NF-κB抑制剂PDTC对人白血病Jurkat细胞凋亡及MMP-9表达的影响
2014-09-14付利李业成苏毅孙浩平帅燕容夏焱
付利,李业成,苏毅,孙浩平,帅燕容,夏焱
(1.成都军区总医院血液内科,四川成都610083;2.中山大学第二附属医院,广东广州510120)
NF-κB抑制剂PDTC对人白血病Jurkat细胞凋亡及MMP-9表达的影响
付利1,李业成1,苏毅1,孙浩平1,帅燕容1,夏焱2
(1.成都军区总医院血液内科,四川成都610083;2.中山大学第二附属医院,广东广州510120)
目的研究NF-κB特异性抑制剂吡咯烷二硫代氨基甲酸(pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate,PDTC)对Jurkat细胞凋亡及基质金属蛋白酶-9(matrxmetallo preteinases-9,MMP-9)基因表达的影响,探讨转录因子NF-κB与MMP-9在白血病发生发展及浸润转移过程中的作用及2者之间的关系。方法取处于对数生长期的Jurkat细胞随机分为6组,包括对照组(培养基中不含PDTC),试验组(培养基中分别含有50、100、150μmol/LPDTC、1μg/mL VCR、1μg/mL VCR+150μmol/L PDTC);MTT法测定PDTC对Jurkat细胞增殖的抑制作用;使用流式细胞术(flow cytometry,FCM)检测PDTC联合长春新碱(vincristine oncovin,VCR)诱导Jurkat细胞凋亡的情况;使用半定量RT-PCR检测Jurkat细胞中MMP-9基因的表达。结果不同浓度的PDTC(50、100、150μmol/L)作用不同时间(12~48 h)后对Jurkat细胞的增殖抑制率随PDTC浓度的增高及作用时间的延长而逐渐增加(P<0.05),但在PDTC处理48 h后,细胞增殖抑制率无明显增加。在不同浓度的PDTC分别处理细胞48 h后,随着PDTC浓度增高,Jurkat细胞凋亡率逐渐增加,各实验组凋亡率显著高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。与单纯VCR组相比,VCR+PDTC组Jurkat细胞凋亡率显著增高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),显示PDTC可以增强VCR诱导的Jurkat细胞凋亡作用。不同浓度的PDTC分别处理各组细胞48 h,RT-PCR结果显示各实验组细胞MMP-9基因表达水平与对照组相比明显降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论白血病细胞中存在MMP-9基因高表达,导致细胞基底膜及细胞外基质降解,促进了白血病的浸润和转移,并引起化疗耐药,而这一过程可被NF-κB抑制剂PDTC所抑制,为临床上白血病的治疗探索了一条新的途径。
NF-κB;PDTC;基质金属蛋白酶-9;Jurkat细胞
目前对于白血病患者最常用的治疗方法是化疗,大多数患者通过化疗可得到缓解,但近年来由于耐药问题的存在,部分患者因为化疗失败而导致死亡[1-3]。在儿童白血病中,最常见的为急性淋巴细胞白血病(acute lymphocytic leukemia,ALL),近年来广泛开展的造血干细胞移植(hematopoietic stem cell transplantation,HSCT)以及不断改进的化疗方案,明显提高了儿童ALL的治愈率,德国研究组统计其总的长期治愈率超过75%[4-8]。但仍存在部分患儿对化疗不敏感,有研究显示,这类患儿化疗失败的主要原因是对治疗药物产生了耐药[9]。如何使这类难治性白血病达到临床完全缓解(complete remission,CR)和长期无病生存(disease free survival,DFS),成为目前儿童白血病研究的重点和难点[10]。
本研究旨在通过体外实验的方法,采用NF-κB特异性抑制剂PDTC作用于Jurkat细胞,检测其对细胞凋亡及MMP-9基因表达的影响,探讨转录因子NF-κB与MMP-9在白血病发生发展及浸润转移过程中的作用及2者之间的关系;另外,通过观察PDTC联合化疗药物VCR对Jurkat细胞凋亡的影响,探讨PDTC在白血病治疗中的潜在价值,为临床应用PDTC治疗儿童难治性ALL提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料 细胞株:人急性T淋巴细胞白血病细胞株Jurkat细胞,由中山医学院细胞中心提供。
