二甲双胍对2型糖尿病患者血清PSA水平的影响及其与前列腺癌的关系
2015-06-01郭颖,吴波
郭 颖,吴 波
二甲双胍对2型糖尿病患者血清PSA水平的影响及其与前列腺癌的关系
郭 颖,吴 波*
目的 观察二甲双胍对2型糖尿病(T2DM)患者PSA水平的影响,并探讨二甲双胍与前列腺癌的关系。方法 将2014年1-8月在我院内分泌科住院的178例T2DM男性患者和96例健康体检男性分为糖尿病组和健康对照组。糖尿病组和健康对照组(年龄和民族匹配)均排除既往或同时患有前列腺疾病或其他恶性肿瘤、急性感染(包括活动性的结核)和严重的肝肾功能损害者,对收集的临床资料和相关的辅助检查结果行回顾性的病例对照分析。结果 ①糖尿病组PSA水平低于对照组(P<0.05)。②T2DM患者中,应用二甲双胍者的总PSA水平及游离PSA水平低于非二甲双胍组(P<0.01,P<0.05)。结论 T2DM 患者血清PSA水平低于健康人群,二甲双胍可能有降低前列腺癌风险的作用。
二甲双胍;2型糖尿病;PSA;前列腺癌
0 引言
流行病学研究显示,2型糖尿病(T2DM)与多种肿瘤的发生密切相关[1-3]。2010年美国糖尿病学会(ADA)和美国癌症学会(ACS)联合发表共识[4]指出,糖尿病(主要是T2DM)患者罹患癌症的风险增高,而罹患前列腺癌的风险较正常人群减低,机制未明。血清总前列腺特异性抗原(Total prostate-specific antigen,TPSA)是目前诊断前列腺癌(Carcinoma of prostate,PCa)的最佳肿瘤标记物,本文观察二甲双胍对糖尿病患者TPSA及TPSA与游离前列腺特异性抗原(Free prostate specific antigen,FPSA)的比值(TPSA/FPSA)的影响,并与健康人群进行对比分析。
1 资料与方法
1.1 资料 收集2014年1-8月在我院内分泌科住院的178例T2DM男性患者(糖尿病组),年龄50~80岁,平均(64.5±15.5)岁,诊断符合WHO (1999年)标准,排除已明确诊断为前列腺癌等其他前列腺疾病的患者。分为二甲双胍组(80例)和非二甲双胍组(98例)。并选取同期我院健康体检中心的96例男性(健康对照组),排除已明确诊断为前列腺疾病及其他恶性肿瘤的患者,均为我院健康体检合格者。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 检测方法 仔细询问受试者的病史,进行查体并记录病程、应用药物种类,晨抽取空腹静脉血,高效液相色谱法测定HbA1c,CA19-9测定采用ROCHE Modular Analytics E170型自动电化学发光免疫分析仪及其配套试剂。HbA1c正常值参考范围:4.8%~6.0%;总PSA正常值参考范围:0~4;游离PSA正常值参考范围:0~0.934。
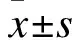
2 结果
2.1 糖尿病组与健康对照组PSA水平比较 糖尿病组TPSA、FPSA均低于健康对照组(P<0.05),而两组TPSA/FPSA比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表1。
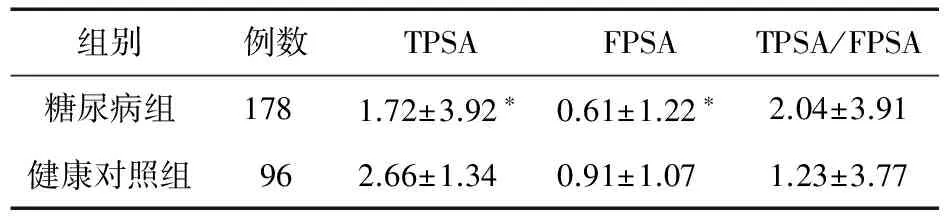
表1 糖尿病组与健康对照组PSA水平比较
注:与健康对照组比较,*P<0.05
2.2 糖尿病患者中,二甲双胍组患者的TPSA、FPSA水平均低于非二甲双胍组(P<0.01,P<0.05)。两组TPSA/FPSA比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表2。
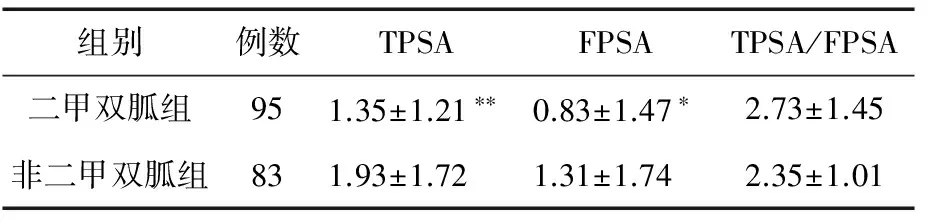
表2 二甲双胍组与非二甲双胍组PSA水平比较
注:与非二甲双胍组比较,*P<0.05,**P<0.01
3 讨论
