两种鼻腔冲洗方法在功能性鼻窦内镜手术后的效果比较
2015-03-13李国贤郭永康齐佳
李国贤 郭永康 齐佳
[摘要] 目的 观察并比较两种鼻腔冲洗方法在功能性鼻窦内镜手术后的应用效果。 方法 选择2012年4月~2014年4月于杭州市萧山区第一人民医院耳鼻喉科行鼻窦内镜下手术治疗的慢性鼻窦炎患者132例,所有患者均给予鼻内镜下Messerklinger术。采用随机数字表法将其分为对照组和观察组,每组各66例。术后给予两组不同的冲洗液,对照组为0.9%氯化钠溶液。观察组为0.9%氯化钠溶液200 mL混合庆大霉素16万U+α-糜蛋白酶8000 U+地塞米松10 mg。所有患者均随访超过3个月,观察比较两组患者的治疗效果。 结果 观察组治愈41例,治愈率为62.12%,对照组治愈29例,治愈率为43.94%,观察组治愈率明显高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(χ2=24.842,P < 0.05)。观察组总有效率为95.45%,对照组总有效率为89.39%,观察组治疗总有效率明显高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(χ2=12.782,P < 0.05)。 结论 功能性鼻窦内镜手术治疗慢性鼻窦炎后给予鼻腔冲洗能有效控制并发症的发生,安全性高,患者易于耐受且操作简便。庆大霉素、α-糜蛋白酶和地塞米松的氯化钠溶液冲洗效果优于单纯氯化钠溶液冲洗,值得临床推广。
[关键词] 鼻腔冲洗;功能性鼻窦内镜手术;慢性鼻窦炎;庆大霉素;地塞米松
[中图分类号] R765.4 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2015)02(c)-0048-04
临床上慢性鼻窦炎的主要表现是鼻塞、流脓涕以及头痛等,程度较重时可累及鼻眶和鼻颅,甚至可威胁到患者生命安全。病因学检测结果表明需氧菌是导致该疾病发生的重要病原菌,且以条件致病菌如表皮葡萄球菌等占据了大多数。目前针对慢性鼻窦炎的治疗中,鼻内镜手术是首选的治疗手段,但从临床上的观察结果看来,手术治疗对发生在鼻窦黏膜上的炎性反应控制效果不理想。而这种炎性反应能否彻底清除在很大程度上影响了手术的效果,清除不彻底则很容易导致症状的反复和迁延。为减少术后复发率,获得满意的治疗效果,常用的方法包括药物治疗、行鼻腔冲洗等。笔者在功能性鼻窦内镜手术后的采用了两种不同冲洗方法,并将效果进行比较,现将相关情况报道如下:
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选择2012年4月~2014年4月于杭州市萧山区第一人民医院耳鼻喉科(以下简称“我院”)行鼻窦内镜下手术治疗的慢性鼻窦炎患者132例,所有患者术前均行CT检查明确诊断。分型标准:Ⅰ型,单纯型慢性鼻窦炎(保守治疗无效);Ⅱ型,慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉;Ⅲ型,多发性鼻窦炎或全组鼻窦炎伴多发性、复发性鼻息肉和(或)筛窦骨质增生。采用随机数字表法将所选患者随机分为对照组和观察组。观察组66例,其中男41例,女25例;年龄21~68岁,平均(39.4±10.9)岁;Ⅰ型32例,Ⅱ型26例,Ⅲ型8例。对照组66例,其中男48例,女18例;年龄19~70岁,平均(35.8±11.6)岁;Ⅰ型35例,Ⅱ型25例,Ⅲ型6例。两组患者的性别比例、平均年龄以及分型分期等资料比较差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05),具有可比性。
1.2 方法
所有患者均给予鼻内镜下Messerklinger术式,术后膨胀海绵填塞止血,常规给予预防感染治疗。鼻腔填塞物取出后第2天开始行鼻腔冲洗。冲洗时嘱患者张口平均呼吸,冲洗液由一侧鼻孔进入,对鼻腔和鼻咽部进行冲洗,由另一侧鼻孔流出,双侧鼻孔按顺序进行冲洗,行冲洗前大约30 min予复方薄荷液(上海坤弘医疗,批号:140105)进行滴鼻。对照组冲洗液为0.9%氯化钠溶液。观察组冲洗液为0.9%氯化钠溶液200 mL混合16万U庆大霉素(容生制药有限公司,批号:140218)+α-糜蛋白酶8000 U(华润双鹤药业股份有限公司,批号:140221)+10 mg地塞米松(金耀药业有限公司,批号:140125)。两组患者术后1周内均冲洗2次/d,1周后改为1次/d,冲洗2个月,随访时间3~12个月,患者门诊复诊随访。
1.3 疗效指标
