Semaphorin家族及其受体对肿瘤血管生成影响的研究进展
2015-03-21鲁艳杰张淑玲耿志军李玉红赵向阳承德医学院河北承德067000承德县医院河北承德06700解放军总医院第一附属医院北京0008解放军第66医院河北承德067000
鲁艳杰,张淑玲,许 倩,耿志军,李玉红,赵向阳承德医学院,河北承德 067000;承德县医院,河北承德 06700;解放军总医院第一附属医院,北京 0008;解放军第66医院,河北承德 067000
Semaphorin家族及其受体对肿瘤血管生成影响的研究进展
鲁艳杰1,张淑玲2,许 倩1,耿志军3,李玉红1,赵向阳4
1承德医学院,河北承德 067000;2承德县医院,河北承德 067400;3解放军总医院第一附属医院,北京 100048;4解放军第266医院,河北承德 067000
信号素(Semaphorin)家族在神经系统的轴突导向中发挥重要作用。近年大量研究表明,这类分子不仅影响神经元的排斥和吸引,而且可以调节细胞的增殖、黏附和迁移,更重要的是发现其对肿瘤的生长、迁移、免疫反应、血管生成起重要调节作用。肿瘤的新生血管对肿瘤发生、发展及预后起着决定性作用。目前抗血管治疗已成为肿瘤治疗的一种新方法。充分了解肿瘤血管生成的调节机制是肿瘤抗血管治疗的基础和临床依据。本文就Semaphorin家族及其受体神经丛素(plexin)和神经激肽(neuropilin)对肿瘤血管生成的调节机制研究进展进行综述。
信号素;神经丛素;神经激肽;肿瘤;血管生成
信号素(Semaphorin,Sema)家族是一类轴突导向因子,其通过调节神经元的增殖、分化、迁移、极性、轴突剪修、突触形成、树突棘密度、成熟等多种过程影响神经系统发育。最早在果蝇体内发现Sema可影响感知觉生长锥的介导,并在神经元和肌细胞中高表达[1]。随后发现在人的神经回路中,Sema也是一个最大的调节神经元相互排斥作用的家族[2]。之后又发现其对中枢神经系统细胞之间的相互吸引也发挥重要作用[3]。在复杂的生物学环境中,Sema作为排斥和吸引分子,具有双向介导轴突导向的作用。近些年也发现Sema对心脏血管形成[4-5]、骨骼内稳定[6]、免疫反应[7]等也具有调节作用。血管系统与神经系统在解剖结构上有相似之处:1)神经血管总是伴行生长;2)都形成复杂而又精密的分支网络结构;3)动脉-静脉运输氧分和排出CO2等废物的模式与神经传入-传出系统传递神经信号相对应;4)血管和神经都由两种细胞组成:内皮细胞/周皮细胞、神经元/胶质细胞[8]。由此推测血管生成与神经系统的发生存在着相似的分子调控机制。研究也证实,Sema家族通过其受体影响内皮细胞增殖、凋亡和细胞基质黏附等调节肿瘤血管生长[8]。本文主要就Sema家族及其受体神经丛素(Plexins)和神经激肽(neuropilins,NPs)对肿瘤血管生成作用的研究进展进行综述。
1 Sema家族及其受体的结构和配体受体间的相互连接
