基于迭代二阶锥的唯相位波束形成
2014-05-29路成军盛卫星韩玉兵马晓峰
路成军 盛卫星 韩玉兵 马晓峰
基于迭代二阶锥的唯相位波束形成
路成军 盛卫星*韩玉兵 马晓峰
(南京理工大学电子工程与光电技术学院 南京 210094)
唯相位自适应波束形成技术对普通相控阵雷达自适应干扰抑制是非常重要的,在数字阵列雷达中,唯相位技术则可以充分利用各阵元发射模块微波功率从而提高雷达的威力。该文提出了一种新的唯相位波束形成方法,假定初始唯相位权重矢量有个较小的相位扰动,将唯相位模型的目标函数和约束函数在该相位扰动区域内分别用泰勒一阶展开式来近似,则可以将原来的非凸问题转化为凸优化问题,通过二阶锥规划方法(SOCP)求得使当前目标函数最小的扰动矢量,然后更新得到新的权重矢量并代替原来的权重矢量,重复上述迭代过程直到满足停止条件,可以得到满足要求的唯相位权重。计算机仿真结果验证了该方法的正确性和有效性。
阵列信号处理;数字波束形成;唯相位;泰勒展开;凸优化;二阶锥规划
1 引言
本文提出了一种新的唯相位波束形成方法,在相位扰动量比较小的情况下,目标函数和约束函数可以用相位矢量的泰勒一阶展开式来近似,此时原来的非凸问题可以转化为凸优化问题,并通过二阶锥规划方法求得使当前目标函数最小的扰动矢量,然后更新得到新的权重矢量并代替原来的权重矢量,重复上述过程直至满足终止条件,最后可以得到满足要求的唯相位权重。
本文其余部分结构安排如下:第2节介绍信号模型;第3节提出本文的唯相位方法;第4节进行计算机仿真;第5节对本文方法进行总结。
2 信号模型
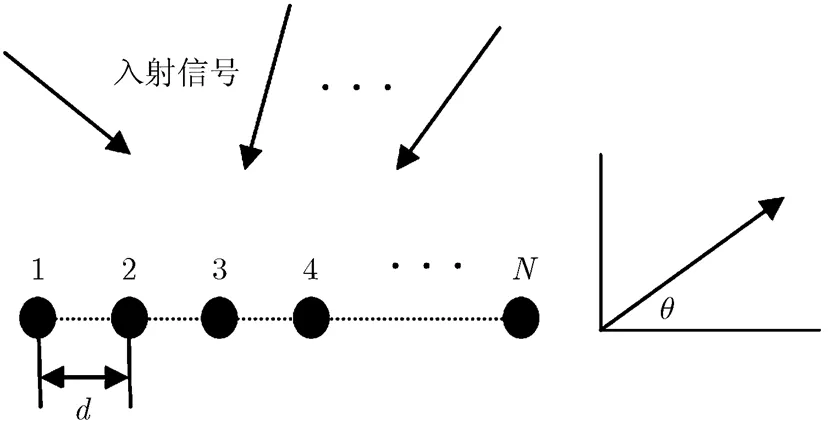
图1 均匀线性阵列
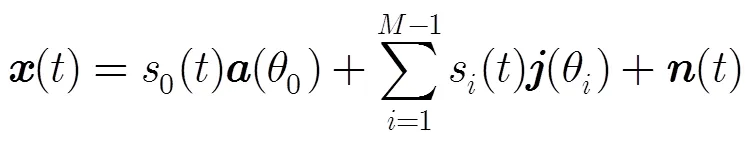
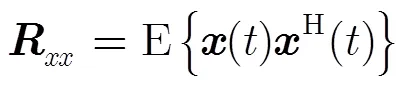
式中H表示共轭转置。
在实际应用中,阵列协方差矩阵是通过有限次快拍数据估计得到,即
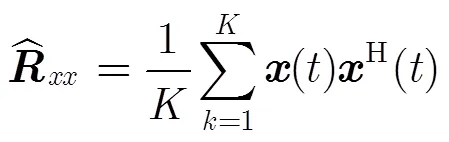
阵列加权输出为
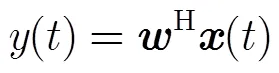
3 迭代二阶锥唯相位算法
