Control of EPS with regulating factor
2014-09-06YuguangCHENSiyiXIANGXiaobinBIAN
Yu-guang CHEN,Si-yi XIANG, Xiao-bin BIAN
1The Key Lab of Advanced Manufacture Technique for Automobile Parts, Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China, Chongqing 400050, China; 2Institute of Electronic Information & Automation, Chongqing University of Technology, Chongqing 400050, China
Control of EPS with regulating factor
Yu-guang CHEN† 1,2,Si-yi XIANG2, Xiao-bin BIAN3
1The Key Lab of Advanced Manufacture Technique for Automobile Parts, Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China, Chongqing 400050, China;2Institute of Electronic Information & Automation, Chongqing University of Technology, Chongqing 400050, China
Abstract:It is difficult to provide assistant torque reasonably using the conventional EPS control when road adhesion coefficient changes. An EPS control with a regulating factor was proposed to solve the problem mentioned above. It can adjust vehicle speed inductance through the regulating factor to achieve that assist characteristic changes with the changes of road adhesion coefficient. Furthermore, it can enhance the self-adaptive ability of EPS. It is approved that the assistant torque could be adjusted reasonably and effectively by the regulating factor, based on the simulation.
Key words:EPS control, Regulating factor, Road adhesion coefficient, Steering safety
The external factors influencing EPS performances are of the discreteness, the nonlinear and the uncertain characteristics. Among them, road adhesion coefficient plays an important role. Road adhesion coefficient is not considered on EPS study at present. An assist characteristic solidified cannot meet the need of EPS control for road adhesion coefficient change. The greater the steering wheel torque is, the more easily the wheel sideslip occurs when the road adhesion coefficient is small[1-3]. Specifically, an accident will occur if assistant torque can't be adjusted in time when road adhesion coefficient goes smaller on continuing steering.
An EPS control with regulating factor is proposed to solve the problems mentioned above. Its power assist characteristic can adapt to different road adhesion coefficient by adjusting vehicle speed inductance, so as to improve steering safety[4].
1.An EPS control with regulating factor
1.1.EPS mathematical model
A brushless DC motor and a PWM module are used in EPS system. Make the following assumptions when establishing mathematical model. Transfer efficiency of torque is 100%. The rotational inertia of torsion bar has been ignored. Mechanical element stiffness is infinite except the torsion bar[5]. It is equivalent to the rotational inertia and damping coefficient of steering wheel and steering shaft that there is the rotational inertia and damping coefficient of the parts, such as steering wheel, steering shaft, torsion bar’s sleeve, jackshaft, reducing mechanism and so on[6-7].
The mathematical model is shown as follow.
(1)
WhereThis steering wheel torque,Ksis the stiffness of torque sensor,θhis steering wheel angle,Jhis the rotary inertia of steering wheel,Bhis the damping coefficient of steering wheel,θsis torsion bar angle,Tdis torque measured by torque sensor,xris the displacement of tie rod,mis the quality of tie rod,bris the damping coefficient of tie rod,Rsis pinion radius,Tris steering resistance torque,Tais assistant torque outputted,Jmis the rotary inertia of motor spindle and load,Bmis the damping coefficient of motor,Lis armature inductance,Ris armature resistance,Gis transmission ratio,θmis motor's rotation angle,Kbis back-emf,Uis terminal voltage.
The diagram of EPS control is shown in Figure 1. There,vis vehicle speed,sis wheel slip rate,αis regulating factor.