1.1 Sema家族成员及其结构特征 Sema家族有30多个成员[9],根据种属发生及其结构特征被分为8类:Sema1A、Sema1B和Sema2A构成的第1 ~ 2家族,主要存在于无脊椎动物中[10];第3 ~ 7家族存在于脊椎动物中(除Sema5C),其中包括Sema3A ~ G、Sema4A ~ G、Sema5A ~ B、Sema6A ~D和Sema7A;第8家族和Sema5C主要是由病毒基因编码。Sema家族每个成员的N端都有由高度保守的500个氨基酸序列构成“Sema”结构域,该结构由7个β螺旋折叠形成。PSI(plexins,semaphorins and integrins)区紧密连接Sema区,两者形成特异的结构是Sema家族的重要功能区。Sema家族的不同亚型由以下蛋白进一步区分,包括免疫球蛋白样结构域(Ig)、血小板凝血酶敏感蛋白重复区(thrombospondin)、基本的C末端区域和糖基磷脂酰肌醇(glycosyphospatidylinositol,GPI)锚点。Sema1和Sema4 ~ 6家族是跨模型蛋白,Sema2、Sema3和Sema5家族为分泌型蛋白,Sema7族是通过GPI锚定在胞膜上的蛋白。
1.2 Sema家族受体成员及其结构特征 Plexins和NPs作为Sema家族的主要受体发挥作用。Plexins受体分为4个亚型:PlexinA(1 ~ 4),PlexinB(1 ~ 3),PlexinC1和PlexinD1。Plexins是一类结构与配体相似的跨膜蛋白,包含膜外的“Sema”结构域、重复的PSI区、3个IPT区(Plexins和转录因子共同作用的免疫球蛋白样折叠区)和细胞质内的GTP酶结合位点、两个与GAP相似的氨基酸结构、相对特殊的PlexinB受体含有1个PDZ区域的C端结合位点[11-12]。Sema家族另一个重要受体NPs由NP1和NP2组成,两者是具有相似结构域的膜糖蛋白且在肿瘤中常表达异常[13]。值得关注的是NPs也是血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)家族的受体[12]。Sema家族及其受体Plexins和NPs的结构和配体受体间的相互连接示意图见图1。
2 肿瘤血管生成在肿瘤进展中的作用
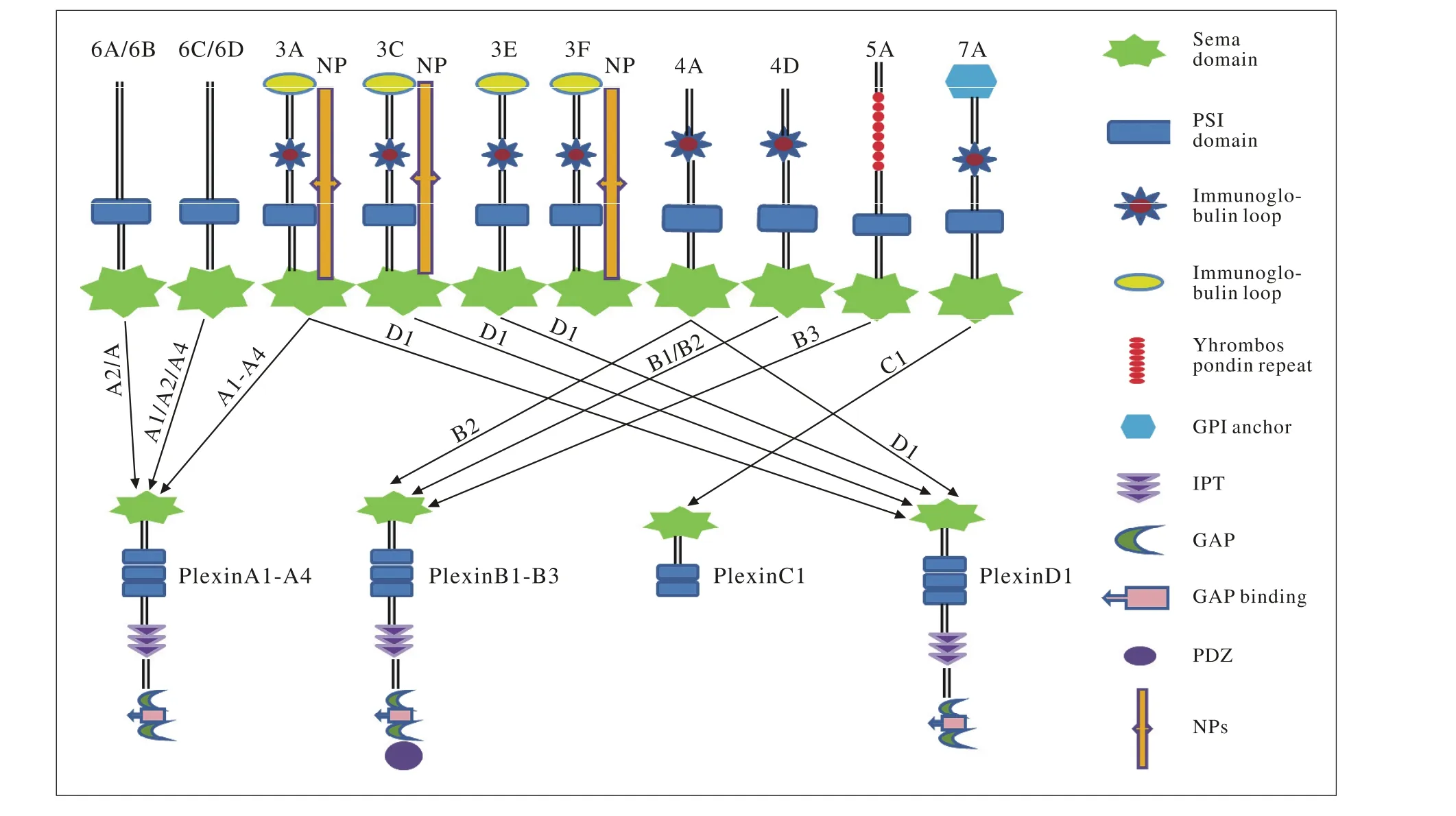
图 1 Sema家族及其受体Plexins和NPs的结构和配体受体间的相互连接示意图Fig. 1 Structure and connection of Sema ligands with their main receptors Plexines and NPs
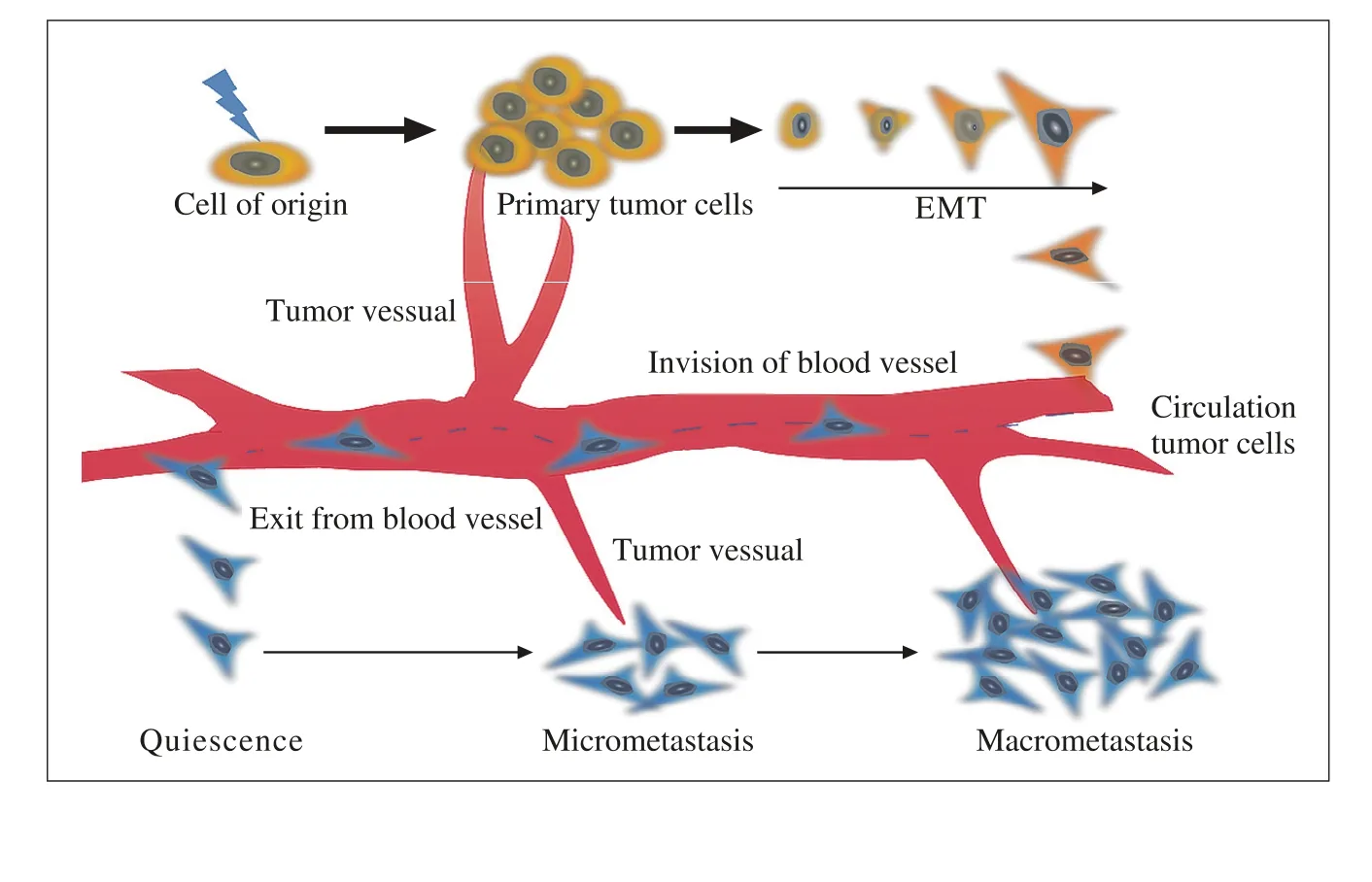
图 2 血管生成在肿瘤细胞增殖和转移过程中的作用示意图Fig. 2 Impact of angiogenesis on tumor cells proliferation and metastasis
肿瘤的发生主要与原癌基因激活和抑癌基因失活有关,并受多种遗传和环境因素影响。近年来提出的肿瘤干性样细胞被认为是肿瘤的“始发”细胞,指具有不断自我更新、多项分化潜能的细胞群。上皮间质转化与肿瘤的侵袭和转移密切相关,使肿瘤进一步恶化。获得间质表型的肿瘤细胞可以突破周围血管基底膜进入循环系统。原发肿瘤本身具有诱导新生血管的能力,肿瘤中的血管一方面为肿瘤细胞生长提供营养物质和氧气,另一方面对肿瘤细胞侵入血管发生血道转移提供条件。以前被广泛认可的是肿瘤细胞突破基底膜进入血管和淋巴管进行转移,然而最近研究表明,淋巴转移是代表死亡尽头的一个信号而不是一个肿瘤细胞的运输通道[14]。事实上,肿瘤蔓延到解剖结构的远处转移器官,几乎全部是通过血道转移实现的[15-16]。因此,肿瘤微环境中的血管生成对肿瘤的发生发展起到更加至关重要的作用。肿瘤血管生成在肿瘤细胞增殖和转移过程中的作用示意图见图2。