主要试剂:长春新碱(VCR)、四甲基偶氮唑蓝(MTT)、二甲基亚砜(DMSO)、PDTC,美国Sigma公司;RPMI1640,美国Gibco公司;胎牛血清(FBS),杭州四季青生物材料公司;焦炭酸二乙酯(DEPC),美国Promega公司;RT-PCR试剂盒,天为时代;Annexin V-FITC试剂盒,武汉晶美生物公司;DNA Marker TaKaRa,生物技术有限公司;Trizol,Invitrogen公司;碘化丙锭,美国库尔特公司;双抗(青霉素、链霉素),华北制药厂;异丙醇、氯仿,武汉联碱厂;琼脂糖,亚法生物试剂公司;无水乙醇,上海振兴化工厂。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 细胞培养 Jurkat细胞生长在含5mLRPMI1640培养基(内含10%FBS及双抗)的无菌细胞培养瓶中,将培养瓶置于37℃,5%CO2,相对湿度为90%的培养箱中进行细胞培养,24 h后更换一次培养液,以后每隔2~3 d进行1次细胞传代,取处于对数生长期的细胞作为实验对象。
1.2.2 实验分组 取处于对数生长期的Jurkat细胞随机分为以下6组:对照组培养基中既不含PDTC,又不含VCR;试验组1:培养基中不含VCR,PDTC浓度为50μmol/L;试验组2:培养基中不含VCR,PDTC浓度为100μmol/L;试验组3:培养基中不含VCR,PDTC浓度为150μmol/L;试验组4:培养基中不含PDTC,VCR浓度为1μg/mL;试验组5:培养基中PDTC浓度为150μmol/L,VCR浓度为1μg/mL。
1.2.3 四甲基偶氮唑蓝(MTT)法测定PDTC对Jurkat细胞增殖的抑制作用 取处于对数生长期的Jurkat细胞,更换新鲜培养液,调整细胞浓度为1×105个/mL,接种于48孔培养板,每孔加入含10%FBS的RPMI1640培养液及PDTC,使PDTC的终浓度分别为0、50、100、150μmol/L,每一个PDTC浓度设4个重复孔,将加好药的培养板置于37℃、5%CO2、饱和相对湿度为90%的培养箱中进行培养,培养时间分别为12、24、36、48 h,在距离培养结束4 h时,于每孔中均加入浓度为5 mg/m L的MTT液10μL,继续培养4 h后,离心培养板(1000 r/min,4min),弃上清液,每孔加入150μL DMSO,置于微孔板振荡器上振荡10min,完全溶解结晶物,于波长570nm处使用自动酶标仪测定各孔OD值,实验共重复4次,实验结果取每次独立实验数据的平均值。其中细胞生长抑制率计算公式为:细胞增殖抑制率=(1-实验孔OD值/对照孔OD值)×100%。
1.2.4 流式细胞术(FCM)检测PDTC联合长春新碱(VCR)诱导Jurkat细胞凋亡的情况 将细胞浓度为1×106个/mL的Jurkat细胞接种于6孔板的6个孔中,依次加入药物及培养基,使得每孔中最终的药物浓度如1.2.2分组所示数值,常规培养48 h,收集各组细胞,分别加入1 mL PBS液,轻轻震荡使细胞悬浮,4℃离心(1000 r/min,5min),小心弃去上清液。重复操作2次后,加入190μL结合缓冲液并轻轻震荡使细胞重新悬浮,滴入10μL Annexinv-FITC,混匀,4℃避光静置30min,离心(1000 r/min,5min),弃上清液,再次加入190μL结合缓冲液使细胞重悬,滴入10μL PI,轻轻震荡混匀,上流式细胞仪进行检测。重复试验3次。记录实验数据并进行凋亡率分析。
1.2.5 半定量RT-PCR检测Jurkat细胞中MMP-9基因的表达 取每组标本的PCR扩增产物各5μL,分别与5μL的β-actin PCR扩增产物及2μL的Loading Buffer经吹打混合均匀后,依次加入琼脂糖凝胶板的上样孔中并做好标记,另选一孔加入5μL DNA Marker作为标准分子量对照。连接电源进行电泳,设置电压100V,时间50min。应用凝胶图像分析系统对各电泳条带进行分析,结果以各组目的基因PCR产物光密度与β-actin PCR产物光密度的比值表示。每组标本重复进行4次实验取平均值。
1.3 统计学方法 使用SPSS16.0软件进行统计学处理;实验结果的数据以“±s”表示,2组间均值的比较采用t检验;多组间均值的比较首先使用单因素方差分析,两两组间的均值比较使用LSD-t检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 PDTC对Jurkat细胞增殖的影响 PDTC对Jurkat细胞的增殖抑制率在各组之间有明显统计学差异(P<0.05)。PDTC在体外对Jurkat细胞增殖的抑制率,随药物浓度的增加及作用时间的延长,呈增加趋势,显示在一定浓度和时间范围内,PDTC对Jurkat细胞增殖的抑制作用呈时间-剂量依赖性(见表1)。
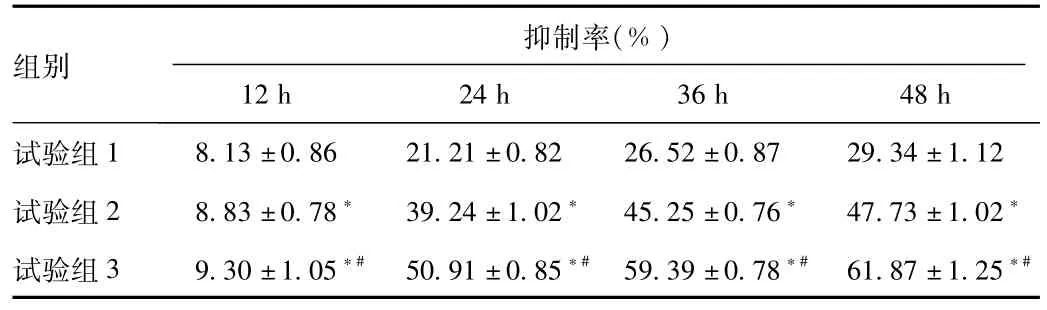
表1 PDTC对人白血病Jurkat细胞增殖的抑制作用Tab.1 Inhibitory effect of PDTC on Jurkat cell proliferation
