他汀类药物对高血压患者降压效应的Meta分析
2013-12-23阮燕萍赵肖奕严健华范中杰
阮燕萍,赵肖奕,严健华,范中杰
心血管危险因素经常是共存的,它们结合的效应往往大于各自效应总和。高血压和血脂异常的两者联合在人群中很多见,而且血压控制和降脂治疗达标能够成功降低心血管疾病危险性[1,2]。羟甲基戊二酰辅酶A还原酶抑制剂(他汀类药物)的降脂治疗已得到广泛认可,且有稳定斑块的作用,能够明显改善冠心病患者的长期预后。近年来他汀类药物独立于降脂之外的降压效应也逐渐被发现,但是目前的结果并不一致。因此,本研究对现有他汀类药物对高血压患者血压影响的随机对照试验进行了Meta分析,以便为临床用药提供科学证据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 文献纳入与排除标准
1.1.1 研究对象 高血压以及高血压合并高脂血症或者糖尿病的患者。
1.1.2 干预及对照措施 试验组患者接受他汀类药物治疗,对照组患者接受安慰剂或者其他非他汀类降脂药物。
1.1.3 结局指标 主要观察指标为治疗前后的收缩压和舒张压。
1.1.4 研究类型 随机对照试验(RCTs)。
1.1.5 排除标准 排除研究质量差、设计不合理、数据不完整和无法获取全文的研究,同时排除有卒中、肾脏疾病或冠心病史,以及在研究期间降压药物发生变化的研究人群。
1.2 文献检索 在Cochrane library、PubMed和Embase网络数据库中检索2012年12月31日之前的关于他汀类药物对高血压患者血压影响的随机对照试验。文献检索策略如下:#1:"hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors";#2:(hydroxymethylglutaryl-coa next reductase next inhibitors);#3:(hmg next coa)or hmg-coa or(hmg next co-a) and (reductase next inhibitor*);#4:statin* ;#5:fluvastatin;#6:simvastatin;#7:pravastatin;#8:lovastatin;#9:cerivastatin;#10:atorvastatin;#11:rosuvastatin;#12:(#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11)Limits: Humans, Randomized Controlled Trial, English;#13:hypertension;#14:MeSH descriptor Hypertension explode all trees;#15:(#13 OR #14)Limits: Humans, Randomized Controlled Trial, English;#16:(#12 AND #15)
1.3 资料提取 按照设计好的资料提取表格,两位研究者分别独立提取以下信息:研究的设计及研究对象的一般特征;药物、剂量和治疗时间;治疗和对照组在治疗前后的收缩压和舒张压的均数和标准差或者治疗前后收缩压和舒张压差值的均数和标准差。
1.4 质量评价 根据改良Jadad量表对所纳入研究进行质量评估,包括随机方法、分配隐藏、盲法和失访或者退出报告。最高分为7分,Jadad量表将纳入的研究根据质量评分,分为两类:1~3分为低质量研究,4~7分为高质量研究。该过程由两位研究者独立完成并交叉核对,如有不同意见,由第三位研究者协助解决。
