表皮生长因子对早期断奶仔猪生长性能及肠道健康的影响
2015-03-14汤小朋方热军
汤小朋 方热军
(湖南农业大学动物科学技术学院,长沙 410128)
仔猪早期断奶是规模化、集约化养猪生产中关键技术之一。仔猪早期断奶不仅可以最大限度发挥母猪的繁殖性能,提高母猪年产胎数,还能减少病原体从母猪向仔猪传递[1]。但是,早期断奶可能会因为环境及饮食成分的改变引发断奶应激,影响仔猪的生产性能及肠道健康。因此提高断奶仔猪采食量及保持仔猪肠道健康是保证仔猪正常生长的关键。大量研究表明表皮生长因子(epidermal grow th factor,EGF)对早期断奶哺乳动物的生长性能、肠道发育、营养物质转运等具有促进作用[2-6]。饲粮中添加外源EGF对降低断奶仔猪腹泻率[7],提高免疫力[6],提高生产性能[7-9],促进肠道发育[5,10-11]及提高胃肠道消化酶活性[12]等具有很好的效果。本文就EGF对早期断奶仔猪生产性能及肠道健康的影响做一综述,为EGF在仔猪饲粮中的应用提供参考。
1 EGF 概述
EGF属于促生长因子家族成员,与转运生长因子 α(transform ing grow th factor-alpha,TGF-α)、肝素结合 EGF(heparin-binding EGF,HB-EGF)、双调蛋白(amphiregulin,AR)、乙胞素(betacellulin,BTC)及上皮调节蛋白(epiregulin,EPR)同属于EGF 蛋 白 家 族[13]。EGF、TGF-α、HB-EGF、AR、BTC及EPR能与EGF受体(EGF receptor,EGFR)结合,激活酪氨酸激酶活性,并形成一个二聚体[13],从而发挥其生物学效应。EGFR是一种分子质量为170 ku的跨膜蛋白,主要由细胞外区、跨膜区和细胞内区3部分组成。
EGF是Stanley Cohen在1962年从小鼠下颌腺中分离提纯出的一种单链多肽类活性物质[14]。氨基酸序列分析发现成熟的EGF含有53个氨基酸残基,活性中心位于第48~53个氨基酸残基之间,在第 6、20 位,14、31 位,33、42 位之间形成 3个二硫键(图 1)[15]。
EGF主要由泌乳乳房、下颌腺、肾脏、十二指肠Brunner腺、胰腺和胎盘等分泌,释放进入乳液、唾液、尿液、肠液、血液、羊水等[15-16]。EGF 对热和酸具有较强耐受性,能抵抗胰蛋白酶、糜蛋白酶及胃蛋白酶的消化,对其维持结构的稳定和发挥生物学作用具有重要意义,也使其可作为饲料添加剂应用在断奶仔猪饲粮中[16]。
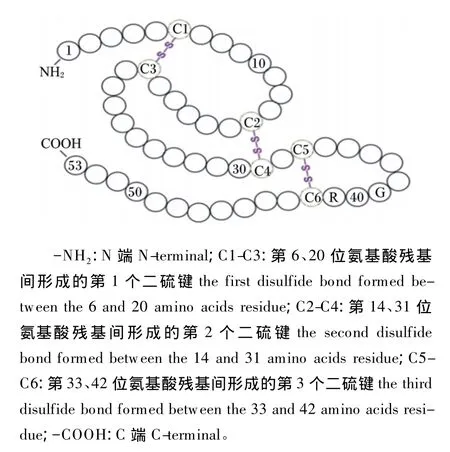
图1 EGF氨基酸序列及二硫键位置Fig.1 The am ino acid sequence and disulfide bond position of EGF[15]
2 EGF对早期断奶仔猪生长性能的影响
2.1 对采食量与日增重的影响
断奶是仔猪生长过程中最大的应激事件,断奶应激可导致仔猪肠道及免疫功能紊乱而引起采食量下降及生长缓慢甚至停滞,影响猪生产性能。据报道,商品猪出栏时间与断奶后1周仔猪的日增重有关,日增重大的仔猪出栏时间比日增重小的仔猪出栏时间更短[17]。因此,提高断奶仔猪采食量及日增重对养猪生产意义重大。
大量研究发现EGF可改善断奶仔猪的断奶应激,提高断奶仔猪生产性能[7-9,18-19]。EGF 的使用可减少高质量氨基酸及抗生素的使用[8],提高饲料转化率,降低料重比和腹泻率[9],降低生产成本,提高经济效益。随着基因工程技术的发展,EGF 已经在大肠杆菌[20],毕赤酵母[21]、酿酒酵母[3,6,22]、乳酸乳球菌[5,7,19]等微生物中表达成功,使EGF来源更为广泛。利用毕赤酵母、酿酒酵母以及乳酸乳球菌等益生菌表达重组EGF产物可以直接添加在仔猪饲粮中,提高仔猪采食量与日增重[6-8,19,23],且在早期断奶仔猪肠道中可检测到重组微生物的活性,对改善肠道微生物菌群有重要作用[5-6,19]。也有研究表明重组微生物的活性不是必要的,甚至高浓度的微生物会对EGF的效果起反作用,导致仔猪腹泻率增加[7]。