3 Sema家族对肿瘤血管生成的作用
血管生成是指从原始脉管系统中形成新的微小血管,其参与多种重要生理和病理过程,如创伤修复、心肌梗死后、子宫内膜周期性变化和糖尿病视网膜病变等。如上文所述,尤其在实体肿瘤中血管生成中发挥重要作用,而Sema家族对肿瘤血管生成的调节作用总结如下。
3.1 Sema家族及其受体促肿瘤血管生成作用 Sema3家族:在肿瘤血管生成中,内皮细胞产生自分泌的Sema3蛋白质可以刺激整合素生成。整合素作为VEGF的受体,是介导内皮细胞生存、黏附和迁移的重要因素[17-18],并与心血管疾病发展和肿瘤血管生成关系密切[19]。Sema3C可刺激胃癌血管生成并增强体外内皮细胞的黏附性[20],其促进肿瘤进展的机制是激活整合素蛋白磷酸化和VEGF120的分泌,该功能类似于VEGF-A[20]。
不同于Sema3家族其他成员需要NP1和(或)NP2作为共同受体,Sema3E可以直接结合PlexinD1[21]。Sema3E/ PlexinD1信号主要存在于肿瘤的新生血管位点。Sema3E/ PlexinD1启动R-Ras失活和ADP-核糖激化因子6(Arf6)的激活,分别影响整合素的活化状态和细胞内物质运输,进而发挥促进血管生长的作用[22]。然而越来越多的数据表明,Sema3E和PlexinD1可能独立发挥作用。如Sema3E基因敲除小鼠可正常生存且没有发现任何异常,但PlexinD1基因缺失的幼狗由于严重的心血管缺陷在生后24 h内就变得全身青紫而死[21]。由此可见,在复杂的Sema家族对脉管系统作用中,PlexinD1是内皮细胞调节的关键信号通路。此外还有数据显示,PlexinD1促进血管尖端内皮细胞的生长并形成“新生芽”[23],这可能与血管的生长方向密切相关。
Sema4家族:Sema4D在多种人类的肿瘤高度表达,如乳腺癌、结肠癌、前列腺癌、软组织肉瘤及头颈癌[24-25],其通过受体PlexinB1 ~ 2在肿瘤细胞介导的血管生成中发挥作用[25]。肿瘤细胞和成纤维细胞等浸润细胞可产生血管生成因子,其分泌物激活的巨噬细胞能影响各个阶段的血管生成,尤其在肿瘤生长的初期会出现大量引起肿瘤血管生成的巨噬细胞。在头颈部鳞状细胞癌中,肿瘤微环境的巨噬细胞产生的Sema4D可促进肿瘤血管生成。另外,Ⅰ型膜金属基质蛋白酶(MT1-MMP)可激活Sema4D,其激活和释放诱导体内肿瘤血管生成。另外,还发现Sema4D能够诱导内皮细胞迁移和促进肾小管上皮细胞增殖[26]。 Sema4D诱导内皮细胞迁移的机制是激活磷脂酰肌醇激酶3(PI3K)-Akt通路,在此过程中,其受体PlexinB1招募一个多聚体信号复合体,其中包括丙酮酸激酶(PYK)2、Src、PI3K和Akt[27]。Sema4D促进肿瘤血管生成功能与VEGF相似,是继VEGF后针对促肿瘤血管生长因子治疗的又一个重要靶点,目前已在一些肿瘤中得以应用。然而,抑制VEGF和Sema4D的实验受肿瘤的血管和瘤体大小限制,抗VEGF药物可以阻断血管的周皮细胞生长而Sema4D/ PlexinB1却不能[28]。因此,根据不同肿瘤血管生成的病理类型中周皮细胞和内皮细胞的情况,有针对地单独使用或者联合Sema4D和抗VEGF药物可能是抗肿瘤血管治疗的一个新策略。
