慢性HBV感染者外周血T细胞亚群与病毒载量、HBeAg的相关性分析
2014-09-01刘坤杨亚萍段银环赵俊梅孙谢文
刘坤 杨亚萍 段银环 赵俊梅 孙谢文
·论著·
慢性HBV感染者外周血T细胞亚群与病毒载量、HBeAg的相关性分析
刘坤 杨亚萍 段银环 赵俊梅 孙谢文
目的分析慢性HBV感染者外周血T细胞亚群与病毒载量、HBeAg的相关性。方法以40例慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)、35例慢性重型乙型肝炎(CSHB)、30例肝硬化(LC)及32例正常对照者为研究对象,采用流式细胞仪和荧光定量PCR法分别检测各组外周血T细胞亚群、HBV DNA载量。结果CHB组仅CD+4亚群明显降低,与对照组比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);CSHB及LC组CD+3、CD+4亚群、CD+4/CD+8比值呈逐渐降低趋势,CD+8亚群呈逐渐增高趋势,与对照组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。HBV DNA载量与CD+4亚群、CD+4/CD+8比值呈负相关(r=-0.638,-0.778,P<0.05),与CD+8亚群呈正相关(r=0.647,P<0.05),与CD+3无关。与HBeAg阳性患者比较,HBeAg阴性患者外周血CD+3+、CD+4和CD+8亚群显著降低(P<0.05)。结论慢性HBV感染者随着疾病加重细胞免疫功能进行性降低,与病毒复制水平密切相关,这是导致疾病慢性化的原因之一。外周血T细胞亚群变化趋势可为判断疾病转归及预后提供可靠指标。
乙型肝炎病毒;慢性肝炎;T细胞亚群

1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取2011年6月至2013年10月期间我院收治的HBsAg阳性患者105例,其中CHB患者40例、CSHB患者35例、LC患者30例。105例中,男78例,女27例;年龄15~76岁,平均年龄(43.5±5.7)岁;均符合2010年《慢性乙型肝炎防治指南》对慢性乙型肝炎及肝硬化的诊断标准[3]。所有患者6个月内均未接受抗病毒治疗。排除其他病毒引起的肝炎、HIV阳性者及肝癌、酒精性肝病等。同时选取我院健康体检者32例为对照组,男20例,女12例;年龄21~68岁,平均年龄(39.8±4.3)岁;均经查体证实HBsAg阴性,肝功能正常。
1.2 检测方法

1.2.2 HBV DNA载量测定:使用美国ABI7300型基因扩增仪,采用实时荧光定量PCR法检测标本,试剂盒由上海生工生物工程技术有限公司提供。HBV DNA≤103copies/ml为阴性,HBV DNA>103~105copies/ml为低载量,HBV DNA 105~107copies/ml为中载量,HBV DNA>107copies/ml为高载量。
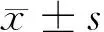
2 结果


组别CD+3CD+4CD+8CD+4/CD+8对照组(n=32)74.35±4.5642.28±4.3624.65±3.241.72±0.39CHB组(n=40)72.12±4.4737.66±4.21*25.06±3.451.50±0.36CSHB组(n=35)66.35±4.47*#30.21±3.89*#32.68±3.99*#0.92±0.32*#LC组(n=30)61.22±4.13*△20.63±3.65*△37.22±5.13*△0.55±0.21*△
注:与对照组比较,*P<0.05;与CHB组比较,#P<0.05;与CSHB组比较,△P<0.05


表2不同HBV DNA载量与HBV患者T细胞亚群比较
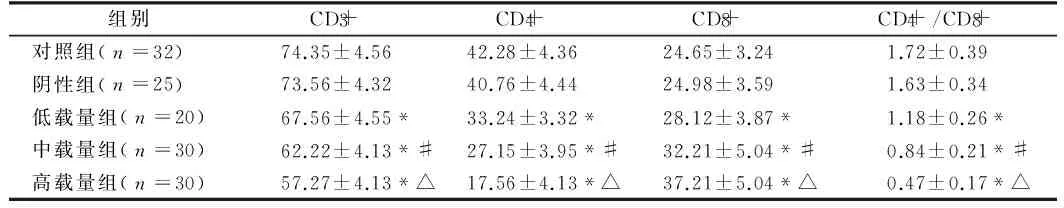
组别CD+3CD+4CD+8CD+4/CD+8对照组(n=32)74.35±4.5642.28±4.3624.65±3.241.72±0.39阴性组(n=25)73.56±4.3240.76±4.4424.98±3.591.63±0.34低载量组(n=20)67.56±4.55*33.24±3.32*28.12±3.87*1.18±0.26*中载量组(n=30)62.22±4.13*#27.15±3.95*#32.21±5.04*#0.84±0.21*#高载量组(n=30)57.27±4.13*△17.56±4.13*△37.21±5.04*△0.47±0.17*△
注:与对照组和阴性组比较,*P<0.05;与低载量组比较,#P<0.05;与中载量组比较,△P<0.05

