Effect of Neoseiulus cucumeiris Carrying Paecilomyces fumosoroseus on the Prevention of Aphids and Spider Mites in Eggplant
2015-02-24LiSUNYanxuanZHANGLinglingZHAOJianzhenLINXiaCHENJieJI
Li SUN,Yanxuan ZHANG,2*,Lingling ZHAO,Jianzhen LIN,2,Xia CHEN,2,Jie JI,2
1.Institute of Plant Protection,Fujian Academy of Agriculture Sciences,Fuzhou 350013,China;2.Research Center of Engineer and Technology of Natural Enemy Resource of Crop Pest in Fujian,Fuzhou 350013,China
Aphidoidea belonging to Hemiptera of Insecta includes Adelgoidea and Aphidoidea.Phytophthira is a large insect group in Hemiptera[1].The Aphid is a kind of important pest of agricultural and forest crops,for example,Myzus persicaeSulzer andAphis glycinesMatsumura cause direct damage and indirect virus transmission damage[2].Therefore,effective control of aphids has always been the focus of the research by scientists,especially under the situation that the requirements for environment quality and agricultural product quality are improving gradually,the research on the control of aphids enters a new stage of biological control from chemical control,and the control techniques includes natural enemy control(ladybug,hoverfly,lacewing,Orius similisZheng,Aphytissp.,Asaphes vulgarisWalker,etc.)and the development and utilization of microbial pesticides and botanical insecticide[3-4].As a large class in biological control,microbial pesticides have developed relatively rapider,and there are many microbial pesticides for controlling aphids.It was reported that there were 37 species of entomogenous fungi which could parasitized aphids,including 7 species in genuses of Entomophthorales,and 16 species in 7 genuses of Hyphomycetes[5].The conidia and metabolites ofBeauveria bassianaboth have pesticidal activity toMyzus persicae[6],andP.fumosoroseushas strong control effect onMyzus persicaeand green peach aphids[7].In addition,pathogenic microorganisms includingMetarhizium anisopliae,Verticillium lecanii,Erwinia chrysanthemi,RhopalosiphumpadiandStreptomyces bacteriaall have remarkable control effect on aphids[8].
Paecilomycesfumosoroseus(Wize)Brown&Smith(also known as Isaria fumosoroseaWize)belonging to Paecilomyces of Moniliaceae in Hyphomycetales of Hyphomycetes in Deuteromycotina is widely distributed in geography,can parasitize a variety of inset hosts belonging to homoptera,lepidoptera,diptera,coleoptera,hymenoptera and so on,and is one of important entomopathogenic fungi[9-10],and it has a very good control efficiency on insects with piercing-sucking mouthparts including aphids and aleyrodid[11-14].There were researches indicated thatP.fumosoroseushad very strong pathogenicity to a variety of pests,as well as certain ovicidal activity,especially for insects of Hemiptera such as aphids and aleyrodid with strong resistance and wide infestation range capable of forming epidemic diseases under proper environments,achieving the effect of long-term control by one-time fungus release[15].
In agricultural production,aphides usually occur with the accompany of other pests including spider mites.The biological control methods of usingNeoseiulus cucumeirisOudermans to control spider mites has been applied to a variety of agricultural and forest crops in China to control pest mites,Bemisiatabaci,Frankliniellaoccidentalisand so on[16-18].Given that the control methods for aphids and red spiders mainly are single chemical or biological control,Zhang put forward an idea ofcontrolling pests with predatorymites dusted with entomogenous fungi,and was authorized with the benefits of the national invention patent“a Method for Pest Control by Predatory Mites Carrying Entomogenous Fungi”in 2009(Patent No.ZL200710008450.5).Developing the fungus-carrying body,“Neoseiulus cucumeiriscarryingPaecilomyces fumosoroseus”,could realize the effect of controlling aphids and spider mites by one-time release,and furthermore,N.cucumeirislikes shade and moves frequently,and thus could carryP.fumosoroseusconidia to dead spaces such as rolled leaves onto which pesticides could not be sprayed.Such method can reduce the application of chemical pesticides as well as labor intensity and cost,and also can give full play to various advantages of biological control.In order to verify the feasibility of controlling aphides and spider mites byN.cucumeiriscarryingP.fumosoroseus,this study conducted research on the germination condition and the pathogenicity to aphids andN.cucumeirisofP.fumosoroseusand pot experiment of eggplant,aiming at providing basis for control of a variety of pests by combining natural enemies and entomopathogenic fungi.