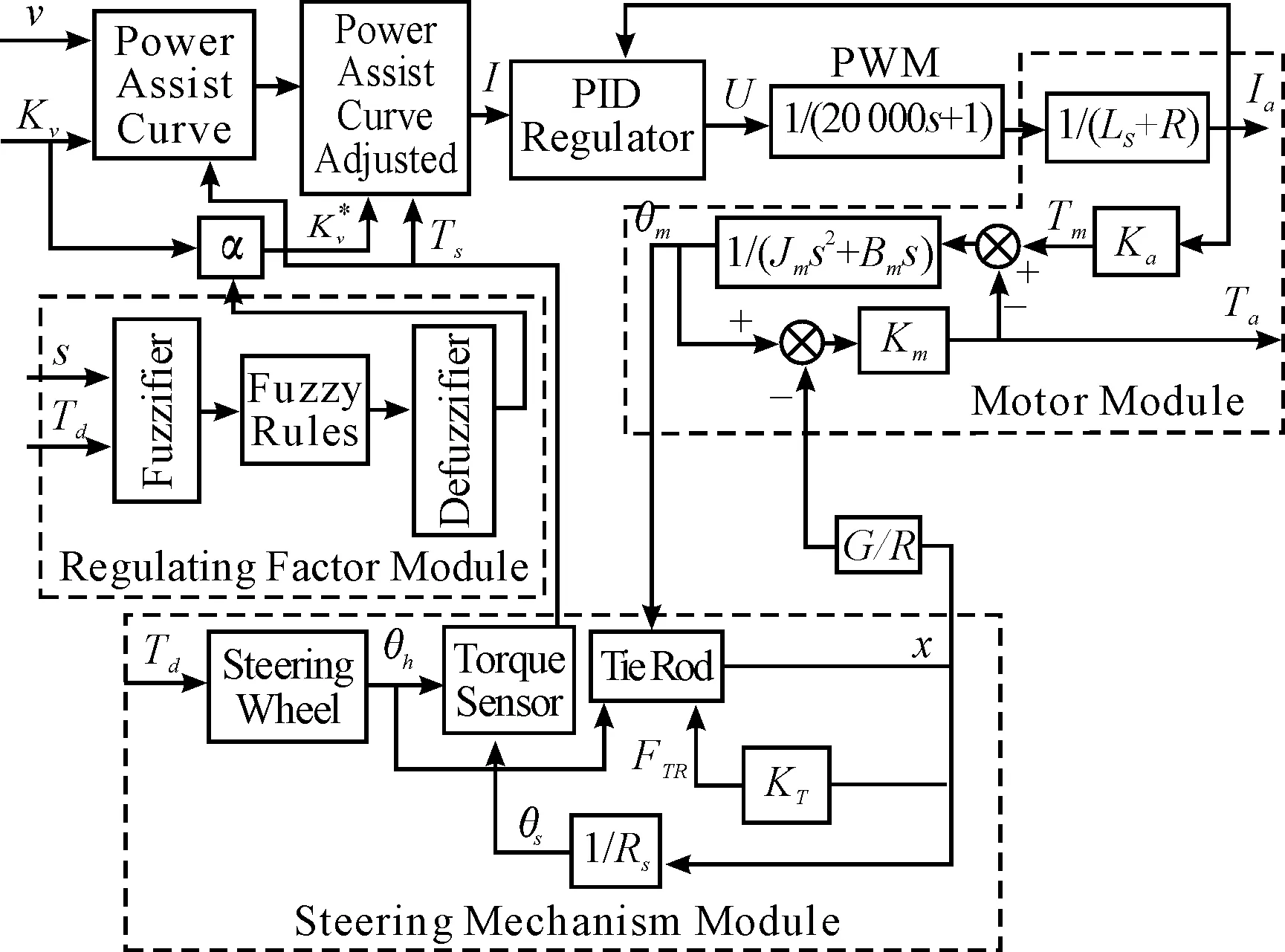
Figure 1.The diagram of EPS control
1.2.Power assist characteristic
Vehicle speed inductanceKvis established by quartic polynomial fit based on experiment data of the vehicle, Big Dipper.
Kv=4.388-0.1571v+0.003 878v2-
4.955×10-5v3+2.332×10-7v4
(2)
SettingTd0=1 N·m andTdmax=7 N·m, whereTd0is critical value of zero assistant torque zone and varied assistant torque zone,Tdmaxis critical value of varied assistant torque zone and saturated assistant torque zone. Power assist curve is shown in Figure 2.
