基于高分辨率熔解曲线技术的CYP2C19、IL-1β基因多态性检测*
2015-02-02洪军波,刘东升,舒徐等
基于高分辨率熔解曲线技术的CYP2C19、IL-1β基因多态性检测*
洪军波#刘东升舒徐祝荫汪安江谢川谢勇张焜和吕农华&
南昌大学第一附属医院消化内科(330006)

*基金项目:江西省科技计划项目(20113BCB24019)
#Email: allen2005066@sohu.com
背景:细胞色素P450同工酶2C19(CYP2C19)和白细胞介素-1β(IL-1β)基因多态性是幽门螺杆菌(Hp)感染根除率的重要影响因素,明确其基因多态性对根除治疗方案的制定具有指导意义。目的:采用高分辨率熔解曲线(HRM)技术鉴别CYP2C19、IL-1β基因单核苷酸多态性(SNPs)位点基因型。方法:采集200名健康体检者外周血,提取基因组DNA,以HRM技术确定CYP2C19*2、*3和IL-1β-31/-511引物的最佳Mg2+浓度,并检测相应SNPs位点基因型,检测结果以基因测序进行验证。结果:CYP2C19*2、*3和IL-1β-31/-511引物的最佳Mg2+浓度分别为3.0、3.0、2.5、2.5 mmol/L。HRM技术能精确鉴别CYP2C19*2、*3和IL-1β-31/-511基因型,与基因测序结果有良好的一致性(κ=0.985和0.968)。结论:HRM技术能精确鉴别CYP2C19、IL-1β基因多态性,可用于指导Hp根除治疗方案的药物选择。
关键词高分辨率熔解曲线;细胞色素P450 CYP2C19;白细胞介素1β;多态性,单核苷酸;
幽门螺杆菌
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide;Helicobacterpylori
含质子泵抑制剂(PPIs)的根除治疗方案是目前国内外共识推荐的幽门螺杆菌(Hp)感染处理方法[1],方案中的PPIs主要由肝脏细胞色素P450(cytochrome P450, CYP)同工酶2C19(CYP2C19)代谢,因此CYP2C19基因多态性引起的酶活性差异可通过影响PPIs代谢而影响Hp根除治疗方案的疗效[2]。促炎细胞因子白细胞介素-1β(interleukin-1β, IL-1β)可通过下调H+/K+ATP酶表达抑制壁细胞分泌胃酸[3],其基因多态性亦为Hp根除治疗效果的影响因素之一。建立有效的检测方法以明确上述基因多态性,对提高Hp感染根除率具有临床指导意义。高分辨率熔解曲线(high-resolution melting curve, HRM)技术是基于有序列变化的扩增子之间微弱的DNA熔解温度(Tm值)差异,通过DNA片段熔解曲线的差异进行突变检测,方法简单,易于操作,能快速、精确地检测大量样本,并具有成本优势[4-12]。本研究采用HRM技术鉴别CYP2C19、IL-1β基因单核 苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphisms, SNPs)位点基因型,以期指导Hp根除治疗方案的制定,提高Hp感染根除率。
材料与方法
一、标本来源和主要试剂
选取南昌大学第一附属医院2013年6月1日—30日健康体检者200名,其中男127名,女73名,平均年龄(44.2±11.8)岁。采集受检者外周静脉血2 mL,EDTA抗凝,4 ℃保存待测。
人外周血总DNA提取:Wizard®基因组DNA纯化试剂盒(Promega Corporation);HRM技术鉴定SNPs:LightCycler®480 High Resolution Melting Master(Roche Diagnostics);基因测序:Platinum®Taq DNA聚合酶、SYBR®Safe DNA Gel Stain(Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.)。
