人参皂苷Rg1对阿尔茨海默病大鼠脑片模型tau蛋白磷酸化的影响
2014-04-23权乾坤袁海峰
李 明,李 玺*,权乾坤,袁海峰,李 源,王 娟
人参皂苷Rg1对阿尔茨海默病大鼠脑片模型tau蛋白磷酸化的影响
李 明1,李 玺1*,权乾坤1,袁海峰2,李 源3,王 娟4
(西安交通大学医学院第二附属医院:1老年病科,2脑病科,西安 710004;3西安市电力中心医院脑病科,西安 710032;4第四军医大学西京医院检验中心,西安 710032)
观察人参皂苷Rg1对阿尔茨海默病(AD)大鼠脑片模型中磷酸化tau蛋白(P-tau)及钙调神经磷酸酶(CaN)表达的影响,探讨人参皂苷Rg1是否通过上调CaN表达从而抑制AD模型大鼠脑片tau蛋白磷酸化。制备5周龄雄性SD大鼠脑片(含皮质和海马),随机分为4组:对照组、模型组和人参皂苷Rg1组,人参皂苷Rg1+他克莫司(FK506)(一种CaN抑制剂)组,每组10张脑片。各组脑片首先置于人工脑脊液中孵育1h,之后人参皂苷Rg1组和人参皂苷Rg1+FK506组分别加入人参皂苷Rg1作用2h,然后除对照组外的各组分别加入冈田酸作用3h。干预结束后脑片经多聚甲醛固定后做冰冻切片,采用免疫组织化学染色、图像分析技术等方法检测各组大鼠脑片P-tau、CaN的表达水平。与对照组比较,模型组各脑区P-tau表达水平增加(<0.05),CaN表达水平减少(<0.05);与模型组比较,人参皂苷Rg1组各脑区P-tau表达水平减少(<0.05),CaN表达水平增加(<0.05);与人参皂苷Rg1组比较,人参皂苷Rg1+FK506组P-tau表达水平增加(<0.05),CaN表达水平减少(<0.05)。人参皂苷Rg1可能通过上调CaN蛋白表达途径抑制AD大鼠脑片模型tau蛋白磷酸化,从而发挥抗痴呆作用。
人参皂苷Rg1;阿尔茨海默病;磷酸化tau蛋白;钙调神经磷酸酶
阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimer’s disease,AD)的核心病理变化之一是神经原纤维缠结(neurofibrillary tangle,NFT)形成,其产生原因是tau蛋白过度磷酸化致使微管正常功能丧失所致[1]。并且NFT的数目与AD患者的痴呆程度密切相关[2]。研究表明,钙调神经磷酸酶(calcineurin,CaN)的活性下降在AD的tau蛋白异常磷酸化中发挥了重要的作用[3]。而且,CaN活性缺陷所致的tau蛋白异常磷酸化是一个可逆的生理过程,CaN激活剂有望在这一过程中扮演重要的角色。人参皂苷Rg1是人参的主要成分之一,有增强记忆和认知功能的作用[4]。目前研究已证实人参皂苷Rg1可以通过抑制细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶5(CDK5)的表达[5],下调蛋白激酶A(PKA)的表达[6]等途径以抑制tau蛋白磷酸化,但其对CaN的研究未见报道。因此,本实验采用磷酸酯酶抑制剂冈田酸(okadaic acid,OA)孵育大鼠脑片制备tau蛋白过度磷酸化AD大鼠脑片模型,观察人参皂苷Rg1对AD大鼠脑片模型中磷酸化tau蛋白(phosphorylated tau protein,P-tau)及CaN表达的影响,拟阐明人参皂苷Rg1是否通过上调CaN蛋白表达途径以降低AD大鼠脑片模型中P-tau水平,从而发挥抗痴呆作用。
1 材料与方法
1.1 动物
5周龄健康雄性SD大鼠10只,体质量110~130g,清洁级,购自西安交通大学医学院实验动物中心,合格证号为SCXK(陕)2007-001。
1.2 主要试剂
人参皂苷Rg1,纯度98.99%,吉林宏久生物科技股份有限公司;OA,美国Alexis生物制剂公司;CaN多克隆抗体,北京博奥森生物技术有限公司;他克莫司(tacrolimus,FK506),爱尔兰Fujisawa公司;P-tau(Ser202)多克隆抗体及SABC试剂盒、抗体稀释液,武汉博士德生物工程有限公司。
1.3 主要仪器
振动切片机(上海之信仪器有限公司,型号:ZQP-86);冰冻切片机(德国Microm公司,型号:HM500);图像处理与分析系统(德国Leica公司,型号:Qwin550CW);6孔培养板(美国Millipore公司)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 AD大鼠脑片模型制备 SD大鼠经水合氯醛麻醉后,断头取脑,快速置于0~4℃的人工脑脊液冰水混合物中,振动切片机以振幅8档,速度3档行冠状切片所切脑片含皮质和海马,平均厚度400μm。挑选形态较好的脑片(含皮质和海马)置入盛有人工脑脊液的6孔板中孵育,温度(32.0±0.5)℃,整个过程人工脑脊液中持续通入混合氧气(95%O2+5%CO2)。人工脑脊液成分(mmol/L):NaCl 150,CaCl22,MgSO41.2,KH2PO40.5,K2HPO41.5,葡萄糖10,pH7.4。