2.2 对营养物质转运的影响
EGF可促进肠道对营养物质的吸收,提高断奶仔猪生产性能。大量研究表明EGF及其相关因子涉及到许多上皮细胞离子通道的调节,如,上皮细胞钠离子通道(epithelial sodium channel,ENaC)[24]、Na+/K+/2Cl-共同转运蛋白(Na+/K+/2Cl-co-transporter,NKCC1)[25]、跨 膜 蛋 白 16A(transmembrane protein 16A TMEM 16A,Ca2+-dependent Cl-channel)[26]、钙激活钾离子通道(calcium-activated K+channels,KCa3.1)[27]及瞬时感受器电位M 6离子通道(transient receptor potential melastatin 6,TRPM 6)与瞬时受体电位阳离子通道蛋白C5(cation-nonselective transient receptor potential channel 5,TRPC5)[28]。说明 EGF 与 Na+、K+、Ca+、Mg+、Cl-等离子的转运有关。EGF 还能调节钠磷转运蛋白NaPi-Ⅱb的表达[29],说明EGF参与小肠磷吸收的调节。研究表明,EGF能促进肠道对葡萄糖[11,24,30]、谷氨酰胺[31]等营养物质的吸收。Cellini等[32]报道,给雌性家兔子宫内胎儿提供含EGF的羊水,可增加小肠葡萄糖的摄取量。这是因为EGF可刺激肠黏膜细胞刷状上的Na+-葡萄糖共转运载体(sodium/glucose cotransporter-1,SGLT-1)移位到黏膜刷状缘顶端,增加刷状缘上SGLT-1浓度,将肠腔内葡萄糖转运至上皮细胞,影响能量摄入[11,23,30]。Na+-依赖性中性氨基酸载体(Na+-dependent neutral amino acids transporter,ASCT2)是一种氨基酸载体,EGF可通过提高肠道上皮细胞中谷氨酰胺载体ASCT2的转运活性、mRNA表达量和蛋白质表达量,促进对Na+-依赖性谷氨酰胺的吸收[31]。
3 EGF对早期断奶仔猪肠道健康的影响
3.1 对消化道酶活性的影响
母乳中EGF是促进新生动物胃、肠道发育的重要生长因子。EGF可促进断奶仔猪胃肠道中胃蛋白酶、糜蛋白酶、胰蛋白酶及空肠碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase,ALP)、蔗糖酶、麦芽糖酶和乳糖酶的活性并能促进ALP、蔗糖酶、麦芽糖酶、乳糖酶、氨基肽酶A(am inopeptidase A,APA)及氨基肽酶 N(am inopeptide N,APN)mRNA的表达[10,12,23]。早期断奶仔猪母源 EGF 突然中断,消化系统发育不完善,胃肠道消化酶分泌不足,不能很好的消化固态食物。饲粮中添加外源EGF可促进仔猪胃肠道消化酶的分泌,改善机体对营养物质的吸收利用。EGF对断奶仔猪消化道酶活性的影响存在剂量效应。给14日龄早期断奶仔猪分别饲喂 0、0.5、1.0、1.5 mg/kg 的 EGF,结果发现饲喂1.5mg/kg的EGF可显著增加空肠ALP及乳糖酶的活性,伴随着ALP mRNA及乳糖酶mRNA的表达量增加[12]。
3.2 对肠道发育的影响
