分散微固相萃取—超高效液相色谱—高分辨质谱法测定果汁饮料中的吗啉残留
2015-06-08殷轶群等
殷轶群等


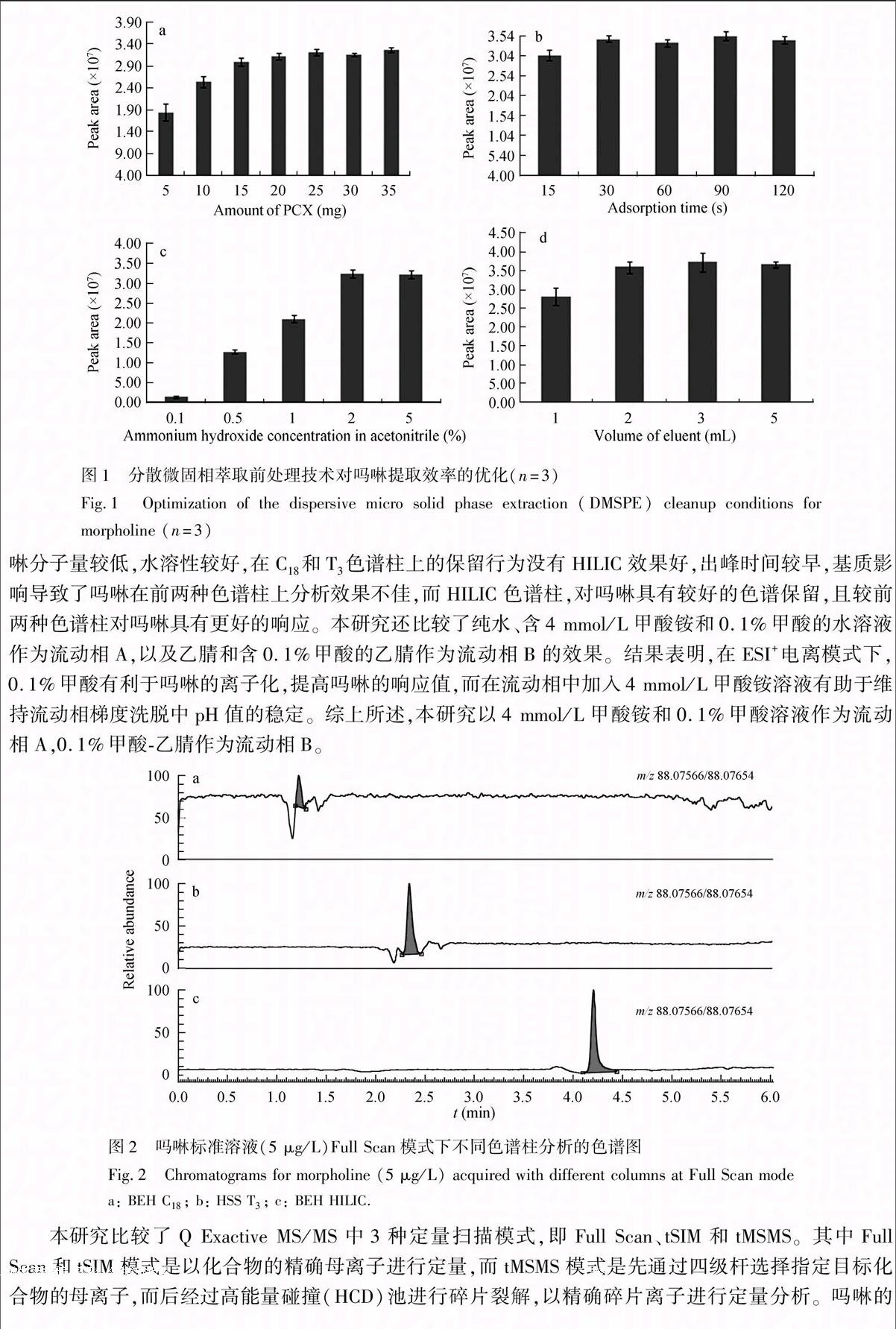
摘 要 基于强阳离子交换填料(PCX),采用分散微固相萃取(DMSPE)前处理技术,结合超高效液相色谱四级杆静电场轨道阱高分辨质谱联用技术(UPLC/Q Orbitrap),建立了果汁饮料中吗啉残留的快速检测分析方法。通过对DMSPE技术中PCX用量、吸附时间、洗脱溶剂氨水浓度和洗脱体积的优化,实现样品中吗啉的最优提取。以BEH HILIC色谱柱(100 mm×2.1 mm, 1.7 μm)进行色谱分离,通过静电场轨道阱质谱tMSMS采集模式获得吗啉的精确母离子及碎片离子质量数,进行定性定量分析。结果显示, 吗啉在1~100 μg/L浓度范围内存在良好的线性关系(R2>0.999),方法检出限和定量限分别为1和2 μg/L; 平均加标回收率为85.9%~103.8%,日内和日间精密度分别为3.7%~5.2%和3.5%~9.4%。本方法简单精确,灵敏度高,样品处理快捷简便,适用于果汁饮料中吗啉残留的快速分析测定。
关键词 分散微固相萃取; 吗啉; 高分辨质谱; 饮料
2 实验部分
2.1 仪器、试剂与材料
Thermo Scientific Q Exactive四级杆静电场轨道阱高分辨质谱系统,Dionex UltiMate 3000快速高效液相色谱系统(美国赛默飞公司); 涡旋混合器(美国Scientific Industries公司)。
乙腈(色谱纯,Fisher Scientific公司),甲酸和甲酸铵(HPLC级,Tedia公司); 高分子阳离子交换填料(PCX,天津博纳艾杰尔公司); 吗啉标准品(纯度>98%,美国Supelco公司); 吗啉d8标准品(纯度>98%,美国Cambridge Isotope Laboratories); 实验用水为超纯水,由美国Millipore公司纯水仪制备果汁饮料购买自北京各大超市。
2.2 标准溶液的配制
References
1 Mcguire R G, Dimitroglou D A. Biocontrol Sci. Techn., 1999, 9(1): 53-65
2 ZHANG XiaoYan, LIU WeiMin. Food Science and Technology, 2000, 26(6): 2-3
张晓彦, 刘伟民. 食品科技, 2000, 26(6): 2-3
3 GB27602011, Ministry of Health of the People′s Republic of China. Standards for use of food additives.2011
GB27602011. 中华人民共和国卫生部. 食品添加剂使用标准, 2011
4 IARC. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Vol. 47. International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1989: 199-213
