双氰胺在不同温度下对碱性土尿素氮转化的影响
2015-03-15皮荷杰周细红蒋朝晖曾清如
张 露, 皮荷杰, 周细红, 蒋朝晖, 曾清如
(1.湖南农业大学 资源环境学院, 湖南 长沙 410128; 2.陕西省土地工程建设集团 国土资源部退化
及未利用土地整治工程重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710075; 3.株洲市环境保护研究院, 湖南 株洲 412007)
双氰胺在不同温度下对碱性土尿素氮转化的影响
张 露1,2, 皮荷杰3, 周细红1, 蒋朝晖1, 曾清如1
(1.湖南农业大学 资源环境学院, 湖南 长沙 410128; 2.陕西省土地工程建设集团 国土资源部退化
及未利用土地整治工程重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710075; 3.株洲市环境保护研究院, 湖南 株洲 412007)
摘要:[目的] 为了提高氮素的利用效率,减少—N淋溶污染,本试验研究了硝化抑制剂双氰胺(DCD)对碱性土壤中氮素转化的影响,为氮素的合理高效利用,增加作物产量提供参考。 [方法] 采用实验室人工气候箱培养法,研究双氰胺在15,25和35 ℃不同温度下对山西省晋城市菜园土(碱性)的pH值、氨挥发量及—N和—N转化的影响。 [结果] 在碱性土壤中施加双氰胺后,其pH值高于对照,且pH值随土壤温度的升高而升高;同时碱性土壤中氨挥发量也随温度升高而增大,每升高10 ℃,氮素以氨气形式损失的增加率约为6.90%;而土壤—N量却随温度的升高有所下降,其变化趋势与土壤—N量变化相反,此外温度的升高可导致—N含量峰值的出现时间提前,每增加10 ℃提前约为1周左右。双氰胺的施加可减少了—N转化为—N的量。 [结论] 双氰胺的施加可减少碱性土壤中氮素转化为—N所带来的淋溶污染问题,且随温度的升高pH值、氨挥发量和—N量增加。
关键词:双氰胺; 氮素; pH值; 氨挥发;;

1材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
在山西省晋城市菜园中用取土转采集土壤剖面0—60 cm的土样,随机找3个取样点,将各自地点所取的土样混合均匀,剔除有机残渣和砾石,经自然风干后过10目筛,贮存备用,其土壤基本理化性质详见表1[4]。

表1 供试土壤基本理化性质
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1pH值的测定取培养试验中土样10 g加入25 ml蒸馏水,在室温下振荡20 min,然后用PHS-3C型精密pH计对其pH值进行测定[5]。