Materials and Methods
Materials
P.fumosoroseusY-1 strains were obtained from deadBemisia tabacion eggplants in Institute of Plant Protection,Fujian Academy of Agriculture Sciences,behind the railway station of Fujian Province,cultured on indoor PDA culture medium,and activated in Bemisia tabaci and aphids,and all used conidia were the generation purified after activation.The second instar larva of aphids (green peach aphids)were collected from eggplants in the Institute of Plant Protection,and cultured under indoor environment for multiple generations.N.cucumeiriswas provided by Fujian Yanxuan Biopreventing and Controlling Technology Co.Ltd.
Methods
Conidialpowdercollection and suspension preparationP.fumosoroseusY-1 strains cultured in planar PDA culture medium at 25℃and illumination of 12 L∶12 D for about 10 d was used as conidia source.The conidia on the culture medium were collected.A certain amount of conidial powder was prepared with 5 ml of 0.05% Tween 80 under a sterile condition into a conidial suspension with a concentration of 1.0×108spores/ml,which was then diluted into four other concentrations,1.0×104,1.0×105,1.0×106and 1.0×107spores/ml,respectively.Each of the five concentrations of suspensions was 5 ml in volume.
Germination rates of spores at differenttemperatureandhumidity conditionsAccording to the method of small container air humidity control,air humidities in small containers were regulated with different saturated salt solutions Mg(NO3)2,NaNO2,NaCl,KCl,Fe2SO4,K2SO4and distilled water),and seven gradients,53%,63%,75%,85%,90%,97% and 100%,were set.After sterilization,into 26 cm×16 cm×9 cm preservation boxes were added 200 ml of different saturated salt solutions,respectively,with a depth of liquid of 2 cm,and after determination,it was shown that the humidities accorded with desired ones substantially.A box with a height of 5 cm was put into each preservation box as a platform.The prepared spore suspension was dropped onto sterile glass slides(about 50 spores per visual field under a microscope with 400 times),spread into thin layers and rapidly air dried.The glass slides were then placed on the platforms in the preservation boxes,each of which was covered,sealed with fresh-keeping films and finally placed into a mould incubator at a corresponding temperature(five temperature gradients in total,i.e.,15,20,25,30 and 35℃).Microscopic examination was performed once every 24 h.The germination of spores was determined according to the standard that the length ofgerminaltube was greater than 1/2 of the length of spore.Each treatment was provided with three replications,each of which was examined in five visual fields.
Determination of pathogenicity of P.fumosoroseus to aphidsA figure tube (1.2 cm×4 cm)was added with soil to a level of 2/3 of its height,and sown with a eggplant seed;when two true leaves grew out,the bottom of the figure tube was adhered with double-faced adhesive tapes to be adhered to the bottom of a to-go box(with an upper diameter of 12 cm,a lower diameter of 9.5 cm and a height of 9 cm);and second-stage larvae of healthy aphids were immersed in the conidialsuspensions with different concentrations for 5 s,and naturally dried,lively ones were then selected and put onto the eggplant leaves with a small writing brush lightly,and the to-go box was covered with a box cover on which was provided with two air holes (with a diameter of 1.5 cm)covered with 400 mesh gauze elements.The to-go box was then placed in an illuminating incubator under the condition of 16 L∶8 D,(25±1)℃ and(95±5)% RH.Sterile water containing 0.05% tween 80 was used as control.Each treatment was provided with 5 replications and observed for 10 days continuously,and mortalities were recorded.
Determination of pathogenicity of P.fumosoroseus to N.cucumerisA culture dish with a diameter of 9 cm was laid with a piece of sponge with a diameter of 7 cm,and added with sweet potato leaves with equal size and a proper amount of corn pollen as the food for predatory mites.Predatory mites was immersed in the conidial suspensions with different concentrations for 5 s,and 30 mites,which were slightly dried capable of move freely,were put onto the sweet potato leaves.Each treatment was provided with 5 replications,and sterile water containing 0.05% tween 80 was used as control with 5 replications.The culture dishes were placed in an illuminating incubator under the condition of 16 L:8 D,(25±1)℃ and (95±5)% RH,and observed from the 1st day for 10 days,and mortalities were recorded.
