基于逆序二叉树的高效可分电子现金系统
2014-05-22张江霄李舟军
张江霄 郭 华② 李舟军
基于逆序二叉树的高效可分电子现金系统
张江霄*①郭 华①②李舟军①
①(北京航空航天大学软件开发环境国家重点实验室 北京 100191)②(中国科学院信息工程研究所信息安全国家重点实验室 北京 100093)
针对于Izabachene等人(2012)在标准模型下构建的可分电子现金系统花费协议和存款协议效率低的问题,该文利用Groth-Sahai(GS)证明系统和累加器原理,首次提出了逆序二叉树构建法,并在标准模型下构建了一个高效的可分电子现金系统。与现有系统相比,新系统在构建二叉树时可以并行计算二叉树叶子节点的序列号和在花费协议中可以直接证明用户花费路径的正确性,从而保证花费协议中用户的计算量是常量;新系统在安全性上不仅具有弱不可诬陷性,同时也具有强不可诬陷性;最后在标准模型下给出了系统的安全性证明,证明了该系统具有不可伪造性、匿名性、不可重复花费性和不可诬陷性。
可分电子现金系统;标准模型;逆序二叉树;有限累加器;Groth-Sahai (GS)证明
1 引言
电子现金系统一般由3个协议组成:取款协议、花费协议和存款协议,用户通过取款协议取出所需的电子现金,然后利用花费协议向商家进行花费,最后商家通过存款协议把电子现金存入银行。其中电子现金的可分性允许用户花费小于或等于用户所取的任意面额的电子现金,从而提高了用户的花费效率。因此,可分电子现金系统变得越来越重要。
本文针对标准模型下可分电子现金系统花费协议和存款协议效率低的问题,首先提出了一个逆序二叉树构建法,从而减少了花费协议和存款协议中商家和银行的计算量,解决了存款协议效率低的公开问题;然后基于累加器原理,采用常量累加器证明的方法,提高了花费协议中证明用户花费正确性的效率;同时,新系统兼具弱不可诬陷性和强不可诬陷性[10]。
本文内容组织如下:第2节给出基本定义;第3节介绍逆序二叉树构建法;第4节构造可分电子现金系统;第5节对新协议和已有的协议进行比较;第6节给出新系统安全性的形式化证明;第7节总结全文。
2 基本定义

