2型糖尿病合并终末期肾病外周血细胞水平的临床研究
2014-08-29何宴清杨萍文莉郑雪松肖丽
何宴清 杨萍 文莉 郑雪松 肖丽
·论著·
何宴清 杨萍 文莉 郑雪松 肖丽
目的分析CD+34细胞与糖尿病肾病代谢参数的相关性及其与糖尿病肾病发病的关系。方法选择终末期肾病患者100例,根据是否合并2型糖尿病分为合并糖尿病的终末期肾病组(n=55),为终末期肾病组(n=45)。糖尿病组(n=50)。同时选取体检中心健康体检者作为健康对照组(n=60)。比较4组三酰甘油(TG)、胆固醇(TC)、空腹血糖(FPG)、餐后2 h血糖(2 hFPG)、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)、CD+34细胞/单核细胞值,尿微量白蛋白、肌酐(Cr)水平测定,肾小球滤过率的差异,以及各指标间的相关性。结果与阴性健康对照组比较,3个试验组CD+34细胞在单核细胞中的比值降低(P<0.05);糖尿病组高于终末期肾病组、糖尿病合并终末期肾病组(P<0.05)。糖尿病合并终末期肾病组外周血 CD+34/单核细胞值与HBA1c、Cr、FPG、微量白蛋白、2 hFPG呈负相关(r值分别为-0.439、-0.241、-0.298、-0.342、-0.447,P<0.05)。结论CD+34细胞可能是肾病患者的危险因素,参与肾病的发生,监测 CD+34细胞水平变化也许能用来预测 2 型糖尿病患者合并终末期肾病的发生发展,其中糖尿病可能进一步导致CD+34细胞数量的下降。
CD34+细胞;2型糖尿病;终末期肾病
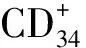
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选择2012年1月至2013年1月在我院肾病内科住院的终末期肾病患者100例,根据是否合并糖尿病分为2组:糖尿病合并终末期肾病组55例,男30例,女25例;终末期肾病组45例,男23例,女22例,为终末期肾病无糖尿病病史。糖尿病组为50例2型糖尿病患者无肾病病史。同时选取体检中心的60例健康体检者作为健康对照组。4组一般资料比较有可比性。见表1。
表1 4组一般资料比较 ±s
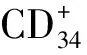
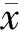
2 结果
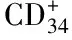

组别CD+34/PMNC健康对照组(n=60)0.094±0.032糖尿病组(n=50)0.075±0.022∗终末期肾病组(n=45)0.038±0.020∗#糖尿病合并终末期肾病组(n=55)0.035±0.020∗#
注:与健康对照组比较,*P<0.05;与糖尿病组比较,#P<0.05
2.2 4组FPG、2 hFPG、HbA1c水平比较 健康对照组与糖尿病组、糖尿病合并终末期肾病组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),与终末期肾病组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);糖尿病组与终末期肾病组、糖尿病合并终末期肾病组比较有统计学意义(P<0.05);终末期肾病组与糖尿病合并终末期肾病组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表3。
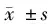
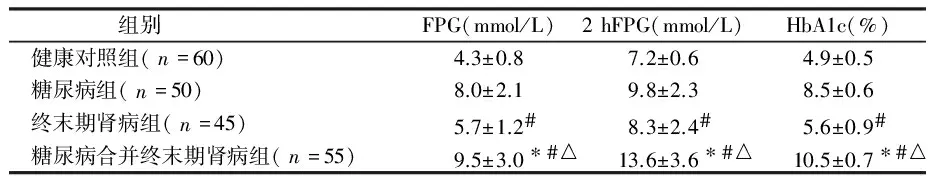
组别FPG(mmol/L)2hFPG(mmol/L)HbA1c(%)健康对照组(n=60)4.3±0.87.2±0.64.9±0.5糖尿病组(n=50)8.0±2.19.8±2.38.5±0.6终末期肾病组(n=45)5.7±1.2#8.3±2.4#5.6±0.9#糖尿病合并终末期肾病组(n=55)9.5±3.0∗#△13.6±3.6∗#△10.5±0.7∗#△
注:与健康对照组比较,*P<0.05;与糖尿病组比较,#P<0.05;与终末期肾病组比较,△P<0.05