参考1997年海口会议中关于鼻内镜手术的相关评估标准:治愈:患者自觉症状完全消失,复查见窦口开放情况较好,窦腔中未查见脓性分泌物,黏膜上皮化程度好;好转:患者自觉症状明显改善,复查见窦腔内可有较少量的脓性分泌物,窦腔黏膜中部分区域仍存在水肿或肉芽组织等情况;无效:患者自觉症状无明显改善,复查见窦口发生明显狭窄甚至闭塞,窦腔内大量脓性分泌物,明显息肉。总有效率=(治愈例数+有效例数)/总例数×100%。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 18.0统计学软件进行数据分析,计量资料数据用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,两组间比较采用t检验;计数资料用率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验,以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
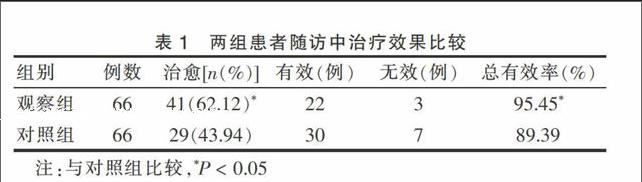
随访结果显示,观察组治愈率明显高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(χ2=24.842,P < 0.05)。观察组中的治疗总有效率明显高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(χ2=12.782,P < 0.05)。见表1。
表1 两组患者随访中治疗效果比较
注:与对照组比较,*P < 0.05
3 讨论
近些年来功能性鼻窦内镜手术在我国基层医院开展日益广泛,尤其在治疗慢性鼻窦炎和鼻息肉等方面,与传统术式比较,鼻内镜术式有更为明显的优势,不但能达到传统术式的治疗效果,同时手术过程中术野更加清晰、对患者造成的创伤更小[1-4]。功能性鼻窦内镜术式的主要目的在于尽可能减小对鼻腔正常结构的破坏,最大可能保留鼻腔的正常功能[5-7],以此为前提下通过手术改变原有的引流和通气情况[8-11]。但在本术式开展初期,并发症的发生率较高,一项美国的统计结果显示发生率为7%~25%[12],随着技术和设备的逐步改进,并发症的发生情况有了明显改善,目前的临床统计结果为5%~6%[13-18]。由于术中手术器械对黏膜造成的不可避免的损伤,术后出现纤维素性渗出并形成大量的血痂[19-22]。术后为止血而采用鼻腔填充的方法亦会使得局部黏膜因血供不足而发生糜烂或肿胀,若不及时进行清理则可能引起术腔发生粘连、窦口被封闭甚至鼻窦炎的复发等[23-25]。过去只能在并发症发生后再次利用鼻内镜对术腔进行清理[26-28],且控制效果并不理想。后来逐渐采用鼻腔冲洗的方法来预防并发症的发生[29-32],并取得了较为理想的效果。目前的研究认为鼻腔冲洗的机制主要包括以下几个方面:①增强了术腔黏膜表面纤毛的功能[33-35];②明显减轻黏膜的水肿程度[36-39];③物理的清洁作用[40-41]。
行鼻腔冲洗是一种安全性较高、操作极为简单、副作用极少的方法[42-44],常见的不良反应主要是患者自觉鼻腔内冲洗后出现烧灼感、痒感等[15,45-46],以及冲洗过程中冲洗液自鼻窦中流出时的不适感等[8]。目前对冲洗液的选择在临床上尚未达成共识,其中应用较多的是0.9%氯化钠溶液,因为这种浓度的冲洗液比较适合鼻黏膜的生理情况,冲洗过程中几乎对鼻黏膜不会造成任何刺激[46],故本资料中对照组亦采用了该种冲洗液。观察组在氯化钠溶液中加入了庆大霉素、α-糜蛋白酶以及地塞米松,因为单纯的氯化钠溶液并不具有消炎消肿的作用,对于术后术腔发生水肿的情况并不能很好地缓解,这样术后出现囊泡、肉芽组织以及术腔粘连等并发症的风险较大。庆大霉素是临床应用较多的一类氨基糖苷类广谱抗生素,该药物对于铜绿假单胞菌、金黄色葡萄球菌等导致慢性鼻窦炎发生的相对常见的病原菌的敏感性较强[46]。α-糜蛋白酶的作用则主要是对脓性分泌物进行稀释,避免窦口发生堵塞而引流不畅。地塞米松一方面能有效缓解术后术腔黏膜的水肿程度,另一方面对息肉的生长亦有明显的抑制作用。从本研究的随访结果可以看出,观察组中治愈41例,治愈率为62.12%,对照组中治愈29例,治愈率为43.94%,观察组治愈率明显高于对照组(χ2=24.842,P < 0.05)。观察组总有效率为95.45%,对照组总有效率为89.39%,观察组治疗总有效率明显高于对照组(χ2=12.782,P < 0.05)。
综上所述,功能性鼻窦内镜手术治疗慢性鼻窦炎后给予鼻腔冲洗能有效控制并发症的发生,安全性高,患者易于耐受且操作简便。庆大霉素、α-糜蛋白酶和地塞米松的氯化钠溶液冲洗效果优于单纯氯化钠溶液冲洗效果,值得临床推广。
[参考文献]
[1] Hayashi Y,Iwato M,Kita D,Hamada JI. Adenoid cystic carcinoma in the cavernous sinus diagnosed with the endoscopic endonasal approach [J]. Turk Neurosurg,2014, 24(5):814-818.