5 Inuin N, Nishi Y, Taketomi M. Inter. J. Cancer, 1979, 24(3): 365-372
6 European Union Food Additives Database; https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/sanco_foods/main/index.cfm (accessed Sept 2013)
7 Health Canada. ArchivedA Summary of Health Hazard Assessment of Morpholine in Wax Coatings of Apples. 2013
8 Ohnishi T, Kubota M, Okada A. Hokuriku Koshu Eisei Gakkaishi, 1983, 10(1): 63-67
9 Cabaleiro I, de la Calle I, Bendicho C, Lavilla I. TRACTrend. Anal. Chem., 2014, 57(1): 34-46
10 Farhadi K, Matin A A, Amanzadeh H, Biparva P, Tajik H, Farshid A A, Pirkharrati H. Talanta, 2014, 128(1): 493-499
11 Asgharinezhad A A, Moliazadeh N, Ebrahimzadeh H, Mirbabaei F, Shekari N. J. Chromatogr. A, 2014, 1338(1): 1-8
12 Mahpishanian S, Sereshti H. Talanta, 2014, 130(1): 71-77
13 Sen N P, Baddoo P A. J. Food Sci., 1988, 53(1): 183-191
14 Sen N P, Baddoo P A. J. Food Sci., 1986, 51(1): 216-217
15 LI Jing, LIU QingHua, YU LianGui, ZHANG ChunFeng. Industrial Water Treatment., 2009, 29(11): 61-63
李 晶, 刘清华, 于连贵, 张春峰. 工业水处理, 2009, 29(11): 61-63
16 Hengel M J, Jordan R, Maguire W. J. Agric. Food Chem., 2014, 62(17): 3697-3701
17 Gros P, Matignon F, Plonevez S. Ann. Falsif. Expert. Chim. Toxicol., 2011, 974(1): 17-22endprint