断奶应激会导致仔猪小肠绒毛萎缩,腺窝增生,不利于营养物质的吸收,影响仔猪生长性能。EGF作为有丝分裂原,可促进肠上皮组织细胞增殖与分化[2,5,11],促进小肠绒毛及隐窝发育[6,18],促进细胞内DNA、RNA和蛋白质合成[6],对肠道发育的调节及肠道损伤的修复具有重要作用。Kang等[5]研究表明口饲EGF可增加早期断奶仔猪的空肠与十二指肠的绒毛高度及肠道长度,促进肠道细胞增殖。槐玉英等[18]研究发现口饲EGF,断奶仔猪十二指肠和空肠的绒毛高度和绒毛/腺窝的比值都明显优于对照组,表明EGF可有效降低断奶应激对仔猪肠道结构和功能的不利影响,促进仔猪肠道发育。EGF可刺激肠道杯状细胞增殖[11],杯状细胞可分泌三叶肽,对胃肠道损伤的修复及伤口愈合有重要作用[33],且EGF与三叶肽共同作用对肠道伤口愈合效果更好[34]。
3.3 对免疫功能的影响
EGF可促进白细胞介素-13(interleukin-13,IL-13)与角质细胞生长因子(keratinocyte grow th factor,KGF)[11]的分泌。IL-13 是一种抗炎细胞因子,可刺激杯状细胞增殖及黏蛋白2(Muc2)的分泌[35]。KGF是成纤维生长因子家族成员(也叫做FGF-7),也可刺激杯状细胞增殖及黏蛋白2(Muc2)的分泌[11]。Muc2是黏液保护层重要成分,对肠道润滑,限制细菌黏附及维持肠道通透性有重要作用[11]。同时,EGF可促进肠道免疫球蛋白(IgA、IgG、IgM)的表达及淋巴细胞的增殖[6,11],促进猪流行性腹泻病毒导致的萎缩性肠炎的恢复[36],提高早期断奶仔猪的免疫功能,降低仔猪腹泻率 。
4 EGF促进早期断奶仔猪生长性能与肠道发育的可能机制
大量研究证实了EGF可以促进早期断奶仔猪生长性能与肠道发育,但其涉及的机制研究还不够深入。总结前人研究推测EGF促进早期断奶仔猪生长性能与肠道发育的可能机制为:1)EGF通过激活 PI3K/AKT、RAS/MAPK信号通路(图2)[16,37],促进小肠 DNA、RNA 合成[6],促进细胞增殖与分化[5,11],从而促进小肠绒毛发育[6,18]促进胃肠道消化酶的分泌表达[6,10,12,18,23],提高小肠养分吸收及养分利用率,同时促进受损肠道组织的修 复[16]。EGF促 发 丝 裂 原 活 化 蛋 白 激 酶(MAPK)信号通路过程为:EGF与其受体EGFR结合后,形成二聚体,并发生自身磷酸化而被激活,其酪氨酸残基与生长因子受体结合蛋白2(Grb2)的SH2结构域特异结合,Grb2的SH3结构域与鸟苷酸交换因子(SOS)结合,SOS与膜上的小G蛋白Ras结合后使非活性的GDP-Ras转化为激活型 GTP-Ras,GTP-Ras与丝氨酸/苏氨酸(Ser/Thr)蛋白激酶Raf(又称MAPKK)的N端结合并使其激活,活化的Raf结合并磷酸化MAPKK,激活MAPK(即 ERK)的苏氨酸和酪氨酸残基,ERK进入细胞核,激活多种转录因子,调节DNA的合成、转录及细胞增殖与分化(图 2-B)[16,37]。EGF 也 能 促 发 磷 脂 酰 肌 醇 3 - 激 酶(PI3K)信号通路。EGF与其受体结合后激活EGFR,酪氨酸残基与PI3K结合,将磷酸肌醇二磷酸(PIP2)磷酸化为 3,4,5-磷脂酰肌醇三磷酸(PI-3,4,5-P3)。活化的 PI-3,4,5-P3与磷酸肌醇依赖性激酶-1(PDK-1)和丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶Akt(PKB)结合,转位到细胞膜上,改变Akt的构象。激活的PKB返回细胞质,通过磷酸化作用激活或抑制下游靶蛋白,进而调节细胞的增殖、分化、凋亡以及迁移等(图 2-A)[16,37]。2)EGF 促进 IL-13及KGF表达[11],刺激杯状细胞增殖,促进 Muc2的分泌[11],保护肠道健康。具体通过何种途径调节促进IL-13及KGF表达还需进一步研究。3)EGF促进营养物质转运蛋白基因表达,如SGLT1[11,23]。研 究 表 明 EGF 在 转 录 水 平 调 控SGLT1基因的表达,其通过EGFR与PI3K信号通路激活cAMP相应元件结合蛋白(cAMP response element-binding protein,CREB)并磷酸化促进SGLT1基因表达与肠道葡萄糖吸收[38]。综上所述,EGF通过促进肠道绒毛发育、消化酶分泌及肠道营养物质转运蛋白表达,促进肠道养分吸收利用,提高断奶仔猪生产性能;通过促进肠道杯状细胞分化维持肠道健康及通过促进肠细胞增殖与分化修复受损肠道(图3)。