二、方法
1. 基因组DNA提取:取300 μL外周血,加入900 μL细胞裂解液,混匀,孵育10 min,14 000×g室温离心20 s至出现白色沉淀;沉淀以300 μL核裂解液重悬,加入100 μL蛋白裂解液,剧烈震荡20 s,加入300 μL异丙醇,14 000×g室温离心1 min,加入300 μL乙醇析出白色絮状DNA,离心,加入100 μL DNA水化液。
2. HRM技术确定各引物最佳Mg2+浓度:CYP2C19、IL-1β HRM引物由上海英俊生物技术有限公司设计、合成,具体信息见表1。1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5、3.0、3.5 mmol/L Mg2+对应的体积分别为0.8、1.2、1.6、2.0、2.4、2.8 μL。在1.5 mL反应管(置于冰上)中制备20 μL的PCR Mix,内含2×Master Mix 10 μL、20×Primer Mix 2 μL、相应体积MgCl2和ddH2O共3 μL、6 ng/μL DNA模板5 μL,以ddH2O为模板作为阴性对照。以LightCycler®480薄片封盖微孔板,将微孔板置于离心机上,1 500×g离心2 min,置于LightCycler®480系统,开始PCR程序。反应条件:预孵育(95 ℃ 10 min)→扩增(95 ℃ 10 s,引物温度15 s,72 ℃ 10 s,45个循环)→HRM程序(95 ℃ 1 min,40 ℃ 1 min,65 ℃ 1 s,95 ℃持续)→冷却(40 ℃ 10 s)。以LightCycler®480 Gene Scanning软件分析实验结果。
3. HRM技术检测CYP2C19、IL-1β SNPs位点基因型:以基因测序方法鉴定出CYP2C19*2、*3和IL-1β-31/-511标本作为阳性对照,根据已确定的各引物最佳Mg2+浓度制备15 μL的PCR Mix,分别加入阳性对照标本和待测标本各5 μL,其余方法同步骤2.。
4. 基因测序验证(上海英俊生物技术有限公司):PCR引物信息见表2,25 μL反应体系中含10×PCR缓冲液2.5 μL、Mg2+0.8 μL(50 mmol/L)、上下游引物各0.5 μL(10 μmol/L)、Platinum®Taq DNA聚合酶0.2 μL(5 U/μL)、DNA模板1 μL和ddH2O 19.5 μL,对扩增产物进行测序。

表1 CYP2C19、IL-1β HRM引物信息

表2 CYP2C19、IL-1β PCR引物信息
三、统计学分析
应用SPSS 17.0统计软件,对CYP2C19、IL-1β基因多态性的HRM技术检测结果与基因测序结果进行一致性检验(kappa检验),κ≥0.75表示两者一致性较好,0.75>κ≥0.4表示两者一致性一般,κ<0.4 表示两者一致性较差。双侧P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结果
一、各引物最佳Mg2+浓度
HRM技术显示,CYP2C19*2、*3和IL-1β-31/-511引物的最佳Mg2+浓度分别为3.0、3.0、2.5、2.5 mmol/L。
二、CYP2C19、IL-1β基因多态性检测
1. CYP2C19:HRM技术能精确鉴别CYP2C19*2、*3等位基因(图1、图2),与基因测序结果比较,共有2例结果不一致,κ=0.985(P<0.001),表明两种技术检测结果的一致性非常好。