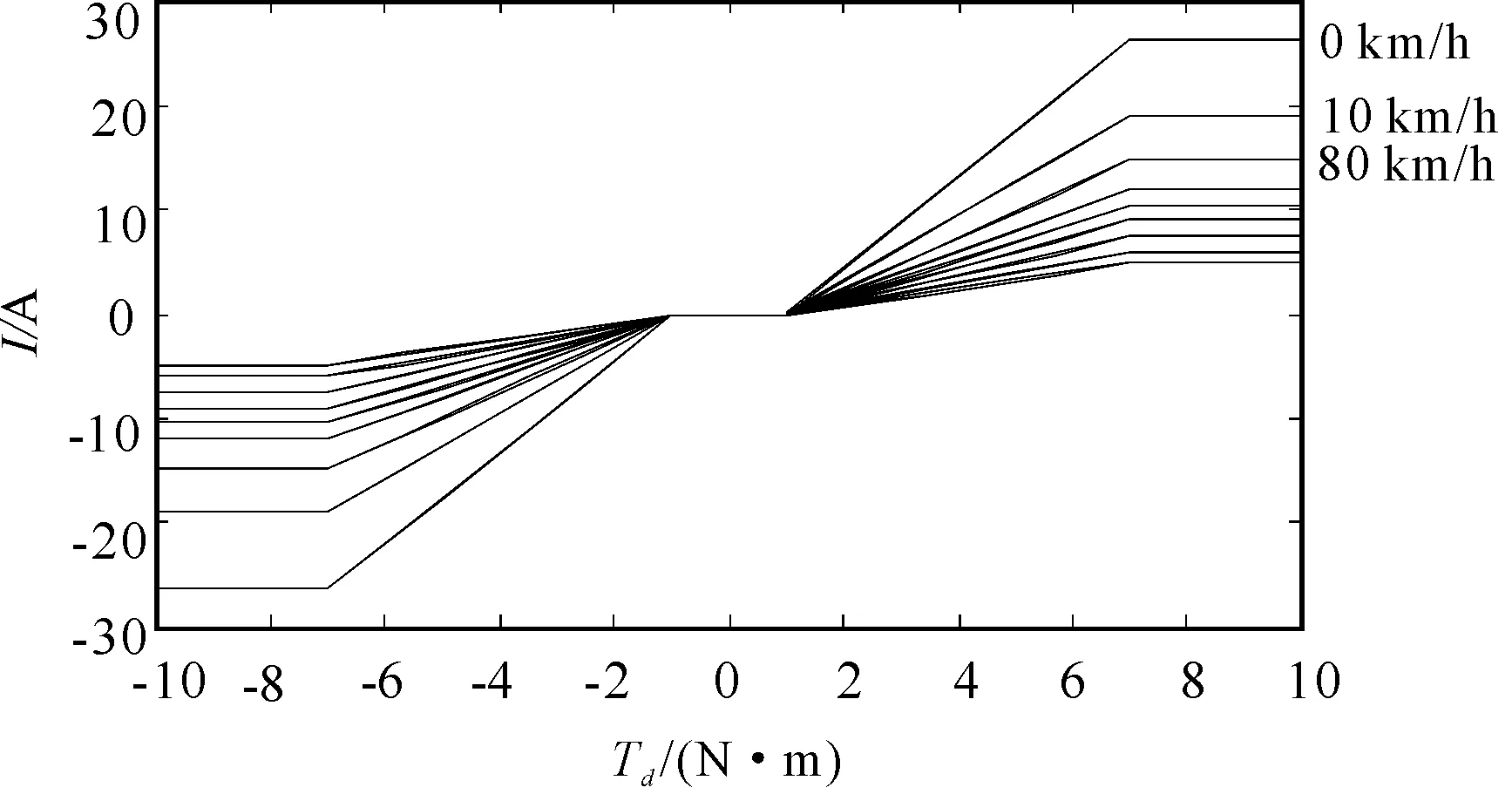
Figure 2.Power assist curve
1.3.Regulating factor
Road adhesion coefficient is described by wheel slip rates.s=1-v/(wr), wherewis the wheel speed,ris wheel radius.αis defined as follow.
