The Impact of Gender,Age and Tissues in vitro on Estimating Postmortem Interval by FTIR Spectroscopy
2013-05-19XUANMiaogenFUGaowenLIUFengMENGHaotianWANGZhenyuan
XUAN Miao-gen,FU Gao-wen,LIU Feng,MENG Hao-tian,WANG Zhen-yuan
(1.Department of Forensic Medicine,College of Medicine,Xi′an Jiaotong University,Xi′an 710061,China;2.Criminal Investigation Team,Shaanxi Baishui Public Security Bureau,Baishui 715600,China;3.Criminal Investigation Team,Shaanxi Mizhi Public Security Bureau,Mizhi 718100,China)
It doesn’t need to repeat the importance of estimating the postmortem interval (PMI).The previous studies[1-15]showed that Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and other spectrometers could be applied to estimating PMI because they could detect accurately and sensitively molecular vibrational changes of relative intracellular material with high specificity.In addition to the impact factors of the external environment,it is necessary to study the internal environmental factors,such as gender,age,tissues in vitro,which could influence the experimental results.
Material and methods
Animal specimens
Thirty-two Sprague-Dawley rats(male:63d,n=8,240-260 g;female:infancy,21 d,n=8,40-50 g;youth,42 d,n=8,110-130 g;adult,63 d,n=8,210-230 g),provided by the Animal Center of Xi′an Jiaotong University,were killed by cervical dislocation,and the corpses were kept in a controlled environment chamber set at(20±2)℃ and 50%humidity.Part of the liver,kidney,spleen,myocardium,lung and skeletal muscle tissues from one of the female groups (63d,n=8,210-230g) were kept out of the body for comparing tissues in vitro with that in vivo.The liver,kidney,spleen,myocardium,brain,lung and skeletal muscle tissues were collected for measurement from time zero to 48 h(0,6,12,24,36 and 48 h)postmortem.The tissues were placed into the 2.5 mL frozen tubes and frozen immediately in liquid nitrogen.All of the animal experiments were performed in accordance with the principles for Care and Use of Laboratory Animal Committee of Xi′an Jiaotong University.
Spectra measurement
The FTIR spectra were quantitatively recorded at room temperature in the range 4 000-900 cm-1on a Shimadzu FTIR-8400S spectrometer equipped with ZnSe ATR device flat crystal(Shimadzu Corporation,Kyoto,Japan).Interferograms were average for 20 scans at 4cm-1resolution.Before each measurement,the ATR crystal was carefully washed with acetone.The sample was deposited on the ZnSe substrate directly and pressed tightly then monitored by the FTIR spectra.
Statistical analysis
IR solution 1.10 software(Shimadzu Corporation,Kyoto,Japan)was used to analyze the spectra and record the data including the calculations of peak position and band intensity.Band absorbance ratios which were used to normalize the data(A1080/A1396,A1168/A1396,A1234/A1396,A1541/A1647,A2850/A2921)were also analyzed.The±s was calculated for each time point;all statistical analysis of the data was performed by SPSS 13.0 software(SPSS Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA).The P-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Complete originalFTIR spectra in different groups showed the same peak shape and peak position seen in Fig.1,Fig.2 and Fig.3.The major FTIR absorbance bands (1080,1168,1234,1396,1 541,1 647,2 850 and 2 921 cm-1)presented no significant changes for the different sex(male and female),ages (infancy,youth,adult) and different store conditions (in vitro and in vivo).
The three groups showed the similar postmortem spectral changes.With prolongation of PMI,the major band absorbance ratios of different tissues showed a decrease (A1080/A1396,A1168/A1396and A1234/A1396).Among them,the first two ratios showed more obvious changes than the third one.As a result,we picked them out in detail.In addition,A1541/A1647and A2850/A2921showed no obvious changes with prolongation of PMI.The postmortem spectral and major band absorbance ratios showed the similar changes seen in Fig.4,Fig.5 and Fig.6.