1.5 统计学分析 统计学分析采用RevMan 5.0版统计软件。本研究的指标为连续性变量,采用加权均数差(weighted mean difference,WMD)和95% 可信区间(confidence interval,CI)作为合并统计量(P<0.05为差异有统计学意义)。通过I2评估纳入研究的统计学异质性,当I2<50%时,表明异质性较小,可采用固定效应模型来分析;反之,采用随机效应模型。此外,当异质性明显时,还可进一步行亚组分析对异质性来源进行定位,本研究根据基线血压水平、不同他汀类药物进行亚组分析,明确异质性来源于基线差异或者药物差异。采用RevMan 5.0绘制漏斗图(Funnel plots)来评价纳入文献是否存在发表偏倚。通过去除低质量研究进行敏感性分析检测。
2 结果
2.1 文献检索结果 共检索出1103篇文献,去除重复发表后得到的文献数量为771篇,阅读题目和摘要初筛后得到的文献数量为98篇,再通过阅读全文排除不符合纳入标准的文献,对于无全文的研究,研究者采取查阅纸质版杂志或者跟作者联系索要,最后纳入33篇文献(图1)。
2.2 纳入研究的一般特征及质量评价 纳入的33篇文献中有5篇文献[3,4,8,15,25]各包括两个研究样本,有1篇文献[16]包括三个研究样本,所以进行Meta分析的研究样本为40个,共包括2915例受试者。在本文所纳入的研究中有72.5%(29/40)的研究评分在4~6分,属于高质量研究,而有11项研究[7,9,11,15,17-18,22,27,32,35]评分为3分。
2.3 Meta分析结果

图1 文献纳入流程图

表1 纳入研究的特征与质量评价
2.3.1 他汀类药物对收缩压的影响 对所有入选研究进行异质性检验,P<0.001,I2=91%,提示各研究间存在明显异质性。根据基线血压水平进行亚组分析,分为两组:收缩压≥140 mmHg组和<140 mmHg组,两组异质性分别为I2=92%和I2=89%(P<0.001),采用随机效应模型进行分析。结果示:与对照组相比,他汀类药物治疗组收缩压下降1.52 mmHg(95%CI:-2.35~ -0.68,P<0.001)。基线收缩压≥140 mmHg时,收缩压下降2.28 mmHg(95%CI:-3.57~ -1.00,P<0.001),而基线收缩压<140 mmHg的受试者收缩压下降0.73mmHg(P=0.29,图2)。
2.3.2 他汀类药物对舒张压的影响 与对照组相比,他汀类药物治疗可使舒张压下降1.02 mmHg(95%CI:-1.70~-0.34,P=0.003)。根据基线舒张压水平进行亚组分析,舒张压≥90 mmHg时,他汀类药物对舒张压的效应[-1.87 mmHg(95%CI:-3.12~-0.62,P=0.003)]明显大于舒张压<90 mmHg者[-0.52mmHg(95%CI: -1.33~0.29,P=0.21)](图3)。
2.3.3 不同他汀类药物对血压影响的的亚组分析 不同他汀类药物分组后,异质性仍然明显(阿托伐他汀组P<0.001,I2=83%;氟伐他汀组组P<0.001,I2=84%;普伐他汀组P<0.001,I2=90%;辛伐他汀组P<0.001,I2=93%),故采用随机效应模型评估他汀类药物对血压的影响。与对照组相比,阿托伐他汀治疗可使收缩压下降4.04 mmHg(95%CI:-6.43~-1.65,P=0.00009),可使舒张压下降2.67 mmHg (95%CI:-4.32~-1.02,P=0.002)。其他他汀类药物对血压的影响不明显(P均>0.05)。

图2 他汀类药物对不同基线收缩压水平的亚组分析