本研究结果显示,T2DM患者总PSA水平较健康人群水平较低,由于TPSA是目前诊断前列腺癌的最佳肿瘤标记物,推断T2DM患者罹患前列腺癌的风险可能降低。而在T2DM患者中,应用二甲双胍的患者TPSA、FPSA水平均明显低于非二甲双胍组,推断二甲双胍可能会降低罹患前列腺的风险。其根本作用机制可能在于以下方面:二甲双胍是一种AMP 活化蛋白激酶(AMPK)[5-6],AMPK可以抑制激活雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR),而后者是调控恶性细胞增殖活化的重要因子,并与对抗抗癌药物有关[7-8]。此外,二甲双胍可以通过调节某些细胞周期蛋白(cycling A /B /D等)诱导细胞周期停滞和凋亡[9-10],干扰Vcap 细胞进入S期,使其停留在G0/G1期。此外,二甲双胍能抑制线粒体complex1 活性来改变细胞呼吸功能,进而影响细胞能量代谢[11-12]。Vazquez-Martin等[13]也对此进行了研究,结果显示,二甲双胍可用于清除上皮起源的非侵入性的肿瘤,即早期原位癌。EMT 指上皮细胞通过特定程序转化为具有间质表型细胞的生物学过程,从而使其获得侵袭和转移的能力[14]。E-cadherin和Vimentin分别是上皮细胞和间质细胞的重要生物标志物[15-16]。Vazquez-Martin等[17]发现,在高侵袭性乳腺癌细胞中,二甲双胍对由TGFβ信号通路诱导的EMT 过程有抑制作用,表现为TGFβ介导的E-cadherin下调与Vimentin上调消失。因此,二甲双胍在mRNA 和蛋白水平上,可抑制前列腺癌Vcap细胞的EMT,并显著抑制肿瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移能力[18]。本试验为回顾性研究,可能存在选择性偏倚,但对糖尿病与前列癌关系的总体结论影响不大。本研究结果表明,二甲双胍在有效控制血糖的同时,可以降低前列腺癌的发病率。因此,二甲双胍可能会为前列腺癌特别是伴有糖尿病的患者提供新的临床治疗选择。既往研究多基于动物模型,只有少部分为已明确诊断为前列腺癌的回顾性研究。本研究首次从前列腺癌相关肿瘤标记物角度探讨糖尿病与前列腺癌的关系,且从血糖水平及其相关药物等多方面综合性分析了二者的关系。糖尿病降低前列腺癌风险的机制一直是研究的热点。Jayachan-dran曾提出糖尿病降低前列腺癌风险可能与肥胖和种族有关[19],也有学者认为HNF1B 和JAZF1是糖尿病和前列癌的关系所在[20],总之,糖尿病与前列癌的关系仍需进一步探讨。
[1] Fang H,Xu HI,Liu YN,et al.The epidemiological characteristics of 1205 cancer patients with previous type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].China Cancer,2013,22:370-372.
[2] Hotta N,Nakamura J,Wamoto Y,et al.Causes of death in Japanese diabetics:a questionnaire survey of 18,385 diabetics over a 10 year period[J].J Diabetes Invest,2010,1:66-76.
[3] 骆秀婷,许岸高,陈利强,等.2型糖尿病与结直肠癌的相关性及合并2型糖尿病的结直肠癌的特点[J].中国医药,2014,9(3):345-349.
[4] Edward Giovannucci MD,David M,Harlan MD,et al.Diabetes and Cancer:A Consensus Report[J].A Cancer Journal for Clinicians,2010,60(4):207-221.
[5] Schneider MB,Matsuzaki H,Haorah J,et al.Prevention of pancreatic cancer induction in hamsters but motorman[J].Gastroenterology,2012,120(5):1263-1270.