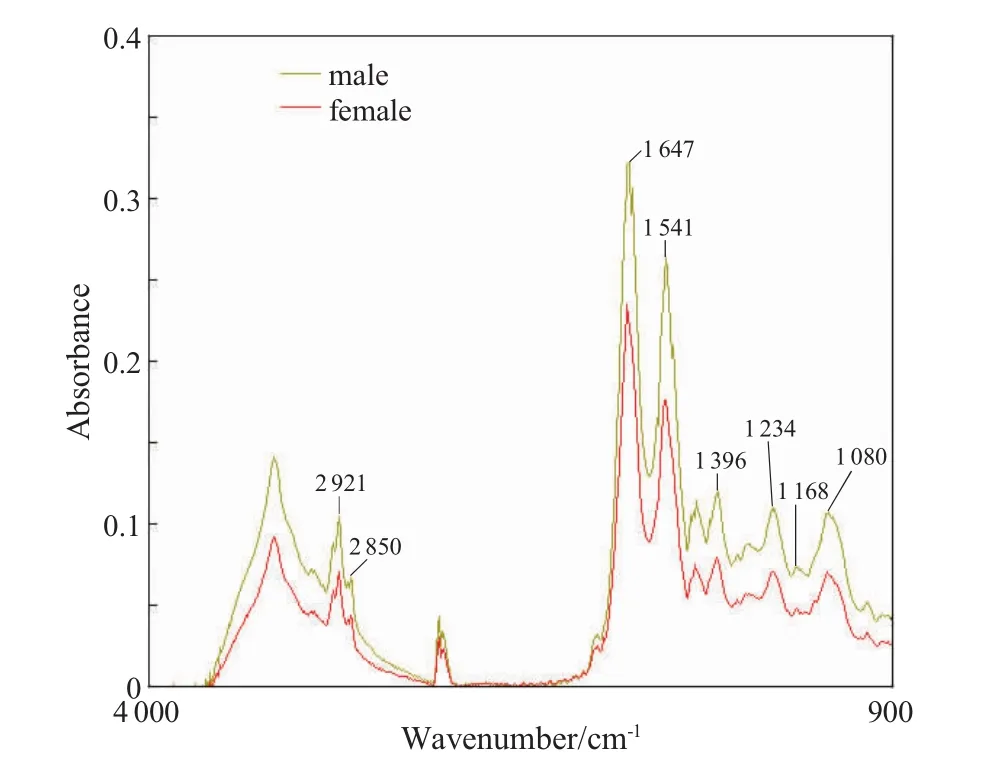
Fig.1 FTIR spectra of the rat’s kidney in gender groups
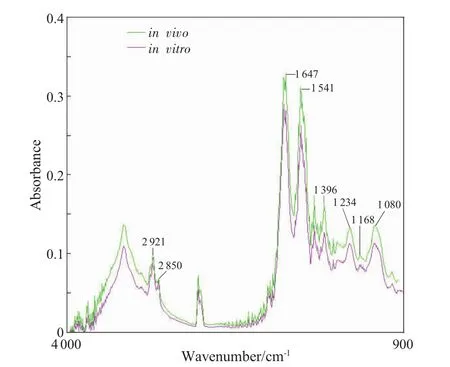
Fig.3 FTIR spectra of the rat’s myocardium in tissues in vitro and in vivo groups
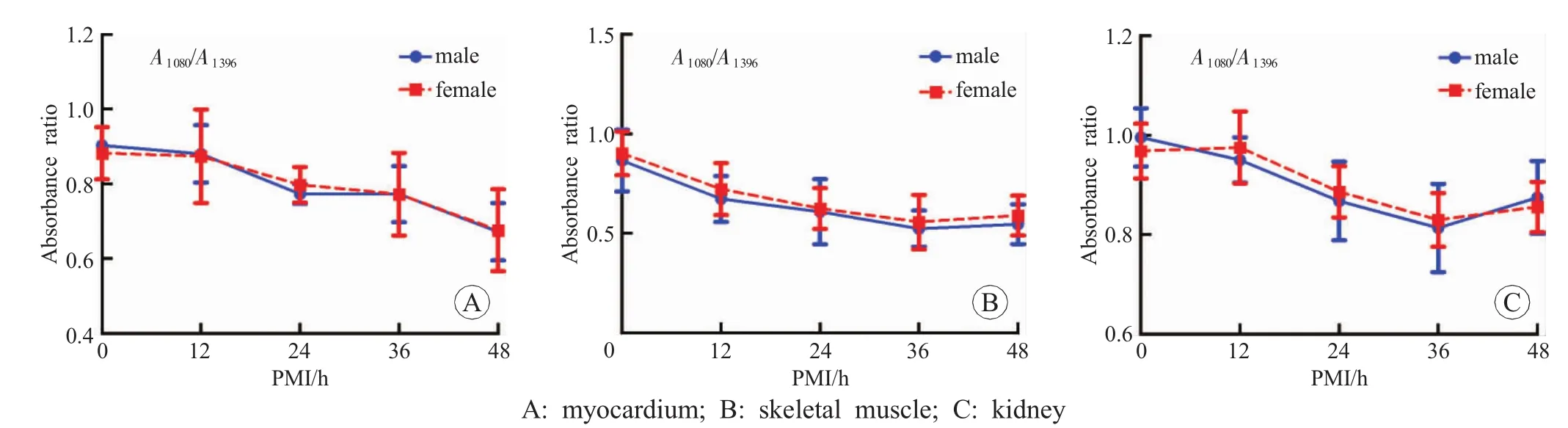
Fig.4 The trend of FTIR spectra of part tissues in gender groups
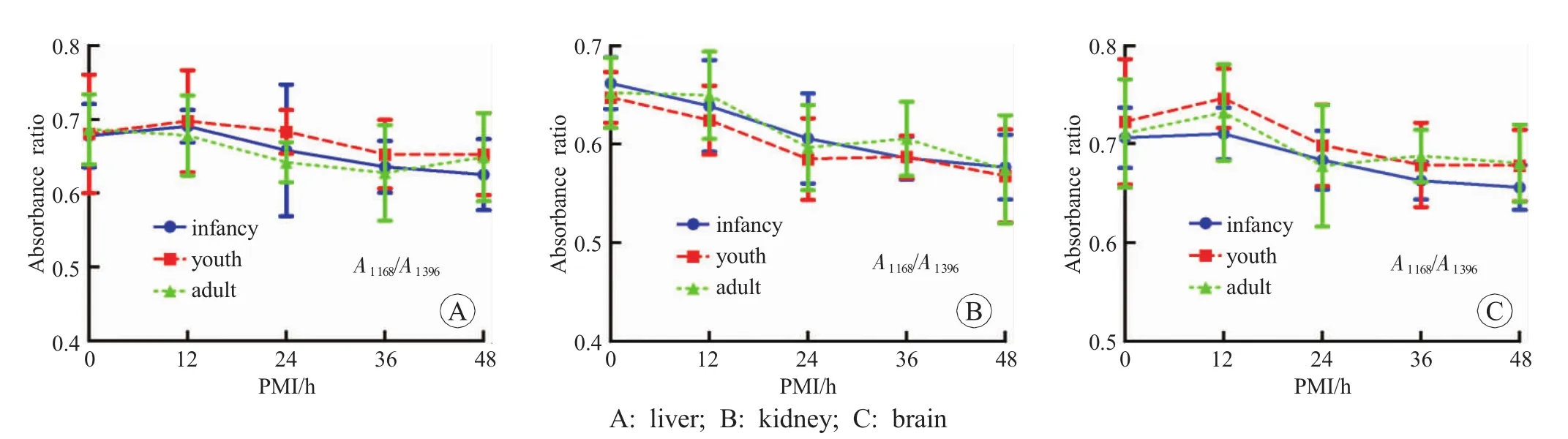
Fig.5 The trend of FTIR spectra of part tissues in different age groups
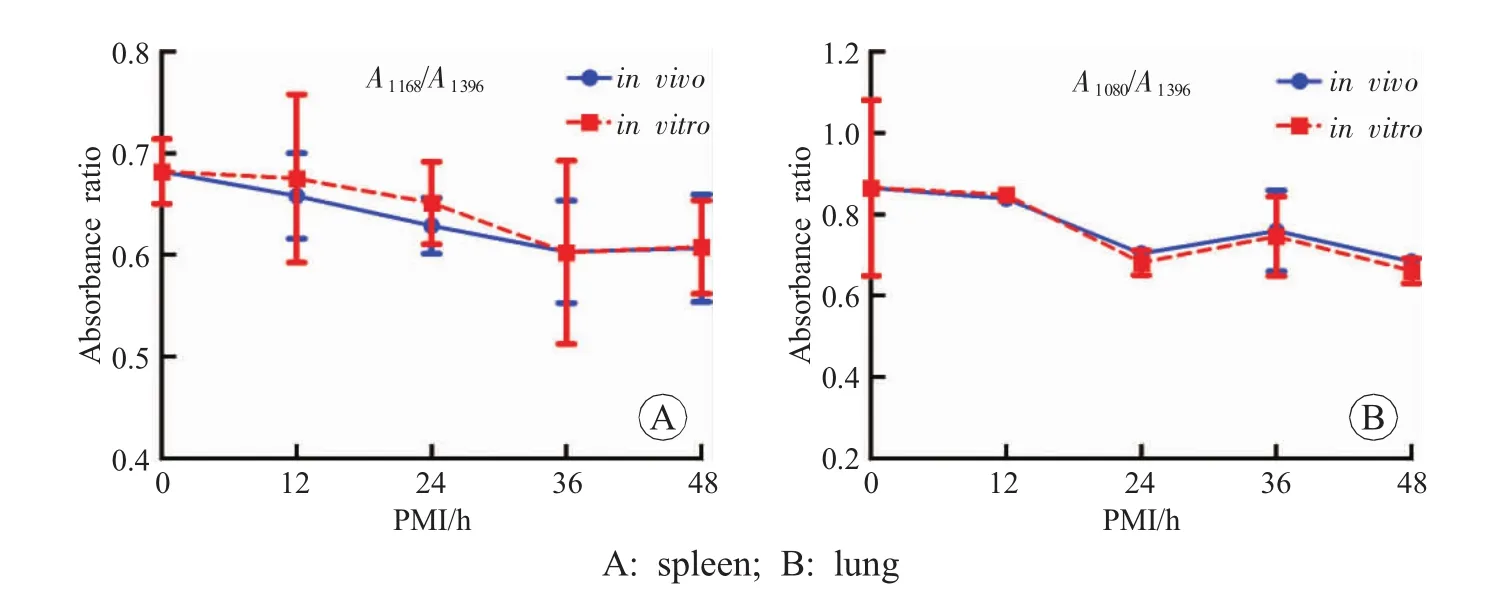
Fig.6 The trend of FTIR spectra of part tissues in tissues in vitro and in vivo groups
A1080/A1396of myocardium,skeletal muscle and kidney in gender groups showed a decrease.A1168/A1396of liver,kidney and brain in different age groups presented a significant decrease.A1168/A1396of spleen,A1080/A1396of lung in tissues in vitro and in vivo groups declined with the time increasing.
Discussion
The assignment of FTIR absorption bands is related to various functional groups of some biochemicalcomponents.In the currentstudy,the chemical groups contained in the rat’s tissues did notchange significantly in allthe experimental groups (Fig.1,Fig.2 and Fig.3).And the results also illustrated that the chemical interactions of the hydrolase and spoilage bacteria in the cells could nothave the spatialconfiguration ofsignificant changes in biological macromolecules.
The results of A1080/A1396and A1168/A1396showed downward trends in all the tissues,which might reflect a relation between FTIR and PMI (Fig.4,Fig.5 and Fig.6).The peaks at 1080cm-1indicate the symmetric and asymmetric stretching vibration of phosphodiester bond in the polynucleotide chain,reflecting the content of nucleic acid.Johnson et al.[16]showed that the degradation of nucleic acid is related to PMI.The current results supported the view on the stage of FTIR spectroscopy.The peak at 1168cm-1indicates the C-O stretching vibration of serine,threonine and tyrosine,reflecting the content of these three amino acids.This is consistent with that the results obtained in the previous studies.
