Initial Research of Four Strobilurin Fungicides’Effect on the Quality and Yield Formation of Fruit Vegetables
2015-02-05XuesongZHENGLijunRUYingbiaoZHANGXiaoboZHANGWeipingLUJingyuCHOUZhinianLI
Xuesong ZHENG,Lijun RU,Yingbiao ZHANG,Xiaobo ZHANG,Weiping LU,Jingyu CHOU, Zhinian LI
1.Sinochem Agro Co.,Ltd.,Shanghai 200002,China;
2.Shenyang Research Institute of Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd.,Shenyang 110021,China
Initial Research of Four Strobilurin Fungicides’Effect on the Quality and Yield Formation of Fruit Vegetables
Xuesong ZHENG1*,Lijun RU1,Yingbiao ZHANG1,Xiaobo ZHANG2,Weiping LU1,Jingyu CHOU2, Zhinian LI2
1.Sinochem Agro Co.,Ltd.,Shanghai 200002,China;
2.Shenyang Research Institute of Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd.,Shenyang 110021,China
[Objective]The effects of four QoI fungicides on potato and tomato and cumumber quality and yield formation under disease-free conditions were studied in order to research the physiological effects of four QoI fungicides on these fruit vegetables and explore the range of minium dose for the obvious physiological effect and the dose for the maximum effect.[Method]The effects of four strobilurin fungicides on yield formation and quality were studied under disease-free conditions in the field.Two applications of each strobilurin fungicide were designed.The yield and commercial ratio for each application were investigated.[Results]The minimum dose for the obvious physical effect on potato and tomato and cucumber was lower than 133 mg/L,the dose for maximum effect on patoto and cucumber of the four strobilurin fungicides maybe also lower than 667 mg/L.The dose of fenaminstrobin and pyraoxystrobin for maximum effect on tomato maybe also lower than 667 mg/L. [Conclusion]The study suggested that enotroburin,fenaminstrobin,pyrametostrobin and pyraoxystrobin were able to increase the yield and ratio of high quality potato and cucumber and tomato.
Strobilurins;Yield;Commercial ratio
A fter introduction of strobilurins, the concept of disease control gained new perspectives especially when considering the advantages obtained by the action of positive physiological effects on plants[1]. The positive physiological within the plant can be detailed as greater chlorophyll retention,increased water and nitrogen use efficiency and delayed senescence[2].
Application of strobilurins(Qo inhibitors)has been repeatedly shown to result in increasing grain yields,kernel weights and protein contents associated with a delay in the senescence of flag leaves[3].The hypothesis has been presented to explain this phenomenon.A variety of physiological processes are directly affected by strobilurins.As the carbon dioxide compensation point and chlorophyll content lead to high photosynthetic activity,thereby ethylene and other plant hormones biosynthesis delay senescence.However,the hypothesis reflecting yields fluctuate in a indoor situation while not field situation is still difficult to accept.
Strobilurins are one of the most important classes of agricultural fungicides.These fungicides control an unusually wide array of fungal disease, including disease caused by water moulds,downy mildew,powdery mildews,leaf spotting and blighting fungi,fruit rotters and rusts.They are used on a wide variety of crops,including cereals,fruits,vegetables and vine[4].China first developed strobilurin fungicide as enostroburin which was first sold in 2002 and in 2011 there had been four commercially available strobilurin fungicides on the market.In China,enostroburin and pyraoxystrobin were approved for registration
Potato rates fourth among the world’s agricultural products in production volume.China is currently the world’s leading potato-growing country,and potatoes are widely cultivated across China[5].Tomato also is one of popular vegetables throughout the world,after potatoes and before onions.Potato and tomato and cucumber are all playing an important role in people’s daily diet.With the development of social economy and the improvement of people’s living condition, people’s demand on these vegetables is changing from quantity to quality gradually[6].Thus commercial ratio is another attribute that drives vegetable planting while colour and appearance (the size,the shape,the wholeness, the presence of defects and consisitency)usually determine whether a disease management programme is accepted or rejected[7].
