常规超声与声触诊组织量化技术鉴别诊断甲状腺结节的对比研究
2015-02-22袁美芹李文肖杜婷婷芦桂林
李 军,袁美芹,李文肖,杜婷婷,童 瑾,芦桂林
·全科医生技能发展·
常规超声与声触诊组织量化技术鉴别诊断甲状腺结节的对比研究
李 军,袁美芹,李文肖,杜婷婷,童 瑾,芦桂林
目的 探讨常规超声与声触诊组织量化技术(VTQ)鉴别诊断甲状腺良、恶性结节的价值。方法 选取2012年2月—2014年10月在石河子大学医学院第一附属医院就诊以甲状腺结节(长径>1 cm)收入院患者94例,均进行常规超声及VTQ检查,并行甲状腺切除术,经病理确诊。常规超声采用半定量评分法;VTQ定量测定结节内剪切波速度(SWV),利用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线比较常规超声与VTQ诊断甲状腺恶性结节的效能。结果 以病理检查为金标准,常规超声诊断甲状腺恶性结节的灵敏度、特异度、正确率分别为80.4%(41/51)、81.4%(35/43)、80.9%(76/94)。甲状腺恶性结节SWV高于甲状腺良性结节〔(3.29±1.20)m/s与(1.98±0.45)m/s〕(t=-6.813,P<0.001)。以SWV=2.75 m/s为截断值,VTQ诊断甲状腺恶性结节的灵敏度、特异度、正确率分别为92.2%(47/51)、88.4%(38/43)、90.4%(85/94)。常规超声与VTQ诊断甲状腺恶性结节的ROC曲线下面积分别为0.804、0.918,差异有统计学意义(Z=5.576,P<0.001)。结论 常规超声与VTQ均有助于鉴别诊断甲状腺良、恶性结节,VTQ明显优于常规超声。
甲状腺结节;超声检查;声触诊组织量化技术;诊断,鉴别;灵敏度;特异度
李军,袁美芹,李文肖,等.常规超声与声触诊组织量化技术鉴别诊断甲状腺结节的对比研究 [J].中国全科医学,2015,18(21):2615-2617.[www.chinagp.net]
Li J,Yuan MQ,Li WX,et al.Identification and diagnosis of thyroid nodules by conventional ultrasound and virtual tough tissues quantification technique:a comparison study[J].Chinese General Practice,2015,18(21):2615-2617.
甲状腺癌是内分泌系统最常见的恶性肿瘤,占头颈科恶性肿瘤发病率的首位,约占全身恶性肿瘤的1%[1]。甲状腺癌多起病隐匿,生物学特性多变,临床、影像学及细胞学特征与良性病变存在交叉,因此寻找一个合适的检查方法至关重要。超声检査不但可以确定肿块的数量、大小、包膜、血供、形态情况,还能检查周围淋巴结肿大的情况,综合评估病情,凭借正确率高、非创伤、无辐射、重复性好等优势,成为临床诊断甲状腺疾病首选的检查方法。但目前超声技术种类较多,各有其优缺点,各自诊断正确率也不尽相同,本研究旨在比较常规超声与声触诊组织量化技术(VTQ)在甲状腺良、恶性结节鉴别诊断中的应用价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料 选取2012年2月—2014年10月在石河子大学医学院第一附属医院就诊并以甲状腺结节(长径>1 cm)收入院患者94例为研究对象,共94个甲状腺结节。其中男13例(13.8%),女81例(86.2%);年龄21~72岁。均进行常规超声及VTQ检查,并行甲状腺切除术,经病理确诊。
1.2 仪器与方法
1.2.1 仪器 使用Siemens Acuson S2000彩色多普勒超声诊断仪(9L4探头),探头频率5.0~14.0 MHz,中心频率7.5 MHz,具有常规超声和VTQ。