2.2 PDTC对Jurkat细胞凋亡的影响 按分组进行加药,不同浓度的PDTC分别处理各组细胞48 h后,流式细胞术(FCM)检测各组细胞凋亡情况。结果显示,细胞凋亡率随PDTC浓度的增高而增加,浓度分别为50、100、150μmol/L的PDTC作用于Jurkat细胞48 h后,其凋亡率均显著高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),且不同浓度组间比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。VCR组和VCR+PDTC组Jurkat细胞凋亡率相比,VCR+PDTC组Jurkat细胞凋亡率显著高于VCR组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01,见表2)。
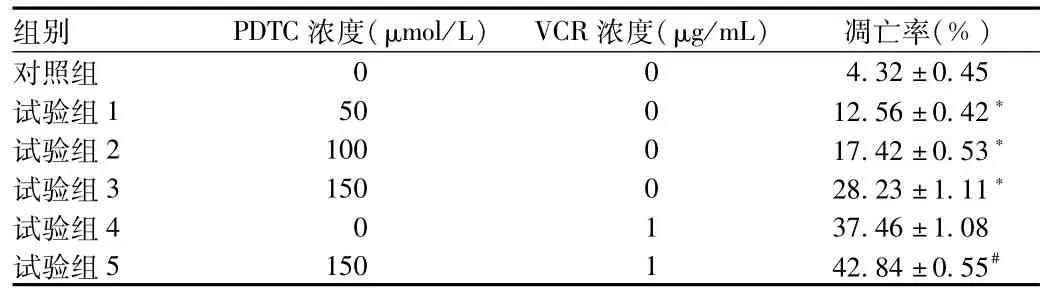
表2 经培养48 h后各实验组Jurkat细胞凋亡率Tab.2 Jurkat cell apoptosis rate in different experimental groups after being cultured for 48 h
2.3 PDTC对Jurkat细胞MMP-9表达的影响 半定量RTPCR结果表明:浓度分别为50、100、150μmol/L的PDTC作用于Jurkat细胞48 h后,各试验组组细胞MMP-9基因表达水平与对照组相比均显著降低(P<0.05),且随PDTC浓度的增高,MMP-9基因表达水平逐渐降低,不同PDTC浓度组间比较差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),说明Jurkat细胞中MMP-9基因表达水平与PDTC浓度成负相关(见图1),而PDTC下调Jurkat细胞中MMP-9基因表达水平可能是通过抑制NF-κB活性实现的。
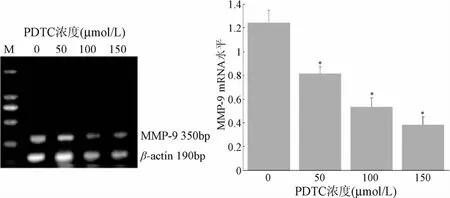
图1 PDTC对Jurkat细胞MMP-9 mRNA表达的影响*P<0.05,与对照组(0μmol/L)比较Fig.1 Effect of PDTC on the expression ofmRNA in Jurkat cells *P<0.05,compared with the control group(0μmol/L)
3 讨论
PDTC是一种氨基甲酸盐类抗氧化剂,通过螯合金属离子,清除活性氧中间产物(ROI)而发挥抗氧化作用。PDTC同时也是NF-κB特异性抑制剂,能够通过阻止IκB的磷酸化降解,阻碍NF-κB的p65和p50亚基向细胞核内转移等多种途径抑制NF-κB的活化[10-15]。
本研究通过观察不同浓度PDTC对Jurkat细胞增殖的抑制作用,阐明了PDTC可以通过抑制NF-κB的活性而抑制Jurkat细胞的生长。流式细胞术的结果进一步证实了PDTC可诱导Jurkat细胞凋亡,并可增强VCR的抗癌作用,且与剂量呈正相关。本研究通过半定量RT-PCR技术检测了不同浓度PDTC处理后Jurkat细胞MMP-9的表达水平,证实PDTC可能通过抑制NF-κB的活性下调Jurkat细胞MMP-9基因的表达,进而诱导细胞凋亡,抑制白血病的浸润转移,降低白血病细胞的化疗耐药性,为临床使用PDTC治疗白血病提供了理论依据。
目前已证实,在肺癌、黑色素瘤等多种肿瘤中NF-κB能够促进MMP-9基因的表达[16-18]。相关体外研究发现,侵袭性较高的癌细胞系通过上调MMP-9基因的表达水平及其活性的激活,而促进癌细胞的移动[19-20]。另有大量研究证实,MMP-9在白血病细胞跨内皮下基膜向髓外浸润中起重要作用。
综上所述,本研究为临床上白血病的治疗探索了一条新的途径。白血病细胞中存在的MMP-9基因高表达,导致细胞基底膜及细胞外基质降解,促进了白血病的浸润和转移,并引起化疗耐药,而这一过程可被NF-κB抑制剂PDTC所抑制,这一发现对治疗儿童难治性ALL具有重要参考价值。但ALL的发生、发展以及预后涉及到多个基因多条信号转导途径的异常激活,这些异常表达基因的具体作用及作用机制尚有待进一步深入研究。
[1]StanullaM,Cario G,Meissner B,etal.Integratingmolecular information into treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia—A perspective from the BFM Study Group[J].Blood Cells,Molecules,and Diseases,2007,39(2):160-163.