The degradation of biological macromolecules after death was reported to be mainly caused by hydrolytic enzymes and corrupt microorganisms.In the previous studies[5-15],our group focused on the influences of environmental factors and the cause of death on the FTIR spectra to obtain a series of achievements,successfully constructing a new way to estimate PMI using spectra.Such environmental factors as temperature,humidity and cause of death,have been well confirmed to influence the forecast of PMI in the early experiments[17].However,it is necessary to have a system analysis of the basic individual factors (gender,age and tissues in vitro)to clarify the extent of the impact on the results of spectroscopic detection when facing the complex individual differences.Our results suggested that there was no significant difference between the results of tissues from the same organ at different ages,and that gender difference had no obvious effect on degradation.Because ofthe experimentundera controlled temperature,humidity,etc.,tissues in vitro or in vivo had no significant effect on macromolecular degradation.The current study provided a good animal experimental model,and a theoretical basis on which to apply the approach to human corpses,since rats show a good biological similarity with humans.
Conclusion
Under the condition of 20℃,the main FTIR absorbance peaks and their ratios showed no significant difference in male and female groups,differentagegroupsand tissuesin vitro orin vivo groups as we expected.The results provided a good experimentaland theoreticalbasisforthe future studies of using FTIR on the human corpses with removing the impact factors of their own.
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81072509)and the ShanghaiKey Laboratory of Forensic Medicine (No.KF0905).
[1]Dang YH,Wang ZY,Zhang LH,et al.Preliminary study on determining pH value of postmortem skeletal muscle of rat with the Thermo Orion KNIpHE electrode to estimate the early PMI[J].Chinese Journal of Forensic Medicine,2005,20(4):202-205.
[2]Zhu XJ,Wang ZY,Yu RJ,et al.The application prospect of the use of bio-photon emission in forensic science[J].The Journal of Law and Medicine,2005,12(1):51-53.
[3]Mao S,Dong X,Fu F,et al.Estimation of postmortem interval using an electric impedance spectroscopy technique:a preliminary study[J].Sci Justice,2011,51(3):135-138.
[4]Li W,Ke Y,He GS,et al.Study on the correlation between PMI and OD changes in rat’s plasma[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2008,28(12):2944-2946.
[5]Huang P,Tian WP,Yang GD,et al.Study on estimation of postmortem interval using FTIR in rat lung[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2007,27(10):1962-1965.
[6]Ke Y,Zhang JG,Huang P,et al.The changes of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy in rat’s Brain[J].Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi,2008,24(3):161-164.
[7]Ke Y,Li Y,Wang ZY.The changes of Fourier transform infrared spectrum in rat brain[J].J Forensic Sci,2012,57(3):794-798.
[8]Huang P,Ke Y,Lu QY,et al.Analysis of postmortem metabolic changes in rat kidney cortex using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy[J].Spectroscopy,2008,22(1):21-31.
[9]Huang P,Tian WP,Tuo Y,et al.Estimation of postmortem interval in rat liver and spleen using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy[J].Spectroscopy Letters:An International Journal for Rapid Communication,2009,42(2):108-116.
[10]Tuo Y,Huang P,Ke Y,et al.Attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic investigation of the postmortem metabolic process in rat and human kidney cortex[J].Appl Spectrosc,2010,64(3):268-274.[11]Huang P,Su CP,Li SS,et al.Estimation of postmortem interval using FTIR spectroscopy in rats’cardiac muscle[J].Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi,2010,26(1):1-5.
[12]Huang P,Tuo Y,Wang ZY.Review on estimation of postmortem interval using FTIR spectroscopy[J].Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi,2010,26(3):198-201.
[13]Huang P,Liu Y,Ke Y,et al.Examination of rat’s skeletal muscle degradation with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy to estimate postmortem interval[J].Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi,2007,23(3):164-166,169.
[14]Huang P,Yu RJ,Li L,et al.Forensic medical analysis of FTIR spectral changes of rat spleen postmortem[J].Chinese Journal of Forensic Sciences,2010,(5):38-42.
[15]Huang P,Wang SW,Bai J,et al.To estimate the postmortem interval using FTIR spectroscopy[J].Chinese Journal of Forensic Medicine,2011,26(2):104-109.
[16]Johnson LA,Ferris JA.Analysis of postmortem DNA degradation by single-cell gel electrophoresis[J].Forensic Sci Int,2002,126(1):43-47.
[17]Ke Y.The relationship between postmortem interval and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrum under complex conditions[D].Xi′an jiaotong University,2011.