PlexinB1在内皮细胞中高度表达[29-30],这点与其在体内是Sema4D一个高亲和力受体相符。然而,研究表明PlexinB1和Sema4D在组织中的分布有互补性,PlexinB1主要分布在没有Sema4D表达的组织中,其可能与Sema4D独立发挥作用[31]。研究也证实,PlexinB1在Sema4D介导的肿瘤血管生成中起到充分不必要的作用[32]。因此,猜测低亲和力受体PlexinB2很可能参与Sema4D对肿瘤血管生成的调节作用[31]。目前有研究指出,在斑马鱼成血管细胞中PlexinB2确实高表达,并在内皮细胞中独立发挥作用[33],而其在人类肿瘤血管发生和发展中的作用尚不清楚。
3.2 Sema家族及其受体抗肿瘤血管生成作用 Sema3家族:Sema3A作为一个抗血管生成因子[17],是第一个被发现可以抑制内皮细胞生长的Sema家族成员。一方面,Sema3A可增加血管通透性,这一点完全不同于大多数抗血管生成的蛋白[34];另一方面,Sema3A可抑制整合素激活,在某种程度上阻断整合素介导的内皮细胞黏附和迁移。此外,Sema3A的共受体NP1可结合VEGF调节血管生成。不过,后又证实Sema3A和VEGF在NP1上的结合位点在很大程度上是独立的[35]。除NP1外,Sema3A受体还有PlexinA1 ~ 4,PlexinA1和PlexinA4在调节内皮细胞和肿瘤细胞中发挥作用[36]。在最近的老鼠动物实验中,Sema3A单独应用或者与不同的抗血管生成药物协同用于抗新生血管治疗,以克服肿瘤的扩散和转移[37]。PlexinA4与VEGFR2、纤维母细胞生长因子受体2紧密相关,这些信号通路可增加内皮细胞和肿瘤细胞的增殖能力[36]。由此可见,PlexinA4的配体Sema3A不仅直接抑制肿瘤细胞迁移和血管生成,而且可以阻断下游PlexinA4受体对肿瘤的促进作用。因此,Sema3A很可能成为肿瘤治疗的一个新靶点。
有研究指出,Sema3B通过抑制肿瘤细胞生长和血管生成发挥抑癌作用[38]。Sema3F是最早发现在小鼠肿瘤模型中发挥抗血管生成作用的Sema成员[39],其可以减少多种肿瘤模型血管化[40]。其作用机制是抑制VEGF和FGF介导的ERK1/2的激活和下调NP2水平以抑制体外内皮细胞的增殖[41]。肿瘤细胞本身可分泌部分Sema3F抵制内皮细胞生长,在小鼠黑素移植瘤中,过表达Sema3F可阻断肿瘤血管生成、肿瘤生长和转移[42]。Sema6家族:Sema6A作为血管化的抑制剂[43],可以抑制移植瘤细胞外域VEGF165介导的血管生成[44]。
3.3 Sema家族对肿瘤血管生成的双向调节作用 Sema4A/ PlexinD1对肿瘤血管生成起双向调节作用,一方面Sema4A/ PlexinD1激活巨噬细胞浸润的血管生成过程,另一方面介导VEGF-A的表达,进而激活磷脂酰肌醇激酶3(PI3K)/Akt信号通路和依赖整合素的血管内皮细胞黏附[45]。究竟是Sema4A通过招募VEGF-A产生的巨噬细胞还是巨噬细胞激活Sema4A/PlexinD1信号通路促进新血管形成,尚不清楚。与此相反,有研究指出Sema4A可以通过Plexin-D1信号通路抑制内皮细胞生长,发挥抑制肿瘤血管生成的作用[46]。