图2 EGF激活的PI3K(A)与MAPK(B)信号通路过程图Fig.2 The process of PI3K(A)and MAPK(B)signal pathway activated by EGF[37]
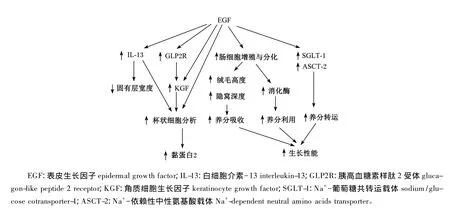
图3 EGF促进早期断奶仔猪生长性能与肠道发育的可能机制Fig.3 Proposed mechanism of EGF on early-weaned piglet grow th performance and intestine development[11]
5 小结
早期断奶对提高母猪繁殖性能及减少病原菌由母体向仔猪传递有重要意义。但是早期断奶也会因为环境及饮食的改变引发断奶应激;同时,早期断奶仔猪胃肠道发育不完善,对养分吸收利用率低下,严重影响断奶仔猪胃肠道健康及生长性能,给养猪生产带来不利影响。大量研究表明EGF可提高断奶仔猪生产性能、促进肠道发育和营养物质转运、提高胃肠道消化酶活性和免疫力及降低腹泻率。但关于EGF促进早期断奶仔猪生长性能及肠道发育的机制研究较少。因此,深入研究EGF促进早期断奶仔猪生长性能及肠道发育的机制可能是今后的研究热点。
[1] WHITING T L,PASMA T.Isolated weaning technology:humane benefits and concerns in the production of pork[J].The Canadian Veterinary Journal,2008,49(3):293-301.
[2] CHEUNG Q C,YUAN Z F,DYCE PW,et al.Generation of epidermal grow th factor-expressing Lactococcus lactis and its enhancement on intestinal development and grow th of early-weaned m ice[J].American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,2009,89(3):871-879.
[3] WANG S J,ZHOU L,CHEN H N,et al.Analysis of the biological activities of Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing intracellular EGF,extracellular EGF,and tagged EGF in early-weaned rats[J].Applied M icrobiology and Biotechnology,2015,99(5):2179-2189.
[4] CELLINIC,XU J,BUCHM ILIER-CRAIR T.Effect of epidermal grow th factor on small intestinal sodium/glucose cotransporter-1 expression in a rabbitmodel of intrauterine grow th retardation[J].Journal of Pediatric Surgery,2005,40(12):1892-1897.