[2]Vormoor J.A new subgroup of high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia[J].The Lancet Oncology,2009,10(2):101-103.
[3]Von Stackelberg A,Hartmann R,Bührer C,et al.High-dose compared with intermediate-dosemethotrexate in children with a first relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia[J].Blood,2008,111(5):2573-2580.
[4]Mehta PA,Gerbing RB,Alonzo TA,et al.FAS promoter polymorphism:outcome of childhood acute myeloid leukemia.A children's oncology group report[J].Clinical Cancer Research,2008,14(23):7896-7899.
[5]Parsons SL,Watson SA,Collins HM,et al.Gelatinase(MMP-2 and-9)expression in gastrointestinalmalignancy[J].British Journal of Cancer,1998,78(11):1495-1502.
[6]Lenz O,Elliot SJ,Stetler-Stevenson WG.Matrix metalloproteinases in renal development and disease[J].JAm Soc Nephro,2000,11(3):574-581.
[7]Aggarwal BB,Takada Y,Shishodia S,et al.Nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B:role in biology and medicine[J].Indian Journal of Experimental Biology,2004,42(4):341-353.
[8]Chen ZJ,Parent L,Maniatis T.Site-specific phosphorylation of IkBa by a novel ubiquitination-dependent protein kinase activity[J].Cell,1996,84(6):853-862.
[9]Higuchi Y,Chan TO,Brown MA,et al.Cardioprotection afforded by NF-kappaB ablation is associated with activation of Aktinmice overexpressing TNF-alpha[J].J Am Coll Cardid,2006,290(2):590-588.
[10]Bruck R,Schey R,Aeed H,et al.A protective effect of pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate in a rat model of liver cirrhosis[J].Liver Int,2004,24(2):169-176.
[11]Dolcet X,Llobet D,Pallares J,et al.NF-κB in development and progression of human cancer[J].VirchowsArchiv,2005,446(5):475-482.
[12]Lee CH,Jeon YT,Kim SH,et al.NF-kappaB as a potentialmolecular target for cancer therapy[J].Biofactors,2007,29(1):19-35.
[13]Liu J,Yang G,Thompson Lanza JA,et a1.A genetically defined model for human ovarian cancer[J].Cancer Res,2004,64(5):1655-1663.
[14]Chen F,Castranova V,Shi X.New insights into the role of nuclear factor-kappaB in cell growth regulation[J].Am J pathol,2001,159(2):387-397.
