Syntheses and Structures of Two Copper(Ⅱ)Complexes with Salicyl Mono-oxime Ligands
2013-09-29DONGWenKuiGONGShangShengTONGJunFengSUNYinXiaWUJianChaoSchoolofChemicalandBiologicalEngineeringLanzhouJiaotongUniversityLanzhou730070
DONG Wen-Kui GONG Shang-Sheng TONG Jun-Feng SUN Yin-Xia WU Jian-Chao(School of Chemical and Biological Engineering,Lanzhou Jiaotong University,Lanzhou 730070)
Syntheses and Structures of Two Copper(Ⅱ)Complexes with Salicyl Mono-oxime Ligands
DONG Wen-Kui*GONG Shang-Sheng TONG Jun-Feng SUN Yin-Xia WU Jian-Chao
(School of Chemical and Biological Engineering,Lanzhou Jiaotong University,Lanzhou 730070)
Two new CuⅡcomplexes,[Cu(L1)2](1)(HL1=(E)-3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde O-methyl oxime)and[Cu(L2)2](2)(HL2=(E)-2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde O-ethyl oxime),have been synthesized and characterized by elemental analyses,IR spectra,UV-Vis spectra and X-ray diffraction methods.X-ray crystallographic analyses show that complexes 1 and 2 are mono-nuclear structure.The four-coordinated CuⅡatoms of the two complexes lie in the N2O2coordination sphere of two mono-oxime ligands,and complex 1 has a square planar geometry distorted tetrahedrally,whereas complex 2 has a regular square planar geometry.Complex 1 forms an infinite 1D chain-like supramolecular structure by intermolecular hydrogen bonds,while complex 2 forms an infinite 2D supramolecular structure by intermolecular hydrogen bonds and π…π packing interaction.CCDC:757700,1;776433,2.
mono-oxime ligand;copper(Ⅱ)complex;characterization;crystal structure;synthesis
Oxime-type compounds(-C=N-OR)are a kind of very important ligands containing N atoms,they are usually synthesized by the condensation of ketones or aldehydes with hydroxylamine et.al.The chemical characteristics of the oxime compounds have been known by more and more people,not only because the O-alkyloxime groups in these complexes resist metathesis of the C=N bonds[1-4]but also because the large electronegativity of the oxygen atoms is expected to affect strongly the electronic properties of the N2O2coordination sphere,which can lead to different and novelproperties and structures ofthe resulting complexes[5-6].Oxime compounds were widely used in analytical chemistry[7],supramolecular chemistry[8-11],molecular magnetism[12], extraction metallurgy[13],medicine[14]and other areas[15].So,preparing new oxime-type complexes and studying their properties and applications are of great importance to the development of coordinatition chemistry.Herein,two new CuⅡcomplexes with the mono-oxime ligands,[Cu(L1)2](1)(HL1=(E)-3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde O-methyl oxime)and[Cu(L2)2](2)(HL2=(E)-2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde O-ethyl oxime) have been synthesized and characterized by elemental analyses,IR and UV-Vis spectra.X-ray crystallographic analyses reveal that the structures of the complexes 1 and 2 are similar.They are both mononuclear structures and all the CuⅡions are four-coordinated.However,the bond angles and distances vary due to the different substituents in the ligand.
1 Experimental
1.1 Reagents and physical measurements
Methoxyamine and ethoxyamine from Alfa Aesar was used without further purification.3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde,2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde and the other reagents and solvent were analytical grade from Tianjin Chemical Reagent Factory.Elemental analysis for Cu was detected by an IRIS ER/S·WP-1 ICP atomic emission spectrometer.C,H,and N analyses were obtained using a GmbH VarioEL V3.00 automatic elemental analysis instrument.IR spectra were recorded on a VERTEX70 FTIR spectrophotometer,with samples prepared as KBr(500~4 000 cm-1)and CsI(100~500 cm-1)pellets.UV-Vis absorption spectra were recorded on a Shimadzu UV-2550 spectrometer.X-ray single crystal structures were determined by a Bruker SmartAPEX CCD diffractometer.
1.2 Synthesis of(E)-3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde O-methyl oxime(HL1)
To a solution of 3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (279.9 mg,1 mmol)in thermal ethanol(3 mL)was added an ethanol(5 mL)solution of methoxyamine (83.5 mg,1 mmol).After stirring the reaction mixture at 338K for 10 h,the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was recrystallized from ethanol to give the title compound.Yield,61% .m.p.356 ~357 K.Anal.Calcd.for C8H7Br2NO2:C,31.10;H,2.28;N,4.53.Found:C,31.18;H,2.33;N,4.49.