α=f(s,Td)
(3)
Itisnormalroadadhesioncoefficientwhensis less than 0.2.αdoes not provide regulating function. The less road adhesion coefficient is the greatersis.αis inverse relation tosandTd.
The functionα=f(s,Td) is achieved by fuzzy logic algorithm. The fuzzy inference mechanism uses Mamdani.sandTdas input variables, whileαis the output variable. The basic ranges ofsandαare all[0, 1]. The basic range ofTdis[0, 7]. The fuzzy subsets ofs,Tdandαare all designed as {VS, S, M, B, VB}.s,Tdandαall use mixed membership function, which consists of membership functions of triangle, Z and S.
The membership function ofαis shown in Figure 3. The membership interval of VB is designed as very small to ensure steering portability of EPS on the normal road. The three-dimensional relationship ofs,Tdandαis shown in Figure 4.
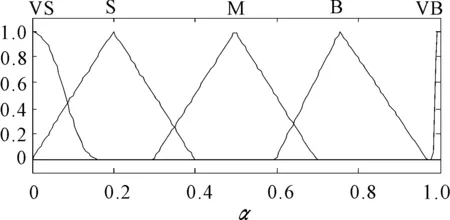
Figure 3.Membership function of α
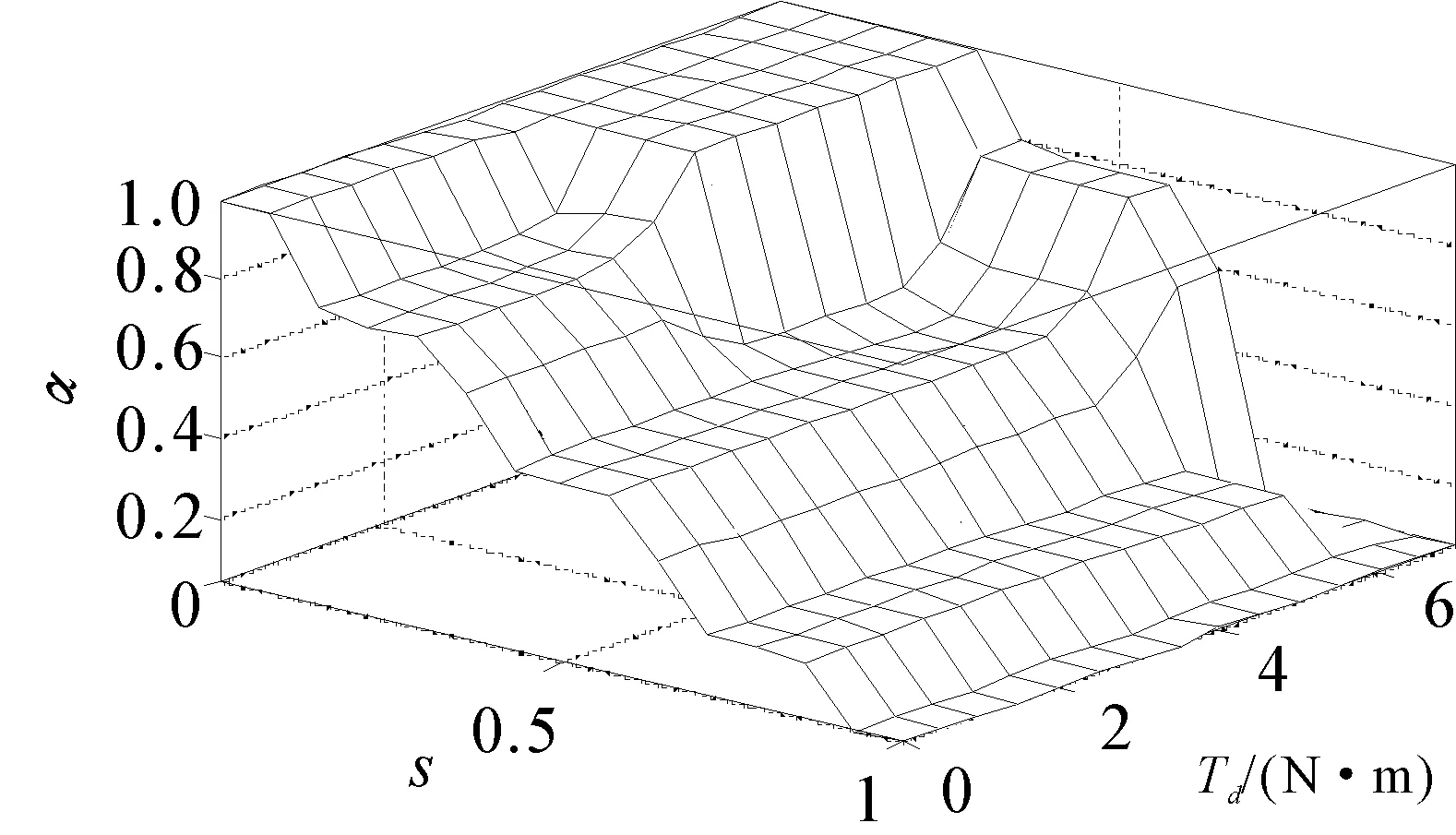
Figure 4.The relationship of s, Td and α
Some conclusions can be drawn from Figure 4. Firstly,αis regulated relatively great whensis very small so as to steering portability of EPS is achieved. Meanwhile, the greaterTdis the greaterαis. Secondly,αdecreases rapidly whensgoes great so as to good steering feeling of driver can be obtained. Meanwhile, the greaterTdis the smallerαis.αis near zero whensis close to 0.7, which forces almost no power assistant torque outputted.