线性约束最小方差准则(LCMV)是通过最小化阵列输出的功率来降低干扰和噪声的增益,但保持对期望信号增益不变,从而提高信号干扰噪声比,即
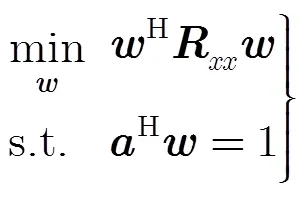
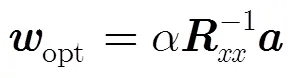
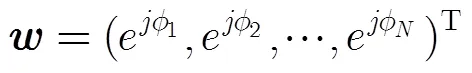
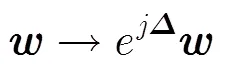
其中
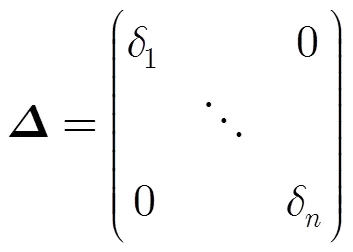
将式(5)的优化问题变换为如式(10)形式:
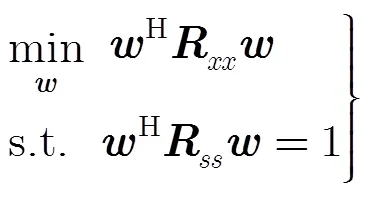
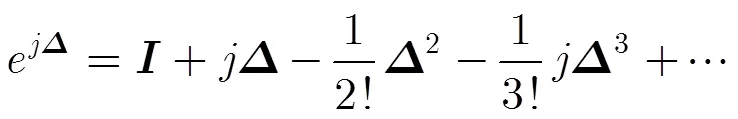
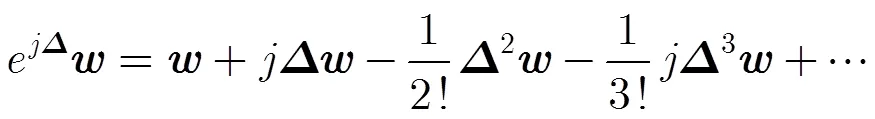
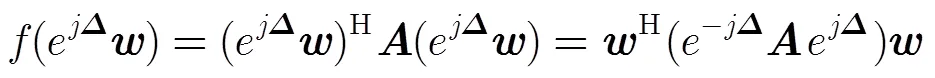
因为