2.3 4组患者微量白蛋白、Cr、eGFR比较 终末期肾病组及糖尿病合并终末期肾病组微量白蛋白、Cr、eGFR与健康组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。糖尿病组与健康对照组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),糖尿病组与终末期肾病组及2型糖尿病合并终末期肾病组微量白蛋白、Cr、eGFR差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。终末期肾病组及糖尿病合并终末期肾病组比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表4。
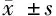
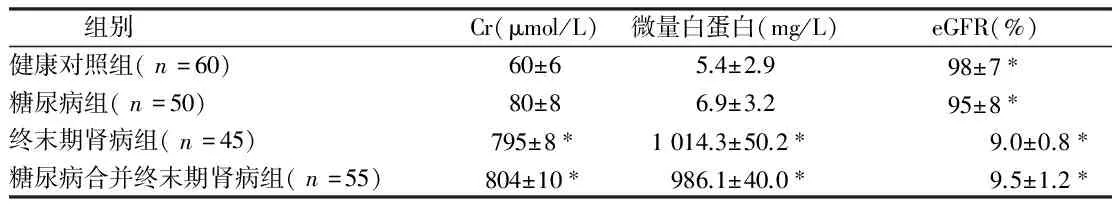
组别Cr(μmol/L)微量白蛋白(mg/L)eGFR(%)健康对照组(n=60)60±65.4±2.998±7∗糖尿病组(n=50)80±86.9±3.295±8∗终末期肾病组(n=45)795±8∗1014.3±50.2∗9.0±0.8∗糖尿病合并终末期肾病组(n=55)804±10∗986.1±40.0∗9.5±1.2∗
注:与健康对照组比较,*P<0.05
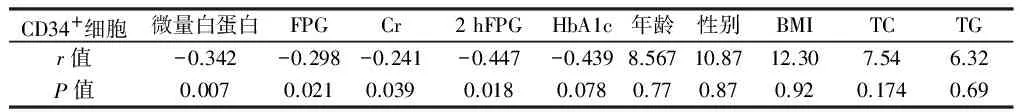
表5 CD34+细胞与各指标相关分析
3 讨论
1 Garg AX,Kibexd BA,Clark WF,et al.Albuminufia and renalinsufficiency prevalence guides population screening: results from the NHANESIII.Kindney Int,2002,61:2165-2175.
2 Coresh J,Selvin E,Stevens LA,et al.Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States.JAMA,2007,298:2038-2047.
3 Chadban SJ,Briganti EM,Kerr PG,et al.Prevalence of kidney damage in Australian adults: the AusDiab kidney study.J Am Soc Nephrol,2003,14:S131-138.
4 Kunitoshi I,Kentaro K,Atsushi S,et al.Changes in the demographics and prevalence of chronic kidney disease in Okinawa.Japan(1993 to 2003).Hypertens Res,2007,30:55-62.
5 Xue JL,Ma JZ,Louis TA,et al.Forecast of the number of patientswith end-stage renal disease in the United States to the year 2010.JAm Soc Nephrol,2001,12:2753-2758.
6 Ati AS,Remuzzi G.Chronic renal diseases as a public health problem: Epidemiology,social,and economic implications.Kidney Int,2005,68:7-10.
7 National Kidney Foundation.K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation,classification and stratification.Am J Kidney Dis,2002,39:S1-S266.
8 Zuo L,Ma CHY,Wang M,et al.Appfieation of glomerular filtration rate estimating equations in chinses with chronic kidneydisease.Am J Kidney Dis,2005,45:463-472.
9 Cepeda FJ,Fernandez E,Pobes A,et al.Utility of cystatin-C in hospitalized patients.Comparing with diferent methods of assessing renal function.Nefrologia,2007,27:168-174.