1.4.A control strategy of EPS with regulating factor
The control block diagram of EPS with regulating factor is shown in Figure 1. Vehicle speed inductanceKvis adjusted online by regulatingαin order to achieve the purpose of adjusting power assist curve of EPS.
(4)
The assistant torque is provided according to the preset power assist curve when EPS works on normal road condition. The smaller assistant torque is provided the smaller road adhesion coefficient is, so as to improve steering feeling and steering safety.
2.Simulation
2.1.Simulation verification
The simulation parameters are shown in Table 1. There,Kais DC torque constant,Kmis DC electromagnetic torque coefficient,KTis equivalent elastic coefficient of tie rod.
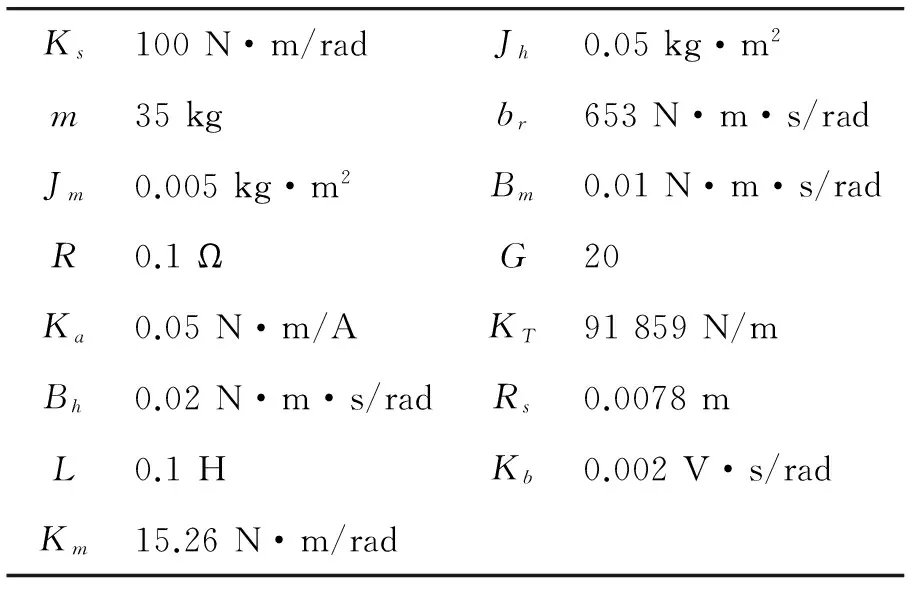
Table 1.Simulation parameters
WhenTd=5 N·m, the armature current under different speed is shown in Figure 5. The armature current decreases along with speed increasing. The current rise time is small and the assistant torque is steady. It proves the correctness of the simulation model.
