GSK3β抑制剂SB216763通过激活小鼠成纤维细胞自噬相关蛋白抑制TGF-β1诱导的I型胶原产生
2014-11-01刘虹王佳平辛冰牧邵荣光
刘虹,王佳平,辛冰牧,邵荣光
GSK3β抑制剂SB216763通过激活小鼠成纤维细胞自噬相关蛋白抑制TGF-β1诱导的I型胶原产生
刘虹,王佳平,辛冰牧,邵荣光
100050 北京,中国医学科学院北京协和医学院医药生物技术研究所(刘虹、邵荣光);100094 北京,中国航天员科研训练中心(王佳平、辛冰牧)
探讨 SB216763 对小鼠成纤维 3T3-NIH 细胞 I 型胶原表达和分泌的影响。
使用转化生长因子 TGF-β1 诱导胶原的表达,使用天狼猩红染色试剂盒及 Western blot 检测 I 型胶原和自噬相关蛋白的表达。
给予 TGF-β1 后,细胞培养上清中胶原含量从(11.85 ± 0.90)mg/ml 上升至(16.70 ± 0.67)mg/ml(< 0.001),说明TGF-β1 可以剂量依赖地促进成纤维细胞中胶原的表达与分泌;同时,TGF-β1 还可以抑制自噬相关蛋白 Vsp34、Beclin-1 的表达,促进 p62 的堆积;给予 SB216763 后,细胞培养上清中胶原的含量从(16.83 ± 0.47)mg/ml 下降为(13.16 ± 0.45)mg/ml(< 0.05),说明 SB216763 可以降低 TGF-β1 诱导 I 型胶原的表达;此外,SB216763 还可以恢复成纤维细胞中自噬相关蛋白 Vsp34、Beclin-1 的表达,降低 p62 的表达。
小分子抑制剂 SB216763 通过激活自噬活性抑制 TGF-β1 诱导的 I 型胶原表达。
自噬; 胶原 I 型; 转化生长因子 β1; SB216763
肺纤维化是各种内、外致病原引起慢性肺疾病的共同后果,以肺组织炎症和纤维化为共同病理特征,严重威胁人类健康和生命[1]。肺纤维化可引起肺泡持续性损伤、细胞外基质反复破坏、修复、重建并过度沉积,导致正常肺组织结构改变、功能丧失[2]。此外,多种慢性肺疾病,包括哮喘、慢性支气管炎、支气管扩张、慢性阻塞性肺病、肺结核、肺癌、间质性肺病等,均伴有纤维化病理改变[3]。细胞外基质的过度沉积是肺纤维化疾病的主要病理改变,其主要来源是成纤维细胞,主要成分是不可溶性纤维蛋白胶原[4]。转化生长因子β1(transforming growth factor β1,TGF-β1)通过促进胶原的转录继而导致胶原表达增加[5];同时,在肺纤维化的肺组织中,胶原的降解能力也是被显著抑制的[3, 6]。因此,恢复肺组织中胶原的降解能力,有可能成为治疗肺纤维化疾病的新思路。