2.3.4 他汀类药物治疗时间对血压影响的亚组分析 根据他汀类药物的治疗时间,将纳入研究分为≤3个月组,3个月~6个月组(包括6个月)和>6个月组。结果显示,与对照组相比,他汀类药物治疗3个月~6个月组收缩压下降4.76 mm Hg(95%CI:-7.89~-1.64,P=0.003)、舒张压下降2.22 mm Hg(95%CI:-3.93~-0.51,P=0.01)。其余两组收缩压和舒张压变化与对照组比较均无有统计学差异(P均>0.05)。
2.4 发表偏倚评价和敏感性分析 他汀类药物对收缩压和舒张压影响漏斗图基本对称(图4),可排除各研究的发表偏倚。将Jadad评分3分的研究排除后,与对照组相比,他汀类药物可使收缩压下降1.33 mmHg(P=0.004),使舒张压降低0.85 mmHg(P=0.03),差异仍具有统计学意义,表明本Meta分析的结果基本稳定。
3 讨论

图3 他汀类药物对不同基线舒张压水平的亚组分析
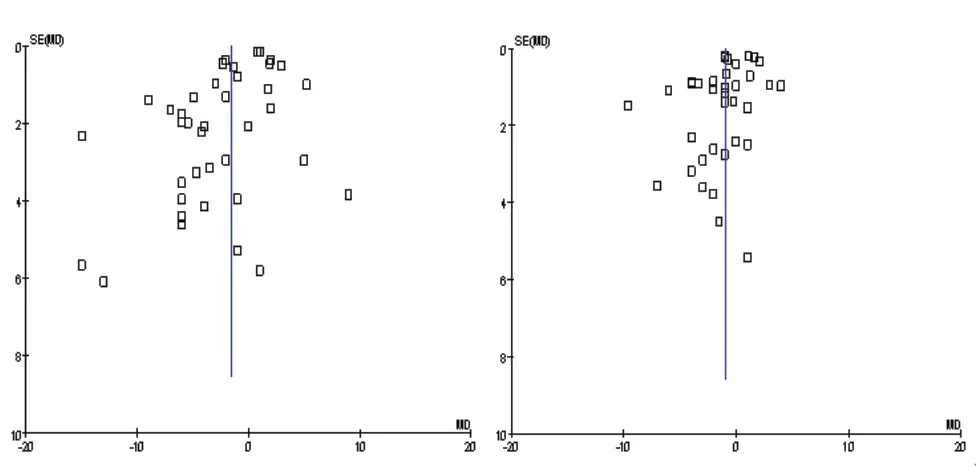
图4 他汀类药物对收缩压(左)和舒张压(右)影响的漏斗图
3.1 纳入研究的特征及质量 本研究根据纳入和排除标准筛选后,共纳入33篇文献,包括40个研究样本,2915例研究对象。根据改良Jadad量表对所纳入研究进行质量评估,只有Derosa的研究[8]描述了随机的方法,评分结果显示有72.5%属于高质量研究,低质量研究仅采用随机方法,未使用盲法,从而有可能影响研究结果的真实性和可靠性。对纳入研究进行敏感性分析,得出较稳定的结果。由于各研究之间异质性明显,研究者根据基线血压水平、不同他汀类药物和不同治疗时间将所纳入研究进行了亚组分析。
3.2 本研究对临床的指导意义 本研究对目前他汀类药物对高血压患者血压影响的研究进行Meta分析,结果显示:他汀类药物可降低高血压患者的收缩压和舒张压,且与基线血压相关,当基线血压高于140/90 mmHg时降压效应具有统计学意义,以阿托伐他汀的降压效应最为明显,且治疗(3~6)个月时效果明显,这将进一步肯定他汀类药物在心血管危险因素管理及心血管疾病治疗方面的地位。在我们国家也有少数研究比较高血压患者氟伐他汀、贝那普利及联合用药的临床疗效,结果发现药物联合治疗高血压,临床疗效优于单一用药,是较理想的降压治疗方案。2012年,Hashimoto等[36]研究他汀类药物对接受不同降压药治疗高血压患者血压的影响,结果显示,他汀类药物可使接受β受体阻滞剂的患者舒张压下降。目前认为他汀类药物可能通过增加一氧化氮(NO)的生物利用度来改善内皮功能,促进再内皮化,并降低氧化应激和抑制炎症反应[14]。
3.3 本研究的局限性及未来临床研究的方向 入选的随机对照试验样本量都比较小,而目前一些大规模的他汀类药物治疗的研究由于没有提供治疗前后的血压值而不能纳入本Meta分析。入选的各研究由于设计不同、采用不同的标准等导致异质性较大。本研究的结果表明他汀类药物的降压效应是存在的,尤其是在治疗(3~6)个月时,以阿托伐他汀最明显。将来还需更多的随机对照研究来探讨他汀类药物对不同降压药物治疗的高血压患者血压程度的影响和机制。
[1] Grundy SM,Cleeman JI,Merz CN,et al. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III Guidelines[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol,2004,44(3):720-32.
[2] Studer M,Briel M,Leimenstoll B,et al. Effect of different antilipidemic agents and diets on mortality:a systematic review[J]. Arch Intern Med,2005,165(7):725-30.