During the last decade,the positive physiological effect of strobilurins has been investigated,but mainly on cereals.Furthermore,research in some crop indicates that physiological effects are inconsistent,or do not always result in a significant yield increasing[3].The aim of this work was to investigate the physiological effects of the four strobilurin fungicides on the yield and commercial ratio of potato and tomato and cucumber.A series of experiments were conducted under disease-free conditions to explore the range of minimum dose for the obvious physiological effect and the dose for the maximum effect in the field.
Materials and Methods
Plant material
During the growing season of 2013,potatoes(‘ZhengShu 5’)were grown according to normal agronomic practice in Dongpo Village(Experiment farm of Yantai plant protection station).Tomato cultivar‘RuiXing F1’and cucumber cultivar‘Wo Ling12’were chosed also in this location. Potato seed tubers(Solanum tuberosum L.)were planted on 16 March,at 50 cm inter row and 20 cm interplant distances.Seed tubers were ridged with 20 cm soil in prepared furrows. The height of the ridge was 30cm measured from top of the ridge to the bottom of the furrows.Tomato plants (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill)were transplanted on May 6,2013.Tomato seedlings were evenly transplanted along the edge of furrow side with row spacing of 50 cm and interplant spacing of 40 cm.The cucumber seedlings selected for size uniformity were transplanted on July 20,2013.Planting beds were prepared 0.4 m apart with 0.6 m width on bed tops.On the top two rows of cucumber plants were transplanted.Plants were spaced 30 cm in row and there was 40 cm between rows.
Test seedlings were carefully inspected in order to control possible fungal and insect infections.The fungicide Fulimain(R)(active ingredient [a.i.]flumorph and mancozep 600 g/Kg,Sinochem agrochemical)and the fungicide Score(R)(active ingredient [a.i.]difenoconazole 100 g/kg,Syngenta(China))were applied to keep plants free form late blight or downy mildew and early blight,respectively. During the experimental period,except for fungicide,other management practices such as pruning branch stem, fertilization and insect control were the same for all treatments.
Fungicide treatments
Four strobilurin fungicides(200 g/L enostroburin,200 g/L fenaminstrobin,200 g/L pyraoxystrobin,and 200 g/L pyrametostrobin,supplied by Shenyang research institute of chemical industry)were applied in eight treatment for each vegetable.Every strobilurin fungicide were applied at two rates(133.3 and 666.7 mg/L).Plots were arranged according to a randomized block design with three replicates for each treatment.Four fungicides plus water control were sprayed on the foliage in the plot from both sides until runoff.
The first fungicide applications on potato were timed to coincide with the beginning of flowering(BBCH69)and the second application at two weeks later.The first fungicide applications on tomato and cucumber were also timed to coincide with the beginning of flowering but the second application at ten days later.
Measurement of commercial ratio and yield
At the harvest time on June 27, ten potato plants in every plot were chosen and marked to measure the total tuber fresh weight,total tuber number.Harvested potato tubers were graded into three categories according to their weight as C1 for those below 50 g;C2 for those between 50 and 100 g;C3 for tuber weight above 100 g. The tuber size categories C2 and C3 were considered marketable tubers.
Tomato fruits were harvested every 3-4 days as the color turned from green to pink.The number of fruits per tomato plant,average fruit weight, yield per plot were measured during 30 days after first hand of tomato harvested.Fruit yield per plant was calculated as fresh weight of fruits,without rotten ones,in all pickings.
The time of cucumber fruit harvest was determined based on visual observations,and all marketable cucumber fruits(length>18 cm and diameter>3 cm)were hand harvested every 3-4 days during 30 days after first cucumber harvested[8].Fruit yield per plot were calculated as fresh weight of fruits in all pickings.
Statistical analysis
All results were presented as means of treatments.Analysis of variance of the treatment effects on measured traits was performed using SAS program(SAS,2000).When F-tests showed statistical significance,the Duncan’s multiple range test(P=0.05) was used to separate means for particular comparisons.
Results and Analysis
Potato yield and commercial ratio
Yield and commercial ratio of potato treated by four strobilurin fungicides at 133 and 667 mg/L were investigated in this study(Table 3).