2. IL-1β:HRM技术能精确鉴别IL-1β-31/-511基因型(图3、图4),与基因测序结果比较,分别有4例结果不一致,κ=0.968(P<0.001),表明两种技术检测结果的一致性非常好。
讨论

蓝色曲线:CYP2C19*1*1;红色曲线:CYP2C19*1*2;绿色曲线:CYP2C19*2*2
图1CYP2C19*2(164 bp)HRM技术检测结果
CYP2C19和IL-1β基因多态性分别可影响PPIs代谢和改变胃内pH值,是Hp感染根除率的重要影响因素[1-3]。CYP2C19基因型可分为快代谢型(extensive metabolizer)、中间代谢型(intermediate metabolizer)和慢代谢型(poor metabolizer)三种,研究发现快代谢型等位基因(CYP2C19*1、*17)携带者的Hp感染根除率显著低于慢代谢型等位基因(CYP2C19*2、*3)携带者[13-14],IL-1β-511 CC基因型携带者的Hp感染根除率显著低于CT 和 TT 基因型携带者,IL-1β-511为CC基因型且CYP2C19为快代谢型的个体,根除治疗失败的风险是非CC基因 型且CYP2C19为慢代谢型者的11.15倍[15]。CYP2C19和IL-1β基因多态性具有较明显的地域和种族差异,因此在制定Hp根除治疗方案前明确患者上述基因的SNPs位点基因型具有重要临床指导意义。亚洲人群中CYP2C19*2、*3等位基因较常见[16],CYP2C19*17等位基因的流行率则低于5%,白种人和非洲人的CYP2C19*17流行率为亚洲人的4倍[14],提示CYP2C19*17在亚洲人群中的临床价值较小,因此本研究未检测该等位基因。

蓝色曲线:CYP2C19*1*1;红色曲线:CYP2C19*1*3;绿色曲线:CYP2C19*3*3

蓝色曲线:IL-1β-31TT;红色曲线:IL-1β-31CT;绿色曲线:IL-1β-31CC
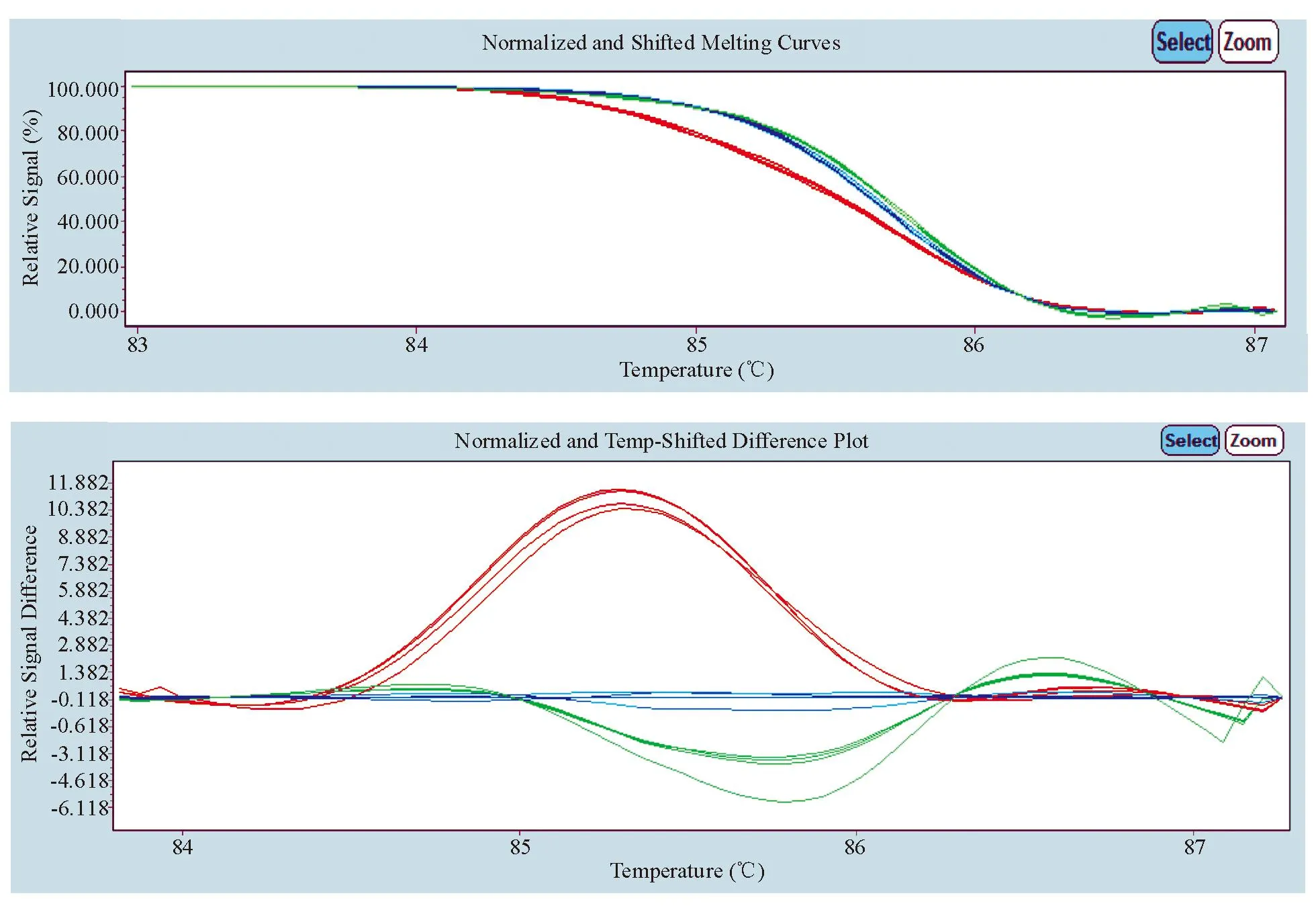
蓝色曲线:IL-1β-511TT;红色曲线:IL-1β-511CT;绿色曲线:IL-1β-511CC
HRM技术具有简单、快速、精确、价廉等优点,并可实现高通量检测[4-12],总体敏感性、特异性和准确性可达99%以上,与DNA测序相当[5,8-10],目前该技术主要用于SNPs分型[4-5,7-8,12]、突变检测[9-10]以及甲基化检测[11]等,在临床实践中的应用日益广泛。既往研究结果显示,HRM技术能很好地鉴别CYP2C19*2、*3、*17等位基因以及IL-1β-31/-511 基因型[4,7-8,12]。有研究[17]指出HRM技术能精确检出杂合子,准确性高达99.7%,但鉴别纯合子的准确性仅为70.3%,在检测纯合子时,其准确性依赖于检测模式、分析软件、PCR产物大小以及纯合子间熔解温度的差异等。本研究结果表明HRM技术能对CYP2C19(*2、*3)和IL-1β(-31/-511)的SNPs进行精确分型,与基因测序结果有良好的一致性(κ=0.985和0.968)。
综上所述,本研究成功建立了能精确鉴别CYP2C19、IL-1β基因多态性的HRM技术,临床实践中可应用该技术明确Hp感染者的PPIs代谢类型和胃内酸分泌情况,从而指导根除治疗方案中PPIs的选择,实现个体化治疗,提高Hp感染根除率。
参考文献
