肺癌患者手术前后血清Lipocalin-2、MMP-9表达的临床意义
2014-08-30马小刚杨晓光赵峥
马小刚 杨晓光 赵峥
·论著·
肺癌患者手术前后血清Lipocalin-2、MMP-9表达的临床意义
马小刚 杨晓光 赵峥
目的研究肺癌患者手术前后血清脂质运载蛋白-2(Lipocalin-2)、基质金属蛋白酶-9(MMP-9)的表达及临床意义。方法采用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测60例肺癌患者手术前后Lipocalin-2、MMP-9蛋白水平,分析其与临床病理特征的关系。结果肺癌组Lipocalin-2、MMP-9表达水平显著高于健康对照组(P<0.05)。二者表达与TNM临床分期、淋巴结转移状况有关(P<0.05),且呈正相关(r=7.217,P<0.05)。手术治疗总有效率为80.0%,治疗后Lipocalin-2、MMP-9水平显著降低,与治疗前比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论肺癌组Lipocalin-2、MMP-9异常高表达,这与肺癌侵袭转移过程密切相关。手术治疗可显著降低二者表达水平,对其表达水平的监测可作为判断手术疗效和评估预后的可靠指标。
肺肿瘤;Lipocalin-2;MMP-9;手术
肺癌是我国最常见的恶性肿瘤,致死率居恶性肿瘤之首。脂质运载蛋白-2(Lipocalin-2)是载脂蛋白家族成员之一,在调节脂代谢、渗透压及抗炎方面发挥重要作用。研究表明,Lipocalin-2与肺癌等恶性肿瘤的发生密切相关[1]。基质金属蛋白酶-9(MMP-9)因对细胞外基质和基膜的降解作用,参与了肿瘤的侵袭转移过程[2]。本研究采用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测60例肺癌患者手术前后Lipocalin-2、MMP-9表达水平,旨在探讨二者在肺癌发生发展中的作用,为疾病诊断、手术疗效及预后判断提供科学依据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取2012年至2012年我院收治、且经病理确诊的原发性肺癌患者60例,男44例,女16例;年龄39~77岁,中位年龄56.5岁;病理类型:鳞癌28例,腺癌20例,小细胞癌12例;TNM临床分期参照2002年UICC制定的标准:Ⅰ+Ⅱ期26例,Ⅲ+Ⅳ期34例。有淋巴结转移者38例,无淋巴结转移者22例。同时选取我院健康体检者50例作为对照组,其中男40例,女20例;年龄35~78岁,中位年龄54.6岁。2组一般资料有均衡性。
1.2 手术疗效的判定标准 疗效评价标准分为临床缓解、部分缓解及无变化,总有效率=临床缓解率+部分缓解率。
1.3 实验方法
1.3.1 标本采集:抽取肺癌患者手术前后和健康人清晨空腹静脉血3 ml,静置30 min,4℃ 1 000 r/min离心15 min,取上清冻于-80℃待测。
1.3.2 ELISA法:采用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测Lipocalin-2、MMP-9蛋白水平,试剂盒由上海生物工程有限公司提供,严格按照说明书操作。

2 结果
2.1 2组Lipocalin-2、MMP-9表达水平比较 肺癌组Lipocalin-2、MMP-9表达水平均显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。见表1。
表1 2组Lipocalin-2、MMP-9水平比较