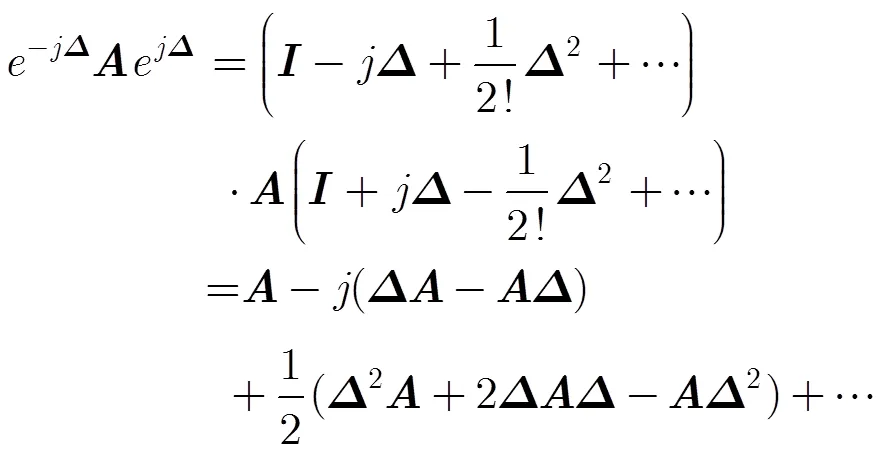
于是,得到
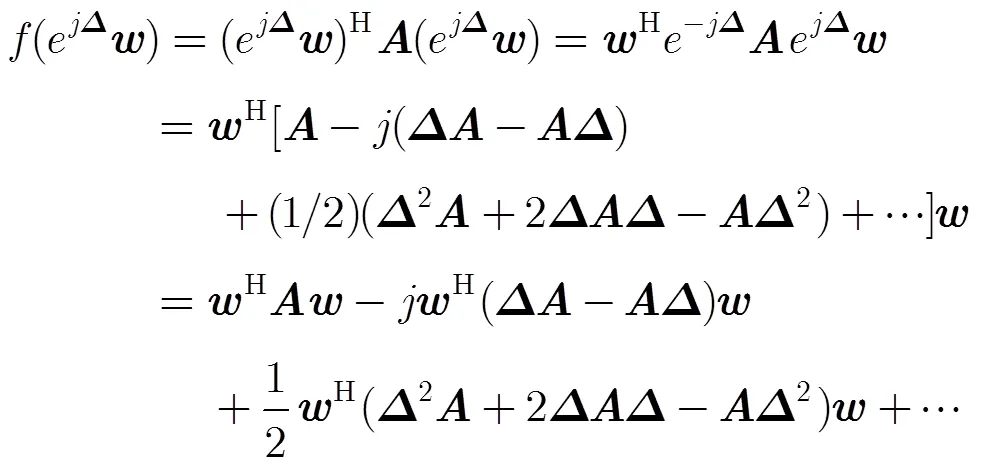
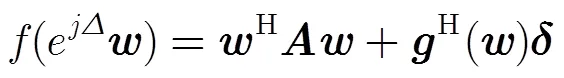
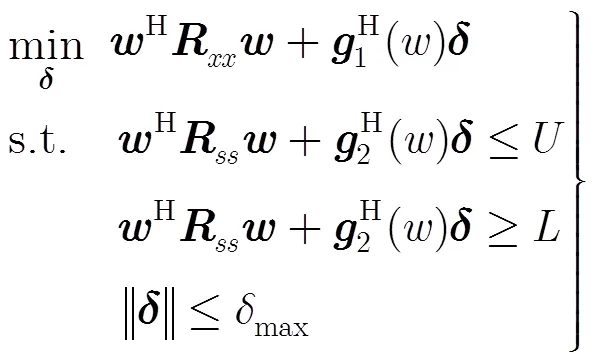
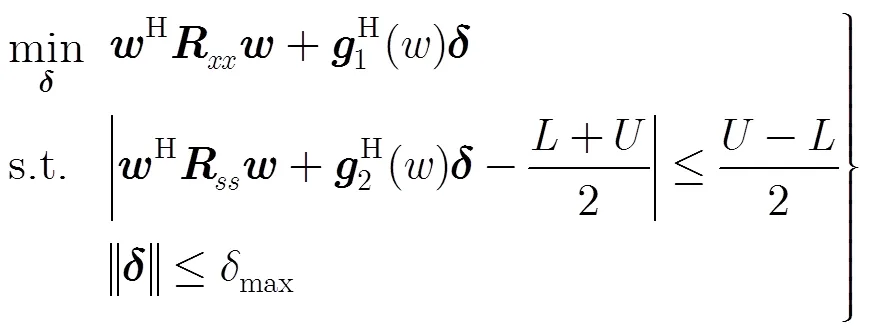
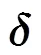
(5)判断是否满足终止条件,若不满足则重复步骤(2)到步骤(5),若满足则停止算法迭代,输出唯相位权重。
4 计算机仿真


图4所示是输出信号干扰噪声比SINR随输入信噪比SNR变化的曲线,图中结果由50次Monte Carlo实验得到。由图4可知,本文方法与传统LCMV算法性能基本接近,而文献[17]中方法在小信噪比情况下输出SINR比本文方法和传统LCMV算法要低一些。