1.4.2 分组及干预 脑片随机分为4组:对照组、模型组、人参皂苷Rg1组、人参皂苷Rg1+FK506组,每组10张脑片。人工脑脊液孵育1h,人参皂苷Rg1组加入人参皂苷Rg1 240μmol/L,人参皂苷Rg1+FK506组加入人参皂苷Rg1 240μmol/L、FK506 1.25μmol/L,培养2h,然后模型组、人参皂苷Rg1组和人参皂苷Rg1+FK506组分别加入OA(1μmol/L)孵育3h。对照组不加任何处理因素。
1.4.3 P-tau、CaN蛋白表达检测 干预结束后,各组大鼠脑片经4%多聚甲醛固定4h,然后转入30%蔗糖溶液浸泡至沉底,做冰冻切片,切片10μm厚,每张切片含皮层、海马、齿状回。采用免疫组化染色(SABC法)分别检测各组脑片皮质和海马P-tau、CaN的蛋白表达情况。P-tau(Ser202)、CaN一抗浓度分别为1∶1000和1∶600,染色步骤按说明书进行,PBS代替一抗作阴性对照。采用图像处理与分析系统检测脑片阳性反应物质的平均灰度值,每张切片同一区域中,随机选取6个视野,检测面积相同,取其平均灰度值代表该切片目标区域的蛋白表达水平。灰度值越低,阳性表达量越高,反之灰度值越高,阳性表达量越低。
1.5 统计学处理
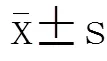
2 结 果
2.1 OA处理后脑片P-tau、CaN表达情况
与对照组比较,模型组各脑区P-tau阳性反应物质表达增加(<0.05),CaN阳性反应物质表达减少(<0.05;表1)。
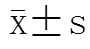
表1 OA对AD大鼠培养脑片P-tau和CaN表达量的影响
OA: okadaic acid; AD: Alzheimer’s disease; CA1: CA1 area of hippocampus;CA3: CA3 area of hippocampus; DG: dentate gyrus. Compared with control group,*<0.05
2.2 人参皂苷Rg1干预后各组大鼠脑片P-tau表达情况
与模型组比较,人参皂苷Rg1组P-tau阳性反应物质均有不同程度减少(<0.05),与人参皂苷Rg1组比较,人参皂苷Rg1+FK506组P-tau阳性反应物质均有不同程度增加(<0.05;表2,图1)。
2.3 人参皂苷Rg1干预后各组脑片CaN表达情况
与对照组比较,模型组CaN阳性反应物质表达明显减少(<0.05)。与模型组比较,人参皂苷Rg1组CaN阳性反应物质表达明显增加(<0.05);与人参皂苷Rg1组比较,人参皂苷Rg1+FK506组CaN阳性反应物质表达明显减少(<0.05;表3,图2)。

图1 各组大鼠脑片CA3区P-tau蛋白表达(免疫组织化学染色,×400)
Figure 1 Expression of P-tau in CA3 of hippocampus in different groups (SABC ×400)
A: control group; B: model group; C: ginsenoside Rg1 group; D:ginsenoside Rg1+FK506 group. P-tau ( tan color ) is expressed in thecytoplasm of neurons in the brain slices, and P-tau expression is stronegest in model group, followed by ginsenoside Rg1+FK506 group, and the lowest in ginsenoside Rg1 and control groups

图2 各组大鼠脑片海马齿状回CaN蛋白表达(免疫组织化学染色,×400)
Figure 2 Expression of CaN protein in dentate gyrus of hippocampus in different groups (SABC ×400)
A: control group; B: model group; C: ginsenoside Rg1 group; D:ginsenoside Rg1+FK506 group. CaN (tan color) is expressed in thecytoplasm of neurons in the brain slices, and CaN expression is strongest in the control group, followed by ginsenoside Rg1 group, and the lowest in ginsenoside Rg1+FK506 and model groups