自噬是细胞的一种自我代谢过程,有利于细胞在外界刺激下维持自身稳态平衡。近来有报道指出,在肺纤维化疾病中,自噬是降解胶原的主要方式[3, 6]。Fernandez 和Eickelberg[7]直接指出,在多种肺部疾病中,自噬是组织细胞维持代谢平衡、促进细胞生存的主要机制。上述研究报道均是在动物模型中探讨自噬的活性与肺纤维化发生的关系,目前仍缺乏在细胞水平,尤其是在成纤维细胞中,自噬活化可以促进胶原降解的证据。
糖原合成激酶 3β(glycogen synthase kinase 3β,GSK3β)是一种丝氨酸-苏氨酸蛋白激酶,可以参与调控多种细胞活动,其中包括能量代谢、神经细胞的形成及发育等。我们的前期工作表明,GSK3β 的小分子抑制剂SB216763 可以通过促进 Bcl-2 与 GSK3β 的结合,抑制 Bcl-2 与 Beclin-1 的结合,激活自噬核心复合物,从而上调自噬的活性[8]。然而,SB216763 能否通过活化自噬改善成纤维细胞中胶原的含量仍需要进一步证实。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 实验细胞 3T3-NIH 细胞购于中国医学科学基础医学研究所细胞培养中心,细胞使用DMEM培养基,10% FBS 培养,每隔 2 天传代一次,细胞培养条件为 37 ℃、5% CO2。
1.1.2 主要试剂 DMEM 细胞培养基、进口血清FBS 和胰酶购于美国 Gibco 公司;天狼猩红染色试剂盒购于英国 Biocolor 公司;SB216763、雷帕霉素及抗小鼠 p62 购于美国 Sigma-Aldrich 公司;抗小鼠 β-actin、Beclin-1、Vps34 抗体购自美国 Cell Signaling Technology 公司;I 型胶原抗体购于英国 Abcam 公司;RIPA 裂解液、BCA 蛋白浓度定量试剂盒购于碧云天生物科技研究所。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 天狼猩红染色检测 I 型胶原 根据文献[6]的方法,使用转化生长因子 TGF-β1 以不同的剂量(0、5 和 10 ng/ml)作用于小鼠成纤维细胞 48 h 后,收集细胞,4 ℃、600 ×离心 20 min 后取上清,按照胶原检测试剂盒说明书检测胶原含量。