图5所示是输出SINR随输入数据样本长度变化的曲线,输入信噪比0 dB,其它参数保持不变。圆圈线表示本文的相位自适应算法,星号线表示传统LCMV算法,图中结果由50次Monte Carlo实验得到。可以看出本文的唯相位算法在数据样本较少的情况下性能优于传统LCMV算法,随着数据样本变大,输出SINR趋于最优值。
图6所示为阵列输出功率随迭代次数变化的曲线。随着迭代次数增加,输出功率值逐渐收敛到1,此时输出信号中只有期望信号。图中可以看出,迭代到40次后算法就已经基本收敛。
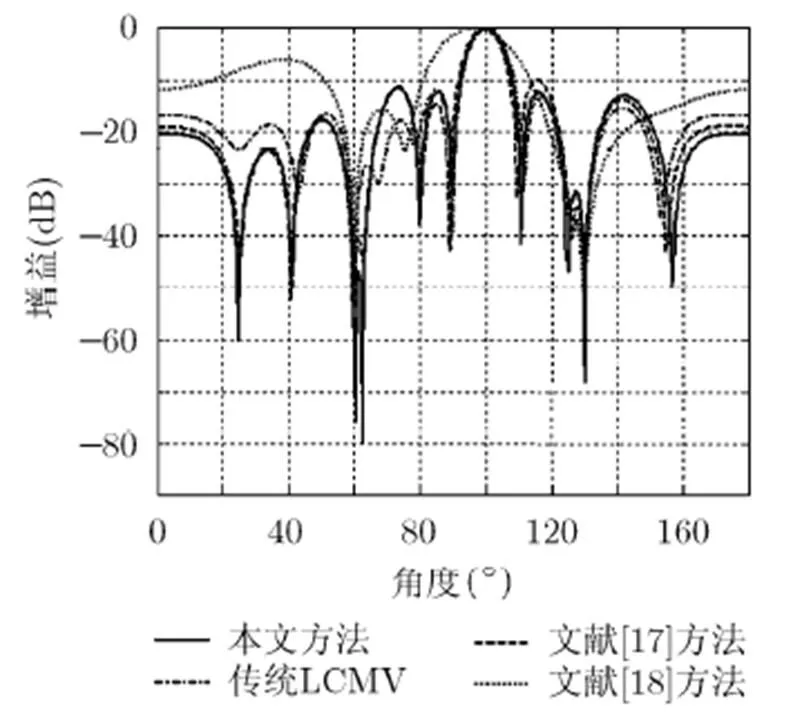
图2 4种算法波束图比较
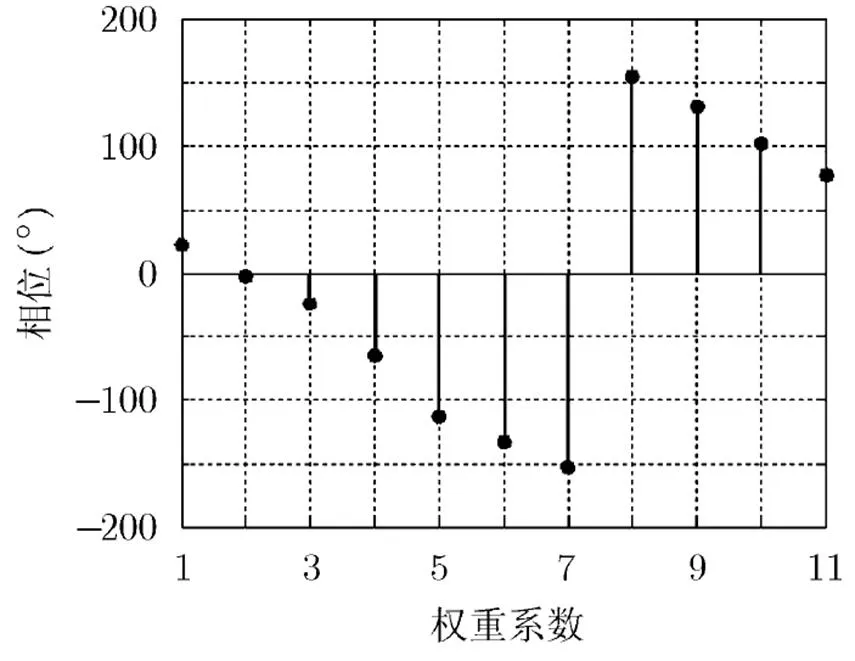
图3 本文唯相位算法权重系数相位
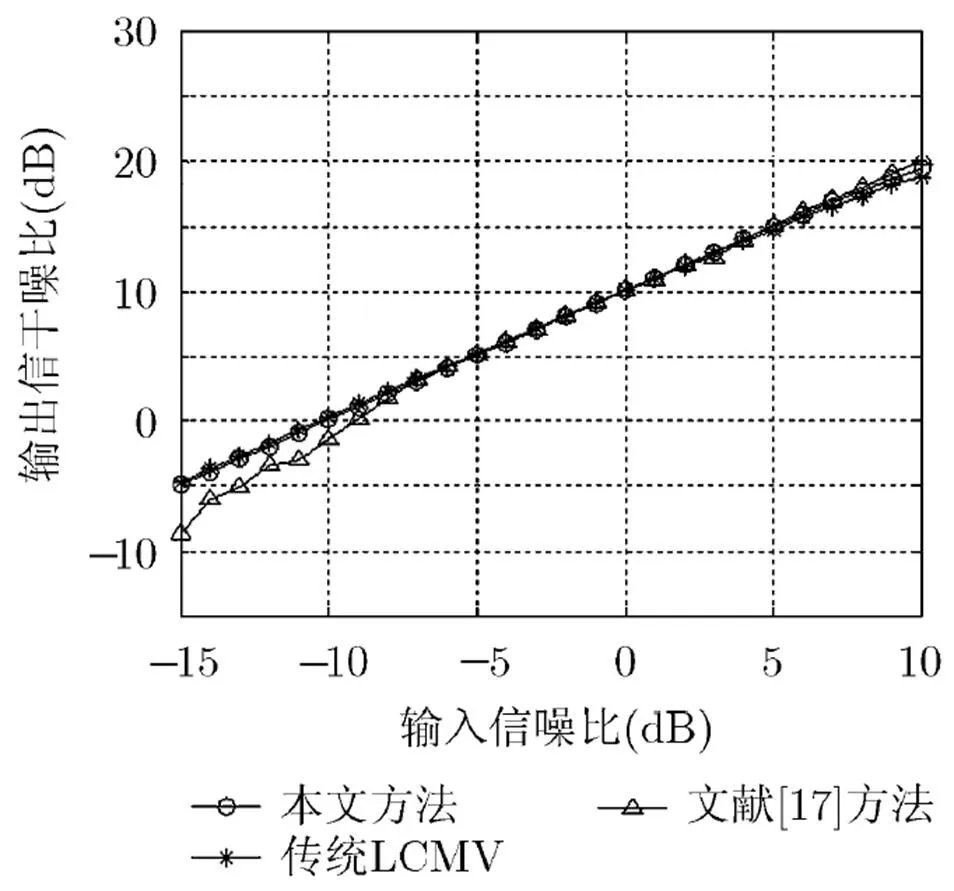
图4 输出SINR随输入SNR的变化曲线
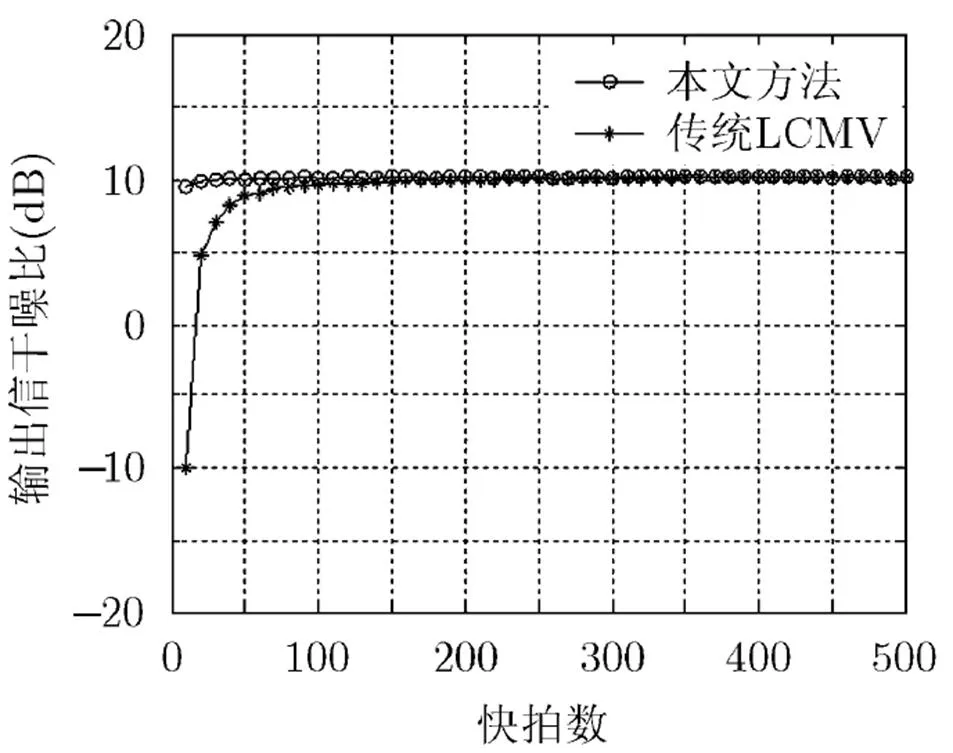
图5 输出SINR随数据样本长度变化曲线
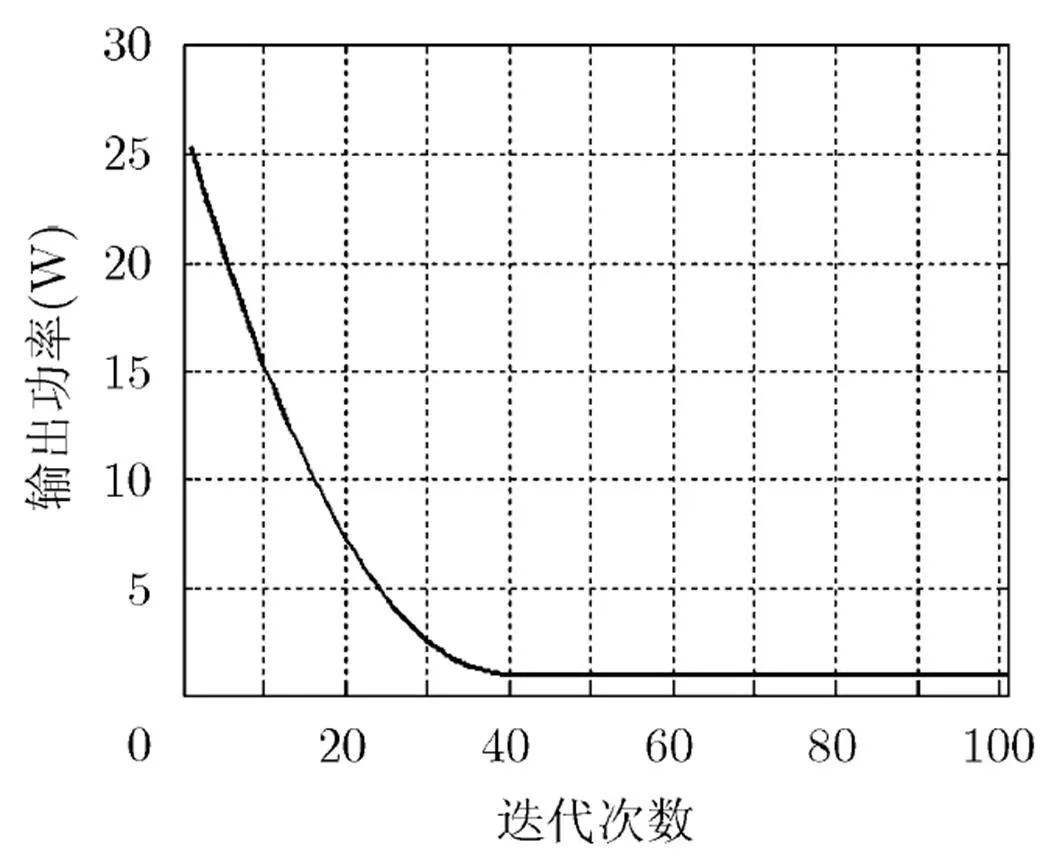
图6 输出功率随迭代次数变化曲线