1.3 Synthesis of(E)-2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde O-ethyl oxime(HL2)
To a solution of 2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzaldehyde(167.1 mg,1 mmol)in thermal ethanol(4 mL)was added an ethanol(3 mL)solution of ethoxyamine(97.6 mg,1 mmol).After stirring the reaction mixture at 338 K for 10 h,the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was recrystallized from ethanol to give the title compound.Yield,48%.m.p.391~392 K.Anal.Calcd.for C9H10N2O4:C,51.43;H,4.80;N,13.33.Found:C,51.46;H,4.89;N,13.28.
1.4 Synthesis of[Cu(L1)2](1)
A solution of copper(Ⅱ) acetate monohydrate(2.0 mg,0.01 mmol)in methanol(4 mL)was added dropwise to a solution of HL1(3.0 mg,0.01 mmol)in acetone(3 mL)at room temperature.The color of the mixing solution turned pale-yellow immediately and allowed to stand at room temperature for two weeks.Then the solvent partially evaporated and yellow prismatic single crystals suitable for X-ray crystallographic analysis were obtained.Anal.Calcd.for C16H12Br4CuN2O4(%):C,28.28;H,1.78;N,4.12;Cu,9.35.Found:C,28.14;H,1.86;N,4.09;Cu,9.41.
1.5 Synthesis of[Cu(L2)2](2)
A solution of copper(Ⅱ) acetate monohydrate(1.3 mg,0.01 mmol)in methanol(3 mL)was added dropwise to a solution of HL2(1.3 mg,0.01 mmol)in dichloromethane(5 mL)at room temperature.The color of the mixing solution turned pale-yellow immediately,and allowed to stand at room temperature for about ten days.Then the solvent partially evaporated and yellow prismatic single crystals suitable for X-ray crystallographic analysis were obtained.Anal.Calcd.for C18H18CuN4O8(%):C,44.86;H,3.76;N,11.63;Cu,13.19.Found:C,44.77;H,3.82;N,11.58;Cu,13.28.
1.6 Crystal structure determination
The single crystals of complexes 1 and 2 with approximate dimensions of 0.17 ×0.11 ×0.07 mm and 0.37 ×0.15 ×0.09 mm were placed on a Bruker Smart 1000 CCD area detector.The diffraction data were collected using a graphite monochromated Mo Kαradiation(λ=0.071 073 nm)at 298(2)K.The LP factor and Semi-empirical absorption corrections were applied to the intensity data.The structures were solved by using the program SHELXS-97,and refined by fullmatrix least-squares method on F2using SHELXL-97.The non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically.Hydrogen atoms were added theoretically.Details of the data collection and refinements of complexes 1 and 2 are given in Table 1.
CCDC:757700,1;776433,2.

Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinement for complexes 1 and 2
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Crystal structure
The ORTEP representations of complexes 1 and 2 are shown in Fig.1 and Fig.3 selected bond lengths are in Table 2.The X-ray structural studies reveal that complex 1 crystallizes in the triclinic system and P1 space group,whereas the complex 2 crystallizes in the monoclinic system and P21/c space group.

Fig.1 ORTEP view of the crystal structure with thermal ellipsoids was drawn at the 30%probability for complex 1 and hydrogen atoms have been omitted for clarity

Fig.2 Part supramolecular network structure containing hydrogen bonds for complex 1

Fig.3 ORTEP view of the crystal structure with thermal ellipsoids was drawn at the 30%probability for complex 2 and hydrogen atoms have been omitted for clarity
In complex 1,the CuⅡatom is four-coordinated by two nitrogen(N1 and N2)and two oxygen(O2 and O4)atoms from two (L1)-units.The four atoms of the donor set(N1,N2,O2 and O4)and Cu1 approximately lie in a plane.The dihedral angle between the coordination plane of N1-Cu1-O2 and that of N2-Cu1-O4 is 11.45(3)°,indicating slight distortion toward tetrahedral geometry from the square planar structure.Four primary coordination(two N and two O)atoms give a mean plane distorted tetrahedrally,with N1 and N2 up average by 0.149(3)and 0.150(3)nm and with O2 and O4 belowaverage by 0.148(3)and 0.151(3)nm,respectively.The CuIIion is situated up the mean plane with the deviation of 0.041(3)nm in complex 1.The lengths of Cu1-N1,Cu1-N2,Cu1-O2 and Cu1-O4 bonds are 0.199 0(6),0.197 5(6),0.189 2(4)and 0.189 0(4)nm,respectively.It is noticeable that Cu-N is longer than Cu-O.The angles of N1-Cu1-O2 and N2-Cu1-O4 are 90.3(2)°and 89.0(2)°,respectively.As shown in Fig.2,the crystal structure of complex 1 is stabilized by inter-molecular C1-H1B…Br1 and C9-H9B…Br3 hydrogen bonds(Table 4)with a graph-motif R22(18),which link neighbouring molecules into extended chains,forming an infinite 1D supramolecular structure.