1.2.2 检查方法 检查均由1位高年资医师操作。采用仪器的甲状腺检查条件,患者取仰卧位,头部后仰充分暴露颈部,首先采取常规超声检查观察并记录甲状腺结节的一般特征:大小、形态、位置、边界、纵横比、回声及有无衰减、钙化等,然后选择VTQ成像条件,探头轻触甲状腺表面不加压,将取样框放在病灶内实性部分,待图像稳定后,VTQ可自动计算出病灶取样区的剪切波速度(SWV)并显示。每个结节测量5次,均在未知病理结果情况下脱机分析;当SWV测量值大于测量上限,以仪器设定最大值9.00 m/s作为统计数据。
1.2.3 评分标准 常规超声采用半定量评分法[2]:常规超声各特征得分之和在4分以上诊断为恶性,3分及以下诊断为良性。采用VTQ定量测定结节内SWV。

2 结果
2.1 常规超声诊断甲状腺恶性结节的评价 常规超声诊断甲状腺恶性结节的灵敏度、特异度、正确率分别为80.4%、81.4%、80.9%(见表1)。
表1 常规超声与病理检查诊断甲状腺良恶性结节的四格表(例)
Table 1 Fourfold table of the diagnosis of benign or malignant thyroid nodules by US and pathological examination
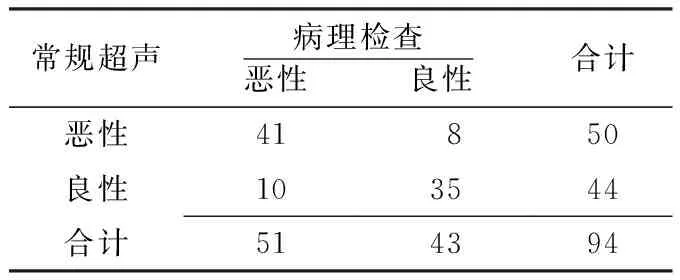
常规超声病理检查恶性 良性合计恶性41 8 50良性103544合计514394
2.2 VTQ诊断甲状腺恶性结节的评价 43例甲状腺良性结节SWV为(1.19~2.93)m/s,平均(1.98±0.45)m/s(见图1);51例甲状腺恶性结节SWV为(2.27~9.00)m/s,平均(3.29±1.20)m/s(见图2)。甲状腺恶性结节SWV高于甲状腺良性结节,差异有统计学意义(t=-6.813,P<0.001)。以2.75 m/s作为最佳截断值,51例甲状腺恶性结节中,47例SWV≥2.75 m/s,4例SWV<2.75m/s;43例甲状腺良性结节中,5例SWV≥2.75 m/s,38例SWV<2.75 m/s。VTQ诊断甲状腺恶性结节的灵敏度、特异度、正确率分别为92.2%、88.4%、90.4%(见表2)。
2.3 常规超声与VTQ的诊断效能比较 常规超声与VTQ诊断甲状腺恶性结节的ROC曲线下面积分别为0.804、0.918,差异有统计学意义(Z=5.576,P<0.001,见图3)。
3 讨论
随着环境污染与电离辐射的增加,甲状腺疾病的发病率也逐渐升高;随着超声诊断技术的发展,甲状腺疾病的检出率也随之增加[3-5]。世界甲状腺癌的发病率每年的增长率大约4%。特别是在女性人群中,甲状腺癌已经上升至女性常见肿瘤的第八位[6]。本文结果也提示,94例甲状腺结节患者中女性占86.2%。传统的常规超声因其无创、方便和经济等优点,是甲状腺疾病的首选检查方法,但常规超声鉴别诊断甲状腺良、恶性结节尚存在一定的缺陷[7]。VTQ是声辐射力弹性成像的一种,是一项新型的组织定征技术[8],其优势在于可以定量检测特定区域内组织的黏弹性,并用相应的指标显示出来。资料表明,VTQ已经具备在临床上应用二维弹性成像技术进行多种脏器检查的能力[9]。本研究比较了常规超声与VTQ在甲状腺良恶性结节诊断中的应用价值。

图1 甲状腺良性结节VTQ图像
图2 甲状腺恶性结节VTQ图像
表2 VTQ与病理检查诊断甲状腺良恶性结节的四格表(例)
Table 2 Fourfold table of the diagnosis of benign or malignant thyroid nodules by VTQ and pathological examination

VTQ病理检查恶性 良性合计恶性47 5 52良性 4 3842合计514394
注:VTQ=声触诊组织量化技术

图3 常规超声与VTQ诊断甲状腺恶性甲状腺结节的ROC曲线
Figure 3 ROC curves of US and VTQ in the diagnosis of malignant thyroid nodules