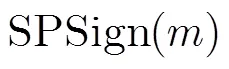

定义4 GS证明[14]在标准模型下给出了有关双线性群中等式的非交互式零知识证明,它适合多种双线性群中群元素关系的等式,包括双线性乘积等式、多标量乘法等式和二次等式等,本文只使用基于SXDH假设下的双线性乘积等式。
定义5 有限累加器[15]最多可以累加有限个元素,同时存在一个证据,可以证明该元素被累加到累加值中,任何人无法证明一个没有累加的元素被累加到累加值中。
3 逆序二叉树构建法
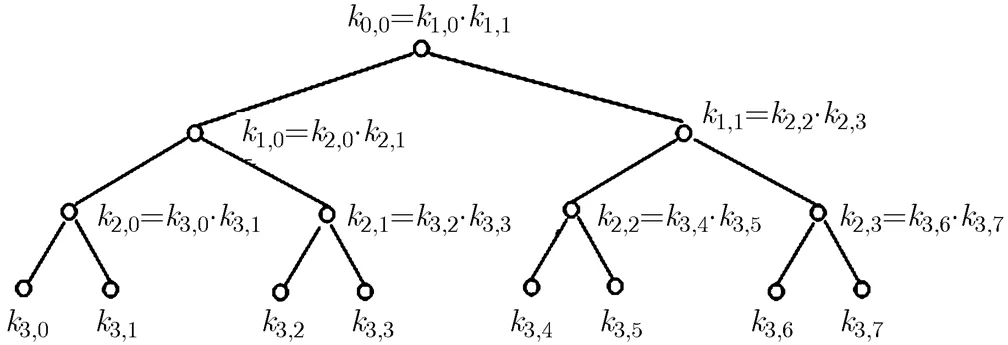
图1 4层二叉树示例
4 可分电子现金的构造
4.1 基本参数
4.2 安全属性
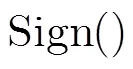
本文所构造的可分电子现金具有不可伪造性、匿名性、不可重复花费性和不可诬陷性。为了描述安全属性,首先引入几个算法:
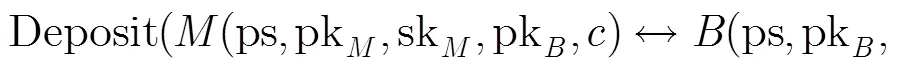

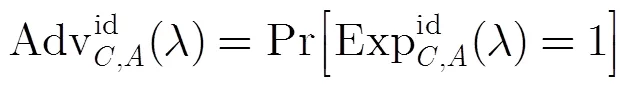
(4)不可诬陷性 不可诬陷性包括弱不可诬陷性和强不可诬陷性[10]。具体定义如下:



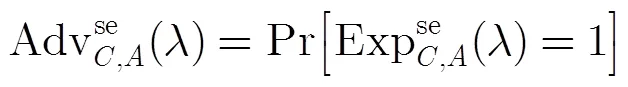
4.3 取款协议
4.4 花费协议
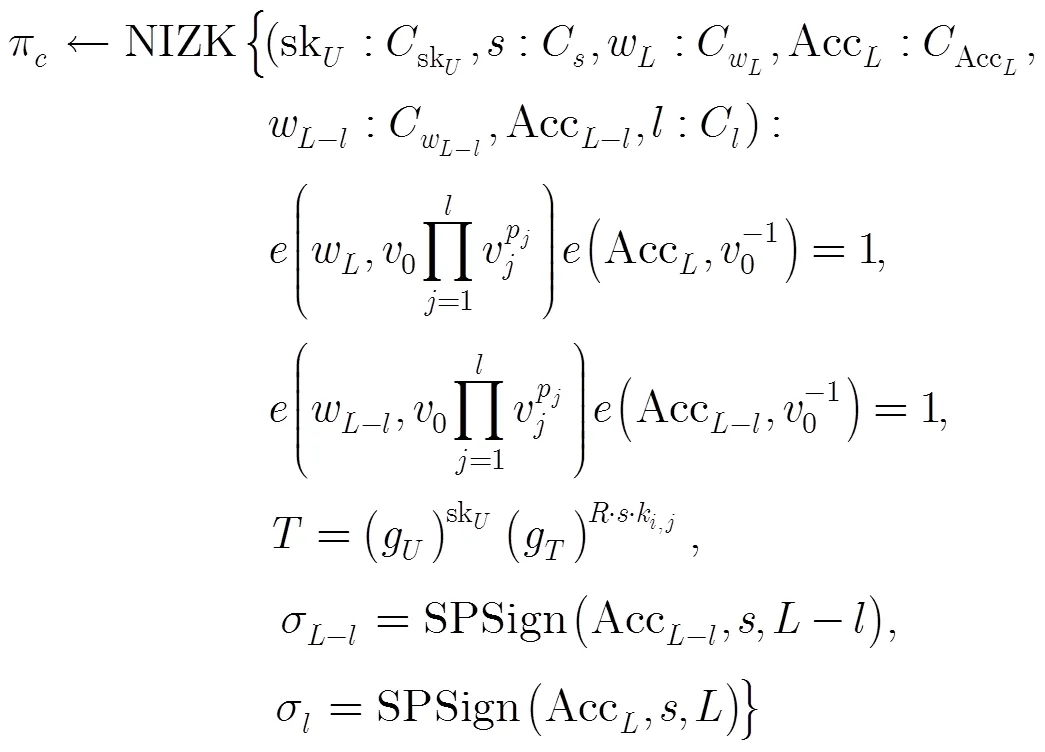
4.5 验证协议
在商家接受到邮件后,验证电子现金的正确性和新鲜性,如果都通过验证,商家就给用户发送商品。具体协议如下:
4.6存款协议
银行收到商家电子现金后,按照图2 进行验证。
如果用户对同一电子现金或者相关的电子现金发生了重复花费。银行通过式(1)分以下3种情况计算重复花费用户的公钥:
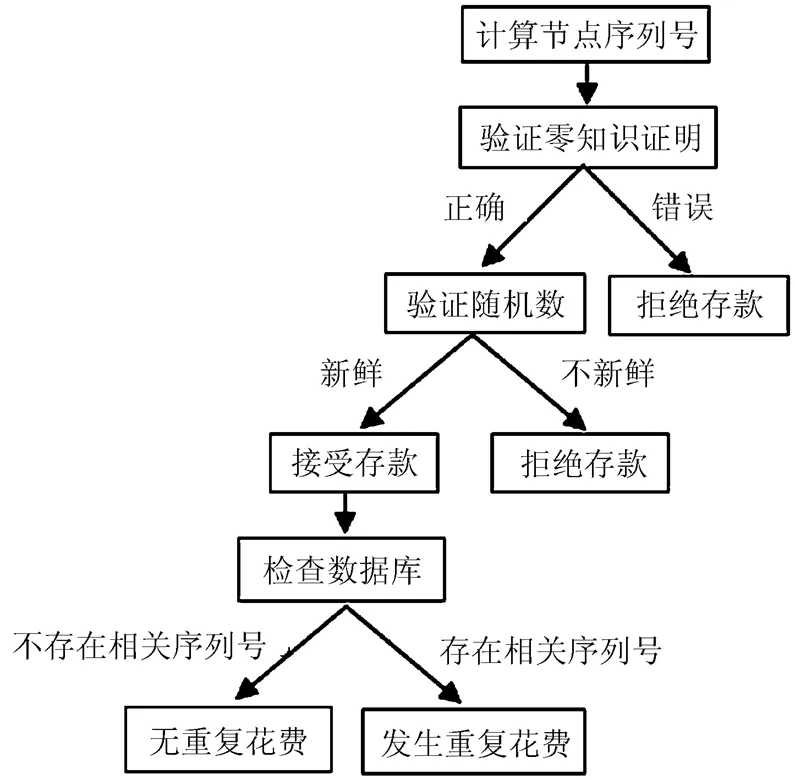
图2 存款协议验证
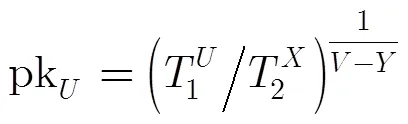
5 效率分析

表1协议计算效率和安全模型的比较
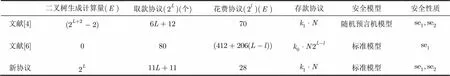