Pot experiment methodTwenty four pots of vigorous eggplants with heights of about 35 cm,the longest leaf lengths of 15 cm and widths of 7-8 cm were selected.Onto each eggplant were placed 20 aphids,and after 3 days,the number of aphid was counted and fixed to 20.Because the potted eggplants were cleaned up without pollen and spider mites,20 red spiders were released to simulate field condition.A small piece of round paper was fastened onto each eggplant at the height of 3 cm from the ground to releaseN.cucumeris,and the potted eggplants were put into large plastic boxes(59 cm×45 cm×40 cm),at the bottom of which were placed salt solutions.Bottomless plastic shelves(60 cm×45 cm×72 cm)were placed in the boxes for the function of supporting,and covered with plastic coats which were clamped to keep a relative humidity of(95±5)%.
Six treatments were designed,i.e.:(1)CK;(2)releasing 50N.cucumeris;(3)spraying 20 ml of 107spores/ml conidial suspension;(4)releasing 50N.cucumerisafter spraying 20 ml of 107spores/ml conidial suspension;(5)releasing 20N.cucumerisdusted with conidia ofP.fumosoroseus;(6)releasing 50N.cucumerisdusted with conidia ofP.fumosoroseus.
Data analysis
Statistics was performed on data with EXCEL to calculate corrected mortality and standard deviation,and regression equations were fitted with DPS data analysis system,to evaluate median lethal concentrations (LC50)and median lethal time (LT50),and the differencesbetween varioustreatments were analyzed with Tukey new multiple range method.
Results and Analysis
Germination rates of P.fumosoroseus conidia under different temperatures and humidities
As shown in Fig.1,the lowest temperature and humidity for germination ofP.fumosoroseuswere 20℃and 90%,respectively,and the optimal temperature and humidity were 25-30℃and 95% -100% RH,respectively.Therefore,in order to create a most suitable infection environment forP.fumosoroseusconidia to tested pests,the experiment was set at the condition of(25±1)℃ and (95±5)% RH.Furthermore,it was observed that it was necessary to maintain the condition for 18 h to enable the germination of the conidia ofP.fumosoroseus.
Mortality of aphides caused by P.fumosoroseus
It could be seen from Table 1,Table 2 and Table 3 that theP.fumosoroseusconidial suspension with the concentration of 1×104spores/ml exhibited a very low mortality of aphids,which was not different with that of the control group in the first 6 days and was 29.21% only until the 10thday.The suspensions with the concentrations of 1×105,1×106and 1×107spores/ml showed the lethal effects on aphides not significantly different,and exhibited the median lethal time of 15.67,9.88 and 8.98 days,respectively.The conidial suspension withtheconcentration of 1×108spores/ml showed the highest mortality of aphides with a median lethal time of 5.76 days,at which the lethal effect on aphids was not significantly different with those of other suspensions,and until the 10thday,the corrected accumulative mortality was 86.52%.The median lethal concentrations of the fungus to aphids at the 7th,8th,9thand 10thday were 4.38×107,6.02×106,2.34×106and 2.34×105spores/ml.To sum up,the lethal effect ofP.fumosoroseuson aphids was enhanced regularly with the increase of conidial concentration,and stably increased over time.The fungus has a stronger lethal effect on aphids and can serve as the bio-control fungus for aphides.
Lethal time of P.fumosoroseus to N.cucumeris
As shown in Table 4,the lethal effects ofP.fumosoroseusconidial suspensions with different concentrations onN.cucumeriswere not significant different;and the corrected accumulative mortalities of aphides caused byP.fumosoroseusconidial suspensions with different concentrations in the range of(1×104)-(1×108)spores/mlwere13.7%,20.55%,25.34%,37.67% and 41.78%,respectively.Median lethal concentrations and median lethal time could not be calculated due to the low mortalities.
It could be seen from the comparison between the lethal effects ofP.fumosoroseuson aphids andN.cucumeristhat,the fungus caused a mortality in aphids far greater than that inN.cucumerisunder the same concentration,i.e.,the fungus could be carried by predatory mites to control aphids.