3 讨 论
NFT是AD患者脑内主要病理改变之一,其产生的原因是tau蛋白的过度磷酸化。tau蛋白是神经元微管相关蛋白,过度磷酸化后,会促进微管组装的生物活性丧失,导致细胞骨架的结构异常而形成NFT[7]。目前已发现tau蛋白有45个磷酸化位点,其中包括Ser202位点。OA是蛋白磷酸酶的高效选择性抑制剂,目前被广泛应用于诱导tau蛋白的过度磷酸化[8,9],研究者在大鼠脑内注射OA可诱导tau蛋白在Ser-198/Ser-199/Ser-202,Ser-396/Ser-404位点发生磷酸化,导致大鼠空间记忆障碍[10]。本实验选用Ser202位点磷酸化进行研究,结果发现模型组大鼠脑片可见少量细胞结构破坏,胶质细胞增生,未见细胞层厚度变化;免疫组化染色结果表明模型组大鼠脑片P-tau蛋白表达较对照组增加,推测OA可能诱导了大鼠脑片tau蛋白在Ser202位点发生磷酸化。实验结果还表明,人参皂苷Rg1组P-tau蛋白表达较模型组明显降低,而且人参皂苷Rg1这种作用可以被CaN抑制剂FK506有效抑制(人参皂苷Rg1+FK506组与人参皂苷Rg1组之间比较,<0.05)。这表明人参皂苷Rg1能有效减轻OA引起的Tau蛋白过度磷酸化,且这种作用可能与CaN相关。
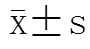
表2 人参皂苷Rg1对AD模型大鼠脑片P-tau表达的影响
AD: Alzheimer’s disease; CA1: CA1 area of hippocampus; CA3: CA3 area of hippocampus; DG: dentate gyrus. Compared with control group,*<0.05; compared with model group,#<0.05; compared with ginsenoside Rg1 group,△<0.05
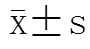
表3 人参皂苷Rg1对AD模型大鼠脑片CaN表达的影响
CA1: CA1 area of hippocampus; CA3: CA3 area of hippocampus; DG: dentate gyrus. Compared with control group,*<0.05; compared with model group,#<0.05; compared with ginsenoside Rg1 group,△<0.05
tau蛋白的磷酸化主要受蛋白激酶和蛋白磷酸酶的调节,蛋白磷酸酶活性的降低可能比蛋白激酶活性的升高在tau蛋白的磷酸化过程中起更大的作用[11]。体外磷酸化的tau蛋白去磷酸化可以使NFT松解,恢复tau蛋白的连接微管及发挥促微管组装的功能[12]。研究发现,将CaN的抑制剂注入小鼠脑室腔里,可导致tau蛋白几个特殊位点过度磷酸化[13]。体外实验研究证实蛋白磷酸酶均可使P-tau蛋白发生去磷酸化,其中CaN导致P-tau去磷酸化的位点最多,另外CaN也是海马区最主要的P-tau去磷酸化磷酸酶[14]。本实验采用人参皂苷Rg1对AD样tau蛋白磷酸化大鼠脑片模型干预后,结果表明大鼠脑片CaN表达明显增多,这种作用同样可以被CaN抑制剂FK506有效抑制。这表明人参皂苷Rg1可能通过上调CaN表达途径从而促进P-tau去磷酸化。另外,本实验还发现CaN抑制剂FK506对人参皂苷Rg1下调P-tau作用的抑制是不完全的,推测除上调CaN途径外,人参皂苷Rg1还可通过其他途径促进P-tau去磷酸化,这在未来实验中需要进一步的证实。
总之,本研究证实了人参皂苷Rg1可能通过上调CaN蛋白表达途径以降低AD大鼠脑片模型中磷酸化tau蛋白水平,从而发挥抗痴呆作用,为人参皂苷Rg1治疗AD的研究提供了新靶点、新思路。
[1] Wang JZ, Tian Q. Mechanism of action on tau hyperphosphorylation and spatial memory of rat[J]. Prog Biochem Biophys, 2012, 39(8): 771−777. [王建枝, 田 青. tau蛋白过度磷酸化机制及其在阿尔茨海默病神经元变性中的作用[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2012, 39(8): 771−777.]