2.2.The simulation of EPS with regulating factor
WhereTd=5 N·m andv=30 km/h, the armature current I under different wheel slip rate s is shown in Figure 6. Whenschanges from 0.2 to 0.6 and then to 0.2 during the continuous turning and steering wheel keeping still, the curves ofI,Tr, andTaare shown in Figure 7.
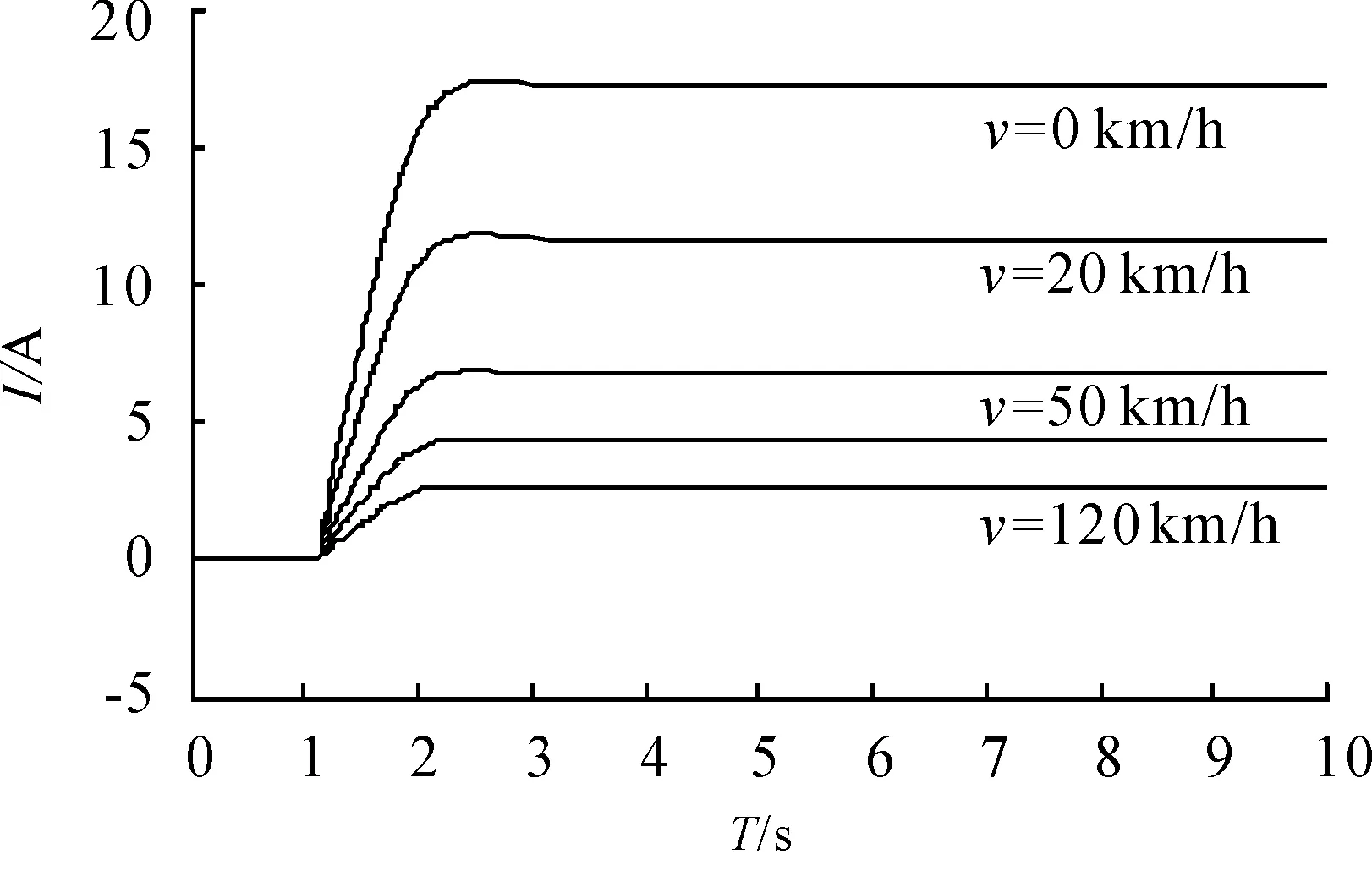
Figure 5.Armature current under different speed
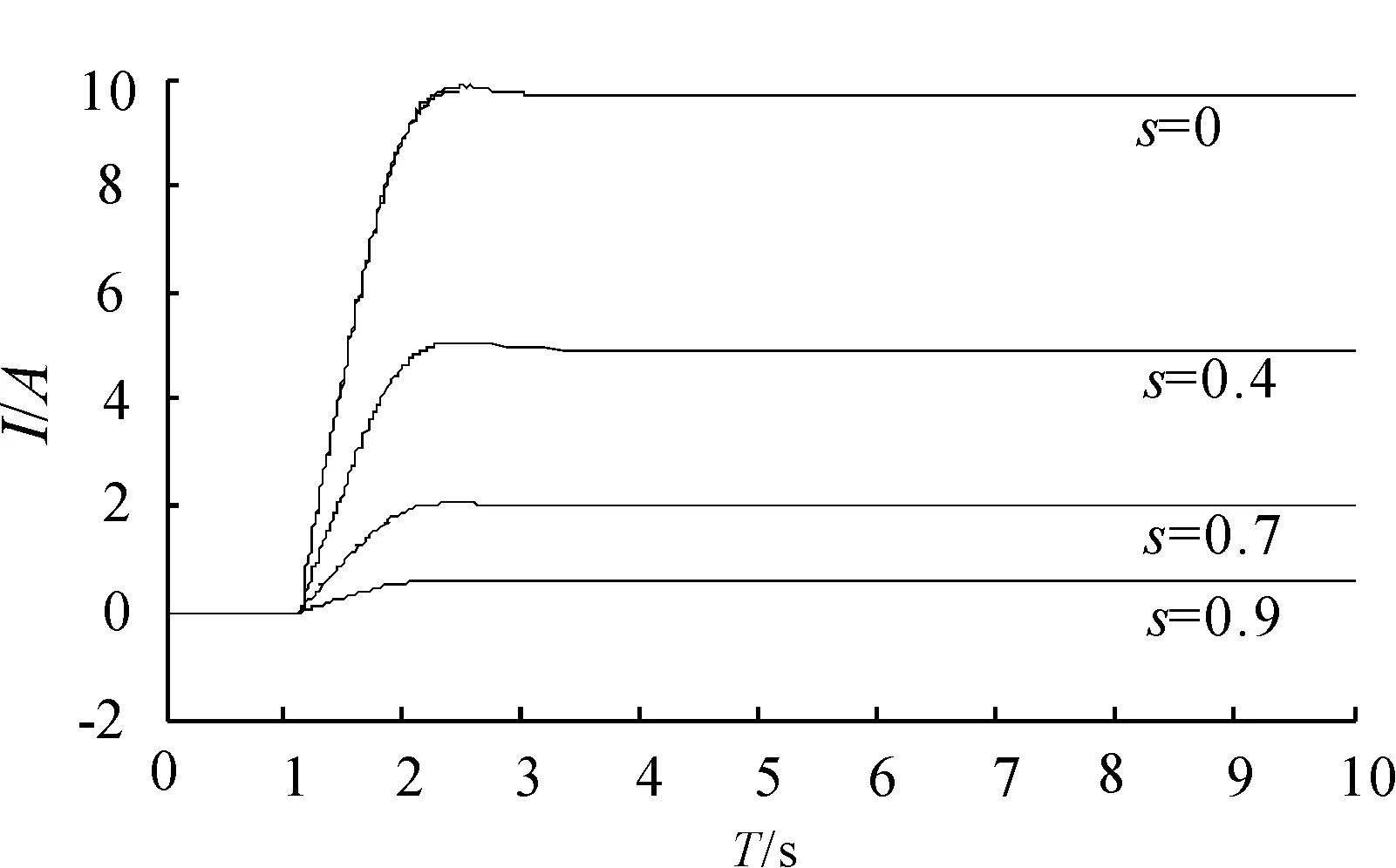
Figure 6.Armature current under different s
Figure 7.The curves of I, Tr and Ta when s changes
3.Analyses of simulation results
The following conclusions can be obtained based on the simulation results.