4 结语
近些年发现Sema蛋白在多种肿瘤中异常表达且对肿瘤的发生和发展有一定的调节作用。肿瘤细胞本身和肿瘤微环境中的基质细胞都可以分泌Sema蛋白[23],它们作为肿瘤的一个新兴调节器可能成为肿瘤治疗的一个潜在靶点。血管生成诱导剂和拮抗剂可以通过调节内皮细胞分裂、游走和增殖等影响肿瘤的血管生成。Sema家族及其受体在肿瘤血管生成中发挥的重要作用,部分Sema家族成员发挥促进血管生长作用,靶向阻断这些蛋白表达可以为肿瘤治疗提供一个新思路。另外,一些成员也有明确的抗血管生成作用,利用其模拟药物有望成为与抗血管生成剂联合应用的一类蛋白分子。同时其下游作用受体NPs由于与VEGF紧密结合,也不失为肿瘤治疗的一个新方向。
1 Takahashi K, Ishida M, Hirokawa K, et al. Expression of the semaphorins Sema 3D and Sema 3F in the developing parathyroid and thymus[J]. Dev Dyn, 2008, 237(6): 1699-1708.
2 Derijck AA, Van Erp S, Pasterkamp RJ. Semaphorin signaling:molecular switches at the midline[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2010, 20(9):568-576.
3 O’connor BP, Ting JP. The evolving role of semaphorins and plexins in the immune system: Plexin-A1 regulation of dendritic cell function[J]. Immunol Res, 2008, 41(3): 217-222.
4 Toyofuku T, Zhang H, Kumanogoh A, et al. Dual roles of Sema6D in cardiac morphogenesis through region-specific association of its receptor, Plexin-A1, with off-track and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor type 2[J]. Genes Dev, 2004, 18(4): 435-447.
5 Toyofuku T, Zhang H, Kumanogoh A, et al. Guidance of myocardial patterning in cardiac development by Sema6D reverse signalling[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2004, 6(12): 1204-1211.