1.2.2 Western blot 取适量培养细胞,加入 RIPA 裂解液后振荡混匀,冰上放置 30 min,间或振荡;4 ℃、4560 ×条件下离心 15 min。取上清,使用蛋白定量试剂盒测定蛋白浓度,其具体步骤参照说明书进行。调节蛋白至相同浓度,分装,加入 5 倍上样缓冲液,96 ℃变性 10 min,一部分用于 SDS 电泳,一部分–80 ℃保存[3];使用 Amersham 显色系统显色,经 Western blot 印迹分析软件测出各条带的光密度值并进行分析[6]。
1.3 统计学处理
2 结果
2.1 TGF-β1 促进小鼠成纤维细胞中胶原的产生
实验结果显示,给予TGF-β1 后,细胞培养上清中胶原含量从(11.85 ± 0.90)mg/ml 上升至(16.70 ± 0.67)mg/ml,说明 TGF-β1 可以剂量依赖地促进小鼠成纤维细胞分泌胶原(图 1A);同时,对成纤维细胞中胶原的表达量检测发现,TGF-β1 可以剂量依赖地增加小鼠成纤维细胞胞内 I 型胶原以及 α-SMA 的表达(图 1B)。以上结果说明,TGF-β1 可以促进成纤维细胞中胶原的产生。
2.2 TGF-β1 抑制小鼠成纤维细胞中自噬的活化
在单独给予雷帕霉素(100 ng/ml)诱导自噬活化时,成纤维细胞中自噬活化蛋白 Vps34 以及Beclin-1 的表达增加,自噬活化蛋白 p62 表达有所降低,说明自噬被活化;而在给予 TGF-β1(5 ng/ml)后,Vps34 以及 Beclin-1 的表达水平有所降低,p62 表达升高,说明自噬的活性下降(图 2)。以上的结果表明,TGF-β1 可以抑制雷帕霉素诱导的自噬活化。

图 1 TGF-β1 诱导小鼠成纤维细胞中胶原的产生(A:天狼猩红染色;B:Western blot)
Figure 1 Type I collagen was induced by TGF-β1 (A: Sirius red staining; B: Western blot)
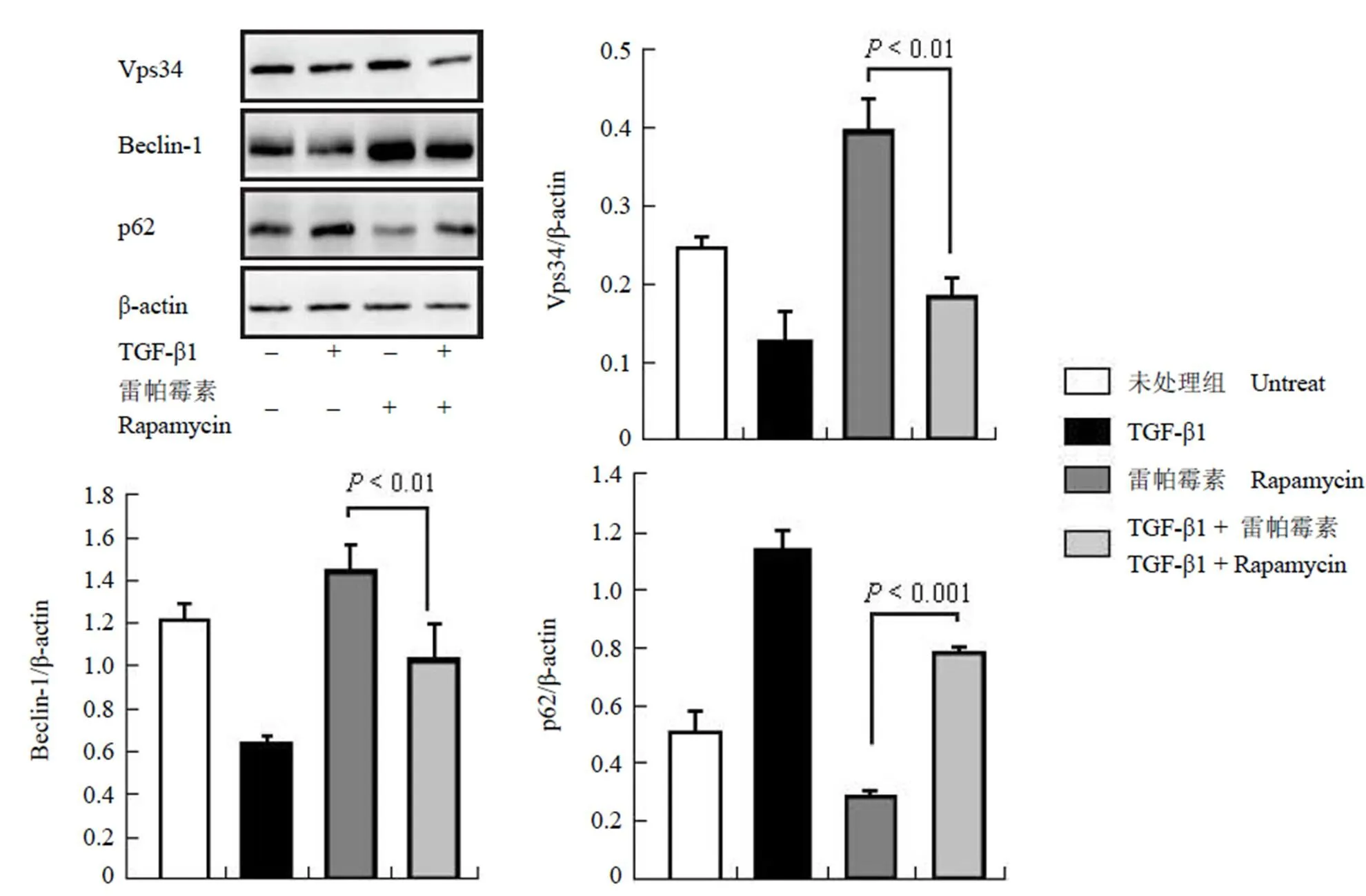
图 2 TGF-β1 抑制小鼠成纤维细胞中自噬的活化
Figure 2 Autophagy-related proteins were regulated by TGF-β1 in mouse fibroblast cells
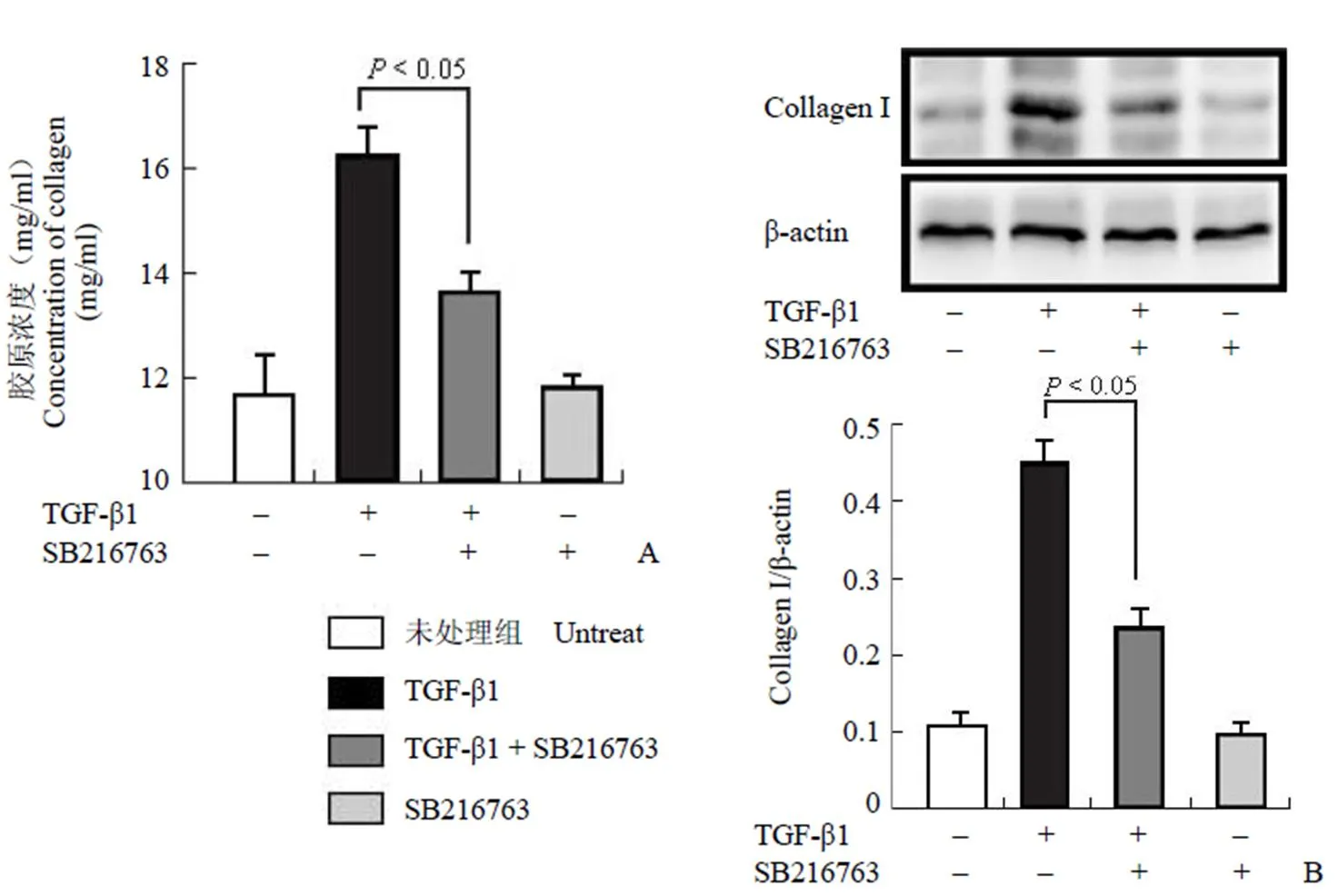
图 3 SB216763 抑制 TGF-β1 诱导的胶原产生(A:天狼猩红染色;B:Western blot)
Figure 3 Increased type I collagen by TGF-β1 was reduced by SB216763 (A: Sirius red staining; B: Western blot)
