肌与肩胛冈之间的间隙;E.上下两个间隙可在冈下肌深面连通 图3 术中图片,改良Judet入路,右肩。A.剥离冈下肌与肩胛冈之间的间隙;B .冈下肌 图4 术中图片,改良Judet入路,右肩。A.冈下肌;B.冈下肌与小圆肌之间的间隙 图5 术中透视,显示复位后用3块板内固定

[6] Braun C,Wirbel R,Mutschler W.The two-portal-approach for internal fixation of scapular fractures[J].Operat Orthop Traumatol,2000,12:209-219.
[7] Obremskey WT,Lyman JR.A modified Judet approach to the scapula[J].J Orthop Trauma,2004,18(10):696-699.
[8] 周东生,李连欣,王鲁博,等.改良Judet手术入路治疗复杂肩胛骨骨折[J].中华外科杂志,2006,44(24):1686-1688.
[9] Jones CB,Cornelius JP,Sietsema DL,et al.Modified judet approach and minifragment fixation of scapular body and glenoid neck fractures[J].J Orthop Trauma,2009,23(8):558-564.
[10] Lewis S,Argintar E,Jahn R,et al.Intra-articular scapular fractures:Outcomes after internal flxation[J].J Orthop,2013,10(4):188-192.
(本文编辑:李静)
赵良瑜,陈爱民,李永川.经改良Judet入路手术治疗肩胛骨骨折的疗效[J/CD].中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2015,3(1):30-34.
Evaluation of modified Judet approach in the treatment of scapula fractures
ZhaoLiangyu,ChenAimin,LiYongchuan.
DepartmentofOrthopedicTrauma,ChangzhengHospital,SecondMilitaryMedicalUniversity,Shanghai200433,China
ChenAimin,Email:orthopsurgery@smmu.edu.cn
Background The scapula locates in the posterior wall of chest.It is an irregular bone with a triangular shape.The scapula connects clavicle and humerus with its structure including the acromion,coracoid and scapular glenoid,forming an important combination of upper limbs and trunk.Various injury factors can cause fracture damage to the scapula,leading to obstacles to the movement of the upper limb.In history,scapular fractures used to be treated conservatively.While in recent years,with the improvement of operative techniques and development of surgical conditions and related devices and equipment,more and more scapular fracture patients accepted surgical treatments and achieved good results.There are different approaches to scapular fractures including anterior approach,the lateral straight incision approach,Judet approach and so on.In this study,modified Judet approach was evaluated as the treatment of some subgroup of scapular fracture cases.Methods From July,2004 to July 2014,71 cases of scapular fractures accepted surgical treatment,with 17 cases underwent Judet approach.The age of the 16 males and 1 female case ranged 29-62 years with the mean age 47.1 years old.The causes of injury included automobile accident in 8 cases,falls from height in 6 cases,fall,sports injuries and other causes of 3 cases.There were scapular neck fracture involving scapular spine or medial border of scapula in 13 cases,fracture involving the scapula glenoid fractures in 3 cases,combined fracture of scapular and ipsilateral clavicle in 1 case.41% (7 out of 17 cases) patients had associate injuries,including 6 cases of rib fracture,1 case of craniocerebral injury,3 cases of contusion of lung and pleural effusion,5 cases of spine fractures,1 case of cervical spinal cord hyperextension injury,1 cases of maxillary sinus fracture,1 case of proximal humerus fracture,1 case of first metacarpal fracture,and 1 case of brachial plexus injury.Bilateral scapular fractures occurred in 1 case.The time interval between injury and operation was 2-15 days,averaging 7.1 days.Operation method:Operations were done under general anesthesia or brachial plexus block anesthesia.The posterior modified Judet approach was performed.The incision started from the projection of scapular glenoid in the dorsal side of scapula,running medial along with the scapula spine,and turned downward in the superior medial corner of scapula,along with the medial edge of the scapula to the inferior corner of scapula.Skin and subcutaneous tissues were dissected.The posterior part of deltoid was dissected from scapula spine.The infraspinatus underneath was partly released from the scapula spine,dorsal surface of scapula,and between infraspinatus and teres minor,remaining attachment of the infraspinatus muscle in the medial border of scapula.Thus two "windows" was made,and scapula spine,dorsal side of scapula neck and glenoid,dorsal side of scapula body and the lateral and medial borders of scapula were exposed.The suprascapular and axillary nerves were carefully protected.Circumflex scapular artery was occasionally ligated for the purpose of expansion of exposure.Periosteotomy was performed nearing the fracture line.Then fractures were reduced and fixed temporarily by K-wires.After X-ray confirmation,final stabilization was done with cannulated screws,2.7- 3.5 mm cortical screws and plates.Reduction and fixation along with exclusion of screws penetrating the glenoid articular surface was confirmed by fluoroscopy,and range of motion of the shoulder joint was examined.Then wound was closed layer by layer.Postoperative treatments:active and passive shoulder circumferential motion was initiated early after operation and range of motion was gradually increased.The injured upper limb was kept without weight lifting within 6 weeks after surgery.Patients were asked to return to the hospital at 6 weeks,12 weeks and 6 months postoperatively.X-ray films were taken for fracture healing evaluation,and further instructions for functional rehabilitation were given by the surgeons.Weight lifting was not permitted until callus growth through the fracture line can be seen on the x-ray film.The shoulder joint function was assessed at the time of the latest follow-up.The standards for radiographic fracture healing were disappearance of fracture line and continuous callus through the fracture line.America shoulder and elbow surgery (ASES) scoring system was used for functional evaluation,with full score of 100 points.Results Seventeen patients underwent 18 scapular surgeries.Modified Judet approach was performed in 17 sides (one patient with bilateral scapular fractures had this approach in one side),accounting for 24% (17/71) scapula fracture operations of the corresponding period.All the 17 cases achieved anatomical reduction.Fractures were fixed by 2 pieces of internal fixation plates in 12 cases,3 pieces of plates in 2 cases,and in 3 cases,rigid stabilization was achieved by one plate.All 17 patients completed follow-up and all fractures healed during the follow-up period of 6 months,with no nonunion case.Six patients had peri-operational complications,including pulmonary infection in 3 cases and cured by antibiotic therapy,incision edge necrosis in one case,superficial infection in 1 case and cured by dressing change and wound care.Implant prominence caused discomfort in one case,which had to be removed in advance after signs of fracture healing occurred in X-ray film.No fracture displacement,implant loosening or displacement,implant penetrating into glenoid articular surface or nerve injury occurred.ASES score of shoulder joints ranged 56-100 points with an average of 85.9 points.Of the 10 cases with scapula fracture alone without other damage,the ASES scores were higher,averaging up to 90.8.Among patients scored less than 70 points,bad compliance to the guidance of physician for functional rehabilitation of shoulder joints,comminution of glenoid fracture,associate injuries and complications leading to prolonged treatment time may be the main influence factors.Conclusion Modified Judet approach is indicated for complex scapula fractures,and it has the advantages of extensive exposure,protection of suprascapular nerve and preservation of infraspinatus.Anatomical reduction,rigid fixation,early postoperative motion and good functional recovery can be achieved.
Modified Judet approach;Scapula;Fracture; Internal fixation
10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-5790.2015.01.007
上海市科委产学研合作项目(13DZ1940705)
200433上海,第二军医大学骨创伤外科
陈爱民,Email:orthopsurgery@smmu.edu.cn
2014-12-26)