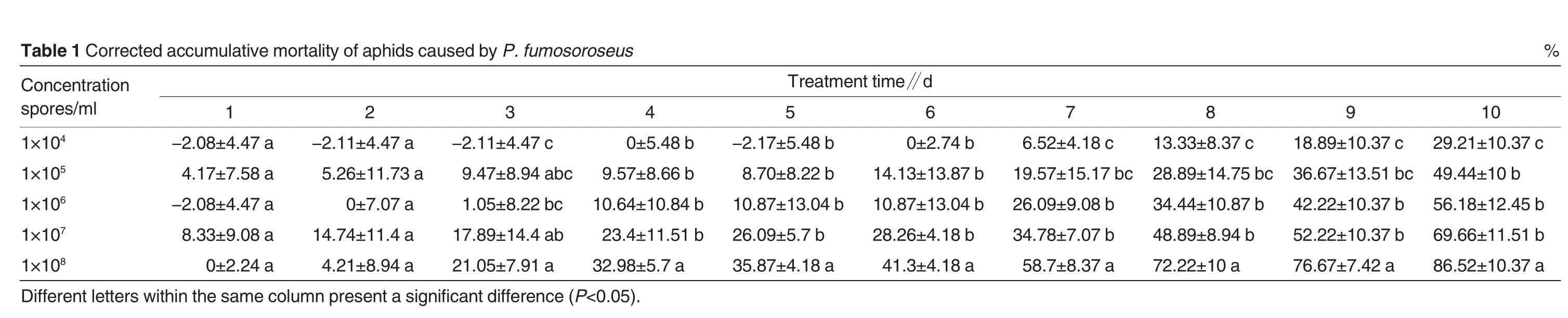
% c 7b b 517 a 0.3.4b.5.3 100210±1±1±1±1±1.2 1.4 4.1 8.6 6.5 2 2 94 95 66 98 6 c b c b b.3 7.5 1.3 7.3 72 a 90300.4±1±1±1±1±7.8 9.6 7.2 2.2 2.6 7 1 83 64 25 27 6 c c b b 7.7 5.8 74 b a 8.340.90±8±1±1±8±1.3 3.8 9.4 4.8 9.2 2 1 32 83 44 87 2 c c b 8.1 78 b 7 b 7 a 7.1 45 1.0 9.0 7.3 8 2±7±9±8±.7±6.5.5.0.78 1 92 63 45 b b b 4.8 7.0 48 b 8 a d 6.7 21 31 34.14.1∥ ±±±±±e 0376.3 tim 4.10.88.24 1 t 112 e n b a tm 8 b 2 b.0 4b 8 a T re 5.4.23.7.1±5±8±1±5±4.1 7.7 0.8 7.0 9.8 7-281 02 63 5 b b b 8b 6.8 4.5 1a 4.4 58.61 01 15.7 s ±±±±±u 0748).se.5.6.4 3.95.0 ro 90 123 2<0 o so b c c b (P.fu m 7 c 4 a 2 b.4 a 1 a ce n re P.4 48.98.21 47.9 y 3 1±7±5±9±5±d iffe d b 2.19.41.07.81.0n t u se -12 n ifica s ca a 3 a a a a sig h id 7.77.44t a f a p 2.4 41 1.0 71 18.9n o ±±±±±se lity 1.1.2 60.7 4.2 1p re rta -251 44 m n m o lu tive co 7 a 8 a 7 a 8 a 4 a e la 14.47.54.49.02.2m m u ±±±±±sa ccu.0 8.1 7.0 8.3 30th e a -24-28in cte d w ith rre n rs o tio l tte 1 C tra t le le n s/m n ce re 45678 b n re o o 0 11 01 01 01 0iffe a T C sp 1×1×1×1×1×D
Control effect of N.cucumeris dusted with P.fumosoroseus on aphids
After pre-experiments,the effects of spaying the fungus swpensions with concentrations of 1×104and 1×105spores/ml were poor,so that the concentration was improved to 1×107spores/ml(hereinafter referred to as 107concentration)to conduct an experiment.
As shown in Fig.2,the treatment of spraying conidial suspension of 107concentration and the treatment of releasing 50N.cucumerisafter spraying conidial suspension of107concentration both showed the aphid number of 0,the treatment of releasingN.cucumerisdusted with conidia ofP.fumosoroseusshowed an aphid number of 10 only,while larger quantities of aphids remained in other treatments.The number of fungus colonies was complementary to the number of aphids,the 3 treatments with fewer aphids(spraying conidial suspension of 107concentration,releasing 50N.cucumerisafter spraying conidial suspension of 107concentration and releasing 50N.cucumerisdusted with conidia ofP.fumosoroseus)showed numbers of colonies remarkably greater than other treatments.The quantity of spider mites was controlled substantially due to the release ofN.cucumeris.