[6] Jee SH,Ohrr H,Sull JW,et al.Fasting serum glucose level and cancer risk in Korean men and women[J].JAMA,2005,293(2):194-202.
[7] Green A S,Chapuis N,Lacombe C,et al.LKB1 /AMPK /mTOR signaling pathway in hematological malignancies:from metabolism to cancer cell biology[J].Cell Cycle,2011,10(13):2115-2120.
[8] 张艳飞,薛耀明,江颖娟,等.二甲双胍联合5-氟尿嘧啶抑制人结肠癌细胞SW620生长的实验研究[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(17):2784-2786.
[9] Ben Sahra I,Laurent K,Loubat A,et al.The ant diabetic drug motorman exerts an antitumoral effect in vitro and in vivo through a decrease of cycling D1 level[J].Ontogeny,2008,27(25):3576-3586.
[10]Ben Sahra I,Laurent K,Giuliano S,et al.Targeting cancer cell metabolism:the combination of motorman and 2-deoxyglucose induces p53-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer cells[J].Cancer Res,2010,70 (6):2465-2475.
[11]Vazquez-Martin A,Oliveras-Ferraros C,et al.Reforming regulates breast cancer stem cell ontogeny by transcriptional regulation of the epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) status[J].Cell Cycle,2010,9(18):3807-3814.
[12]王小玉,刘建英.二甲双胍的抗肿瘤作用及相关机制研究进展[J].中国医药,2014,9(5):759-761.
[13]Zhang L,Yang M,Gan L,et al.DLX4 up regulates TWIST and enhances tumor migration,invasion and metastasis[J].Into J Biol Sci,2012,8(8):1178-1187.
[14]Su YW,Xie TX,Sano D,et al.IL-6 stabilizes twist and enhances tumor cell motility in head and neck cancer cells through activation of casein kinas 2[J].PLoS One,2011,6(4):e19412.
[15]Vazquez-Martin A,López-Bonetc E,Cufí S,et al.Repositioningchloral equine and motorman to eliminate cancer stem cell traits in premalignantlesions[J].Drug Resist Update,2011,14:212.
[16]Azoulay L,Dell Aniello S,Gagnon B,et al.Metformin and the incidence of prostate cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers Prep,2011,20(2):337-344.
[17]He XX,Tu SM,Lee MH,et al.Thiazolidinediones and motorman associated with improved survival of diabetic prostate cancer patients[J].Ann Oncol,2011,22(12):2640-2645.
[18]Carnata D,Fierz Y,Vijayakumar A.Type 2 Diabetes and Cancer:What Is the Connection[J].Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine,2010,77:197-213.
[19]Wu C,Aronson WJ,Terris MK,et al.Diabetes predicts metastasis after radical prostatectomy in obese men:results from the SEARCH database [J].BJU Int,2013,111(8):E310-E318.
[20]Stevens VL,Ahn J,Sun J,et al.HNF1B and JAZF1 genes,diabetes,and prostate cancer risk[J].Prostate,2010,70(6):601-607.
Effect of metformin on plasma PSA level of type 2 diabetes and the relationship between metformin and prostate cancer
GUO Ying,WU Bo*
(The First Endocrinology Ward,Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University,Shenyang 110004,China)
Objective To observe the effect of metformin on plasma PSA of T2DM patients,and explore the relationship between metformin and prostate cancer.Methods 178 cases of T2DM male patients of Department of Endocrinology in our hospital from January to August 2014 were collected as experimental group,and 96 healthy men were chose as control group.Patients with previous or simultaneous with prostate disease or other malignant tumor,acute infection (including active tuberculosis) and serious liver and kidney injury were excluded.The retrospective case-control analysis for the clinical data and related auxiliary examination results of the cases in the two groups were done.Results ①The level of PSA in experimental group was lower than that of control group (P<0.05).②In T2DM patients,the total PSA and free PSA levels in patients using metformin were obviously lower than the patients without using metformin group (P<0.01,P<0.05).Conclusion The plasma PSA level in patients with T2DM was lower than that of healthy people,and metformin may reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
Metformin;Type 2 diabetes;PSA;Prostate cancer
2014-05-11
中国医科大学附属盛京医院第一内分泌病房,沈阳 110004
*通信作者
10.14053/j.cnki.ppcr.201504010