表1 2组Lipocalin-2、MMP-9水平比较
组别血清Lipocalin-2(ng/ml)血清MMP-9(pg/ml)肺癌组(n=60)118±35512±103对照组(n=50) 37±10*112±32*
注:与肺癌组比较,*P<0.05
2.2 Lipocalin-2、MMP-9表达与肺癌临床病理特征的关系 Lipocalin-2、MMP-9表达与患者年龄、性别、病理类型无关(P>0.05),而与TNM临床分期、淋巴结转移情况密切相关(P<0.05)。见表2。
2.3 肺癌组Lipocalin-2、MMP-9表达的相关性分析 直线相关分析显示,肺癌患者血清Lipocalin-2、MMP-9水平呈显著正相关(r=7.217,P<0.05)。
2.4 手术治疗肺癌的临床疗效 60例肺癌患者手术后,治疗总有效率为80.0%。见表3。2.5 手术治疗肺癌的远期疗效 60例肺癌患者手术后死亡2例,术后跟踪随访5年,患者1、3、5年生存率分别为69.0%(40/58)、41.4%(24/58)、20.7%(12/58)。
2.6 手术后患者血清Lipocalin-2、MMP-9水平的变化 60例肺癌患者手术后Lipocalin-2、MMP-9水平与治疗前比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表4。
2.7 复发组与未复发组Lipocalin-2、MMP-9水平的变化 60例肺癌患者手术治疗1年后有20例复发,复发组Lipocalin-2、MMP-9水平显著升高,与未复发组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表5。
3 讨论
表2 Lipocalin-2、MMP-9水平与肺癌临床病理特征的关系

表2 Lipocalin-2、MMP-9水平与肺癌临床病理特征的关系
病理特征血清Lipocalin-2(ng/ml)P值血清MMP-9(pg/ml)P值年龄(岁) <60(n=39)114±320.273506±1000.292 ≥60(n=21)127±37516±105性别 男(n=44)116±320.297511±1010.267 女(n=16)110±28524±107病理类型 鳞癌(n=28)128±360.302502±1000.283 腺癌(n=20)119±30519±105 细胞癌(n=12)113±26516±103TNM分期 Ⅰ+Ⅱ期(n=26)79±210.010438±850.006 Ⅲ+Ⅳ期(n=34)140±40589±124淋巴结转移 无(n=22)72±220.008422±810.004 有(n=38)145±42593±128
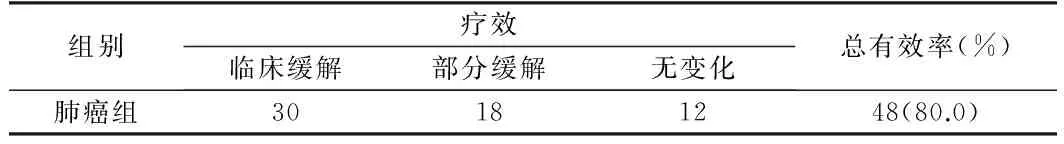
表3 手术治疗肺癌的临床疗效 n=60,例
表4 手术治疗前后Lipocalin-2、MMP-9水平比较

表4 手术治疗前后Lipocalin-2、MMP-9水平比较
组别Lipocalin-2(ng/ml)手术前手术后1个月MMP-9(pg/ml)手术前手术后1个月肺癌组118±3570±18*512±103327±61*
注:与手术前比较,*P<0.05
表5 复发组与未复发组Lipocalin-2、MMP-9水平比较