2.3 小分子抑制剂 SB216763 抑制 TGF-β1 诱导的胶原产生
给予 TGF-β1(5 ng/ml)以及 SB216763(10 μmol/L)共同作用 48 h 后,我们发现细胞培养上清中胶原的含量从(16.83 ± 0.47)mg/ml 下降为(13.16 ± 0.45)mg/ml,说明 SB216763 可以降低 TGF-β1 诱导的胶原分泌(图 3A);此外,我们对小鼠成纤维细胞胞内 I 型胶原进行检测,结果显示,SB216763 可以降低小鼠成纤维细胞胞内 I 型胶原的含量(图 3B)。以上的结果说明,在小鼠成纤维细胞中,SB216763 可以抑制 TGF-β1 诱导的胶原产生。
2.4 小分子抑制剂 SB216763 恢复成纤维细胞中自噬的活性
在 TGF-β1 诱导胶原表达的同时给予SB216763 刺激后,检测自噬相关蛋白的表达。我们发现,自噬相关蛋白 Vps34 及 Beclin-1 的表达水平有所降低,p62 表达升高,说明自噬的活性下降;而在给予 SB216763 刺激时,成纤维细胞中 Vps34 及 Beclin-1 的表达增加,p62 的表达有所降低,说明自噬被活化(图 4)。以上的结果表明,SB216763 可以恢复自噬活性。
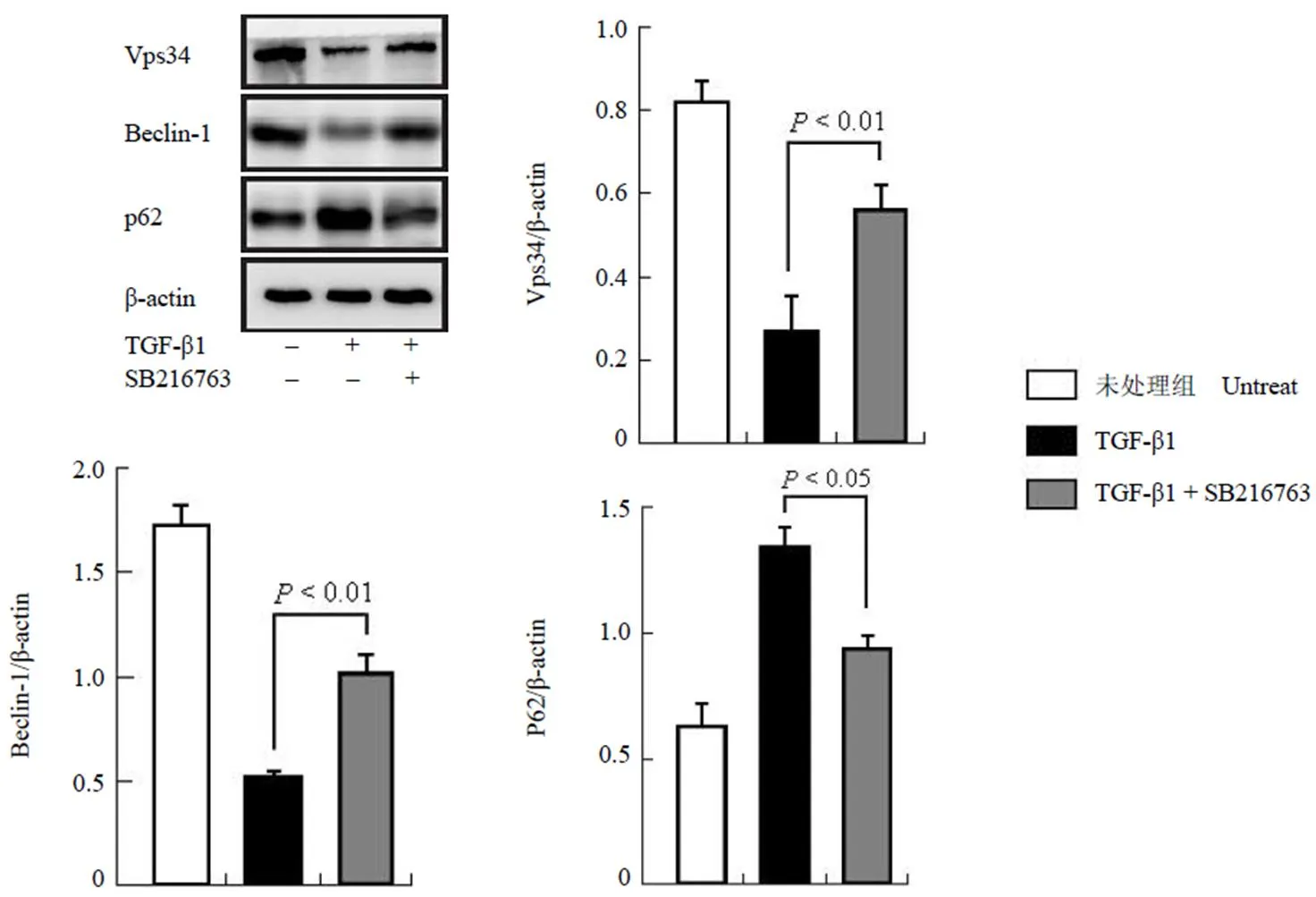
图 4 SB216763 恢复小鼠成纤维细胞中自噬的活化
Figure 4 Autophagy-related proteins were regulated by SB216763 in mouse fibroblast cells
3 讨论
组织纤维化是许多慢性疾病致残和致死的主要原因,组织损伤是纤维化的始动环节。当疾病的病程较短、组织受损伤较小时,受损组织周边的正常实质细胞或少量的间质细胞发生反应性增生,促进损伤被修复,恢复正常组织结构和功能,不会导致纤维化病理过程;如果组织受损伤严重,大量组织细胞坏死,会导致器官功能的衰竭,引起坏死后硬化或机体死亡;如果损伤长时间不愈合,反复出现细胞损伤坏死,超出了周围正常实质/间质细胞的修复能力,则会造成实质/间质细胞不断增生以修复受损的组织,即发生纤维化病理过程[9]。在上述过程中,受到损伤的组织(细胞)主要是指 3 种细胞,即成纤维细胞、上皮细胞和单核细胞[9]。其中,成纤维细胞是胶原沉积过程中胶原的主要来源[3]。因此,我们选择了在成纤维细胞中观察 SB216763 对胶原分泌的影响。