1 Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O’Morain CA, et al; European Helicobacter Study Group. Management ofHelicobacterpyloriinfection -- the Maastricht Ⅳ/ Florence Consensus Report[J]. Gut, 2012, 61 (5): 646-664.
2 Furuta T, Shirai N, Sugimoto M, et al. Influence of CYP2C19 pharmacogenetic polymorphism on proton pump inhibitor-based therapies[J]. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 2005, 20 (3): 153-167.
3 Guo T, Qian JM, Zhao YQ, et al. Effects of IL-1β on the proliferation and apoptosis of gastric epithelial cells and acid secretion from isolated rabbit parietal cells[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2013, 7 (1): 299-305.
4 Temesvári M, Paulik J, Kóbori L, et al. High-resolution melting curve analysis to establish CYP2C19*2 single nucleotide polymorphism: Comparison with hydrolysis SNP analysis[J]. Mol Cell Probes, 2011, 25 (2-3): 130-133.
5 Vaclavikova R, Ehrlichova M, Hlavata I, et al. Detection of frequent ABCB1 polymorphisms by high-resolution melting curve analysis and their effect on breast carcinoma prognosis[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2012, 50 (11): 1999-2007.
6 Guillard T, de Champs C, Moret H, et al. High-resolution melting analysis for rapid characterization of qnr alleles in clinical isolates and detection of two novel alleles, qnrB25 and qnrB42[J]. J Antimicrob Chemother, 2012, 67 (11): 2635-2639.
7 You CG, Li XJ, Li YM, et al. Association analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms of proinflammatory cytokine and their receptors genes with rheumatoid arthritis in northwest Chinese Han population[J]. Cytokine, 2013, 61 (1): 133-138.