The commercial ratios of potato treated by enostroburin at 133 and 667mg/L were 85.2%and 79.7%,fenaminstrobin and pyraoxystrobin also had obvious improvement of commercial at both rates with ratio values of 76.8%-80.0%,compared with non-strobilurins treatment.Pyrametostrobin had the lower commercial ratio with values of 74.5%and 75.6%. There were no difference of ratios in pyrametostrobin application compared to non-strobilurins treatment. Obvious variations between rates in pyraoxystrobin and pyrametostrobin were observed.
The yield of potato treated by pyrametostrobin at 133 and 667 mg/L were 18.2 and 16.1 Kg,application of pyrmetostrobin to potato at 133 mg/L increased yield by 24.1%,relative to the control.Pyraoxystrobin at 133 mg/L also had obvious improvement of yield with values of 16.7 kg.there were no difference between yield of fenaminstrobin and enostroburin and non-strobilurins treatment.
Tomato average weight and yield
Yield and average weiht of tomato treated by four strobilurin fungicides at 133 and 667 mg/L were investigated in this study(Table 2).
The average weiht of tomato treated by pyraoxystrobin at 133 and 667 mg/L were 213.5 and 211.5 g.Fenaminstrobin at 133 mg/L and enostroburin at 667 mg/L had average weight with values of 208 and 207.8 g, pyrametostrobin and enostroburin at 133 mg/L and fenaminstrobin at 667 mg/L also had obvious improvement of average weight weiht values of 202.7-205.7 g.Obvious variations between rates in fenaminstrobin and pyrametostrobin and enostroburin were observed.