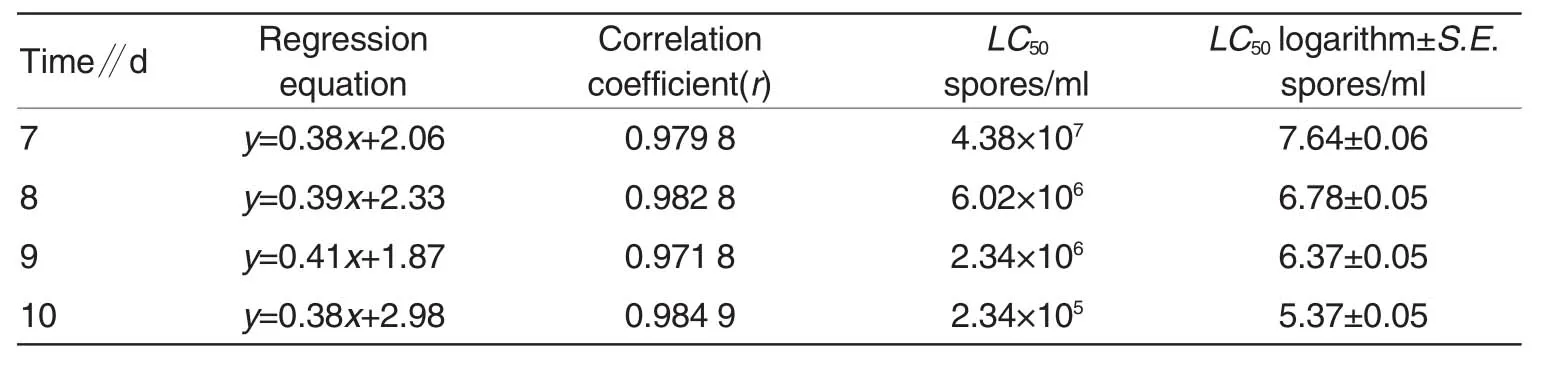
Table 2 Median lethal concentrations of P.fumosoroseus to aphids

Table 3 Median lethal time of P.fumosoroseus to aphids

% b b a 06a 5a 52 0.1.1 1.3 81.3.23±1491 0±±±±.75478 3.5.3.6.7 10 25 27 31 4 b b a a 01.1a 02.14.5 9.6 90.830±1311 3±±±±.99378 2.6.1.9.7 17 13 21 38 3 c c b 9b 4a 5a 5a 0 8.2 8.9.3.2.6±8499 8±±±±.89593 0.2.0.8.7 14 19 17 26 3 c 7c b.2b 2a 6a 7a 0 70 1.6.0.6.6±8679 6±±±±.14131 8.2 2.0.1.0 17 13 24 3 c c b 9b 0a 8a a 7.64 8.3.3.9 8.4 T/d 6±584 e 2±8±5±1±5 tim.1.4.6.4.2 t 67509 n 122 e tm b a re a b b a a 4 T 5864.4 5.4 7.5.3.90±5281 1±±±±.46642 5.7 6.1 2.2.3 18 14 2 b b b a b s a a u 4.37.79.77.61.0 ro se 445279 so ±5±1±9±1±7).5 o.3.4.4.5.2.0 m 151 13 10 20<P.fu (P y b a a a a a ce n d 58590 se 3.3 4.9 2.3 4.7 2.6 9re u ±±±±±iffe ca 77637d t ris.6 24.6.3 7.6 4n e 1 m ifica cu n.cu a 5a 5a 9a 9a 2sig a t f N 2.3 4.3 4.4 1.7 2.8 7n o ±±±±±se lity 7.6.6 7460 1re p rta 22n o m m lu tive a co 9a 0a 9a 9e la m u 1.4 1.5 1a.4 1.7 2 m ±±0±±sa ccu 6.6.6 77.67.6e th a 0002in d cte ith w rre n rs o tte C tio tra l t le le 4n ce s/m n re 4050607080re a b n o o 11111 C sp 1×1× ×1×1×1iffe D
It was observed that the treatment of the conidial suspension of 107concentration and the treatment of 50N.cucumerisdusted with conidia ofP.fumosoroseusshowed the fungus infection rate of 100% (Fig.3 and Fig.4).In pathogenicity determination,the conidial suspensions of 105and 106concentrations exhibited the best lethal effects,while potted eggplants needed the 107concentration,due to the fact that leaves of eggplants were rich in hair which prevented the suspension from reaching aphids directly,resulting in a higher suspension concentration.Meanwhile,the conidia powder carried by 50N.cucumeriswas 105-106spores only with a very well controleffect,indicating thatpredatory mites dusted with fungi for preventing spider mites and aphids could reduce the dosage of conidia powder as well as saving labor.