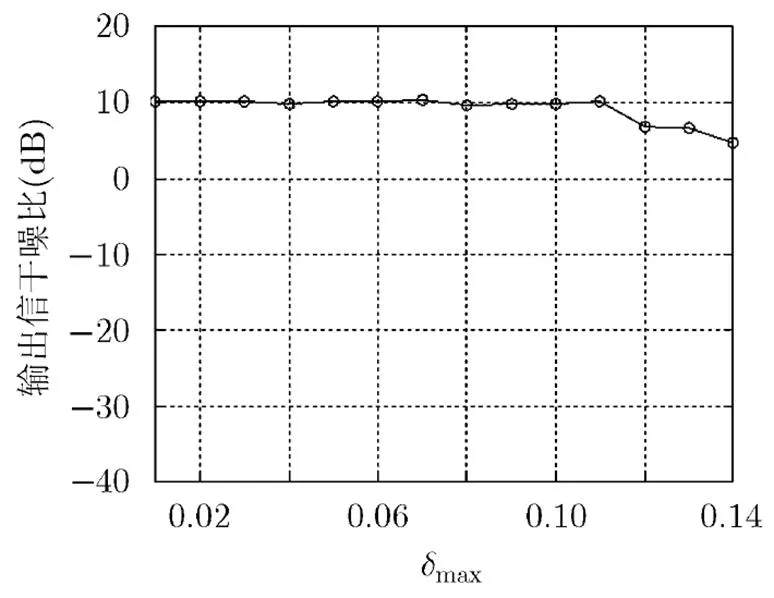
图7 输出SINR随变化曲线
表1运行时间比较(s)
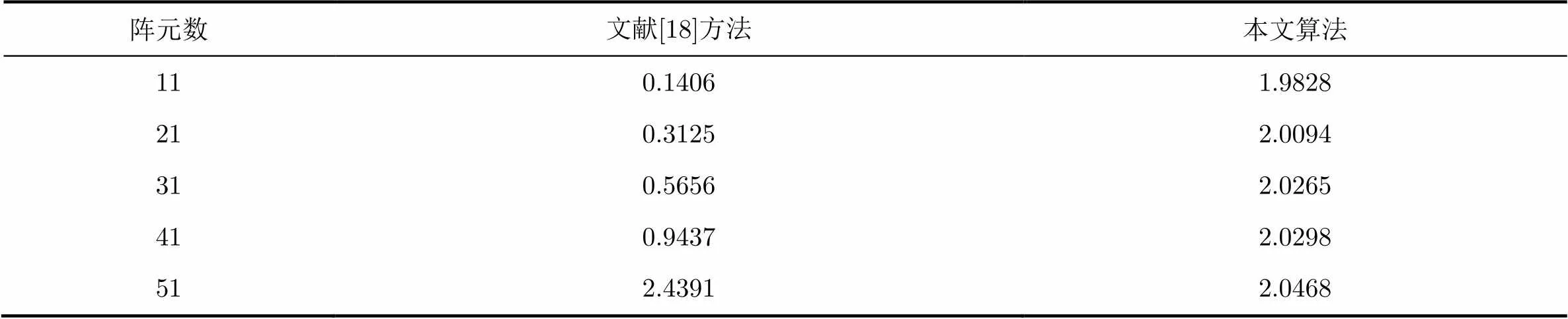
阵元数文献[18]方法本文算法 110.14061.9828 210.31252.0094 310.56562.0265 410.94372.0298 512.43912.0468
5 结论
本文提出了一种新的唯相位波束形成算法,在相位扰动量比较小的情况下,目标函数和约束函数可以用相位矢量的泰勒一阶展开式来近似,此时原来的非凸问题可以转化为凸优化问题,并通过二阶锥规划方法求得使当前目标函数最小的扰动矢量,然后更新得到新的权重矢量并代替原来的权重矢量,重复迭代上述过程直到满足终止条件。计算机仿真表明,本文提出的唯相位算法可以有效地在干扰方向形成零陷,输出SINR接近传统LCMV波束形成器。
[1] 易锋, 孙超. 总体最小二乘算法模波束形成方法研究[J]. 声学学报, 2013, 38(1): 35-41.
Yi Feng and Sun Chao. Matched-mode beamforming based on total least square algorithm[J].,2013, 38(1): 35-41.
[2] 杨杰, 李春晓, 马永阳. 基于Bayesian准则的鲁棒自适应波束形成算法[J]. 杭州电子科技大学学报, 2012, 32(4): 17-20.
Yang Jie, Li Chun-xiao, and Ma Yong-yang. Robust adaptive beamforming algorithm based on Bayesian criteria[J]., 2012, 32(4): 17-20.
[3] Gu Yujie and Amir Leshem. Robust adaptive beamforming based on interference covariance matrix reconstruction and steering vector estimation[J]., 2012, 60(7): 3881-3885.