[2] Mori R,Cavallo LM,Cappabianca P. Extracranial spheno-ethmoidal sinus meningioma: case report [J]. Turk Neurosurg,2014,24(5):788-792.
[3] Han JK,Forwith KD,Gawlicka AK. RESOLVE:a randomized, controlled,blinded study of bioabsorbable steroid-eluting sinus implants for in-office treatment of recurrent sinonasal polyposis [J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol,2014, 29(3):981-990.
[4] Chahed H,Bachraoui R,Besbes G. Management of ocular and orbital complications in acute sinusitis [J]. J Fr Ophtalmol,2014,25(4):151-160.
[5] Liu JK,Mendelson ZS,Eloy JA. The modified hemi-Lothrop procedure:a variation of the endoscopic endonasal approach for resection of a supraorbital psammomatoid ossifying fibroma [J]. J Clin Neurosci,2014,25(3):577-580.
[6] Taniguchi M,Hosoda K,Kohmura E. Endoscopic endonasal transsellar approach for laterally extended pituitary adenomas:volumetric analysis of cavernous sinus invasion [J]. Pituitary,2014,27:331-338.
[7] Jang DW,Lachanas VA,Kountakis SE. Supraorbital ethmoid cell:a consistent landmark for endoscopic identification of the anterior ethmoidal artery [J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg,2014,25(3):902-907.
[8] H?覽kansson K,Thomsen SF,von Buchwald C. A comparative and descriptive study of asthma in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps [J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy,2014, 28(5):383-387.
[9] Cingi C,Bayar MN,Manea C. International study of the incidence of particular types of septal deformities in chronic rhinosinusitis patients:the outcomes from five countries [J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2014,28(5):404-413.
[10] Spadijer-Mirkovi■ C,Vukomanovi■--Dur?鬍evi■ B,Stanojevi■ I. Clinical case report of a large antrochoanal polyp [J]. Acta Medica Hradec Kralove,2014,57(2):78-82.
[11] Ow R,Groppo E,Gawlicka AK. Steroid-eluting sinus implant for in-office treatment of recurrent polyposis:a pharmacokinetic study [J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol,2014, 25(4):38-42.
[12] Zhang Z,Adappa ND,Palmer JN. Quality of life improvement from sinus surgery in chronic rhinosinusitis patients with asthma and nasal polyps [J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2014,25(4):422-428.
[13] Tomazic PV,Hubmann F,Stammberger H. The Problem of High Recurrence Rate in Endoscopic Revision Surgery for Inverted Papilloma [J]. Laryngorhinootologie,2014,25(6):123-129.
[14] Lee KY,Woo SY,Cho YS. The Prevalence of preauricular sinus and associated factors in a nationwide population-based survey of South Korea [J]. Otol Neurotol, 2014, 23(2):303-307.
[15] ElBadawey MR,Alwaa A,Carrie S. Quality of life benefit after endoscopic frontal sinus surgery [J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy,2014,28(5):428-432.
[16] Frauenfelder C,Woods C,Carney AS. Aquaporin expression profiles in normal sinonasal mucosa and chronic rhinosinusitis [J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol,2014,22(3):28-33.
[17] Bienert A,Wawrzyniak K,Grze■kowiak E. Melatonin and clonidine premedication has similar impact on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of propofol TCI [J]. J Clin Pharmacol,2014,22(2):31-39.
[18] Banglawala SM,Mulligan JK,Schlosser RJ. Impact of intraoperative hydrodebrider treatment on postoperative sinonasal inflammation [J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy,2014, 28(5):438-442.
[19] Cebula H,Kurbanov A,Keller JT. Endoscopic,endonasal variability in the anatomy of the internal carotid artery [J]. World Neurosurg,2014,16(3):676-679.
[20] Lewis CT,Bethencourt DM,Tyndal CM. Robotic repair of sinus venosus atrial septal defect with partial anomalous pulmonary venous return and persistent left superior vena cava [J]. Innovations (Phila),2014,9(5):388-390.
[21] Sharouny H,Narayanan P. Maxillary Sinus Mucopyocele in a Fifty-eight-year-old man:a possible late complication of irradiation to head and neck [J]. Iran Red Crescent Med J,2014,16(7):133-138.