Conclusions and Discussion
P.fumosoroseusis a kind of entomogenous fungus which has a very good control efficiency on insects with piercingsucking mouthparts,there have been numerous studies on the pathogenicity of its conidia or metabolites to aphids and spider mites[7,13,19],but no study on the comprehensive control of aphids and spider mites by combiningP.fumosoroseusconidia and predatory mites has been reported.This study determined that the fungus showed a mortality in aphids far higher than that inN.cucumerisat the same conidial suspension concentration by determining the pathogenicity ofP.fumosoroseusto aphids andN.cucumeris,respectively,that was to say when releasingN.cucumeriscarryingP.fumosoroseusconidia (eachN.cucumeriscould carry about 104spores),N.cucumeriscould transportP.fumosoroseusconidia powder to aphids on eggplants without being infected. Furthermore,predatory mites were capable of self cleaning,and during movement,they could unload the conidia on their bodies,so that the harm ofP.fumosoroseusto them was reduced on one hand,and on the other hand,the conidia were shaken off onto plants or aphids which then suffered the infection ofP.fumosoroseus,thereby achieving the effects of controlling aphids.
The feasibility of controlling aphids byN.cucumerisdusted withP.fumosoroseusconidia powder was also verified by pot experiment.However,owing to the high requirements ofP.fumosoroseusto conditions including temperature and humidity,the technique of predatory mites carrying fungi is more suitable for vegetables in greenhouses.When aphids and spider mites appeared simultaneously,by releasing predatory mites carrying fungi,the predatory mites could eat spider mites as well as transporting the conidia to aphids,achieving double effects by one-time release,and it was reported that,P.fumosoroseusalso had strong control effect onBemisia tabaci[20]and was capable of forming epidemic diseases under proper environments,achieving the effect of longterm control.This study provides certain basis for the research on the action mechanism ofP.fumosoroseusto aphids and the research on field release effect.
[1]XU L(徐蕾),XU GQ(许国庆),LIU PB(刘培斌),et al.Progress on the research of biology of aphids(蚜虫生物学研究进展)[J].Hubei Agricultural Sciences(湖北农业科学),2010,49(12):3204-3206.
[2]HUANG XL(黄晓磊),QIAO GX(乔格侠).Research status and trends in aphidology(蚜虫学研究现状与学科发展趋势)[J].Acta Entomologica Sinica(昆虫学报),2006,49(6):1017-1026.
[3]WU YP(武宇鹏),LI YL(李友莲).The development of aphides prevention technology(蚜虫防治技术与研究应用新进展)[J].Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences(山西农业科学),2003,31(2):64-68.
[4]GUO QG(过七根),ZHOU YM(周瑶敏).Recent advances in prevention and control of aphid(蚜虫防治研究新进展)[J].Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi(江西农业学报),2008,20(9):90-91.
[5]LI W(李伟),XUAN WJ(宣维健),WANG HT(王红托),et al.Review of entomogenous fungi infecting aphids in China(我国大陆寄生蚜虫的病原真菌)[J].Entomological Knowledge(昆虫知识),2005,42(1):31-35.
[6]HUANG G(黄刚),XU MY(徐明勇),QIAN FY(钱凤英),et al.Study on Pathogenicity ofBeauveria bassianaon Tobacco Aphid(白僵菌对烟蚜的致病性研究)[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences(安徽农业科学),2011,39(33):20528-20529.
[7]YANG B(杨斌),WANG XB(王晓波),HE MJ(何美军).Insecticidal activity of metabolites produced byPaecilomyces fumosoroseusto tobacco aphides(玫烟色拟青霉代谢产物对烟蚜的毒杀活性)[J].Journal of Southwest Forestry College(西南林学院学报),2004,24(4):38-41.
[8]TANG PH(唐平华),CHEN GP(陈国平),ZHU MK(朱明库),et al.Advances in aphid control technology(蚜虫防治技术研究进展)[J].Plant Protection(植物保护),2013,39(2):5-12.