[3] Anderssen SA,Hjelstuen AK,Hjermann I,et al. Fluvastatin and lifestyle modification for reduction of carotid intima-media thickness and left ventricular mass progression in drug-treated hypertensives[J]. Atherosclerosis,2005,178(2):387-97.
[4] Bak AA,Huizer J,Leijten PA,et al. Diet and pravastatin in moderate hypercholesterolaemia: a randomized trial in 215 middle-aged men free from cardiovascular disease[J]. J Intern Med,1998,244(5):371-8.
[5] Balletshofer BM,Goebbel S,Rittig K,et al. Intense cholesterol lowering therapy with a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor does not improve nitric oxide dependent endothelial function in type-2-diabetes—a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, three-arm placebo-controlled clinical trial[J]. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes,2005,113(6):324-30.
[6] Beck AL,Otto ME, D'Avila LB,et al. Diastolic function parameters are improved by the addition of simvastatin to enalapril-based treatment in hypertensive individuals[J]. Atherosclerosis,2012,222(2):444-8.
[7] Danaoglu Z,Kultursay H,Kayikcioglu M,et al. Effect of Statin Therapy Added to ACE-Inhibitors on Blood Pressure Control and Endothelial Functions in Normolipidemic Hypertensive Patients[J]. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg,2003,3(4):331-7.
[8] Derosa G,Mugellini A,Ciccarelli L,et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled comparison of the action of orlistat, fluvastatin or both, on anthropometric measurements, blood pressure and lipid profile in obese patients with hypercholesterolemia prescribed a standardized diet[J]. Clin Ther,2003,25(4):1107-22.
[9] Fogari R,Derosa G,Lazzari P,et al. Effect of amlodipine-atorvastatin combination on fibrinolysis in hypertensive hypercholesterolemic patients with insulin resistance[J]. Am J Hypertens,2004,17(9):823-7.
[10] Fogari R,Preti P,Zoppi A,et al. Effects of amlodipine-atorvastatin combination on inflammation markers and insulin sensitivity in normocholesterolemic obese hypertensive patients[J]. Eur J Clin Pharmacol,2006,62:817-22.
[11] Ge CJ,Lu SZ,Chen YD,et al. Synergistic effect of amlodipine and atorvastatin on blood pressure,left ventricular remodeling, and C-reactive protein in hypertensive patients with primary hypercholesterolemia[J]. Heart Vessels,2008,23(2):91-5.
[12] Glorioso N,Troffa C,Filigheddu F,et al. Effect of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension and primary hypercholesterolemia [J]. Hypertension,1999,34(6):1281-6.
[13] Gomes ME,Tack CJ,Verheugt FW,et al. Sympathoinhibition by Atorvastatin in Hypertensive Patients[J]. Circ J,2010,74(12):2622-6.
[14] Han SH,Koh KK,Quon MJ,et al. The effects of simvastatin, losartan, and combined therapy on soluble CD40 ligand in hypercholesterolemic, hypertensive patients[J]. Atherosclerosis,2007,190(1):205-11.
[15] Hjelstuen A,Anderssen SA,Holme I,et al. Effect of lifestyle and/or statin treatment on soluble markers of atherosclerosis in hypertensives [J]. Scand Cardiovasc J,2007,41(5):313-20.
[16] Ichihara A,Hayashi M,Koura Y, et al. Long-term effects of statins on arterial pressure and stiffness of hypertensives [J]. J Hum Hypertens,2005,19(2):103-9.
[17] Ikeda T,Sakurai J,Nakayama D,et al. Pravastatin has an additional depressor effect in patients undergoing long-term treatment with antihypertensive drugs[J]. Am J Hypertens,2004,17(6):502-6.
[18] Jenkins DJ,Kendall CW,Marchie A,et al. Effects of a dietary portfolio of cholesterol-lowering foods vs. Lovastatin on serum lipids and C-reactive protein [J]. JAMA,2003,290(4):502-10.
[19] Kanaki AI,Sarafidis PA,Georgianos PI,et al. Low-dose atorvastatin reduces ambulatory blood pressure in patients with mild hypertension and hypercholesterolaemia: A double-blind, randomized, placebocontrolled study [J]. J Hum Hypertens,2012,26(10):577-84.