6 Kang S, Kumanogoh A. Semaphorins in bone development,homeostasis, and disease[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2013, 24(3):163-171.
7 Takegahara N, Kumanogoh A, Kikutani H. Semaphorins: a new class of immunoregulatory molecules[J]. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, 2005, 360(1461):1673-1680.
8 Autiero M, De Smet F, Claes F, et al. Role of neural guidance signals in blood vessel navigation[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2005, 65(3):629-638.
9 Pasterkamp RJ, Kolodkin AL. Semaphorin junction: making tracks toward neural connectivity[J]. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2003, 13(1):79-89.
10 Kolodkin AL, Matthes DJ, Goodman CS. The semaphorin genes encode a family of transmembrane and secreted growth cone guidance molecules[J]. Cell, 1993, 75(7):1389-1399.
11 Tamagnone L, Artigiani S, Chen H, et al. Plexins are a large family of receptors for transmembrane, secreted, and GPI-anchored semaphorins in vertebrates[J]. Cell, 1999, 99(1): 71-80.
12 Kolodkin AL, Ginty DD. Steering clear of semaphorins: neuropilins sound the retreat[J]. Neuron, 1997, 19(6): 1159-1162.
13 Potiron VA, Roche J, Drabkin HA. Semaphorins and their receptors in lung cancer[J]. Cancer Lett, 2009, 273(1):1-14.
14 Joyce JA, Pollard JW. Microenvironmental regulation of metastasis[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2009, 9(4): 239-252.
15 Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2002, 2(8):563-572.