[5] KANG P,TOMSD,YIN Y L,etal.Epidermal grow th factor-expressing Lactococcus lactis enhances intestinal development of early-weaned pigs[J].The Journal of Nutrition,2010,140(4):806-811.
[6] WANG S J,GUO C H,ZHOU L,etal.Comparison of the biological activities of Saccharomyces cerevisiaeexpressed intracellular EGF,extracellular EGF,and tagged EGF in early-weaned pigs[J].Applied M icrobiology and Biotechnology,2015,doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6468-6.
[7] BEDFORD A,HUYNH E,FU M L,et al.Grow th performance of early-weaned pigs is enhanced by feeding epidermal grow th factor-expressing Lactococcus lactis fermentation product[J].Journal of Biotechnology,2014,173:47-52.
[8] BEDFORD A,LI Z,LI M,et al.Epidermal grow th factor-expressing Lactococcus lactis enhances grow th performance of early-weaned pigs fed diets devoid of blood plasma[J].Journal of Animal Science,2012,90(4S):4-6.
[9] 王勇飞,段叶辉,夏连喜,等.重组猪表皮生长因子对早期断奶仔猪生长性能的影响[J].动物营养学报,2014,26(12):3787-3792.
[10] LEE D N,CHANGW F,YU IT,etal.Effects of diets supplemented w ith recombinant epidermal grow th factor and glutam ine on gastrointestinal tract development of early-weaned piglets[J].Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences,2008,21(4):582-589.
[11] BEDFORD A,CHEN T,HUYNH E,et al.Epidermal grow th factor containing culture supernatant enhances intestine development of early-w eaned pigs in vivo:potentialmechanisms involved[J].Journal of Biotechnology,2015,196-197:9-19.
[12] LEE D N,CHUANG Y S,CHIOU H Y,etal.Oral adm inistration recombinant porcine epidermal grow th factor enhances the jejunal digestive enzyme genes expression and activity of early-weaned piglets[J].Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition,2008,92(4):463-470.
[13] SCHNEIDER M R,WOLF E.The epidermal grow th factor receptor ligands at a glance[J].Journal of Cellular Physiology,2009,218(3):460-466.
[14] COHEN S.Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal[J].The Journal of Biological Chem istry,1962,237:1555-1562.
[15] ZENG H F,HARRIS R C.Epidermal grow th factor,from gene organization to bedside[J].Sem inars in Cell& Developmental Biology,2014,28:2-11.
[16] 刘淑杰,徐子伟,齐珂珂,等.表皮生长因子对肠道功能调控的研究[J].动物营养学报,2014,26(3):565-570.
[17] CAMPBELL JM,CRENSHAW JD,POLO J.The biological stress of early weaned piglets[J].Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology,2013,4:19.
[18] 槐玉英,纪少丽,李明,等.表达表皮生长因子的乳酸球菌对早期断奶仔猪生长性能和肠道形态学结构的影响[J].中国兽医杂志,2013,49(3):21-23.
[19] WANG D Y,XU SY,LIN Y,et al.Recombinant porcine epidermal grow th factor-secreting Lactococcus lactis promotes the grow th performance of earlyweaned piglets[J].BMC Veterinary Research,2014,10:171.
[20] ABDULL RAZISA F,ISMAIL EN,HAMBALIZ,et al.Expression of recombinanthuman epidermal grow th factor in Escherichia coli and characterization of its bi-ological activity[J].Applied Biochem istry and Biotechnology,2008,144(3):249-261.
[21] LEE D N,KUO T Y,CHEN M C,et al.Expression of porcine epidermal grow th factor in Pichia pastoris and its biology activity in early-weaned piglets[J].Life Sciences,2006,78(6):649-654.
[22] 王蜀金,周琳,陈慧娜,等.重组猪表皮生长因子在酿酒酵母中的克隆表达及其生物学活性鉴定[J].畜牧兽医学报,2014,45(12):1971-1980.