二叉树生成计算量()取款协议()(个)花费协议()()存款协议安全模型安全性质 文献[4]70随机预言机模型 文献[6]080标准模型 新协议28标准模型
6 安全证明
定理1如果SP签名是不可伪造的,并且有限累加器的累加具有有限性,则新协议是不可伪造的;如果Groth-Sahai证明具有零知识性,且DDH问题是困难的,则新协议具有匿名性;如果SP签名是不可伪造的,则新协议具有不可重复花费性;如果Groth-Sahai证明具有零知识性,并且一对多离散对数问题[13]是困难的,则新协议具有不可诬陷性(包括弱不可诬陷性和强不可诬陷性)。
7 结论
本文针对Izabachene等人在标准模型下构建的可分电子现金系统花费协议和存款协议效率低的问题,提出了一个逆序二叉树构建法,同时利用Groth-Sahai证明系统和累加器原理,在标准模型下,构建了一个高效的离线可分电子现金系统。新系统在二叉树构建和花费协议上均优于现有的系统。最后在标准模型下给出了可分电子现金系统的安全性证明,而且新的协议在安全性上,不仅具有弱不可诬陷性,也具有强不可诬陷性。
[1] Canard S and Gouget A. Divisible e-cash systems can be truly anonymous[C]. The 26th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques’07, Barcelona, 2007: 482-497.
[2] Au M H, Susilo W, and Mu Y. Practical anonymous divisible e-cash from bounded accumulators[C]. Proceedings of Financial Cryptography and Data Security’08, Cozumel, 2008: 287-301.
[3] 刘文远, 张江霄, 胡庆华, 等. 可直接计算的高效的可分电子现金系统[J]. 电子学报, 2009, 37(2): 367-371.