1.2.2挥发氨的吸收及测定取供试土样60 g于玻璃密封瓶中,在3种温度下采用两种处理,3个平行(3种温度和2种处理同1.2试验方法)。调水分至绝对含水量80%,然后分别置于15,25和35 ℃人工气候箱中培养。每个玻璃密封瓶内放置一个50 ml小烧杯,小烧杯内盛2%的硼酸指示剂溶液5 ml以吸收挥发的氨。实验于2013年3月12日开始,每隔一定的时间换取小烧杯测定挥发氨的量[6]。用0.005 M的硫酸滴定吸收了氨气由红色转变为绿色的硼酸吸收液,再将滴定所消耗的硫酸体积进行计算得到挥发氨量[7]。

2结果与分析
2.1 不同温度下双氰胺对土壤pH值的影响
图1为供试碱性土在不同温度下两种处理下的pH值变化趋势图。从图1可以看出,两种处理pH值大体上都呈现出先升高再降低的趋势。在处理Ⅱ下,15 ℃时pH值从第14 d开始明显高于对照0.1~1.0,25 ℃时pH值从第4 d以后开始明显高于对照0.0~1.0,35 ℃时pH值从第4天开始明显高于对照0.0~1.0。
在碱性土中,添加硝化抑制剂DCD后pH峰值的出现随温度的升高而提前(图1)。在处理Ⅱ下,15 ℃时pH值在第14 d出现峰值,25 ℃时在第7 d出现峰值,35 ℃时在第4 d就出现了峰值。在碱性土中,35 ℃的pH峰值高出25 ℃的0.1,高出15 ℃的0.2。
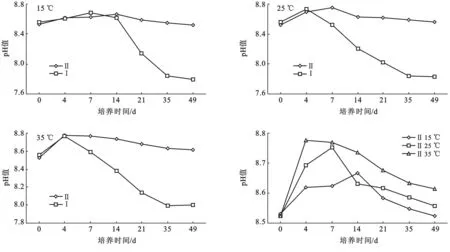
图1 供试碱性土硝化抑制剂对土壤pH值的影响
2.2 不同温度下双氰胺对氨挥发的影响
图2为供试碱性土在不同温度下两种处理下的挥发氮量变化。从图2可以看出,两种处理的氨挥发量都是先增加后减少,这和pH值的变化趋势一致,说明氨挥发量与土壤pH值成正相关。施加硝化抑制剂DCD前后氨的变化趋势,添加DCD后氨气挥发量要普遍大于没添加的,说明DCD能加大氨气的挥发量。在碱性土壤中,添加硝化抑制剂DCD后,在3种温度下,都是从第4 d起NH3开始挥发,15 ℃时在第14 d达到峰值,25 ℃时在第7 d达到峰值,35 ℃时在第4 d达到峰值(图2),可以看出在碱性土中添加硝化抑制剂DCD后随着温度的升高氨气挥发量出现峰值的时间提前。在处理Ⅱ下测定时间内氨气挥发总量为15 ℃时为7.4 mg/kg,占全氮的0.31%,25 ℃时为21.5 mg/kg,占全氮的0.89%,35 ℃时为36.2 mg/kg,占全氮的1.51%,所以从15~35 ℃,每升高10 ℃,氮素以氨气形式损失的增加率约为6.90%,说明温度越高NH3的挥发量越大。
2.3 硝化抑制剂对土壤-N和的影响
图3为供试碱性土在不同温度下两种处理下的铵态氮含量变化。
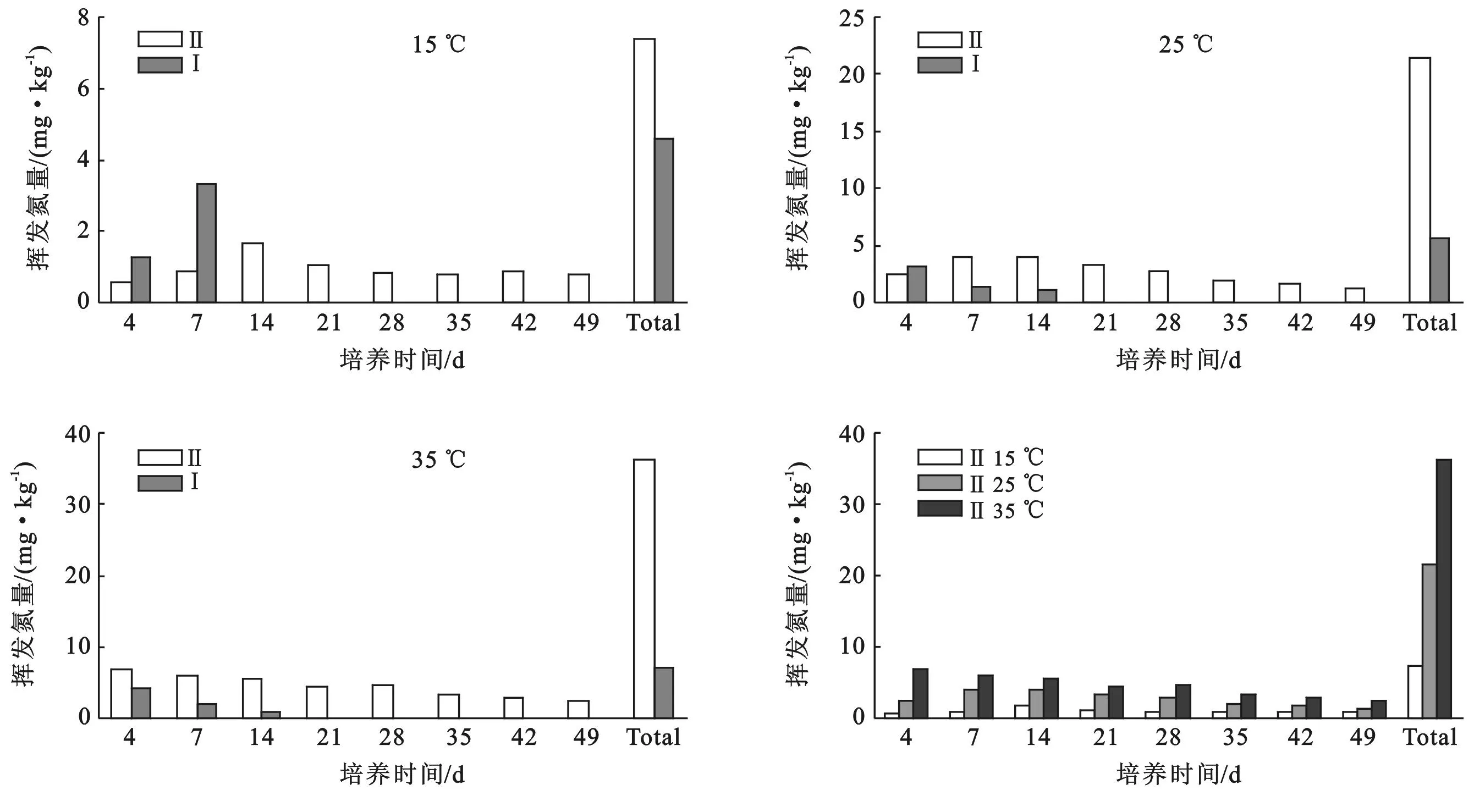
图2 供试碱性土硝化抑制剂对氨挥发的影响

图3 供试碱性土硝化抑制剂对-N的影响


图4 供试碱性土硝化抑制剂对-N的影响
3讨 论



4结 论
[参考文献]
[1]朱兆良,文启孝.中国土壤氮素[M].江苏 南京:江苏科学技术出版社,1992:122-129.