本研究结果显示,常规超声诊断甲状腺恶性结节的灵敏度、特异度、正确率分别为:80.4%、81.4%、80.9%,具有一定的鉴别诊断甲状腺结节性质的效能。而应用VTQ,设定机器的SWV最高速度为9.00 m/s。43例甲状腺良性结节SWV为(1.98±0.45) m/s,51例甲状腺恶性结节SWV为(3.29±1.20) m/s,甲状腺恶性结节SWV高于甲状腺良性结节,提示甲状腺恶性结节的组织硬度高于良性结节。以病理检查为金标准,常规超声与VTQ诊断甲状腺恶性结节的ROC曲线下面积分别为0.832和0.928。VTQ诊断甲状腺恶性结节的ROC曲线下面积高于常规超声。VTQ的诊断效能优于常规超声。SWV以2.75 m/s为最佳截断值,与张凤娟等[10]的最佳截断值2.95 m/s相近,与何勇等[11]的最佳截断值2.87 m/s亦相近。本研究误诊和漏诊的原因可能与以下原因相关:甲状腺良性结节发生纤维化及钙化使SWV升高,而甲状腺恶性结节发生液化及出血使SWV降低;数据测量过程中患者屏气配合欠佳;测量的深度、结节的大小不一等因素。本研究为了保证数据的合理性,选取长径>1 cm的甲状腺结节作为研究对象,从而避免了VTQ取样框的影响。
综上所述,常规超声与VTQ对于甲状腺良、恶性结节有一定的诊断价值,但VTQ的诊断价值明显优于常规超声。
[1]Bojunga J,Herrmann E,Meyer G,et al.Real-time elastography for the differentiation of benign and malignant thyroid nodules:a meta-analysis[J].Thyroid,2010,20(10):1145-1150.
[2]Liu JJ,Cong SZ,Li K,et al.Ultrasonic semi-quantitive scores in diagnosing thyroid solitary nodules[J].Chinese J Ultrasound Med,2009,25(7):646-648.(in Chinese) 刘娟娟,丛淑珍,李康,等.甲状腺单发结节的超声半定量诊断研究[J].中国超声医学杂志,2009,25(7):646-648.
[3]Jin ZQ,Li XR,Zhou HL,et al.Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography of breast imaging reporting and data system category 4 breast lesions[J].Clin Breast Cancer,2012,12(6):420-427.
[4]Sporea I,Sirli R,Bota S,et al.ARFI elastography for theevaluation of diffuse thyroid gland pathology:preliminary results[J].World J Radiol,2012,4(4):174-178.
[5]D′onofrio M,Gallotti A,Salvia R,et al.Acoustic radiation force impulse(ARFI) ultrasound imaging of pancreatic cystic lesions[J].Eur J Radiol,2011,80(2):241-244.
[6]Frates MC,Benson CB,Charboneau JW,et al.Management of thyroid nodules detected at US:Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound consensus conference statement[J].Ultrasound Q,2006,22(4):231-238.
[7]Friedrich-Rust M,Romenski O,Meyer G,et al.Acoustic radiation force impulse-imaging for the evaluation of the thyroid gland:a limited patient feasibility study[J].Ultrasonics,2012,52(1):69-74.