It is indicated in Figure 6 that armature current I changes along with the wheel slip rate s. Armature current is larger when the wheel slip rate is less than to 0.2 to ensure the steering portability. Armature current decreases to zero along with the increasing of wheel slip rate when the wheel slip rate is greater than 0.2.
It is indicated in Figure 7 that assistant torque can be adjusted automatically along with the change of the wheel slip rate when the vehicle speed and steering wheel torque are constant value. Armature current drops rapidly when s goes to 0.6 and armature current restores rapidly then when s returns to 0.2.
It is indicated also in Figure 7 that assistant torque decreases rapidly when the wheel slip rate increase so as to enhance steering road feel of the driver.
As a result, EPS with regulating factor can enhance the self-adaptive ability of EPS to improve steering safety.
4.Conclusion
The self-adaptive ability of EPS can be improved by regulating factor, which adjusted automatically power assist characteristic according to road adhesion coefficient change. The simulation results show that the steering performance of EPS system can be improved greatly. The system can overcome the effect of road adhesion coefficient change effectively.
References
[1]Amberkar S, Kushion M, Eschtruth K, et al. Diagnostic Development for an Electric Power Steering System[J].SAE technical paper series,2000,1:819.
[2]Osuka A, et al.Development of Pinion—Assist Type Electric Power Steering System[J]. KOYO Engineering Journal Edition No.161E, 2002:46-51.
[3]Yuji Kozaki, et al. Electric Power Steering(EPS)[J].Motion&Contr01.No.6—1999 NSK: 9-15.
[4]Davis F W. Hydraulic steering mechanism[S].US Patent:US1790620,1931.
[5]Noguchi A.Development of a Steering Angle and Torque Sensor of Contact-type[J]. Furukawa Review,2004(25):36-41.
[6]Liu Guang,Kurnia. A low torque ripple PMSM drive for EPS applications[C].IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Expositi,2004(2):1130-1134.
[7]Kim J, Song J. Control logic for all electric power steering system using assistmotor[J]. Mechatronics, 2002,12,447-459.
带调节因子的EPS助力控制
陈渝光† 1,2,向思怡2,边晓彬2
1汽车零部件先进制造技术教育部重点实验室,重庆400050;2重庆理工大学 电子信息与自动化学院,重庆400050
摘要:针对常规EPS助力控制难以随路面附着系数的变化提供合理的助力力矩的问题,提出了一种带有调节因子的助力控制。该方法通过调节因子在线调节车速感应系数,使EPS的助力特性随路面附着系数的变化而变化,从而增强EPS助力控制的自适能力。Matlab/simulink仿真研究表明,该方法能够随路面附着系数变化合理有效地调节助力力矩。
关键词:EPS助力控制;调节因子;路面附着系数;转向安全
中图分类号:U270.2
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2014.06.005
Received: 2013-10-25
† Yu-guang CHEN, Professor. E-mail: cyg6610@qq.com
杂志排行
机床与液压的其它文章
- Influence of salt fog test on the performance of the composite coating on avionics cases
- Numerical simulation of the double suction balance type screw compressor working process*
- Cam profile optimization design of variable cycle reciprocating piston engine*
- Design and implementation of a wireless electronic inverter welding machine*
- A Sort of fusion control strategy for uncertainty complex process with large time lag*
- Flow field CFD analysis of axial flow blood pump*