TGF-β1 在肺纤维化的过程中发挥了重要的作用。一方面,TGF-β1 可以活化核转录因子,调节相关启动子区组件,从而启动胶原和纤连蛋白基因转录[10],促进胶原的表达;另一方面,TGF-β1 还通过抑制胶原降解的过程,进一步加重胶原的沉积:增加自噬活性可以促进胶原的降解,从而改善组织中胶原的沉积[3, 6];然而,在特发性肺纤维化患者的肺组织中,自噬活性是被显著抑制的,TGF-β1 可以通过激活 mTORC1 抑制纤维母细胞中自噬的活性[11]。上述研究表明,TGF-β1 可以通过增加胶原转录及抑制胶原通过自噬途径降解两方面,共同促进胶原的沉积。
目前,已有证据表明 SB216763 可以调节纤维化疾病的发生发展。有研究指出,SB216763 可以改善由博来霉素诱导的小鼠急性肺纤维化,同时降低炎性细胞因子[12],但却不能影响肺纤维化组织中胶原的转录水平[8],说明SB216763 是有可能通过促进胶原降解降低胶原的表达。在体外培养的人肺成纤维细胞中,SB216763 可以抑制 TGF-β1 诱导的肌成纤维细胞标志物,抑制成纤维细胞的活化[13]。然而,也有报道指出,SB216763 可以通过激活 Wnt/β-caternin 信号通路加重皮肤纤维化[14]。以上的研究表明,SB216763 对纤维化疾病的调节作用可能存在组织差异性。
大量文献表明,自噬活性与胶原的降解密切相关[3, 6]。Kim 等[15]也指出在肾纤维化中,TGF-β1 可以诱导胶原的产生,而活化自噬可以促进胞外胶原的降解。在本研究中,我们发现SB216763 可以通过诱导多种自噬相关蛋白的产生(例如Beclin-1、Vps34 以及 p62),从而激活自噬的活化。Zhou 等[16]发现在缺血损伤的大鼠脑组织中,SB216763 可以促进LC3-II 的表达,增加 LC3 点状聚集,从而改善其脑损伤情况。然而,也有报道表明,在具有耐药性的慢性骨髓性白血病细胞中,SB216763 可以通过增加 Atg5 以及 mTOR 的蛋白表达水平,从而降低自噬的活性[17]。以上研究表明,SB216763 在纤维化疾病以及肿瘤中对自噬的活性具有不同的调节作用,这可能是由于 SB216763 抑制GSK3β 的活性后,导致一种生长因子被剥夺的生理状态,而这种状态在纤维化疾病以及肿瘤组织中会对自噬产生截然不同的影响。
自噬核心复合物在自噬的活化过程中发挥了重要的作用。在静息状态下,Bcl-2 通过BH3 结构域与 Beclin-1 结合,抑制自噬的活化[18]。尽管 SB216763 可以抑制 Bcl-2 的降解[19],但是,SB216763 可以通过促进 Bcl-2 与 GSK3β 的结合,抑制 Bcl-2 与 Beclin-1 的结合,激活自噬核心复合物,从而活化自噬的发生[8]。我们的结果显示,SB216763 还可以通过调节自噬相关蛋白 Vps34、Beclin-1 以及 p62 的表达影响自噬的活化,上述研究补充了 SB216763 调控自噬活化的分子机制。