16 Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer[J]. Cell,2000, 100(1):57-70.
17 Serini G, Valdembri D, Zanivan S, et al. Class 3 semaphorins control vascular morphogenesis by inhibiting integrin function[J]. Nature,2003, 424(6947): 391-397.
18 Casazza A, Fu X, Johansson I, et al. Systemic and targeted delivery of semaphorin 3A inhibits tumor angiogenesis and progression in mouse tumor models[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2011, 31(4): 741-749.
19 Geretti E, Shimizu A, Klagsbrun M. Neuropilin structure governs VEGF and semaphorin binding and regulates angiogenesis[J]. Angiogenesis, 2008, 11(1):31-39.
20 Banu N, Teichman J, Dunlap-Brown M, et al. Semaphorin 3C regulates endothelial cell function by increasing integrin activity[J]. FASEB J, 2006, 20(12): 2150-2152.
21 Gu C, Yoshida Y, Livet J, et al. Semaphorin 3E and plexin-D1 control vascular pattern independently of neuropilins[J]. Science,2005, 307(577): 265-268.
22 Sakurai A, Gavard J, Annas-Linhares Y, et al. Semaphorin 3E initiates antiangiogenic signaling through plexin D1 by regulating Arf6 and R-Ras[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2010, 30(12): 3086-3098.
23 Tamagnone L. Emerging role of semaphorins as major regulatory signals and potential therapeutic targets in cancer[J]. Cancer Cell,2012, 22(2): 145-152.
24 Ch’ng E, Tomita Y, Zhang B, et al. Prognostic significance of CD100 expression in soft tissue sarcoma[J]. Cancer, 2007, 110(1):164-172.
25 Basile JR, Castilho RM, Williams VP, et al. Semaphorin 4D provides a Link between axon guidance processes and tumor-induced angiogenesis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2006, 103(24):9017-9022.
26 Ch’ng ES, Kumanogoh A. Roles of Sema4D and Plexin-B1 in tumor progression[J]. Mol Cancer, 2010, 9:251.
27 Basile JR, Afkhami T, Gutkind JS. Semaphorin 4D/plexin-B1 induces endothelial cell migration through the activation of PYK2,Src, and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2005, 25(16):6889-6898.
28 Zhou H, Yang YH, Basile JR. The Semaphorin 4D-Plexin-B1-RhoA signaling axis recruits pericytes and regulates vascular permeability through endothelial production of PDGF-B and ANGPTL4[J]. Angiogenesis, 2014, 17(1):261-274.
29 Conrotto P, Valdembri D, Corso S, et al. Sema4D induces angiogenesis through Met recruitment by Plexin B1[J]. Blood,2005, 105(11): 4321-4329.
30 Basile JR, Barac A, Zhu T, et al. Class IV semaphorins promote angiogenesis by stimulating Rho-initiated pathways through plexin-B[J]. Cancer Res, 2004, 64(15): 5212-5224.
31 Fazzari P, Penachioni J, Gianola S, et al. Plexin-B1 plays a redundant role during mouse development and in tumour angiogenesis[J]. BMC Dev Biol, 2007, 7:55.
32 Worzfeld T, Swiercz JM, Looso M, et al. ErbB-2 signals through Plexin-B1 to promote breast cancer metastasis[J]. J Clin Invest,2012, 122(4): 1296-1305.
33 Lamont RE, Lamont EJ, Childs SJ. Antagonistic interactions among Plexins regulate the timing of intersegmental vessel formation[J]. Dev Biol, 2009, 331(2):199-209.
34 Treps L, Le Guelte A, Gavard J. Emerging roles of Semaphorins in the regulation of epithelial and endothelial junctions[J]. Tissue Barriers, 2013, 1(1):e23272.
35 Appleton BA, Wu P, Maloney J, et al. Structural studies of neuropilin/antibody complexes provide insights into semaphorin and VEGF binding[J]. EMBO J, 2007, 26(23): 4902-4912.
36 Kigel B, Rabinowicz N, Varshavsky A, et al. Plexin-A4 promotes tumor progression and tumor angiogenesis by enhancement of VEGF and bFGF signaling[J]. Blood, 2011, 118(15): 4285-4296.
37 Maione F, Capano S, Regano D, et al. Semaphorin 3a overcomes cancer hypoxia and metastatic dissemination induced by antiangiogenic treatment in mice[J]. J Clin Invest, 2012, 122(5):1832-1848.