[22] DeConde AS,Mace JC,Smith TL. Investigation of change in cardinal symptoms of chronic rhinosinusitis after surgical or ongoing medical management [J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol,2014,18(2):780-784.
[23] Wu PX,Liang YF,Xu WH. Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of the paranasal sinuses:a case report and review of literature [J]. Int J Clin Exp Med,2014,7(8):2369-2372.
[24] Sillers MJ,Lay KF,Holy CE. In-office balloon catheter dilation:analysis of 628 patients from an administrative claims database [J]. Laryngoscope,2014,17(3):43-49.
[25] DeConde AS,Barton MD,Smith TL. Can sinus anatomy predict quality of life outcomes and operative times of endoscopic frontal sinus surgery? [J]. Am J Otolaryngol,2014,27(2):283-292.
[26] Tomifuji M,Araki K,Shiotani A. Risk factors for dysphagia after transoral videolaryngoscopic surgery for laryngeal and pharyngeal cancer [J]. Head Neck,2014,15(2):906-911.
[27] Matheny KE,Carter KB Jr,Fong KJ. Safety, feasibility,and efficacy of placement of steroid-eluting bioabsorbable sinus implants in the office setting:a prospective case series [J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol,2014,15(2):54-58.
[28] Awad Z,Touska P,Tolley NS. Face and content validity of sheep heads in endoscopic rhinology training [J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol,2014,15(4):62-66.
[29] Fadda GL,Gisolo M,Succo G. Intracranial complication of rhinosinusitis from actinomycosis of the paranasal sinuses:a rare case of abducens nerve palsy [J]. Case Rep Otolaryngol,2014,14(2):601-611.
[30] Parida PK,Gopalakrishnan S,Saxena SK. Pediatric recurrent acute suppurative thyroiditis of third branchial arch origin-Our experience in 17 cases [J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol,2014,1(3):34-39.
[31] Jiang RS,Kuo LT,Liang KL. Validation of the applicability of the traditional Chinese version of the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Allergy Rhinol (Providence),2014,5(1):28-35.
[32] Awad Z,Taghi A,Tolley NS. Construct validity of the ovine model in endoscopic sinus surgery training [J]. Laryngoscope,2014,8(2):11-17.
[33] Askar MH,El-Sherif HS,Senior BA. Use of a Foley Catheter balloon as a tool during endoscopic frontal sinus surgery in a resource-poor environment [J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol,2014,9(3):13-17.
[34] Jankowski R,Russel A,Nguyen DT. Olfactory neuroblastoma behavior inside and outside the olfactory cleft [J]. Surg Radiol Anat,2014,14(3):517-519.
[35] Chang DT,Truong MT. A child with silent sinus syndrome and spontaneous improvement after sinus surgery [J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol,2014,10(2):341-343.
[36] Lal D,Rounds A,Dodick DW. Comprehensive management of patients presenting to the otolaryngologist for Sinus pressure,pain,or headache [J]. Laryngoscope,2014, 12(2):102-107.
[37] Magit A. Pediatric Rhinosinusitis [J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2014,47(5):733-746.
[38] Smith KA,Smith TL,Rudmik L. Endoscopic sinus surgery compared to continued m7.4edical therapy for patients with refractory chronic rhinosinusitis [J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol,2014,11(3):366-369.
[39] Rudmik L,Smith KA,Smith TL. Routine magnetic resonance imaging for idiopathic olfactory loss:a modeling-based economic evaluation [J]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg,2014,11(2):179-184.
[40] Honeycutt JH. Endoscopic-assisted craniosynostosis sur-gery [J]. Semin Plast Surg,2014,28(3):144-149.
[41] Trimarchi M,Tomazic PV,Stammberger H. Video endoscopic oronasal visualisation of the anterior wall of maxillary sinus:a new technique [J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital,2014,34(4):259-263.
[42] Simuntis R,Kubilius R,Vaitkus S. Odontogenic maxillary sinusitis:a review [J]. Stomatologija,2014,16(2):39-43.
[43] Shao L,Qin X,Ma Y. Removal of maxillary sinus metallic foreign body like a hand sewing needle by magnetic iron [J]. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent,2014,7(1):61-64.
[44] Jiang RS,Kuo LT,Liang KL. Validation of the applicability of the traditional Chinese version of the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis [J]. Allergy Rhinol(Providence),2014,5(1):28-35.
[45] Paramasivan S,Jones D,Tan L. The use of chitosan-dextran gel shows anti-inflammatory,antibiofilm, and antiproliferative properties in fibroblast cell culture [J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy,2014,28(5):361-365.
[46] Sanjuan de Moreta G,Cardoso-López I,Poletti-Serafini D. Centripetal endoscopic sinus surgery in chronic rhinosinusitis:a 6-year experience [J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy,2014,28(4):349-352.
(收稿日期:2014-10-09 本文编辑:任 念)