[8]Huang Y,Li JL,Wang ZL,et al.Quantitive research on supersonic shear imaging in diagnosis of thyroid nodules by elastography[J].Chinese Journal of Medical Ultrasound(Electronic Edition),2011,8(6):1282-1288.(in Chinese) 黄炎,李俊来,王知力,等.实时组织弹性成像在甲状腺实性结节的定量研究[J].中华医学超声杂志:电子版,2011,8(6):1282-1288.
[9]Wang B.Acoustic radiation force elastography:the new development of elastography[J].Chin J Med Imaging Technol,2011,27(4):853-854.(in Chinese) 王彬.声辐射力弹性成像:弹性成像的新发展[J].中国医学影像技术,2011,27(4):853-854.
[10]Zhang FJ,Han RL,Zhou JH,et al.Virtual touch tissue quantification in diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma[J].Chin J Med Imaging Technol,2012,28(5):877-880.(in Chinese) 张凤娟,韩若凌,周军华,等.声触诊组织量化技术诊断甲状腺乳头状腺癌[J].中国医学影像技术,2012,28(5):877-880.
[11]He Y,Xu HX,Zhang YF,et al.Value of virtual touch tissue imaging in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant thyroid nodules[J].Chin J Ultrasonogr,2012,21(4):320-323.(in Chinese) 何勇,徐辉雄,张一峰,等.声触诊组织弹性成像鉴别诊断甲状腺结节良恶性的价值[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2012,21(4):320-323.
修回日期:2015-05-06)
(本文编辑:陈素芳)
Identification and Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules by Conventional Ultrasound and Virtual Tough Tissues Quantification Technique:A Comparison Study
LIJun,YUANMei-qin,LIWen-xiao,etal.
DepartmentofFunction,theFirstAffiliatedHospitaloftheMedicalCollegeofShiheziUniversity,Shihezi832000,China
Objective To explore the value of conventional ultrasound(US) and virtual tough tissues quantification(VTQ) technique in the identification and diagnosis of benign and malignant thyroid nodules.Methods We enrolled 94 patients with thyroid nodules(long diameter>1 cm) who received treatment in the First Affiliated Hospital of the Medical College of Shihezi University from February 2012 to October 2014.The subjects all received US and VTQ examination,thyroidectomy,and pathological examinations.Semi-quantitative scoring method was employed in US examination.Shear wave velocity(SWV) was used in VTQ examination.Receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curves was employed to compare the effectiveness in the diagnosis of thyroid nodules between US and VTQ.Results Under the golden standard determined according to the pathological examination,the sensitivity,specificity and accuracy of the diagnosis of thyroid nodules by UC were 80.4%(41/51),81.4%(35/43) and 80.9%(76/94) respectively.Malignant thyroid nodules were higher than benign thyroid nodules in SWV 〔(3.29±1.20)m/s vs.(1.98±0.45)m/s〕(t=-6.813,P<0.001).With SWV=2.75 m/s as the cutoff value,the sensitivity,specificity and accuracy of the diagnosis of thyroid nodules by VTQ were 92.2%(47/51),88.4%(38/43) and 90.4%(85/94).The area under ROC curve was 0.804 for US and 0.918 for VTQ in the diagnosis of malignant thyroid nodules,with a significant difference between them(Z=5.576,P<0.001).Conclusion US and VTQ are all helpful in differentiating malignant and benign thyroid nodules,while VTQ is obvious superior to US.
Thyroid nodule;Ultrasonography;Virtual tough tissues quantification technique;Diagnosis,differential;Sensitivity;Specificity
832000 新疆石河子市,石河子大学医学院第一附属医院功能科
芦桂林,832000 新疆石河子市,石河子大学医学院第一附属医院功能科;E-mail:lgl-shz@qq.com
R 581
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2015.21.027
2014-11-18;