在本文中,我们发现在小鼠成纤维细胞中,GSK3β 抑制剂 SB216763 可以通过增加自噬相关蛋白的表达,激活自噬的发生,促进胶原的降解,最终改善由 TGF-β1 诱导的胶原分泌。本研究表明,使用小分子化合物 SB216763 适度激活自噬的活性,可以为改善肺纤维化提供新的治疗思路与方案。
[1] Wynn TA. Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. J Exp Med, 2011, 208(7):1339-1350.
[2] Noble PW, Barkauskas CE, Jiang D. Pulmonary fibrosis: patterns and perpetrators. J Clin Invest, 2012, 122(8):2756-2762.
[3] Yang HZ, Wang JP, Mi S, et al. TLR4 activity is required in the resolution of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis after acute and chronic lung injury. Am J Pathol, 2012, 180(1):275-292.
[4] Kravis TC, Ahmed A, Brown T, et al. Pathogenic mechanisms in pulmonary fibrosis: collagen-induced migration inhibition factor production and cytotoxicity mediated by lymphocytes. J Clin Invest, 1976, 58(5):1223-1232.
[5] Gressner AM, Weiskirchen R, Breitkopf K, et al. Roles of TGF-beta in hepatic fibrosis. Front Biosci, 2002, 7:d793-d807.
[6] Mi S, Li Z, Yang HZ, et al. Blocking IL-17A promotes the resolution of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis via TGF-beta1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Immunol, 2011, 187(6):3003-3014.
[7] Fernandez IE, Eickelberg O. New cellular and molecular mechanisms of lung injury and fibrosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet, 2012, 380(9842):680-688.
[8] Liu H, Mi S, Li Z, et al. SB216763, a selective small molecule inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase-3, improves bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via activating autophagy. Acta Pharm Sinica B, 2013, 3(4):226-233.
[9] Liu H, Xie Q, Li YZ, et al. The overexpression of tribbles homolog 3 promotes the secretion of collagen I in mouse fibroblast cell. Chin Med Biotechnol, 2014, 9(1):37-42. (in Chinese)
刘虹, 谢琼, 李勇枝, 等. 过表达Tribbles同源蛋白3促进成纤维细胞分泌I型胶原的研究. 中国医药生物技术, 2014, 9(1):37-42.
[10] Dai C, Liu Y. Hepatocyte growth factor antagonizes the profibrotic action of TGF-beta1 in mesangial cells by stabilizing Smad transcriptional corepressor TGIF. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2004, 15(6): 1402-1412.