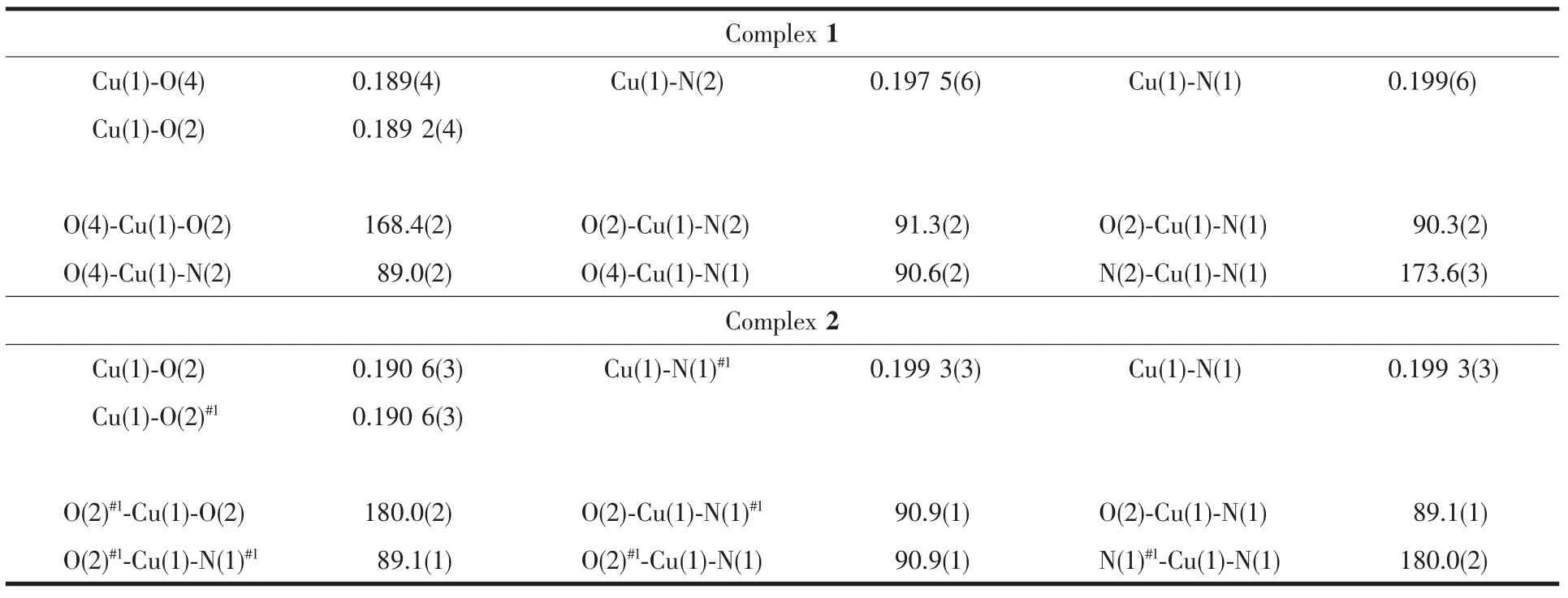
Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and bond angles(°)for complexes 1 and 2
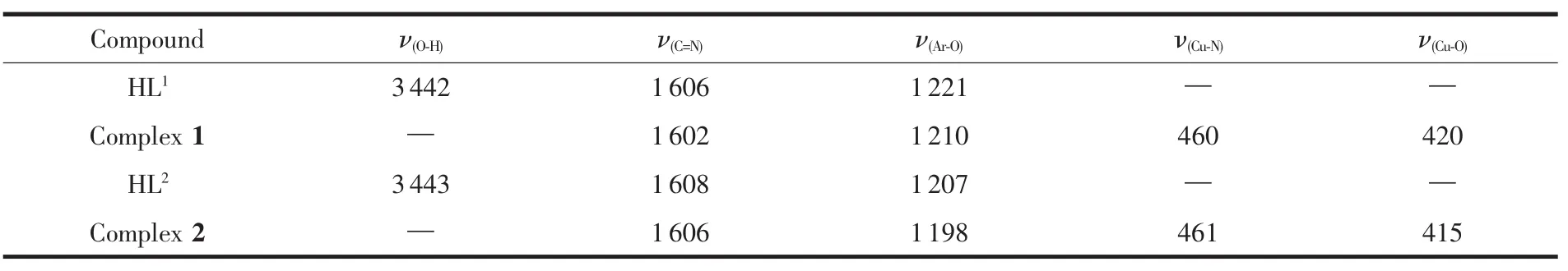
Table 3 Main IR bands for the ligands and theirs complexes(cm-1)

Table 4 Possible hydrogen bonds in complexes 1 and 2
Complex 2 can be described as centrosymmetric mononuclear CuⅡcomplex,the CuⅡion,lying on the inversion centre,is four-coordinated in a trans-CuN2O2square-planar geometry,with two phenolate O and two oxime N atoms from two N,O-bidentate oxime-type ligands HL2.The four donor atoms(N1,N1#1,O2 and O2#1)and Cu1 absolutely lie in a plane.It is noteworthy that the Cu-N bond lengths,0.1993(3)nm,are considerably longer than the Cu-O bond lengths,0.190 6(3)nm.The angles of N1-Cu1-O2 and N1#1-Cu1-O2#1are equal(89.1(3)°).There exist intermolecular C1-H1B…O1 and C3-H3…O3 hydrogen bonds(Fig.4 and Table 4)as well as π … π stacking interaction (Fig.5 and Table 5)in the complex 2,forming an infinite 2D supramolecular structure.

Fig.4 Part of 3D supramolecular structure showinghydrogen bonds of complex 2

Table 5 Possible π-π stacking interaction for complex 2

Fig.5 Digram showing π…π stacking interaction of complex 2
2.2 FTIR spectra