38 Kigel B, Varshavsky A, Kessler O, et al. Successful inhibition of tumor development by specific class-3 semaphorins is associated with expression of appropriate semaphorin receptors by tumor cells[J]. PLoS One, 2008, 3(9): e3287.
39 Kessler O, Shraga-Heled N, Lange T, et al. Semaphorin-3F is an inhibitor of tumor angiogenesis[J]. Cancer Res, 2004, 64(3):1008-1015.
40 Futamura M, Kamino H, Miyamoto Y, et al. Possible role of semaphorin 3F, a candidate tumor suppressor gene at 3p21.3, in p53-regulated tumor angiogenesis suppression[J]. Cancer Res,2007, 67(4):1451-1460.
41 Coma S, Shimizu A, Klagsbrun M. Hypoxia induces tumor and endothelial cell migration in a semaphorin 3F- and VEGF-dependent manner via transcriptional repression of their common receptor neuropilin 2[J]. Cell Adh Migr, 2011, 5(3):266-275.
42 Bielenberg DR, Hida Y, Shimizu A, et al. Semaphorin 3F, a chemorepulsant for endothelial cells, induces a poorly vascularized,encapsulated, nonmetastatic tumor phenotype[J]. J Clin Invest,2004, 114(9): 1260-1271.
43 Oliveras-Ferraros C, Vazquez-Martin A, Cuyàs E, et al. Acquired resistance to metformin in breast cancer cells triggers transcriptome reprogramming toward a degradome-related metastatic stem-like profile[J]. Cell Cycle, 2014, 13(7):1132-1144.
44 Dhanabal M, Wu F, Alvarez E, et al. Recombinant semaphorin 6A-1 ectodomain inhibits in vivo growth factor and tumor cell line-induced angiogenesis[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2005, 4(6): 659-668.
45 Meda C, Molla F, De Pizzol M, et al. Semaphorin 4a exerts a proangiogenic effect by enhancing vascular endothelial growth factor-A expression in macrophages[J]. J Immunol, 2012, 188(8):4081-4092.
46 Toyofuku T, Yabuki M, Kamei J, et al. Semaphorin-4a, an activator for t-cell-mediated immunity, suppresses angiogenesis via Plexin-D1[J]. EMBO J, 2007, 26(5): 1373-1384.
Advances in effect of Semaphorin family and their receptors on tumor angiogenesis
LU Yanjie1, ZHANG Shuling2, XU Qian1, GENG Zhijun3, LI Yuhong1, ZHAO Xiangyang4
1Chengde Medical College, Chengde 067000, Hebei Province, China;2Chengde Country Hospital, Chengde 067400, Hebei Province, China;3First Affiliated Hospital of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100048, China;4Chinese PLA 266th Hospital, Chengde 067000, Hebei Province, China
LI Yuhong. Email: youngcheer2003@yahoo.com.cn; ZHAO Xiangyang. Email: 949673924@qq.com
Semaphorin family plays an important role in the development of nervous system axonal guidance. Recently, many reports have shown that these molecules not only affect the rejection and attraction of neurons, but also regulate cell proliferation, adhesion and migration. More importantly, they also play an important role in tumor growth, migration, immune response and tumor angiogenesis which is of great importance in tumor occurrence, development and prognosis. Now, antiangiogenic therapy has become a new method for tumor treatment. However, it still has some limitations and shortcomings. Therefore, it is necessary to fully understand the regulation mechanism of tumor angiogenesis, thus we can provide theoretical basis and clinical evidence for antiangiogenic therapy. Following is a review of Semaphorin and their receptors acting as regulators in tumor angiogenesis.
Semaphorin; plexin; neuropilin; neoplasms; angiogenesis
R 730.2
A
2095-5227(2015)10-1056-05 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-5227.2015.10.025
时间:2015-06-12 10:07
http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3275.R.20150612.1007.003.html
2015-04-14
河北省科技计划项目(13277779D)
Supported by the Science and Technology Program of Hebei Province(132 77779D)
鲁艳杰,女,在读硕士。研究方向:肿瘤。Email: luya njiehappy@163.com
李玉红,女,教授,硕士生导师。Email: youngcheer2003 @yahoo.com.cn;赵向阳,男,教授。Email: 949673924@qq.com