The yields of tomato treated by pyraoxystrobin at 133 and 667 mg/L were 136.8 and 109 kg,pyrametostrobin at both rates and enostroburin at 667 mg/L had yield with values of 102.9-109.3 kg.Application of pyraoxystrobin to tomato at 133 mg/L increased yield by 47.1%,compared with the control.There were no difference among yield of fenaminstrobin at both rates and enostroburin at 133 mg/L and non-strobilurins treatment.Obvious variations between rates in pyraxoystrobin and enostroburin were observed.
Cucumber yield
Yield of cucumber treated by four strobilurin fungicides at 133 and 667 mg/L were investigated in this study (Table 3).The yield of cucumber treated by pyraoxystrobin and pyrametostrobin at 133 mg/L were 90.1 and 85.7 kg.Application of pyraoxystrobin to cucumber at 133 mg/L increased yield by 32%,compared with the control.Fenaminstrobin and enostroburin at both rates also had obvious improvement of yield with values of 75.8-78.4 kg.Obvious variations between rates in pyraoxystrobin were observed.
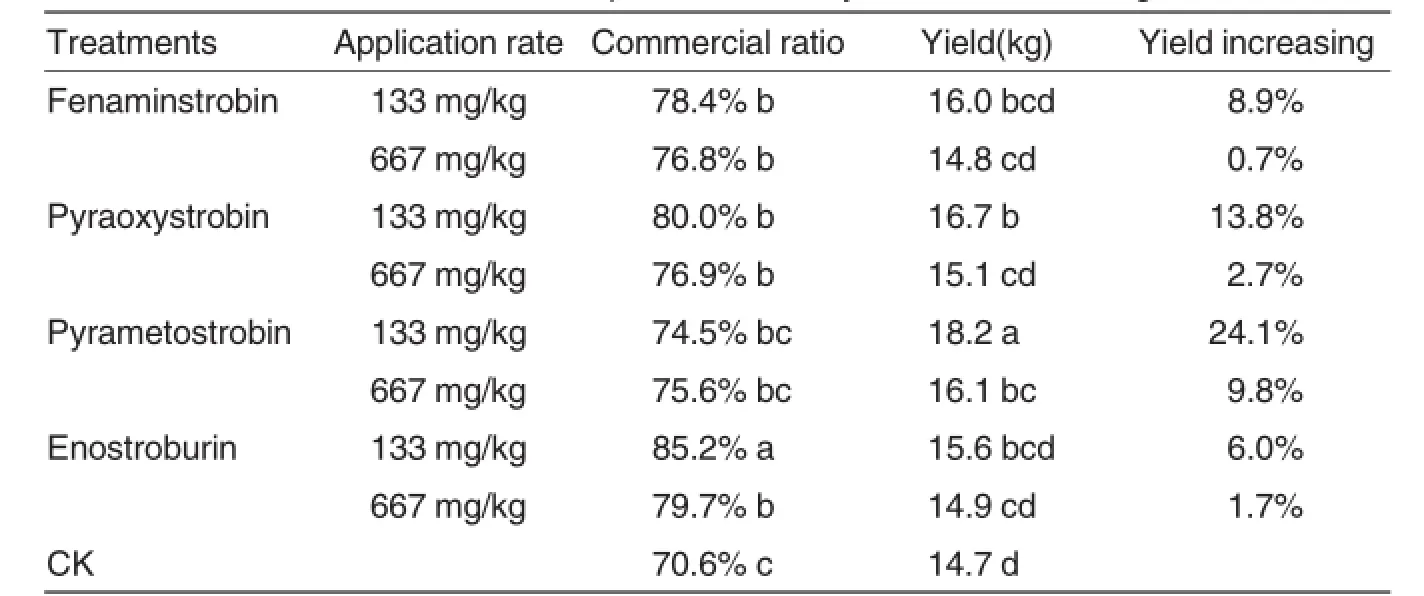
Table 1Yield and commercial ratio of potato treated by four strobilurin fungicides
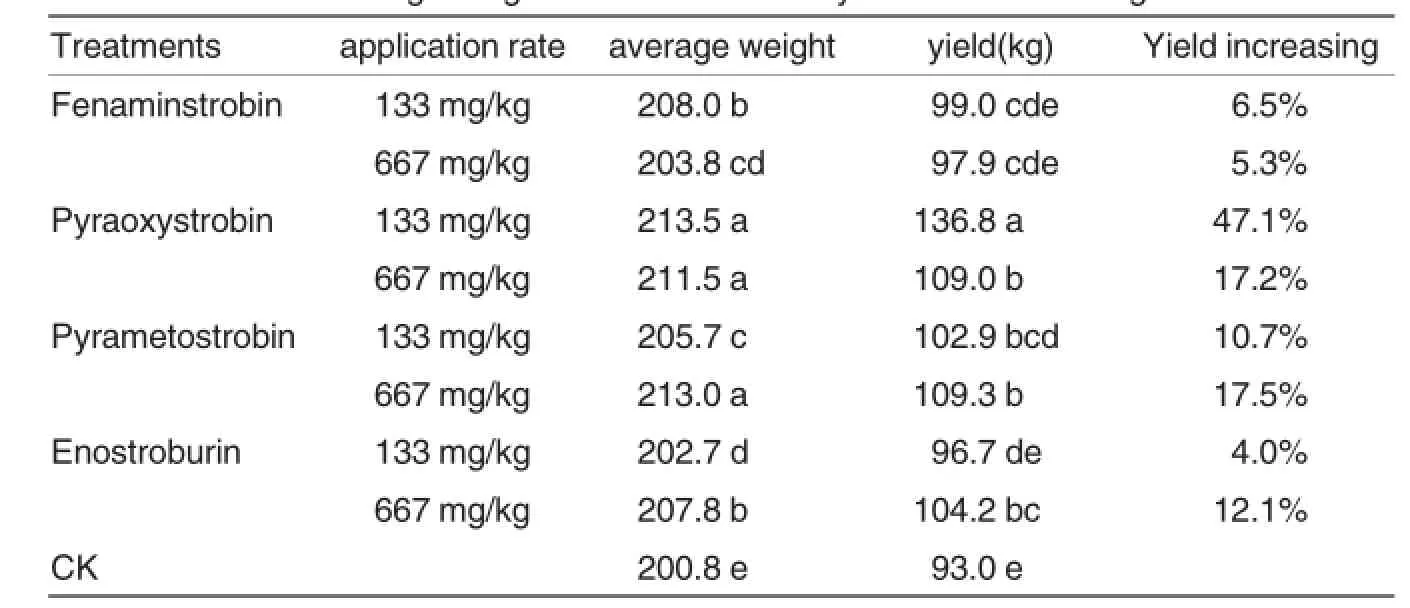
Table 2Yield and average weight of tomato treated by four strobilurin fungicides
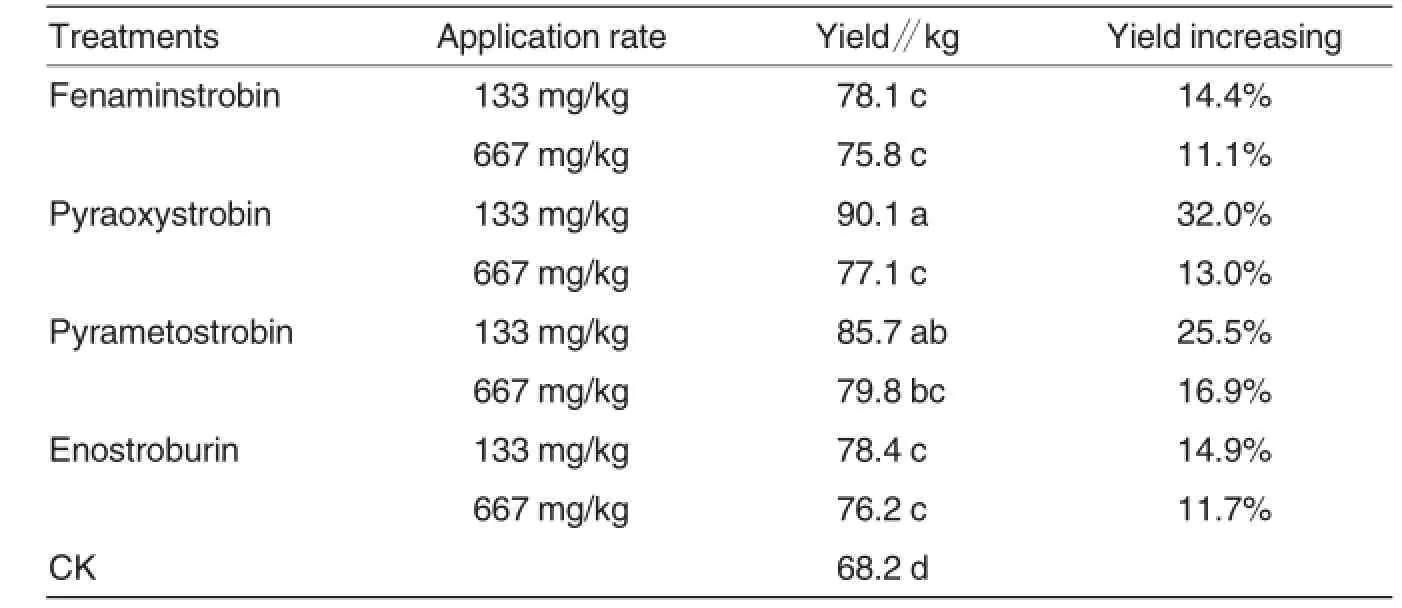
Table 3Yield of cucumber treated by four strobilurin fungicides
Disscusion
In the past,growers have adopted cultural practices to increase yields. However,growers are increasingly shifting towards chemical application to enhance yields,and the prophylactic use of fungicide and insecticides has recently been advocated as a means to optimize plant health and increase yields,even in the absence of significant pest pressure[9].Fungicide have been associated with yield increase due to the maintenance of the photosynthetic life of the canopy during grain filling.The inclusion of strobilurin fungicides in disease control programmes for wheat has been associ-ated with extended flag leaf life[10].For example,Kresoxim-methyl has been shown to cause changes in the hormonal balance of wheat which results in increased grain yield,apparently from delayed leaf senescence[11].Documented benefits of azoxystrobin have included bigger grain size and better milling quality in rice,improved tuber size in potatoes[4],increased soluble sugars and longer shelf life in tomatoes.In some research,strobilurin fungicide such as pyraclostrobin applied in the absence of foliar disease didn’t produce nonfungicidal physiological effect or associated yield improvement[12].Either the near-optimal growth condition or the incorporate dose for physiological effects may be the factor for this phenomenion.We hypothesize that the application of strobilurins during crop cultivation can improve the productive and qualitative characteristics,there must be a minimum dose for obvious physical effect and a dose for maximum physical effect.