The FTIR spectra ofHL1,HL2and their corresponding CuⅡcomplexes exhibit various bands in the 100~4 000 cm-1region.The most important FTIR bands for HL1,HL2and complex 1,complex 2 are given in Table 3.The O-H stretching frequency of oxime-type ligand is expected in the 3 300~3 800 cm-1,however,these frequencies of HL1and HL2are generally displaced toca.3 442 and 3 443 cm-1,respectively,due to the internal hydrogen bond OH … N=C[16].The free ligand HL1and HL2exhibitcharacteristicC=N stretching bands at 1 606 cm-1and 1608 cm-1,while theC=N of thecomplex 1 and complex 2 were observed in the 1 602 and 1 606 cm-1,respectively.The C=N stretching frequencies are shifted byca.4 and 2 cm-1upon complexation,indicating a decrease in the C=N bond order due to the coordinated bond of the CuⅡatom with the oxime nitrogen lone pair.The Ar-O stretching frequency appears as a strong band within the 1273~1211 cm-1as reported for similar ligands[17].This band occurs at 1221 cm-1for the ligand HL1,and at 1210 cm-1for complex 1,the band occurs at 1 207 cm-1for the ligand HL2,and at 1 198 cm-1for complex 2.The Ar-O stretching frequency is shifted to a lower frequency,indicating that the Cu-O bond was formed between the CuⅡ ion and oxygen of phenolic group.