[23] XU S,WANG D,ZHANG P,etal.Oral adm inistration of Lactococcus lactis-expressed recombinant porcine epidermal grow th factor stimulates the development and promotes the health of small intestines in earlyweaned piglets[J].Journal of Applied M icrobiology,2015,119(1):225-235.
[24] ZHELEZNOVA N N,W ILSON P D,STARUSCHENKO A.Epidermal grow th factor-mediated proliferation and sodium transport in normal and PKD epithelial cells[J].Biochim ica et Biophysica Acta:Molecular Basis of Disease,2011,1812(10):1301-1313.
[25] O’MAHONY F,TOUM IF,MROZ M S,et al.Induction of Na+/K+/2Cl-cotransporter expression mediates chronic potentiation of intestinal epithelial Cl-secretion by EGF[J].American Journal of Physiology Cell Physiology,2008,294(6):C1362-C1370.
[26] MROZ M S,KEELY S J.Epidermal grow th factor chronically upregulates Ca2+-dependent Cl-conductance and TMEM 16A expression in intestinal epithelial cells[J].The Journal of Physiology,2012,590(8):1907-1920.
[27] TRINH N T,PRIVE A,MAILLE E,etal.EGF and K+channel activity control normal and cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelia repair[J].American Journal of Physiology Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology,2008,295(5):L866-L880.
[28] BEZZERIDES V J,RAMSEY I S,KOTECHA S,et al.Rapid vesicular translocation and insertion of TRP channels[J].Nature Cell Biology,2004,6(8):709-720.
[29] XU H,INOUYE M,HINES E R,et al.Transcriptional regulation of the human NaPi-Ⅱb cotransporter by EGF in Caco-2 cells involves c-myb[J].American Journal of Physiology Cell Physiology,2003,284(5):C1262-C1271.
[30] YANG C B,ALBIN D M,WANG Z R,et al.Apical Na+-d-glucose cotransporter 1(SGLT1)activity and protein abundance are expressed along the jejunal crypt-villus axis in the neonatal pig[J].American Journal of Physiology:Gastrointestinaland Liver Physiology,2011,300(1):G60-G70.
[31] RAY E C,AVISSAR N E,SALLOUM R,et al.Grow th hormone and epidermal grow th factor upregulate specific sodium-dependent glutam ine uptake systems in human intestinal C2BBe1 cells[J].The Journal of Nutrition,2005,135(1):14-18.
[32] CELLINIC,XU J,ARRIAGA A,et al.Effect of epidermal grow th factor infusion on fetal rabbit intrauterine grow th retardation and small intestinal development[J].Journal of Pediatric Surger,2004:39(6):891-897.
[33] PAULSEN F P,WOON CW,VAROGA D,et al.Intestinal trefoil factor/TFF3 promotes re-epithelialization of corneal wounds[J].The Journal of Biological Chem istry,2008,283(19):13418-13427.
[34] HUYNH E,LI J L.Generation of Lactococcus lactis capable of coexpressing epidermal grow th factor and trefoil factor to enhance in vitro wound healing[J].Applied M icrobiology and Biotechnology,2015,99(11):4667-4677.
[35] MANNON P,REINISCH W.Interleukin 13 and its role in gut defence and inflammation[J].Gut,2012,61(12):1765-1773.
[36] JUNG K,KANG B K,KIM J Y,et al.Effects of epidermal grow th factor on atrophic enteritis in piglets induced by experimental porcine epidem ic diarrhoea virus[J].The Veterinary Journal,2008,177(2):231-235.
[37] BRAND T M,LIDA M,LIC,et al.The nuclear epidermal grow th factor receptor signaling network and its role in cancer[J].Discovery Medicine,2011,12(66):419-432.
[38] WANG CW,CHANG W L,HUANG Y C,et al.An essential role of cAMP response element-binding protein in epidermal grow th factor-mediated induction of sodium/glucose cotransporter 1 gene expression and intestinal glucose uptake[J].The International Journal of Biochem istry & Cell Biology,2015,64:239-251.