[4] 李洪涛, 贺亚鹏, 肖瑶, 等. 基于压缩感知的单通道鲁棒自适应波束形成算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(10): 2421-2426.
Li Hong-tao, He Ya-peng, Xiao Yao,.. Compressive sensing based single-channel robust adaptive beamforming algorithm[J].&, 2012, 34(10): 2421-2426.
[5] 郑东卫, 白亚莉. 阵列雷达接收通道校正技术分析[J]. 火控雷达技术, 2012, 41(3): 44-48.
Zheng Wei-dong and Bai Ya-li. Receiving channel calibration technology for array radar[J].,2012, 41(3): 44-48.
[6] Leavitt M K. A phase adaptation algorithm[J].,1976, 24(5): 754-756.
[7] Shore R A. The use of nonlinear programming techniques for phase-only null synthesis[C]. Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, USA, 1983: 207-210.
[8] Steyskal H. Simple method for pattern nulling by phase perturbation[J].,1983, 31(1): 163-166.
[9] Baird C A and Rassweiler G G. Adaptive sidelobe nulling using digital controlled phase-shifters[J]., 1976, 24(5): 638-649.
[10] Shore R A. Nulling at symmetric pattern location with phase- only weight control[J]., 1984, 32(5): 530-533.
[11] Giusto R and Vincenti P D. Phase-only optimization for the generation of wide deterministic nulls in the radiation pattern of phased arrays[J]., 1983, 31(5): 814-817.
[12] Khzmalyan A D and Kondrat’yev A S. Fast iterative methods for phase-only synthesis of antenna array pattern nulls[J]., 1995, 31(8): 601-602.
[13] Haupt R L. Phase-only adaptive nulling with a genetic algorithm[J]., 1997, 45(6): 1009-1015.
[14] Mismar M J, Ismail T H, and Abu-Al-Nadi D I. Analytical array polynomial method for linear antenna arrays with phase-only control[J].,2007, 61(7): 485-492.
[15] Kajenski P J. Phase only antenna pattern notching via a semidefinite programming relaxation[J].2012, 60(5): 2562-2565.
[16] Khzmalyan A D and Kondratiev A S. The phase-only shaping and adaptive nulling of an amplitude pattern[J]., 2003, 51(2): 264-272.
[17] Smith S T. Optimum phase-only adaptive nulling[J].1999, 47(7): 1835-1843.
[18] Choi W S and Sarkar T K. Phase-only adaptive processing based on a direct data domain least squares approach using the conjugate gradient method[J]., 2004, 52(12): 3265-3272.
路成军: 男,1984年生,博士生,研究方向为阵列信号处理、自适应波束形成技术.
盛卫星: 男,1966年生,教授,博士生导师,主要研究方向为数字波束形成、智能天线、电磁散射模型以及图像处理.
韩玉兵: 男,1971年生,副教授,硕士生导师,主要研究方向为阵列信号处理、视频图像处理.
马晓峰: 男,1981年生,讲师,主要研究方向为雷达信号处理、MIMO以及高速数字信号处理.
Phase-only Beamforming Based on Iterative Second-order Cone
Lu Cheng-jun Sheng Wei-xing Han Yu-bing Ma Xiao-feng
(,,210094,)
The adaptive phase-only beamforming technique is very important for conventional phased array radar to suppress interference. For the digital array radar, the phase-only technique can be used to enhance the radar power by making full use of transmitting module microwave power of each array element. In this paper, a novel phase-only algorithm is proposed. Assuming that the initial phase weight vector has a small phase perturbation, the objective function and constraint function can be replaced by the first-order Taylor expansion, thus the original non-convex problem becomes the convex optimization problem, which can be solved using Second-Order Cone Programming (SOCP). The new weight vector is obtained through updating the current weight vector using the solved perturbation vector. The current weight vector is replaced by the new weight vector and the above procedure is repeated until the array pattern meets the termination condition. The computer simulation results demonstrate the correctness and effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Array signal processing; Digital beamforming; Phase-only weighting; Taylor expansion; Convex optimization; Second-Order Cone Programming (SOCP)
TN911.7
A
1009-5896(2014)02-0266-05
10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00593
盛卫星 shengwx@njust.edu.cn
2013-04-27收到,2013-08-23改回
国家自然科学基金(11273017)资助课题