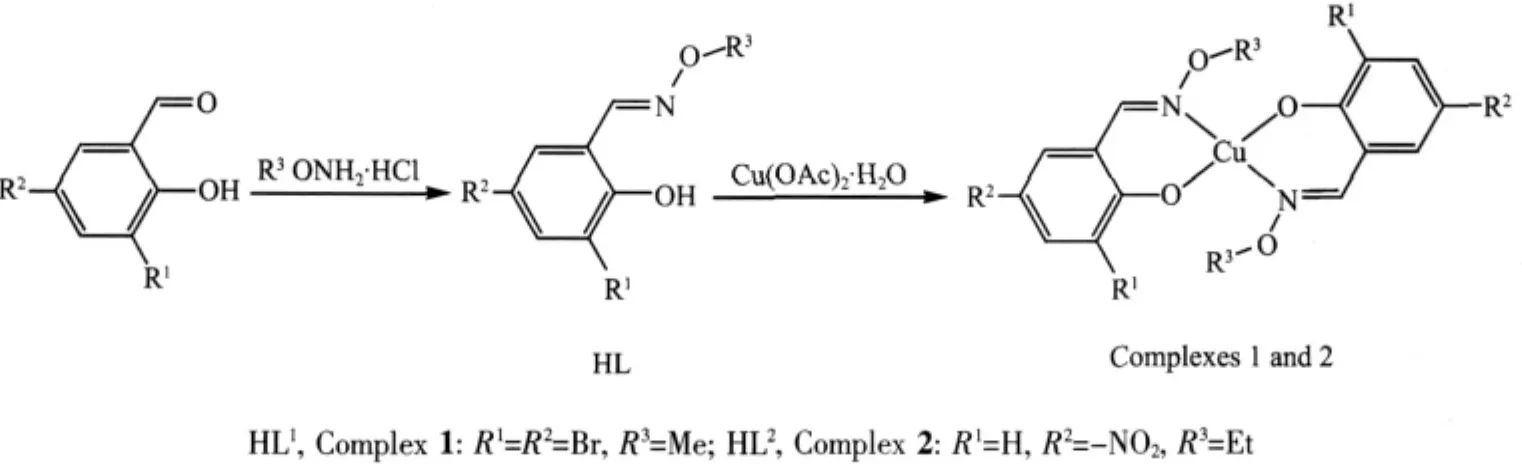
Scheme 1 Synthetic routes of HL1,HL2and their CuIIcomplexes 1 and 2
The far-infrared spectra of complexes 1 and 2 was also obtained in the region 500~100 cm-1in order to identify frequencies due to the Cu-O and Cu-N bonds.The FTIR spectrum of complex 1 showed ν(Cu-N)and ν(Cu-O)vibration absorption frequencies at 460 and 420 cm-1(or 461 and 415 cm-1for complex 2)[18],respectively.These assignments are consistent with the literature frequency values[19-22].complexes are bathochromically shifted, further demonstrating the coordination behavior between CuⅡions and ligands.Compared with the ligands HL1and HL2,an important feature of the absorption spectra of complexes 1 and 2 is shown that a new absorption peak is observed at ca.370 nm and ca.372 nm,indicating that the coordination of Cu atom with the ligands HL1and HL2.
2.3 UV-Vis spectra
The absorption spectra of ligands HL1,HL2and their corresponding CuⅡcomplexes were determined in 5×10-5mol·L-1DMF solution show that the spectra of them are similar to each other.The absorption spectrum of HL1shows absorptions at 272 and 310 nm,while two absorption peaks are observed at 291 and 317 nm in the spectrum of complex 1.The absorption spectrum of HL2shows absorptions at 271 and 311 nm,while two absorption peaks are observed at 285 and 317 nm in the spectrum of complex 2.Compared with HL1and HL2,the absorption peaks of their corresponding CuⅡ
[1]Akine S,Taniguchi T,Nabeshima T.Chem.Lett.,2001,30(7):682-683
[2]Akine S,Taniguchi T,Dong W K,et al.J.Org.Chem.,2005,70(5):1704-1711
[3]Dong W K,Zhao C Y,Sun Y X,et al.Inorg.Chem.Commun.,2009,12:234-236
[4]Kalarani N,Sangeetha S,Kamalakannan P,et al.Russ.J.Coord.Chem.,2003,29(12):845-851
[5]Dong W K,He X N,Yan H B,et al.Polyhedron,2009,28:1419-1428
[6]Akine S,Dong W K,Nabeshima T.Inorg.Chem.,2006,45(12):4677-4684
[7]Kukushkin V Y,Tudela D,Pombeiro A J L.Coord.Chem.Rev.,1996,156:333-362
[8]Costes J P,Dahan F,Dupuis A,et al.J.Chem.Soc.Dalton Trans.,1998,8:1307-1314
[9]DONG Wen-Kui(董文魁),LV Zhong-Wu(吕忠武),SUN Yin-Xia(孙 银 霞),et al.Chinese J Inorg.Chem.(Wuji Huaxue Xuebao),2009,25(9):1627-1634
[10]DONG Wen-Kui(董文魁),TANG Xiao-Lu(唐晓璐),HE Xue-Ni(何 雪 妮 ),et al.Chinese J Inorg.Chem.(Wuji Huaxue Xuebao),2009,25(3):528-532