表3 HBeAg阳性HBV感染者与HBeAg阴性HBV感染者T细胞亚群的比较
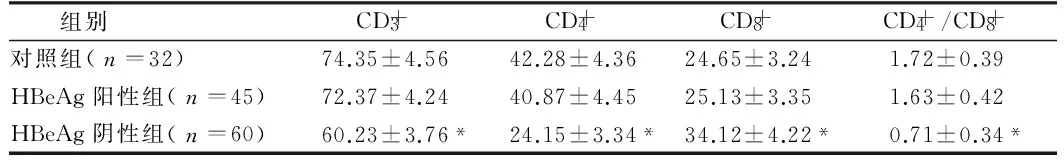
组别CD+3CD+4CD+8CD+4/CD+8对照组(n=32)74.35±4.5642.28±4.3624.65±3.241.72±0.39HBeAg阳性组(n=45)72.37±4.2440.87±4.4525.13±3.351.63±0.42HBeAg阴性组(n=60)60.23±3.76*24.15±3.34*34.12±4.22*0.71±0.34*
注:与HBeAg阳性组比较,*P<0.05
3 讨论


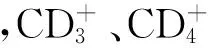
总之,如果我们能够在慢性乙肝逐步进展至慢重肝及肝硬化的早期提高机体的细胞免疫功能就有可能成功阻断HBV的复制,这也为慢性乙肝的治疗、疾病预测及改善预后提供了理论依据。
1 Shi YH,Shi CH.Molecular characteristics and stages of chronic hepatitis B virus infection.World J Gastroenterol,2009,15:3099-3105.
2 Rehermann B.Pathogenesis of chronic viral hepatitis:differential roles of T cells and NK cells.Nat Med,2013,19:859-868.
3 中华医学会肝病学分会和感染病学分会.慢性乙型肝炎防治指南.实用肝脏病杂志,2011,14:81-89.
4 Chisari FV,Isogawa M,Wieland SF.Pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection.Pathol Biol (Paris),2010,58:258-266.
5 Liu A,Chert BF,Chert EJ,et al. Role of hepatitis B viral load and bass core pranoter mutation in hepatocellular Careinoma in hepatitis BcaerS.Infect Dis,2006,193:1258-1265.
6 朱苏兰,鲁陈,熊德琴,等.慢性乙型肝炎病毒感染者外周血 T 细胞亚群分析及与病毒载量相关性研究.赣南医学院学报, 2012,32:360-362.
7 朱银芳,顾锡炳,蒋亦明,等.HBeAg 阴性的慢性乙型病毒性肝炎外周血 T 细胞亚群的变化.现代中西医结合杂志,2011,20:2625-2626.
ThecorrelationbetweenTlymphocytesubsetsinperipheralbloodandHBVDNAlevelsaswellasHBeAginpatientswithchronichepatitisBvirusinfection
LIUKun,YANGYaping,DUANYinhuan,etal.DepartmentofLiverDiseases,TheThirdHospitalofQinhuangdaoCity,Hebei,Qinhuangdao066000,China
ObjectiveTo investigate the relationship between T-lymphocyte subsets and HBV DNA levels,HBeAg in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.MethodsThe 40 cases of chronic hepatitis(CHB),35 cases of chronic severe hepatitis B (CSHB),30 cases of liver cirrhosis (LC) and 32 healthy subjects were enrolled in the study.The T lymphocyte subsets and HBV DNA load in peripheral blood were detected by flow cytometry and fluorescence quantitative PCR for all the patients and healthy subjects.ResultsThe CD+4subset was significantly decreased in CHB group,as compared with that in control group (P<0.05);the CD+3,CD+4subsets,the ratio of CD+4/CD+8in CSHB group and LC group were gradually decreased,however,CD+8subset was gradually increased,as compared with those in control group (P<0.05).HBV DNA load was negatively correlated to CD+4subset,ratio of CD+4/CD+8(r=-0.638,-0.778,P<0.05),however,which was positively correlated to CD+8subset (r=0.647,P<0.05),moreover,which was not related with CD+3subset.As compared with those of patients with positive HBeAg,the CD+3 subset,CD+4subset and CD+8subset in peripheral blood of patients with negative HBeAg were significantly decreased (P<0.05).ConclusionThe cellular immune function in patients with chronic HBV infection is progressively decreased with the aggravation of disease condition,which is closely correlated to the levels of virus replication,and it is one of the reasons that results in chronicity of disease.The changing trend of T lymphocyte subsets in peripheral blood can be regarded as a reliable index for evaluating disease’s prognosis.
hepatitis B virus;chronic hepatitis;T-lymphocytes subsets
10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2014.13.006
066000 河北省秦皇岛市第三医院肝病科
R 512.62
A
1002-7386(2014)13-1940-03
2014-02-09)