表5 复发组与未复发组Lipocalin-2、MMP-9水平比较
组别Lipocalin-2(ng/ml)MMP-9(pg/ml)未复发组(n=40)79±19330±63复发组(n=20)126±36* 518±103*
注:与未复发组比较,*P<0.05
Lipocalin-2是1993年Kjeldsen等[3]在中性粒细胞中发现和分离的一种脂质运载蛋白。研究证实,Lipocalin-2生物学功能广泛,在肥胖、胰岛素抵抗、代谢综合征、血管病变、炎性反应等方面发挥关键作用,是这些疾病的潜在治疗靶点。近年来,国外研究发现Lipocalin-2在乳腺癌、结肠直肠癌、口腔癌等多种恶性肿瘤中异常高表达,在肿瘤细胞凋亡、黏附、浸润转移过程中扮演重要角色[4]。
恶性肿瘤侵袭转移的关键是对细胞外基质中胶原等多种蛋白成分的降解,其中MMP-9是基质金属蛋白酶家族中分子量最大、最重要的酶。MMP-9在肺癌等多种恶性肿瘤中异常高表达,与癌细胞的侵袭转移密切相关。本研究显示,Lipocalin-2和MMP-9在肺癌患者血清中均表达上调,这与他人研究结果[1,2]一致,且其表达水平与临床分期和淋巴结转移状况密切相关,提示二者与肺癌发生及侵袭转移有关,是肺癌恶化和转移的重要风险因子。Leng等[4]采用抑制性单克隆抗体阻断乳腺癌细胞Lipocalin-2的功能,结果发现癌细胞的侵袭和肺转移受到明显抑制,作者推测可能是由于Lipocalin-2功能受抑导致MMP-9降解增加、活性降低。Kubben等[5]也发现人胃癌组织Lipocalin-2和MMP-9异常高表达,Lipocalin-2可保护MMP-9免受降解,从而增加肿瘤的侵袭转移能力。因此,Lipocalin-2可能通过促进MMP-9的活化在肺癌的侵袭转移过程中发挥关键作用。
本研究结果显示,肺癌手术总有效率达80.0%,且术后患者Lipocalin-2和MMP-9水平明显下降,提示二者在肺癌患者高表达主要是恶性肿瘤源性。我们随访发现,术后1年复发患者Lipocalin-2和MMP-9水平较未复发者明显升高。因此,因此,Lipocalin-2和MMP-9水平可作为判断疗效及预后的可靠指标,若术后Lipocalin-2和MMP-9水平回升或持续处于高水平状态,提示肿瘤复发、转移和预后差,二者可为评价肺癌发生发展、侵袭转移及判断预后提供重要参考价值,并可成为肺癌治疗的新靶标。
1 王宇,陈伟,曾婷婷.肺癌患者血清中脂质运载蛋白-2的表达及临床意义.华西医学,2013,28:44-46.
2 钱海红.非小细胞肺癌化疗前后血清 VEGF 和 MMP-9水平的对照观察.河北医药,2013,35:496-497.
3 Kjeldsen L,Johnsen AH,Sengelov H,et al.Isolation and primary structure of NGAL,a novel protein associated with human neutrophil gelatinase.J Biol Chem,1993,268:10425-10432.
4 Leng X,Ding T,Lin H,et al.Inhibition of lipocalin 2 impairs breast tumorigenesis and metastasis.Cancer Res,2009,69:8579-8584.
5 Kubben FJ,Sier CF,Hawinkels LJ,et al.Clinical evidence for a protective role of lipocalin-2 against MMP-9 autodegradation and the impact for gastric cancer.Eur J Cancer,2007,43:1869-1876.
ExpressionandclinicalsignificanceofserumLipocalin-2andMMP-9beforeandafteroperationinpatientswithlungcancer
MAXiaogang,YANGXiaoguang,ZHAOZheng.DepartmentofThoracicSurgery,CentralHospitalofHandanCity,Hebei,Handan056001,China
ObjectiveTo investigate the expression and clinical significance of Lipocalin-2 and MMP-9 before and after operation in patients with lung cancer.MethodsThe serum levels of Lipocalin-2 and MMP-9 before and after operation were detected by ELISA in 60 patients with lung cancer and 50 healthy subjects.The correlation between the expressions and clinical pathological characteristics was analyzed.ResultsThe serum levels of Lipocalin-2 and MMP-9 in patients with lung cancer were significantly higher than those of healthy subjects (P<0.05).The expression levels of Lipocalin-2 and MMP-9 were closely correlated to clinical staging and lymph node metastasis (P<0.05),and the expression levels of Lipocalin-2 were positively related to those of MMP-9 (r=7.217,P<0.05).The total effective rate of operation was 80.0%.The serum levels of Lipocalin-2 and MMP-9 were significantly decreased after operation,as compared with those before operation (P<0.05).There were significant differences in the serum levels of Lipocalin-2,MMP-9 betweem the patients with relapse and the patients without relapse (P<0.05).ConclusionThe overexpression of Lipocalin-2 and MMP-9 is closely related with invasion and metastasis process of lung cancer,which may play an important role in carcinogenesis,invasion and metastasis of lung cancer.After operation,the Lipocalin-2 and MMP-9 levels are significantly decreased,and the detection of serum levels of Lipocalin-2 and MMP-9 may be regarded as reliable indexes for evaluating operation efficiency and patient's prognosis.
lung cancer;lipocalin-2;MMP-9;operation
10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2014.09.002
056001 河北省邯郸市中心医院胸外科
R 734.2
A
1002-7386(2014)09-1288-03
2013-11-21)