[11]XU Li(许 力),ZHANG Yan-Ping(张艳萍),SUN Yin-Xia(孙 银 霞 ),et al.Chinese J Inorg.Chem.(Wuji Huaxue Xuebao),2007,23(11):1999-2002
[12]Cervera B,Ruiz R,Llore F,et al.J.Chem.Soc.Dalton Trans.,1997,3:395-401
[13]Mahmoud M H H,Nakamura S,Akiba K.Anal.Sci.,1997,13:149-152
[14]Blower P J.Trans.Met.Chem.,1998,23:109-112
[15]XU Guo-Jin(徐国津),TANG Yu-Hai(唐玉海),WEI Sai-Li(魏赛丽),et al.Chinese J Inorg.Chem.(Wuji Huaxue Xuebao),2009,25(8):1359-1365
[16]Dong W K,Sun Y X,Zhang Y P,et al.Inorg.Chim.Acta,2009,362(4):1129-1134
[17]Tumer M,Koksal H,Sener M K,et al.Trans.Met.Chem.,1999,24(4):414-420
[18]Sen S,Talukder P,Dey S K,et al.J.Chem.Soc.Dalton Trans.,2006,14:1758-1767
[19]Dong W K,Shi J Y,Xu L,et al.Appl.Organometal.Chem.,2008,22(2):89-96
[20]Dong W K,Feng J H,Yang X Q.Synth.React.Inorg.Met-Org.Nano-Met.Chem.,2007,37(3):189-192
[21]Dong W K,Feng J H,Wang L,et al.Trans.Met.Chem.,2007,32(8):1101-1105
[22]Dong W K,Tong J F,Sun Y X,et al.Trans.Met.Chem.,2010,35:419-426
两种水杨醛型单肟铜(Ⅱ)配合物的合成及结构研究
董文魁*宫尚生 同军锋 孙银霞 吴健超
(兰州交通大学化学与生物工程学院,兰州 730070)
2种新的水杨醛型单肟配体HL1(HL1=(E)-2-{1-甲氧基亚氨基甲基}-4,6-二溴苯酚)和HL2(HL2=(E)-2-{1-乙氧基亚氨基甲基}-4-硝基苯酚)分别与一水合乙酸铜反应,合成了2个铜配合物[Cu(L1)2](1)和[Cu(L2)2](2),利用元素分析、红外光谱和紫外光谱等进行了表征,并用X-射线单晶衍射测定了其晶体结构。结果表明,配合物1、2均为单核结构,由1个CuⅡ离子和2个配体组成。中心CuⅡ离子的配位数是4。配合物1为扭曲的平面四边形,而2为规则的平面四边形。配合物1以分子间氢键形成了无限的一维链状超分子结构,而配合物2以分子间氢键和π…π作用形成了二维超分子结构。
单肟配体;铜配合物;表征;晶体结构;合成
O614.121
:A
:1001-4861(2010)10-1868-07
2010-05-17。收修改稿日期:2010-05-31。
董文魁,男,46岁,教授;研究方向:功能超分子配位化学与材料。
甘肃省教育科研基金(No.0904-11)资助项目。
*通讯联系人。 E-mail:dongwk@126.com;会员登记号:S06N9030M1004。
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
无机化学学报的其它文章
- Solvothermal Synthesis,Crystal Structure and Photoluminescence Property of a Coordination Polymer Based on 1,1′-Ethynebenzene-3,3′,5,5′-tetracarboxylate
- Synthesis,Structure and Fungicidal Activity of Organotin 1H-Tetrazolyl-1-acetates
- Synthesis and Characterization of Tungsten Oxide Nanostructures
- Syntheses,Crystal Structure and Optical Property of Two Bis-ligand Silver(Ⅰ)Complexes Containing Diphenic Acid and Bidentate N-donor Ligands
- Synthesis,Crystal Structure,Luminescent and Electrochemical Properties of a New Binuclear Cd(Ⅱ)Complex with 2,4-DAA as Ligand
- Graphene-RuO2Nanocomposites:Hydrothermal Synthesis and Electrochemical Capacitance Properties