[9]CHEN WW(陈巍巍),FEN MG(冯明光).Current status in basic and applied research on theEntomopathogenic fungus,Paecilomyces fumosorseus(玫烟色拟青霉的研究与应用现状)[J].Natural Enemies of Insects(昆虫天敌),1999,21(3):140-144.
[10]WU JW(武觐文),WANG DX(王德祥).Study and application of entomogenous fungi in China(中国虫生真菌研究与应用)(3)[M].Beijing:China Agriculture Science and Technique Press(北京:中国农业科技出版社),1993.
[11]XU WS(徐伟松),HU MY(胡美英),ZHONG GH(钟国华),et al.Study on the bioactivities of several metabolic products ofPaecilomyceslilacinusagainst aphid(几种拟青霉代谢产物对蚜虫生物活性的研究)[J].Guangdong Agricultural Sciences(广东农业科学),2003,(5):45-48.
[12]XU WS(徐伟松),ZHONG GH(钟国华),LI CF(李畅方),et al.Laboratory and field evaluation on insecticidal activity of the metabolites from twoPaecilomycesspp.against aphids(两种拟青霉菌提取物对菜蚜的控制作用)[J].Plant Protection(植物保护),2007,33(6):35-38.
[13]ZHANG XH(张仙红),JI NH(嵇能焕).Bioassay for the Virulence of Paecilomyces Fumosoroseus(玫烟色拟青霉菌株的毒力测定)[J].Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University:Natural Science(山西农业大学学报:自然科学版),2006,26(1):24-26.
[14]HUANG Z(黄振),REN SX(任顺祥),LI CJ(黎崇军).Bioassay ofPaecilomyces fumosoroseusonBemisia tabaci(玫烟色拟青霉对烟粉虱的致病力测定)[J].Journal of South China Agricultural University(华南农业大学学报),2007,28(1):40-44.
[15]WANG QH(王 清 海),WANG PP(万 平平),HUANG YJ(黄玉杰),et al.Application of Entomogenous fungus in biocontrol of pest(虫生真菌在害虫生物防治中的应用研究)[J].Shandong Science(山东科学),2005,18(4):37-41.
[16]ZHANG YX(张艳璇),JI J(季洁),LIN JZ(林坚贞),et al.Release ofAmblyseius cucumeris(Acari:Phytoseiidae)to control pest mites of moso bamboo(释放胡瓜钝绥螨控制毛竹害螨的研究)[J].Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences(福建农业学报),2004,19(2):73-77.
[17]ZHANG YX(张艳璇),LIN JZ(林坚贞),JI J(季洁),et al.Studies onAmblyseius cucumerisOudemans for controlling the pest mites on citrus trees(胡瓜钝绥螨控制柑桔害螨研究)[J].Plant Protection(植物保护),2003,29(5):31-33.
[18]ZHANG YX(张艳璇),WANG FT(王福堂),JI J(季洁),et al.Evaluation ofAmblyseiuscucumerisOudemans for control of pest mites of koerle pear and strategy for its practical application(胡瓜钝绥螨对香梨害螨控制作用的评价及其应用策略)[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica(中国农业科学),2006,39(3):518-524.
[19]DENG JH(邓建华),WU XF(吴兴富),ZHUANG H(庄辉),et al.Infection Effect ofPaecilomycessp.on Myzus nicotianae(Blackman)(两种拟青霉菌对烟蚜感染作用试验)[J].Tobacco Science&Technology(烟草科技),2005,3:46-48.
[20]SUN L(孙莉),ZHANG YX(张艳璇),ZHAO LL(赵玲玲),et al.A study onpotential ofBeauveria bassianaandPaecilomyces fumosoroseusin wntrolling whitefly nymphs(白僵菌与玫烟色拟青霉菌两菌株防控烟粉虱若虫的潜力研究)[J].Chinese Agricultural Scien&Bulletin(中国农学通报),2013,29:225-229.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Tolerance of a Restorer Line R1056 to High Temperature and Its Application in Rice Breeding
- Combining Ability Analysis of Panicle Traits in Six CIMMYT Maize Inbred Lines
- A Comparative Study of Nitrogen Loss after Application of Biochar Coated Urea and Common Urea in Vegetable Soil at Chaihe Catchment of Dianchi Lake
- Effects of Vermicompost Leach Liquor on Yield and Quality of Wheat
- Analysis on Morphological Variations among Six Wild Groups of Anthocidaris crassispina from South China Sea
- The Sterilization Technology of Medicinal Flowers