[20] Koh KK,Quon MJ,Han SH,et al. Additive beneficial effects of losartan combined with simvastatin in the treatment of hypercholesterolemic, hypertensive patients [J]. Circulation,2004,110(24):3687-92.
[21] Koh KK,Quon MJ,Han SH,et al. Additive beneficial effects of atorvastatin combined with amlodipine in patients with mild-tomoderate hypertension [J]. Int J Cardiol,2011,146(3):319-25.
[22] Kuklinska AM,Mroczko B,Musial WJ,et al. Hypotensive effect of atorvastatin is not related to changes in inflammation and oxidative stress[J]. Pharmacological reports,2010,62(5):883-90.
[23] Lee TM,Chou TF,Tsai CH. Association of pravastatin and left ventricular mass in hypercholesterolemic patients: role of 8-isoprostaglandin F2α formation [J]. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol,2002,40(6):868-74.
[24] Lewandowski J,Sinski M,Bidiuk J,et al. Simvastatin reduces sympathetic activity in men with hypertension and hypercholesterolemia [J]. Hypertension Research,2010,33(10):1038-43.
[25] Liu L,Zhao SP,Zhou HN,et al. Effect of fluvastatin and valsartan, alone and in combination, on postprandial vascular inflammation and fibrinolytic activity in patients with essential hypertension[J]. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol,2007,50(1):50-5.
[26] Mancia G,Parati G,Revera M,et al. Statins, antihypertensive treatment, and blood pressure control in clinic and over 24 hours: evidence from PHYLLIS randomised double blind trial [J].BMJ,2010,340:c1197.
[27] Manisty C,Mayet J,Tapp RJ,et al. Atorvastatin Treatment Is Associated With Less Augmentation of the Carotid Pressure Waveform in Hypertension : A Substudy of the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcome Trial (ASCOT)[J]. Hypertension,2009,54(5):1009-13.
[28] McDowell IF,Smye M,Trinick T,et al. Simvastatin in severe hypercholesterolemia: a placebo controlled trial[J]. Br J Clin Pharmac,1991,31(3):340-3.
[29] Nakamura T,Ushiyama C,Hirokawa K,et al. Effect of cerivastatin on urinary albumin excretion and plasma endothelin-1 concentrations in type 2 diabetes patients with microalbuminuria and dyslipidemia [J]. Am J Nephrol,2001,21(6):449-54.
[30] O’Callaghan CJ,Krum H,Conway EL,et al. Short term effects of pravastatin on blood pressure in hypercholesterolaemic hypertensive patients[J]. Blood Pressure,1994,3(6):404-6.
[31] Orr JS,Dengo AL,Rivero JM,et al. Arterial Destiffening With Atorvastatin in Overweight and Obese Middle-Aged and Older Adults [J]. Hypertension,2009,54(4):763-8.
[32] Pan XD,Zeng ZH,Liang LY,et al. The effects of simvastatin on left ventricular hypertrophy and left ventricular function in patients with essential hypertension [J]. Clin Exp Hypertens,2011,33(8):558-64.
[33] Straznicky NE,Howes LG,Lam W,et al. Effects of pravastatin on cardiovascular reactivity to norepinephrine and angiotensin II in patients with hypercholesterolemia and systemic hypertension [J]. Am J Cardiol,1995,75(8):582-6.
[34] Teixeira AA,Buffani A,Tavares A,et al. Effects of fluvastatin on insulin resistance and cardiac morphology in hypertensive patients [J]. J Hum Hypertens,2011,25(8):492-9.
[35] Terzoli L,Mircoli L,Raco R,et al. Lowering of Elevated Ambulatory Blood Pressure by HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors[J]. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol,2005,46(3):310-5.
[36] Hashimoto S,Urushihara H,Hinotsu S,et al. Effect of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on blood pressure in hypertensive patients treated with blood pressure-lowering agents: retrospective study using an anti-hypertensive drug database[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2012,16(2):235-41.