[11] Patel AS, Lin L, Geyer A, et al. Autophagy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS One, 2012, 7(7):e41394.
[12] Gurrieri C, Piazza F, Gnoato M, et al. 3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-(1- methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione (SB216763), a glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor, displays therapeutic properties in a mouse model of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2010, 332(3):785-794.
[13] Baarsma HA, Engelbertink LH, van Hees LJ, et al.Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) regulates TGF-β1-induced differentiation of pulmonary fibroblasts. Br J Pharmacol, 2013, 169(3):590-603.
[14] Bergmann C, Akhmetshina A, Dees C, et al. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3β induces dermal fibrosis by activation of the canonical Wnt pathway. Ann Rheum Dis, 2011, 70(12):2191-2198.
[15] Kim SI, Na HJ, Ding Y, et al. Autophagy promotes intracellular degradation of type I collagen induced by transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287(15):11677-11688.
[16] Zhou X, Zhou J, Li X, et al. GSK-3β inhibitors suppressed neuroinflammation in rat cortex by activating autophagy in ischemic brain injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2011, 411(2):271-275.
[17] Reddiconto G, Toto C, Palamà I, et al. Targeting of GSK3β promotes imatinib-mediated apoptosis in quiescent CD34+ chronic myeloid leukemia progenitors, preserving normal stem cells. Blood, 2012, 119(10):2335-2345.
[18] Sinha S, Levine B. The autophagy effector Beclin 1: a novel BH3-only protein. Oncogene, 2008, 27 Suppl 1:S137-S148.
[19] Liu H, Mi S, Li Z, et al. Interleukin 17A inhibits autophagy through activation of PIK3CA to interrupt the GSK3B-mediated degradation of BCL2 in lung epithelial cells. Autophagy, 2013, 9(5):730-742.
GSK3β inhibitor SB216763 suppresses the expression and secretion of TGF-β1-induced collagen I through stimulating autophagy-related proteins in mouse fibroblast cells
LIU Hong, WANG Jia-ping, XIN Bing-mu, SHAO Rong-guang
The aim of this study is toinvestigate the effects of SB216763 on the expression and secretion of type I collagen in mouse fibroblast 3T3-NIH cells.
Type I collagen was induced by treatment with TGF-β1, and the expression of type I collagen was detected by Sirius red staining kit and Western blot. Autophagy related proteins were detected by Western blot.
TGF-β1 dose-dependently induced the expression and secretion of type I collagen from (11.85 ± 0.90)mg/ml to (16.70 ± 0.67)mg/ml (< 0.001) in 3T3-NIH cells. Meanwhile, TGF-β1 affected the expressions of autophagy-related proteins, as shown by the decrease of Vsp34 and Beclin-1, and the increase of p62. In contrast, SB216763 markedly reduced the expression and secretion of type I collagen from (16.83 ± 0.47)mg/ml to (13.16 ± 0.45)mg/ml (< 0.05). Moreover, SB216763 restored the levels of Vsp34 and Beclin-1, and down-regulated the expression of p62 in TGF-β1-treated cells.
SB216763 suppresses the expression and secretion of thetype I collagen induced by TGF-β1 through stimulating autophagy-related proteins in mouse fibroblast cells.
Autophagy; Collagen type I; Transforming growth factor beta 1; SB216763
SHAO Rong-guang, Email: shaor@imb.pumc.edu.cn
10.3969/cmba.j.issn.1673-713X.2014.06.001
国家自然科学基金(31401186);“重大新药创制”国家科技重大专项(2012ZX09301002-001- 015);中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务专项(IMBF201407)
邵荣光,Email:shaor@imb.pumc.edu.cn
2014-04-22
Author Affiliations: Department of Oncology, Institute of Medicinal Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100050, China (LIU Hong, SHAO Rong-guang); State Key Laboratory of Space Medicine Fundamentals and Application, China Astronaut Research and Training Centre, Beijing 100094, China (WANG Jia-ping, XIN Bing-mu)