10 Yang YS,Peng CH,Liu CK,et al.Use of serum eystatin C to detect Early- decline of glomerular filtration rate in type 2 diabetes.Intern Med,2007,46:801-806.
11 Hooligan CA,Tsalam an dris C,Akdeniz A,et al.Albumin to ereatinine ratio:a screening test with limirations.Am J Ki dneyDis,2002,39:1183-1189.
12 Skalova S.The diagnostic role of urinary N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) activity in the detection of renal tubular impairment.Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove),2005,48:75-80.
13 Sawshima K,Mizuno S,Mizuno HY,et al.Protein restriction ameliorates renaltubulointerstitial nephritis and reducesrenal transforming groeth factor beta expression in unilateraluretral obstruction.Exp Nephro1,2002,10:7-18.
14 Prakash S,Pande DP,Shanna S,et al.Randomized,double- blind,place-bo-controlled trial to evaluate efficacy of keto dietin predialytic chlonic renal failure.J Ren Nutr,2004,14:89-96.
15 Giordano M,De Feo P,Lucidi P.Effects of dietary protein restriction on fibrinogen and albumin metabolism in ne-phritic patients.Kidney Int,2001,60:235-242.
16 Kaplan NM.Kaplan’s-clinical hypertension 9th ed.Lippincott Wilkins.2006.373.
17 Fair DE,Ogbem MR,Weiler HA,et al.Dietary soy protein attenuates renal disease progression after 1 and 3 weeks in Han:SPRD-cy weaning rats.Nutr,2004,134:1504-1507.
18 Jamerson K,Weker MA,Bakris GL,et al.Benazepril plus amlodipine or hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension in high-risk patients.Engl J of Med,2008,359:2417-2428.
19 KDOQL Clinical Practice Guidelines and Clinical Practice Recommendations for Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease.Am J Kidney Dis,2007,49(2 Suppl 2):S12-154.
20 Dasgupta I,Porter C,Innes A,et al.“Benign”hypertensive nephrosclerosis.QJM,2007,100:113-119.
ClinicalstudyonthechangesofCD+34cellsinpatientswithtype2diabetesmellituscomplicatedbyterminalstagenephropathy
HEYanqing,YANGPing,WENLi,etal.
DepartmentofDermatology,TaiheHospitalAffiliatedtoHubeiMedicalCollage,Hubei,Shiyan442000,China
ObjectiveTo analyze the correlation between CD+34cells and the parameters of diabetic nephropathy as well as the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy.MethodsOne hundred patients with terminal stage nephropathy were divided terminal stage nephropathy A group (with diabetes,n=55) and terminal stage nephropathy B group (without diabetes,n=45),simple diabetes group (n=50),at the same time,60 healthy subjects were enrolled as control group.The TG,TC,FPG,2 hFPG,HbA1c,ratio of CD+34cells/monocytes,urine microcontent albumin,muscle anhydride levels,glomerular filtration rate were detected and comparted in the four groups.ResultsAs compard with that in control group,the ratio of CD+34cells/monocytes in three experimental groups were obviously decreased (P<0.05),which in diabetes group was significantly higher than that in terminal stage nephropathy A group and terminal stage nephropathy B group (P<0.05).The ratio of CD+34cells/monocytes was negatively correlated to HbA1c,Cr,FPG in terminal stage nephropathy A group (r=-0.439,-0.241,-0.241,-0.342,-0.298,respectively,P<0.05).ConclusionCD+34cells may be risk factors for patients with diabetic nephropathy,which may be involved in the pathiogenesis of diabetic nephropathy,so monitoring the changes of CD+34cells may predict the pathogenesis and development of type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by terminal stage nephropathy,in which diabetes mellitus may result in further decrease of CD+34cells.
CD+34 cells;type 2 diabetes mellitus;terminal stage nephropathy
10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2014.23.003
442000 湖北省十堰市,湖北医药学院附属太和医院皮肤科
R 587.1
A
1002-7386(2014)23-3531-04
2014-05-13)