Liu W, Zhang J X, Hu Q H,.. Divisible e-cash system with direct computation and efficiency[J]., 2009, 37(2): 367-371.
[4] Canard S and Gouget A. Multiple denominations in e-cash with compact transaction data[C]. Proceedings of Financial Cryptography and Data Security’10, Tenerife, 2010: 82-97.
[5] Goldwasser S and Tauman Y. On the (In) security of the Fiat-Shamir paradigm[C]. The 44th Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Cambridge, 2003: 102-115.
[6] Izabachene M and Libert B. Divisible e-cash in the standard model[C]. Proceedings of Pairing-Based Cryptography- Paring’12, Cologne, 2012: 314-332.
[7] Zhang J X, Li Zh J, and Guo H. Anonymous transferable conditional e-cash[C]. Proceedings of Security and Privacy in Communication Networks’12, Padua, 2013: 45-60.
[8] Liu J W, Liu J H, and Qiu X F. A proxy blind signature scheme and an off-line electronic cash scheme[J]., 2013, 18(2): 117-125.
[9] Blazy O, Canard S, Fuchsbauer G,.. Achieving optimal anonymity in transferable e-cash with a judge[C]. The 4th International Conference on Cryptology in Africa’11, Dakar, 2011: 206-223.
[10] Rosenberg B. Handbook of Financial Cryptography and Security[M]. London: Chapman & Hall, 2010: 19-20.
[11] Groth J and Sahai A. Efficient non-interactive proof systems for bilinear groups[C]. The 27th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques’08, Istanbul, 2008: 415-432.
[12] Abe M, Groth J, Haralambiev K,.. Optimal structure-preserving signatures in asymmetric bilinear groups[C]. The 31th Annual Conference on Advances in Cryptology’11, Santa Barbara, 2011: 649-666.
[13] Bresson E, Monnerat J, and Vergnaud D. Separation results on the “one-more” computational problems[C]. Proceedings of the Cryptographer’s Track at the RSA’08, San Francisco, 2008: 71-87.
[14] Fuchsbauer G. Commuting signatures and verifiable encryption[C]. The 30th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques’11, Tallinn, 2011: 224-245.
[15] Camenisch J, Kohlweiss M, and Soriente C. An accumulator based on bilinear maps and efficient revocation for anonymous credentials[C]. The 12th International Conference on Practice and Theory in Public Key Cryptography’09, Irvine, 2009: 481-500.
[16] Abe M, Fuchsbauer G, Groth J,. Structure-preserving signatures and commitments to group elements[C]. The 30th Annual Cryptology Conference’10, Santa Barbara, 2010: 209-236.
张江霄: 男,1983年生,博士生,研究方向为密码学和电子现金.
郭 华: 女,1981年生,讲师,研究方向为信息安全.
李舟军: 男,1963年生,博士生导师,研究方向为密码学和数据挖掘.
Efficient Divisible E-cash System Based on Reverse Binary Tree
Zhang Jiang-xiao①Guo Hua①②Li Zhou-jun①
①(,,100191,)②(,,,100093,)
There exist some defects such as low efficiency in the spending protocol and deposit protocol of the proposed by Izabachene. (2012) divisible E-cash system based on the standard model. Using the Groth-Sahai (GS) proof system and accumulator, this paper proposes a reverse binary tree algorithm and designs an efficient divisible E-cash system under the standard model. The new system can calculate simultaneously the series number of the leaf nodes of the binary tree in the process of the binary tree construction. A user can prove the correctness of spending path directly, thus the computation load of user is constant in the spending protocol. The new system achieves both the weak exculpability and the strong exculpability. Finally, the security proof of the system is given in the standard model which includes unforgeability, anonymity, identification of double spender and exculpability.
Divisible E-cash system; Standard model; Reverse binary tree; Bounded accumulator; Groth-Sahai
TP393
A
1009-5896(2014)01-0022-05
10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00466
2013-04-09收到,2013-10-08改回
国家自然科学基金 (60973105, 90718017, 61170189, 61300172),软件开发环境国家重点实验室自主研究课题(SKLSDE-2011ZX-03, SKLSDE-2012ZX-11)和博士点基金(20111102130003, 20121102120017)资助课题
张江霄 orange_0092008@live.cn