There was no difference on commercial ratios of potato among four applications of both fenaminstrobin and pyraoxystrobin.However,commercial ratios of these four applications obviously differ from control’s. Three applications of enostroburin at different rates and control were obviously different from each other.Furthermore,the commercial ratio of enostroburin at 133 mg/L was higher obviously than 667 mg/L.the yield of tomato treated by pyrametostrobin at 133 and 667 mg/L were significantly different and higher than control’s. Yields of pyraoxystrobin and pyrametostrobin at 133 mg/L were significantly higher than 667 mg/L.It was concluded that the minimum dose for the obvious physical effect of the four strobilurin fungicides were lower than 133 mg/L and the dose of for maximum effect maybe also lower than 667 mg/L.Due to decreasing commercial ratio or yield of pyraoxystrobin and pyrametostrobin and enostroburin, maybe the dose for the maximum physical effect were also lower than 667 mg/L.
The economic yield of fruit vegetables,such as cucumber and tomato is determined by the total fresh weight of the fruits and fruit quality. Yield takes into account both fruit number and fruit weight.It’s obvious that tomato yield is not an isolated trait,as it is strongly correlated with factors influencing the overall growth of the plant.Currently,the quality of fruits/vegetables is considered more important than yield for market value. Furthermore,average weight is considered as one of the most important attributes determining the tomato quality[6].The average weights of all strobilurin fungicides treatment were significantly different from control.There were no differences in average weights between two applications of pyraoxystrobin.The yield of treatments by fenaminstrobin at 133 and 667 mg/L and enostroburin at 133 mg/L were not significantly different from that of control.The yields in treatments by pyraoxystrobin were different from each other.It was concluded that the minimum dose for the obvious physical effect of the four strobilurin fungicides were lower than 133 mg/L,and the dose of fenaminstrobin and pyraoxystrobin for maximum effect maybe also lower than 667 mg/L.
The yield of all cucumber treated by strobilurin fungicides were significantly different from control.There were singnificant differences in yield between two applications of pyraoxystrobin.It was concluded that the minimum dose for the obvious physical effect of the four strobilurin fungicides were lower than 133 mg/L,and the dose of all the strobilurin fungicides for maximum effect maybe also lower than 667 mg/L.
The physical effect on tomato and cucumber of pyrametostrobin at different rates was similar to results reported by Cao et al[13].Cao’s results showed that the content of chlorophyll in cucumber and tomato leaves were promoted by pyrametostrobin significantly to the control,the effect with 300 mg/L was fastest and most significant.To a certain extent, the bigger concentration of pyrametostrobin,the higher the content of chlorophyll.The activities of protective enzymes under the treatment of pyrametostrobin with different concentrations all increased in certain time.The activities of POD,PPO,CAT and SOD with 300 mg/L were 34.67%,34.78%, 36.36%,and 11.94%higher than the control,respectively.
The research indicated that on potato pyrametostrobin and enostroburin were worthy researching because of obvious physical effect at relative low rates and pyraoxystrobin on tomato while pyraoxystrobin and pyrametostrobin on the cucumber.
[1]MUHAMMAD L,BERND H.Effect of triazole and strobilurin fungicides on seed yield formation and grain quality of winter rapeseed(Brassica napus L.)[J]. Field Crops Research,2012,130(29): 80-86.
[2]WILSON S V,MARCO A T R,EDSON B,et al.Physiological effects of strobilurin fungicides on plants[J].Exact Soil Sci,Agr Sci Eng,2003,9(3):59-68.
[3]RYAN S H,WILLIAM G J,KIERSTEN A W.The impact of a fungicide and an insecticide on soybean growth,yield, and profitability[J].Crop Protection, 2011,30(12):1629-1634.
[4]DAVE W B,JOHN M C,JEREMY R G, et al.Review the strobilurin fungicides [J].Pest Management Science,2002, 58(7):649-662.
[5]LIU T J,CHENG Z H,MENG H W,et al. Growth yield and quality of spring tomato and physicochemical properties of medium in a tomato/garlic intecropping system under plastic tunnel organic medium cultivation[J].Scientia Horticulturae,2014,170(7):159-168
[6]VERONIQUE B.The history of tomato: from domestication to biopharming[J]. Biotechnology Advances,2004,32(1): 170-189.