[2]Amberger A. Research on dicyandiamide as a nitrification inhibitor and future outlook [J].Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 1989, 20(19/20):1933-1955.
[3]McCarty G W. Mode of action of nitrification inhibitors [J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 1999,29(1):1-9.
[4]鲁如坤.土壤农化分析方法[M].北京:中国农业科技出版社,1999:42-56.
[5]蒋朝辉,曾清如,周细红,等.不同温度下施入尿素后土壤短期内pH的变化和氨气释放特性[J].土壤通报,2004,35(3):299-302.
[6]孙克君,毛小云,卢其明,等.几种控释氮肥减少氨挥发的效果及影响因素研究[J].应用生态学报,2004,15(12):2347-2350.
[7]凌莉,李世清,李生秀.石灰性土壤氨挥发损失的研究[J].土壤侵蚀与水土保持学报,1999,5(6):119-122.
[8]聂文静,李博文,郭艳杰,等.氮肥与DCD配施对棚室黄瓜土壤NH3挥发损失及N2O排放的影响[J].环境科学学报,2012,32(10): 2500-2508.
[9]马建华,樊明寿,田东海.双氰胺对马铃薯农田土壤铵态氮、硝态氮[J].中国农学通报,2010,26(2):149-151.
[10]杜玲玲.双氰胺的硝化抑制作用及其应用[J].土壤学进展,1994,22(4): 26-31.
[11]刘源,钱薇,徐仁扣.双氰胺对施氮肥引起的红壤酸化的抑制作用[J].生态与农村环境学报, 2013,29(1):76-80.
[12]Kelliher F M, Clough T J, Clark H, et al. The temperature dependence of dicyandiamide(DCD)degradation in soils: A data synthesis [J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2008, 40(7):1878-1882.
[13]Klein C A M, Cameron K C, Di H J, et al. Repeated annual use of the nitrification inhibitor dicyandiamide(DCD)does not alter its effectiveness in reducing N2O emissions from cow urine[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2011,166(7):480-491.