[2] Giannakopoulos P, Herrmann FR, Bussière T,. Tangle and neuron numbers, but not amyloid load, predict cognitive status in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Neurology, 2003, 60(9): 1495−1500.
[3] Mansuy IM. Calcineurin in memory and bidirectional plasticity[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2003, 311(4): 1195−1208.
[4] Zhang JT. Nootropic mechanisms of ginsenoside Rg1—influence on neuronal plasticity and neurogenesis[J]. Acta Pharm Sin, 2005, 40(5): 385−388. [张均田. 人参皂苷Rg1的促智作用机制—对神经可塑性和神经发生的影响[J]. 药学学报, 2005, 40(5): 385−388.]
[5] Zhang J, Huang TW, Chen XC,. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates tau hyperphosporylation induced by fibrillar Aβ25-35 in primary cortical neuronscyclin-dependent kinase 5 signaling[J]. J Fujian Med Univ, 2008, 42(1): 9−11. [张 静, 黄天文, 陈晓春, 等. 人参皂苷Rg1通过CDK5途径减轻Aβ25-35诱导的神经元tau蛋白磷酸化[J]. 福建医科大学学报, 2008, 42(1): 9−11.]
[6] Li X, Zhang X, Zhang ZY,. The effects of gensenoside Rg1 on the expressions of P-tau and PKA on the brain slices of AD model rats[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2009, 29(19): 2468−2470. [李 玺, 张 欣, 张智燕, 等. 人参皂苷Rg1对AD模型大鼠脑片P-tau、PKA影响的实验研究[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2009, 29(19): 2468−2470.]
[7] Zhou FT, Chen SR, Sun XC. Research progress in abnormal phosphorylation of microtubule-associated tau protein and of the targeted inhibition of the phosphorylation[J]. J Biomed Eng, 2012, 29(4): 788−792. [周付涛, 陈双容, 孙学川. 微管相关蛋白tau磷酸化及其靶向抑制作用研究进展[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2012, 29(4): 788−792.]
[8] Qian W, Shi J, Yin X,. PP2A regulates tau phosphorylation directly and also indirectlyactivating GSK-3beta[J].J Alzheimers Dis,2010, 19(4): 1221−1229.
[9] Li KJ, Hu JP. Estradiol on tau protein phosphorylation of SH SY5Y cells induced by okadaic acid[J]. Chin J gerontol, 2014, 34(2): 412−413. [李凯军, 胡江平. 雌二醇对冈田酸诱导的SH-SY5Y细胞tau蛋白磷酸化的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2014, 34(2): 412−413.]