[7]ANNA B,GIULIA C,CORRADO L,et al. Pre-harvest nitrogen and azoxystrobin application enhances postharvest shelflife in butterhead lettuce[J].Postharvest Biology and Technology,2013,85(11): 67-76.
[8]ZHANG H X,CHI D C,WANG Q,et al. Yield and quality response of cucumber to irrigation and nitrogen fertilization under subsurface drip irrigation in solar greenhouse[J].Agricultural Science in China,2011,10(6):921-930
[9]DANIEL G,VALERIU T,SIMONA N,et al.Research regarding the influence of fungicide treatments with strobilurin on the production and quality of canola[J]. Journal of Biotechnology,2012,161: 19-48
[10]MASSIMO B,AMEDEO R.Effect of fungicide and foliar fertilizer application to winter wheat at anthesis on flag leaf senescence,grain yield,flour breadmaking quality and Don contamination[J].European Journal of Agronomy, 2009,30(4):275-282
[11]KLAUS G,RETZLAFF G.Bioregulatory effects of the fungicidal strobilurin kresoxim-methyl in Wheat[J].Pesticide Science,1997,50(1):11-20
[12]CATHERINE S,PALLE P.Effect of fungicide on soybean growth and yield [J].Agronomy Journal,2009,101(2): 352-356
[13]CAO X F,LIU J L,LI Z N,et al.Effects of pyrametostrobin on physiological indices and protective enzymes in cucumber and tomato[J].Acta Phytophylacica Sinica,2010,37(2):182-186.
Responsible editor:Xiaoxue WANG
Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
4种QoI类杀菌剂对果实类蔬菜的保健增产效应初探
郑雪松1*,茹李军1,张英彪1,张晓波2,卢伟平1,丑靖宇2,李志念2
(1.中化农化有限公司,上海200002;2.沈阳化工研究院,辽宁沈阳110021)
[目的]研究4种甲氧基丙烯酸酯类杀菌剂对马铃薯、番茄、黄瓜保健增产效应,探索4种杀菌剂无病害压力下保健增产的有效起始剂量或饱和剂量存在范围及保健增产的幅度。[方法]供试药剂共4种,每种药剂设2个浓度。通过田间试验,调查了每个处理马铃薯、番茄及黄瓜的产量或优质率。[结果]烯肟菌胺、烯肟菌酯、唑菌酯与唑胺菌酯对马铃薯、番茄、黄瓜保健增产有效起始剂量应低于133 mg/L;对马铃薯、黄瓜保健增产的饱和剂量应低于666.7 mg/L。烯肟菌胺与唑菌酯使番茄保健增产的饱和剂量应低于667 mg/L。[结论]烯肟菌胺、烯肟菌酯、唑菌酯及唑胺菌酯3种杀菌剂对马铃薯、番茄及黄瓜均具有明显的保健增产效应,值得推广。
甲氧基丙烯酸酯类;产量;商品率from Institute for the Control of Agrochemicals,Ministry of Agriculture on cucumber to control downy mildew while pyrametostrobin and fenaminstrobin were to control powdery mildews.Fenaminstrobin was also registered on wheat while the mixture containing enostroburin received registration on apple and vine.These four fungicides were all developed and launched by Shenyang Research Institute of Chemical Industry.
郑雪松(1985-),男,河北秦皇岛人,工程师,研究方向:创制产品应用技术研究与推广。*通讯作者,E-mail:xuesong716@163.com。
2015-04-04
修回日期 2015-05-15
*Corresponding author.E-mail:xuesong716@163.com
Received:April 4,2015 Accepted:May 15,2015
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Highly-efficient Stereo-cultivation Model in Kiwifruit Orchards Interplanting Konjak
- The Breeding of New Indica-japonica Intersubspecific Hybrid Rice Combination Chunyou 84
- Comparative Analysis between Triple Cross and Double Cross among Three Parents of Crop
- Optimization of Field Arrangement of Doublecropping Glutinous Sorghum and Soybean Intercropping Pattern
- Principal Component Analysis on Traits Related to Lodging Resistance of Plateau Japonica Rice
- Inheritance of Aroma of Good-quality Indica Type Rice PTGMS Line GHS and Its Application in Hybrid Rice Breeding