[14]Bronson K F, Touchton J T, Hauck R D. Decomposition rate of dicyandiamide and nitrification inhibition [J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 1989,20(19):19-20.
[15]Rajbanshi S S, Benckiser G, Ottow J C G. Mineralizaiton kinetics and utilizaiton as an N source of dicyandiamide(DCD) in soil [J]. Nautrwissenschaften, 1992, 79(1):26-27.
[16]Schwarzer C, Haselwandter K. Enzymatic degradation of the nitrification inhibitor dicyandiamide by a soil bacterium [J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1991, 23(3):309-310.
[17]罗涛,王煌平,张晓玲,等.土壤中双氰胺降解及与降解菌的关系[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2012,31(11):2174-2179.
[18]Das P, Sa J H, Kim K H, et al. Effect of fertilizer application on ammonia emission and concentration levels of ammonium, nitrate, and nitrite ions in a rice field [J]. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 2008,154(1/4):275-282.
[19]皮荷杰,曾清如,蒋朝晖,等.两种硝化抑制剂对不同土壤中氮素转化的影响[J].水土保持学报,2009,23(1):68-72.
[20]刘常珍,胡正义,赵言文,等.元素硫和双氰胺对菜地土壤铵态氮硝化抑制协同效应研究[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2008,14(2):334-338.
Effects of Dicyandiamide on Urea Nitrogen Transformation in Alkaline Soil in Different Temperatures
ZHANG Lu1,2, PI Hejie3, ZHOU Xihong1, JIANG Zhaohui1, ZENG Qingru1
(1.CollegeofResourceandEnvironment,Hu’nanAgriculturalUniversity,Changsha,Hu’nan410128,China; 2.ShaanxiLandConstructionGroup,KeyLaboratoryofDegradedandUnusedLandConsolidationEngineeringoftheMinistryofLandandResourcesofChina,Xi’an,Shaanxi710075,China; 3.ZhuzhouEnvironmentalProtectionInstitute,Zhuzhou,Hu’nan412007,China)
Abstract:[Objective] In order to increase the utilization efficiency of nitrogen, reduce the leaching pollution of nitrifying nitrogen, the study explored the effect of nitrification inhibitor DCD on nitrogen transformation in alkaline soils, which may provide a reference for rational and efficient use of nitrogen and increasing crop yields. [Methods] The laboratory artificial climate chamber culture was used to study the effects of DCD on pH value, ammonia volatilization, nitrifying nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen conversion of Jincheng City of Shaanxi Province(alkalinity) garden soils in different temperatures of 15 ℃, 25 ℃ and 35 ℃. [Results] The result indicated that the pH value with DCD was higher than the control, which increased with the temperature increasing. The ammonia volatilization increased with the temperature increasing in alkaline soil, so the temperature increase by 10 ℃, the increasing rate of nitrogen loss in the form of ammonia was about 6.90%. The nitrifying nitrogen content decreased with temperature increasing, whose variation was opposite with ammonia nitrogen content. Moreover, the peak time of ammonia nitrogen content with temperature increasing was about one week ahead with the increase of temperature by each 10 ℃. DCD reduced the conversion of ammonia nitrogen to nitrifying nitrogen. [Conclusion] DCD can reduce the leaching pollution problems by lowering the nitrogen conversion to nitrifying nitrogen, and the pH value, ammonia volatilization and ammonia nitrogen increase with the temperature increasing.
Keywords:dicyandiamide; nitrogen; pH value; ammonia volatilization; nitrifying nitrogen; ammonia nitrogen
文献标识码:A
文章编号:1000-288X(2015)06-0172-06
中图分类号:S158.5
通信作者:曾清如(1964—),男(汉族),湖南省邵阳县人,教授,主要从事环境污染化学的教学与科研工作。E-mail:qrzeng@163.com。
收稿日期:2014-10-29修回日期:2014-11-25
资助项目:农业部重大专项“湖南省重金属污染耕地修复及农作物种植结构调整”(农办财函〔2014〕28号)
第一作者:张露(1987—),女(汉族),四川省南部县人,博士研究生,研究方向为土壤物理及其改良。E-mail:luluqiaofeng@126.com。