[15]Siriwardena BS,Kudo Y,Ogawa I,et al.VEGF-C is associated with lymphatic statusand invasion in oral cancer[J].JClin pathol,2008,61(1):103-108.
[16]Shi shodia S,Potdar P,Gairola CG,et al.Curcumin(diferuloylmethane)down-regulatescigarette smoke-induced NF-κB activation through inhibition of IκB kinase in human lung epithelial cells correlation with suppression of COX-2,MMP-9 and cyclin D1[J].Carcinogenesis,2003,24(7):1269-1279.
[17]Rhee JW,Lee KW,Kim D,et al.NF-kappaB-dependent regulation of matrixmetalloproteinase-9 gene expression by lipopolysaccharide in a macrophage cell line RAW264[J].J Cell Biochem,2007,40(1):88-94.
[18]Ko HM,Kang JH,Jung B,et al.Critical role for matrix metalloproteinase-9 inplatelet-activating factor-induced experimental tumormetastasis[J].Int JCancer,2007,120(6):1277-1283.
[19]Maity G,Choudhury PR,Sen T,et a1.Culture of human breast cancer cell line(MDA-MB-231)on fibronectin-coated surface induces promatrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and activity[J].Tumor Biol,2011,32(1):129-138.
[20]Jensen SA,Vainer B,Bartels A,et a1.Expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9(MMP-9)andtissue inhibitor ofmetalloproteinases 1(TIMP-1)by colorectal cancer cells and adjacent stromacells associations with histopathology and patients outcome[J].Eur J Cancer,2010,46(18):3233-3242.
(编校:吴茜,刘路路)
Effect of PDTC,an inhibitor of NF-κB,on apoptosis and expression of MMP-9 in human acute lymphocytic leukem ia Jurkat cells
FU Li1,LIYe-cheng1,SU Yi1,SUN Hao-ping1,SHUAIYan-rong1,XIA Yan2
(1.Department of Hematology,General Hospital of Chengdu Military Region,Chengdu 610083,China;2.Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhongshan University,Guangzhou 510120,China)
ObjectiveTo investigate the effect of PDTC,a specific inhibitor of NF-κB,on cell apoptosis of Jurkat cell and expression of MMP-9 in Jurkat cell,and investigate the relationship between NF-κB and MMP-9 in genesis,development,infiltration and metastasis of leukemia.MethodsJurkat cells in logarithmic growth phase were divided into six groups randomly,including control group in which the culturemedium was free of PDTC,and experimental groups in which Jurkat cellswere treated respectively with 50,100,150μmol/L of PDTC,1μg/mL of VCR,1μg/mL of VCR and 150μmol/L of PDTC.MTT assay was performed to evaluate the inhibition effect of PDTC on the proliferation of Jurkat cells.The apoptosis rate of Jurkat cells induced by the PDTC with VCR were detected by FCM.The expression of MMP-9 in Jurkat cellswere detected by semi-quantitative RT-PCR.ResultsAfter being treated with different concentrations of PDTC,the proliferation inhibition rate of PDTC on Jurkat cell increased with the raise of PDTC concentration and time extension.However,after being treated with PDTC for 48 hours,there was no obvious growth of proliferation inhibition rate,which showed the inhibitory effect of PDTC depending on time and dose within a certain range of concentration and time.The experimental group with high dose of PDTC presented highest inhibitory effect.After being treated with PDTC for 48 hours,apoptosis rate of Jurkat cell increased with the raise of PDTC concentration.Apoptosis rate of experimental groups were significantly higher than control group(P<0.05). Compared with VCR group,the apoptosis rate of VCR+PDTCwas significantly higher than VCR group(P<0.05),which showed PDTC could enhance induction of VCR in the aspect of promoting apoptosis.After being treated with different concentrations of PDTC,levels of MMP-9 mRNA were detected by RT-PCR.The results showed that levels of MMP-9 mRNA in experimental groups were significantly lower than control group(P<0.05).Conclusion This study explores a new way for the clinical treatment of leukemia.The high expression of MMP-9 gene existed in leukemia cells leads to degradation of cellbasementmembrane and extracellularmatrix,promotes leukemic infiltration andmetastasis,causes chemotherapy resistance,and this process can be inhibited by PDTC.This discovery isworthy of reference for treatment of children with ALL.
NF-κB;PDTC;MMP-9;Jurkat cell
R725.5
A
1005-1678(2014)08-0008-04
国家自然科学基金(30872785)
付利,男,硕士研究生,主治医师,研究方向:恶性血液病的诊断和治疗,E-mail:fuli583904940@126.com。