8 Zhang L, Cui G, Li Z, et al. Comparison of high-resolution melting analysis, TaqMan Allelic discrimination assay, and sanger sequencing for Clopidogrel efficacy genotyping in routine molecular diagnostics[J]. J Mol Diagn, 2013, 15 (5): 600-606.
9 Chen D, Wang YY, Chuai ZR, et al. High-resolution melting analysis for accurate detection of BRAF mutations: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Sci Rep, 2014, 4: 4168.
10Yadav R, Sethi S, Mewara A, et al. Rapid detection of rifampicin, isoniazid and streptomycin resistance inMycobacteriumtuberculosisclinical isolates by high-resolution melting curve analysis[J]. J Appl Microbiol, 2012, 113 (4): 856-862.
11Yang X, Dai W, Kwong DL, et al. Epigenetic markers for noninvasive early detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by methylation-sensitive high resolution melting[J]. Int J Cancer, 2015, 136 (4): E127-E135.
12曹春鸽,孙海燕,周芳芳,等. 应用HRM技术对CYP2C19*2和CYP2C19*3进行双重SNP分型[J]. 遗传, 2013, 35 (7): 923-930.
13Okudaira K, Furuta T, Shirai N, et al. Concomitant dosing of famotidine with a triple therapy increases the cure rates ofHelicobacterpyloriinfections in patients with the homozygous extensive metabolizer genotype of CYP2C19[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2005, 21 (4): 491-497.
14Li-Wan-Po A, Girard T, Farndon P, et al. Pharmacogenetics of CYP2C19: functional and clinical implications of a new variant CYP2C19*17[J]. Br J Clin Pharmacol, 2010, 69 (3): 222-230.
15Sugimoto M, Furuta T, Yamaoka Y. Influence of inflammatory cytokine polymorphisms on eradication rates ofHelicobacterpylori[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2009, 24 (11): 1725-1732.
16Djaffar Jureidini I, Chamseddine N, Keleshian S, et al. Prevalence of CYP2C19 polymorphisms in the Lebanese population[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2011, 38 (8): 5449-5452.
17Li M, Zhou L, Palais RA, et al. Genotyping accuracy of high-resolution DNA melting instruments[J]. Clin Chem, 2014, 60 (6): 864-872.
(2015-04-27收稿;2015-06-03修回)
Identification of CYP2C19 and IL-1β Polymorphisms Based on High-resolution Melting Curve AnalysisHONGJunbo,LIUDongsheng,SHUXu,ZHUYin,WANGAnjiang,XIEChuan,XIEYong,ZHANGKunhe,LÜNonghua.DepartmentofGastroenterology,theFirstAffiliatedHospitalofNanchangUniversity,Nanchang(330006)
Correspondence to: LÜ Nonghua, Email: lunonghua@163.com
Background: The eradication rate ofHelicobacterpylori(Hp) infection is strongly influenced by cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) polymorphisms, identification of these gene polymorphisms may provide a guidance for the selection of eradication regimen. Aims: To identify the genotypes of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in CYP2C19 and IL-1β genes by using high-resolution melting curve (HRM) analysis. Methods: Peripheral blood was obtained from 200 healthy subjects and the genomic DNA was extracted. The optimal concentrations of Mg2+for primers of CYP2C19*2, *3 and IL-1β-31/-511 were determined by HRM analysis. Then, the genotypes of SNPs in CYP2C19 and IL-1β were identified by HRM analysis and verified by gene sequencing. Results: The optimal concentrations of Mg2+for primers of CYP2C19*2, *3 and IL-1β-31/-511 were 3.0, 3.0, 2.5 and 2.5 mmol/L, respectively. CYP2C19 *2, *3 and IL-1β-31/-511 genotypes could be accurately identified by HRM analysis, which had excellent consistency with the results of gene sequencing (κ=0.985 and 0.968, respectively). Conclusions: CYP2C19 and IL-1β polymorphisms can be accurately identified by HRM analysis, which might be used as a reference for the selection of Hp eradication regimen.
Key wordsHigh-Resolution Melting Curve;Cytochrome P-450 CYP2C19;Interleukin-1beta;
通信作者&本文,Email: lunonghua@163.com
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-7125.2015.12.005