[10] Tian Q, Zhang Q, Wang Q,. Hyperphosphorylation of tau and decrease in Ach level in the Meynert nucleus basalis of rat brain induced by OA[J]. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol (Nature Sci Ed), 2004, 32(12): 94−96. [田 青, 张 蕲, 王 群, 等. OA诱导大鼠基底核Ach降低及τ蛋白过度磷酸化[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 32(12): 94−96.]
[11] Song MJ, Dai XL, Jiang ZF. Tau protein phosphorylation and Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Chin Bull Life Sci, 2013, 25(3): 315−319. [宋明洁, 戴雪伶, 姜招峰. tau蛋白过磷酸化与阿尔茨海默病[J]. 生命科学, 2013, 25(3): 315−319.]
[12] Luo J, Wei J. Calcineurin as a novel target in drug therapy of Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Chin J Pharmacol Toxicol, 2004, 18(1): 71−74. [骆 静, 魏 群. 阿尔茨海默病药物治疗的新靶点钙调神经磷酸酶[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2004, 18(1): 71−74.]
[13] Luo J, Ma J, Yu DY,. Infusion of FK506, a specific inhibitor of calcineurin, induces potent tau hyperphosphorylation in mouse brain[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2008, 76(5): 464−468.
[14] Kayyali US, Zhang W, Yee AG,. Cytoskeletal changes in the brains of mice lacking calcineurin A alpha[J]. J Neurochem, 1997, 68(4): 1668−1678.
(编辑: 周宇红)
Effect of gensenoside Rg1 on tau phosphorylation in rat brain slice model of Alzheimer’s disease
LI Ming1, LI Xi1*, QUAN Qian-Kun1, YUAN Hai-Feng2, LI Yuan3, WANG Juan4
(1Department of Geriatrics,2Department of Encephalopathy, the Second Affiliated Hospital, College of Medicine, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710004, China;3Department of Encephalopathy, Xi’an Central Hospital of Electrical Power Inc, Xi’an 710032, China;4Center for Laboratory Medicine, Xijing Hospital, the Fourth Military Medical University, Xi’an 710032, China)
To determine the effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on the expression of phosphorylated tau protein(P-tau) and calcineurin (CaN) in a rat brain slice model of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) induced by okadaic acid (OA), and to investigate whether gensenoside Rg1 inhibits tau phosphorylation through up-regulating CaN in the process.Brain slices (containing cerebral cortex and hippocampus) in 400 µm thickness were obtained from 5-week-old SD rats, and then randomly divided into control, model, ginsenoside Rg1 and ginsenoside Rg1+tacrolimus (FK506, CaN inhibitor) groups, with 10 slices in each group. All these brain slices were cultured with artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) firstly, and then ginsenoside Rg1 with or without FK506 was added into the ACSF of the corresponding groups for 2 h. Then, OA was administrated into ACSF of model, ginsenoside Rg1 and ginsenoside Rg1+FK506 groups separately for 3 h to induce tau phosphorylation to prepare AD model. There was no any intervention for the control group. Expression of P-tau and CaN proteins in brain slices as determined by immunohistochemical staining, and the results were analyzed by image acquisition and analysis system.Compared with the control group, the level of P-tau protein was significantly higher (<0.05) and that of CaN protein was obviously lower (<0.05) in the model group. Compared with the model group, the expression of P-tau was markedly lower (<0.01) and that of CaN protein was remarkably higher (<0.05) in the ginsenoside Rg1 group. Compared with the ginsenoside Rg1 group, the expression of P-tau was higher (<0.01) and the expression of CaN protein was lower (<0.05) in the ginsenoside Rg1+FK506 group.Ginsenoside Rg1 inhibits tau phosphorylation probably by enhancing CaN expression in rat brain slice model of AD, and thus exerts anti-dementia effect.
gensenoside Rg1; Alzheimer’s disease; phosphorylated tau protein; calcineurin
[2007K16-07(5)](2005030).
R745.7
A
10.3724/SP.J.1264.2014.000162
2014−06−03;
2014−07−11
陕西省科技攻关计划项目[2007K16-07(5)]; 陕西省中医药管理局基金项目(2005030)
李 玺, E-mail: lixi2100@sohu.com
